Rutgers Dinosaurs Exam 1
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
Nicholas Steno
Known as the Father of Stratigraphy, Steno's Principles of Stratigraphy
Law of Original Horizontality
This principle states sediments are deposited under the influence of gravity as nearly horizontal beds.
Law of Superposition
Sedimentary layers are deposited in a time sequence, with the oldest on the bottom and the youngest on the top.
Law of Faunal (Floral) Succession
Sedimentary rock strata contain fossilized flora and fauna that these fossils succeed each other vertically in a specific, reliable order that can be identified over wide horizontal distances
Fossils
Remnants or traces of ancient living organisms preserved in rock; form when organisms become buried with sediment
Ex: Bones, teeth, foot prints, burrows, etc...
***Fossilization Process
1) Something dies
2) Flesh rots away
3) Bones/footprints/remains get buried in sentiment
4) Time passes, more sediments build on top and the organic matter is replaced with rock material (aka a fossil)
Body Fossils
Whole bodies or pieces of bodies of a once-living organism
Ex: Skeletons/bones, teeth, claws/nails, shells & shell impressions, amber, frozen organisms
Trace Fossils
Preserved evidence of biological activity of a once-living organism; evidence that something living was once there
Ex: Footprints, coprolites (fossilized poop, tells you their diet), burrows (resting or hiding places), trails
Index Fossil
Fossilized species used to date/correlate strata conditions
1) Wide Distribution
2) Alive for a short time span
3) Distinguishing Features
***Good Index Fossils
Trilobites, Brachiopods
***Bad Index Fossils
Horseshoe Crabs
Absolute Dating
This type of dating method helps give events a numerical date. It is also called Chronometric Dating.
Ex: saying "this human fossil is x years old"
Relative Dating
This type of dating method helps put events in order.
Ex: Human fossils are younger than Dinosaur fossils
Half-Life
The time it takes for half of the radioactive parent to decay to the daughter; the ratio of the measurement of how much of the parent and how much of the daughter is left can be used to determine the age (technique for absolute dating)
Geologic Time Scale
See Evo Events pdf on announcements page
Plate Tectonics
Large segments of the outer Earth move relative to one another over the asthenosphere (the earth's surface is broken into plates that move)
***Divergent Boundaries
Boundary where plates move away from each other
***Convergent Boundries
Boundary where plates converge/come together/collide. One will either go under the other or both will collide and go upwards forming mountains.
***Transform Boundries
Boundary where plates move side to side against each other.
Evidence for Plate Tectonics
1) Obvious fit of continents
2) Paleoclimate data (glaciers, climate belts) (striations)
3) Similar fossils separated by oceans
4) Rock type and structural similarities
Alfred Wegener
Father of Continental Drift
*** Continental Drift Theory
Low-density continents "floating" on higher density ocean floor rocks and "sailing through them)
Pangea
This was known as the super continent where all continents were connected as one. 250 Million years ago.
Life
- First life had cell membrane but no nucleus
- A states characterized by the capacity for self-replication and self-regulation
- Living organisms are complex and highly organized
- Take energy from environment and change its for to another
- Homeostatic
- Respond to stimuli
- Reproduce itself
- Grow and develop
Prokaryotes
This type of cell has a cell membrane but no nucleus.
Ex: Bacteria
Eukaryotes
Cell membrane, nucleus with DNA, organelles
Ex: animals, plants, fungi, protists (multicellular organisms)
Autotrophic
This type of organism self feeds through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
Heterotrophic
This type of organism feeds on other organisms, "other-feeding"
The Big Five Mass Extinctions
End-Ordovician, Late Devonian, End Permian, End Triassic, and End-Cretaceous
***End-Permian Extinction
The biggest mass extinction the world has ever seen, "The Great Dying," more than half of all families in the marine ecosystem died and most of all species were killed, caused by giant eruption and an impact.
***End-Ordovicia Extinction
22% of all families in the marine ecosystem died, 2nd largest mass extinction, caused by Ice Age/Climate Change
***Late Devonian Extinction
21% of all families in the marine ecosystem died, 3rd largest mass extinction, caused by oceanic crisis or impact.
End-Triassic Extinction
20% of all families in the marine ecosystem died, 2nd smallest mass extinction, dinosaurs dominate after, caused by large eruption possibly with impact.
***End-Cretaceous Extinction
15% of all families in the marine ecosystem died, smallest mass extinction, dinosaurs go extinct and mammals dominate, caused by an impact plus giant eruption.
