Ecosystems, Biomes, and Water Security Overview
1/534
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
535 Terms
Ecosystem
Interaction of biotic and abiotic factors.
Biotic factors
Living components of an ecosystem.
Abiotic factors
Non-living components of an ecosystem.
Nutrient cycle
Movement of nutrients between organisms and environment.
Energy flows
Transfer of energy through an ecosystem.
Biosphere
Global sum of all ecosystems supporting life.
Biome
Large ecological area with similar climate and vegetation.
Tropical rainforest
High biodiversity, warm temperatures, and high rainfall.
Desert
Area with very low rainfall and extreme temperatures.
Grassland
Ecosystem dominated by grasses, with few trees.
Tundra
Cold, treeless region with low-growing vegetation.
Soil formation
Process influenced by climate and vegetation types.
Leaching
Removal of dissolved nutrients from soil by water.
Urbanisation
Expansion of urban areas into natural ecosystems.
Deforestation
Clearing of forests for agriculture or urban use.
Aquatic biome
Ecosystem located in water environments.
Climate impact
Influence of temperature and precipitation on ecosystems.
Rainfall
Key factor determining ecosystem types and soil.
Vegetation types
Plant communities characteristic of specific biomes.
Woody vines
Plants climbing trees to access sunlight.
Buttress roots
Wide roots supporting tall trees in rainforests.
Drip tips
Leaf adaptations for water runoff in rainforests.
Photosynthesis optimization
Leaf angles maximizing light capture for energy.
Desert
A biome with low precipitation, high evaporation.
Cacti
Succulent plants adapted to arid environments.
Transpiration
Water loss from plants through stomata.
Thorns
Sharp structures on plants for protection.
Dormancy
State of inactivity during unfavorable conditions.
Entisols
Soils with no significant horizons, poorly developed.
Tundra
Cold biome with low temperatures and short summers.
Permafrost
Layer of permanently frozen ground in tundra.
Solifluction
Slow movement of water-saturated soil down slopes.
Ecological Succession
Process of ecosystem change over time.