Linnaean Classification System
This system classifies all living organisms in these categories based on their traits
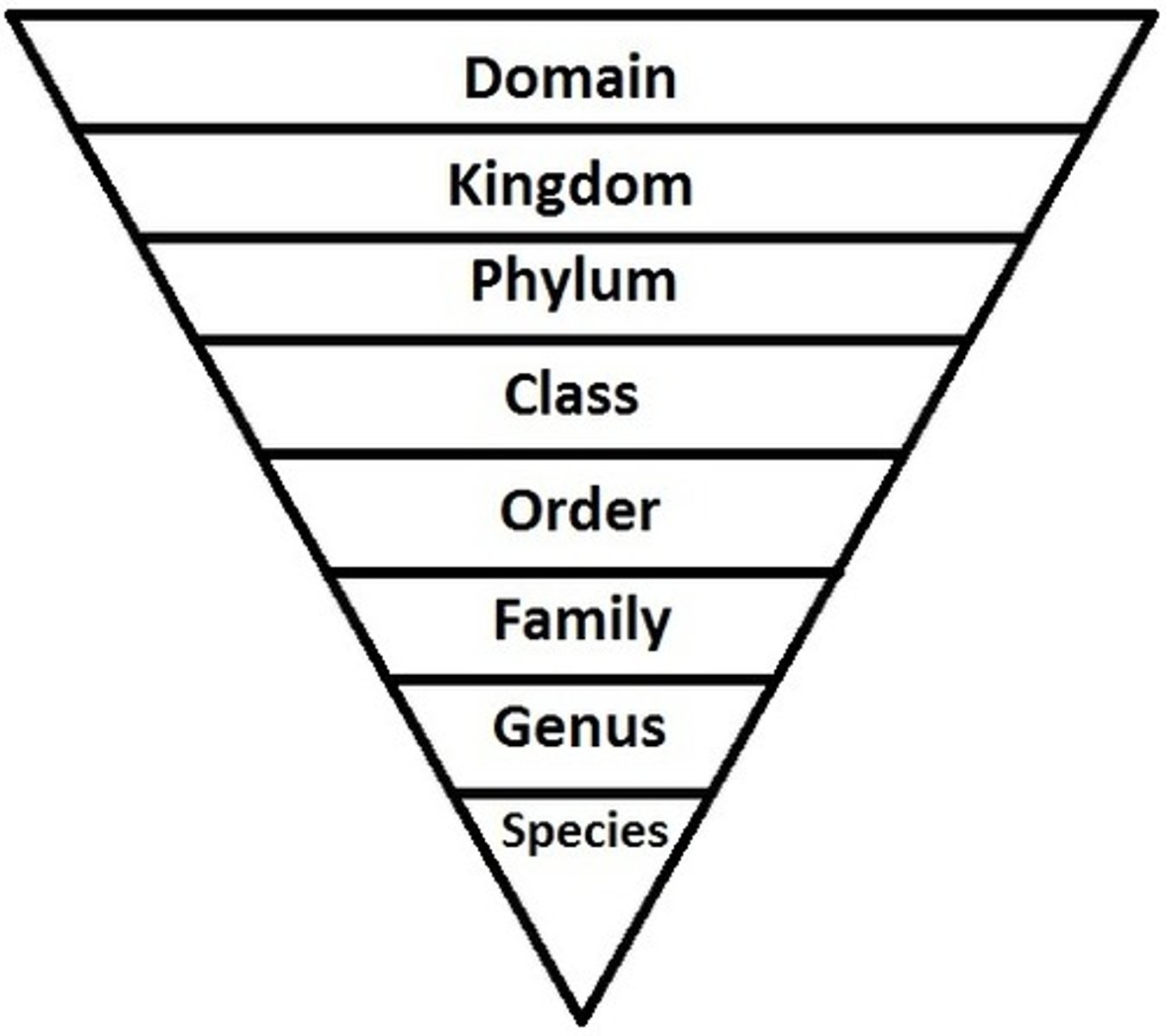
***Binomial Nomenclature
All species must have two names, this is done by using the Genus and Species of an organism, this called a
Georges Cuvier
"Father of Vertebrate Paleontology," developed catastrophism - ide where earth is affected by sudden short lived, violent effects that were sometimes worldwide in scope.
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Developed the theory of acquired traits (when an organism is alive they acquire or change their trait to pass on to offspring; ex: giraffes acquiring a long neck over time through their offspring).
Charles Lyell
Developed uniformitarianism, where the present is the key to the past, and processes that alter earth are uniform (principles of geology).
Charles Darwin
Father of Evolution, wrote the Origin of Species where he discussed Natural Selection
Evolution
Descent with modification, change in biological species through time, change in gene frequencies in a population through time.
Ex: Peppered Moths becoming black-bodied moths during the industrial revolution due to environmental changes.
Natural Selection
1) Traits are inherited from parent to offspring
2) Organisms vary
3) Too many offspring are produced to survive
4) Organisms with traits suited to the environment will survive and reproduce
Evidence for Evolution
Comparative Anatomy - Similarities and differences in anatomy/structure of different kinds of animals
***Comparative Morphology (Evidence for Evolution)
Structures which serve similar functions but derive from different origins
Ex: Both a bird and a bat have modified their forearms into wings differently to achieve the same function
***Homology (Evidence for Evolution)
Structures deriving from similar origins, exhibiting a common underlying plan and serving a similar purpose
Ex: Similar structure of bones/structures of a human's arm used to grab things, cat's leg used to walk, whale's fin used to swim, and bat's wing used to fly.
***Vestigial Structures (Evidence for Evolution)
Structures that remain in an organism but serve no purpose
Ex: Femur and Pelvis in a whale
***Embryology (Evidence for Evolution)
The study of the development of organisms.
Ex: Similar structure of embryos of different animals
*** Biogeography (Evidence for Evolution)
The study of patterns in the distribution of plants and animals over the earth.
Ex: Seeing the same fossils of organisms on different continenets
*** Experimental Evidence (Evidence for Evolution)
Man-made or artificial selection shows the effects of selection within the relatively short time period of recorded human history.
Ex: Selective Breeding, Artificial Selection (Dog Breeding)
*** Paleontology (Evidence for Evolution)
Study of ancient organisms
Ex: Studying fossil anatomy and drawing relationships overtime between different species
Species
Used in Binomial Nomenclature
Ex: Homo (Genus) sapiens (Species)
Phylogenetic Systematics
We use cladograms made with this method to show evolutionary relationships and which groups have what traits and which groups do not
Cladistics
A classification method, which uses specific homologous characters to draw evolutionary interpretations between organisms
Used to form Cladograms
Plesiomorph
A primitive character (An old character inherited from ancestors)
Apomorph
A derived character (a newly evolved character)
Symplesiomorph
A shared primitive character
Synapomorph
A shared derived trait
Iguanodon
1 dinosaurs found in Belgium, viewed as large, extinct reptiles
Richard Owen
He coined the term Dinosauria.
Dinosauria
Broken down this word means fearfully great lizard.
Hadrosaurus
Found in Haddonfield NJ, "heavy lizard"
Early Views of Dinosaurs (old view)
The view of dinosaurs as evolutionary failures, and slow brutish, and dimwitted is
Modern Views of Dinosaurs (new view)
The view that dinosaurs are ancestral to birds, show diversity, and are fast, agile, and active is
Monophyletic
All members have a single common ancestor
Holophyletic
All members are descendants of a single common ancestor.
Polyphyletic
Members are descended from different anscestors
Paraphyletic
Some members are descendants of a single common ancestor.
Exoskeletons
An external skeleton that allowed organisms grow larger and to anchor their muscles which made them more efficient swimmers.
Cambrian Explosion
- This was about 544-500 million years ago at the end of the paleozoic time period.
- 1st "conspicuous" fossil record
- Cells evolved tough walls and coverings, but not mineralized
- Most animals have mineralized exterior
- Evolution of hard parts increased fossil record
Trilobites
Most abundant/common animal during the Cambrian, evolved because of the Cambrian explosion, and are really good index fossils.
Vertebrae origins
invertebrates with notochords
Notochord
A nerve cord running along the back of the body providing sensation for movement: swimming, feeding; acted as an anchor for muscles.
Urochordates
- 1st step to becoming vertebrae
- soft-bodied chordates
- filter feeders, pack of muscles
-ex: sea squirts
Cephalochordates
- no true skeleton or limbs
- ancestor to vertebrates
Agnathans
- jawless vertebrates
- first group to have vertebrates
- early Devonian
ex: hagfish and lampreys
Gill Arches
Evolution to Jaws
Filter-Feeders --> cilia around the mouth
Gills --> pump for food & water
1st gill arch became jaws --> scales transformed into teeth
2nd gill arch moved forwards to support jaws --> muscles and teeth refined
4th gill arch modified to "hyoid arch" --> teeth present
-1st jawed fish appeared in Silurian and continued through Devonian
Chondrichthyes
- cartilage rather than bones
- tough skin instead of scales
- fossil outlines show they haven't changed much in shape
- Devonian to present
- Cladogram --> cartilaginous endoskeletons, vertebrates with jaws
Osteichthyes
- Bony fish
- small thin fins
- maneuver very well
- light skeletons, fast movement
- Devonian
- cladogram --> bony endoskeleton
Actinopterygians
- very think fins (webs of skin) supported by numerous thin, radiating bones
- light fish that swim fast and maneuver well
- late Devonian
- cladogram --> ray fins
Crossopterygii
- bony fish with fleshy, lobed-paired fins
- have lungs
- differentiated arm bones similar to tetrapods
- late Silurian
Labyrinthodont
- Teeth characterized by folded sheets of dentine
- Found in extinct amphibians and advanced fish
***Dipnoi
- lobe fin fish
- 1st primative limbs
- late Devonian
- lungfish
Amphibia
- four feet
Evolution of Life on Land
First plants, then invertebrates, and finally vertebrates
- 1st plants must have been largely aquatic (swamps & marshes)
- Major characters of plants are solutions to life with air and on land
- Grow against gravity, leaves, roots, internal support, spreading nutrients, reproduction
- By Devonian, ALL major innovations have evolved except flowers and fruit
- All major adaptations for life in air had to be evolved first in water
- Only then would it be possible for organisms to emerge into air for long periods of time
Problems with Life on Land
(Plants and animals)
- No buoyancy, support needed.
- Danger of drying out.
- Extremes of temperature
- Gases behave differently
- No nutrients in air
(animals only)
- Refraction of light changes
- Hearing must be modified
***Problem #1 --> Breathing Air
Solution: evolved lungs and nostrils
***Problem #2 --> Structural Support
Solution: Evolved Limbs and Vertebra
Advantages of Breathing Air
- Easier to extract O2 from air than water.
- Water is hundreds of times more dense and viscous than air.
- Water at best contains little O2.
- Gills have to work much harder to get enough O2 from water.
- Seasonal O2 levels can decrease.
- Oxygen poor air is rare.
Evolution of Limbs
- Old Story --> Limbs gave ability to withstand air exposure while finding another water source.
- Transition from Fins to Limbs --> Helped hunt prey in shallow water.
- Basking --> Sunning to increase metabolism (aid digestion), limbs take pressure off body to breath
- Reproduction --> Most vulnerable during early life, short land trips to spawn in small pools.
Evolution of Better Swimming Mechanisms
- Dipnoians & Crossopterygians --> Developed complex way of beating their lobe fine to stalk prey (swimming)
- Pattern is the exactly the same that Tetrapods used to walk on land (squirming pattern)
2 Major Lineages of Amphibia
1) Labyrinthodonta
- Ithyostegalis, Temnospondyli, Anthracosauria
- Anceint Extinct Amhibians
- Led to living reptiles, birds, and mammals
2) Amphibia
- Lestpondyli, Lissamphibia
- Led to living Amphibians
Aspidospondyly
All vertebral elements (centra, arches) remain as separate units
***3 Types of Aspidospondyly Vertebrae
1) RHachitomus (IC > PC)
2) Stereospondylus (PC = 0)
3) Embolomerous (IC = PC)
Lepospondyli
- Elements of the vertebra are fused into a single piece; centra have hollow core allowing for notochord to pass through
- Small but diverse group
- Not clear what descendants were, but possibly modern amphibians
- Include newt, eel, snake, and lizard-like variations
- Lepospondylic vertabrae
Ichthyostegalia
- 1st Devonian tetrapods to be described and studied
- "four-legged fish"
- resembled salamanders
- limbs for bearing weight, but not full extension
Anthracosauria
- A group of extinct reptile-like, amphibian-like tetrapods.
- Life primarily in water.
- Legs not sturdy, but good at squirming.
- Closest relatives to early reptiles.
- Modern Reptiles, Birds, and Mammals evolved from this group
- Embolomerous vertebra
- Carboniferous --. Triassic
Early Reptiles
- Hylonomus
- Small bodied
- Five-fingered forelimb
- Small skull
- Short jaw
- Neck joint for swiftness
- Carnivorous (could not process plant material)
- Tree-dwelling
- Insect hunting
- Thermoregulation
- Warming up by basking in sun
- Cooling off by finding shade
Paleozoic Plant Ecology
Devonian Land Floras
- Swamps with mosses and seed ferns
Carboniferous Land Floras
- Forests with seed ferns, cycads conifers
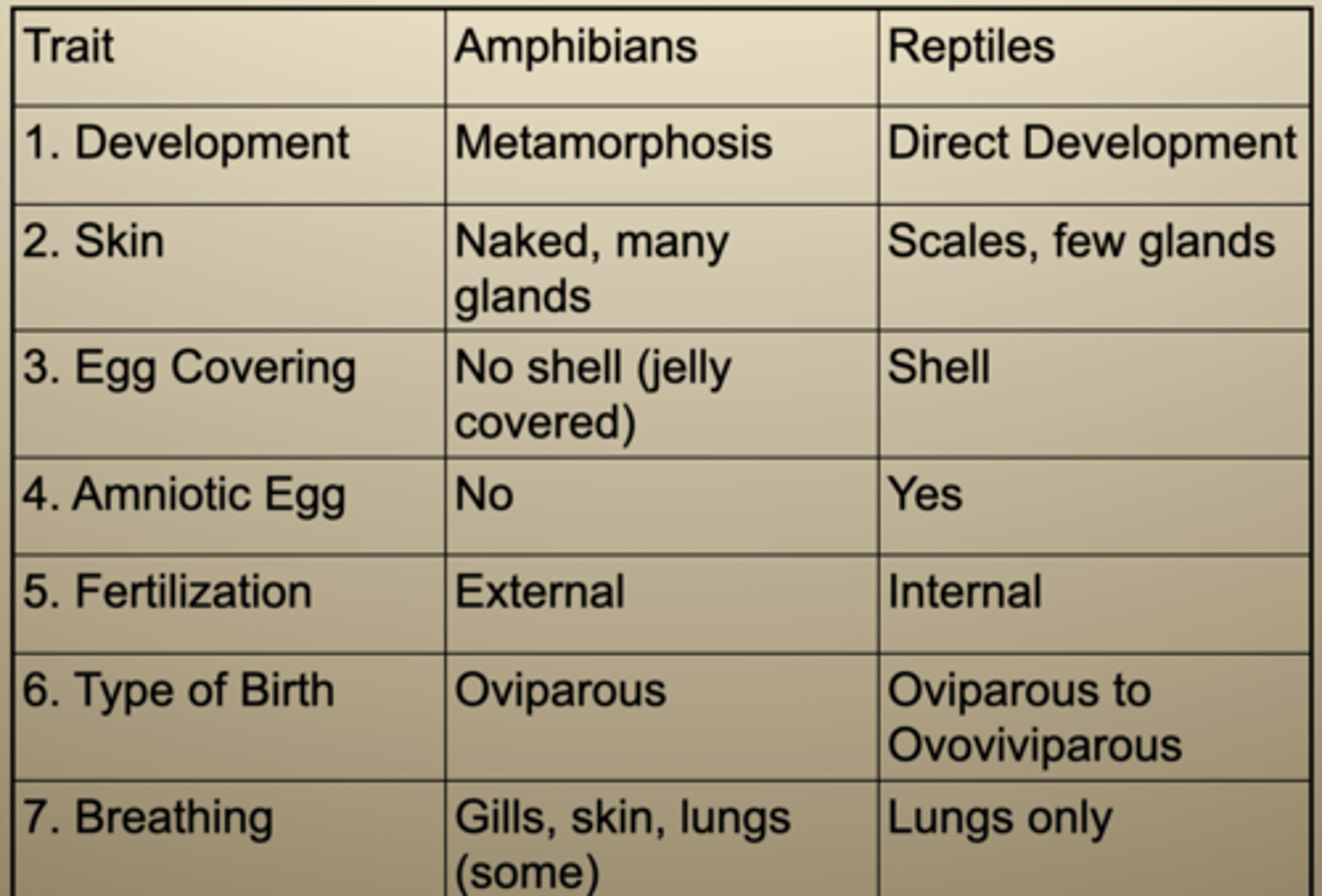
Reptile vs. Amphibian characteristics
1) Development
- Amphibians --> Metamorphosis
- Reptiles --> Direct Development
2) Skin
- Amphibians --> Naked, many glands
- Reptiles --> Scales, few glands
3) Egg Covering
- Amphibians --> No shell, jelly covered
- Reptiles --> Shell
4) Amniotic Egg
- Amphibians --> No
- Reptiles --> Yes
5) Fertilization
- Amphibians --> External
Reptiles --> Internal
6) Type of Birth
- Amphibians --> Oviparous
- Reptiles --> Oviparous to Ovoviviparous
7) Breathing
- Amphibians --> Gills, skin, lungs (some)
- Reptiles --> Lungs only
Advantage of Amniotic Egg
- Nourishment: large YOLK sac
- Waste removal: ALLANTOIS
- Regulation: AMNION ("seawater")
- Gas Exchange/Protection: Hard, but permeable SHELL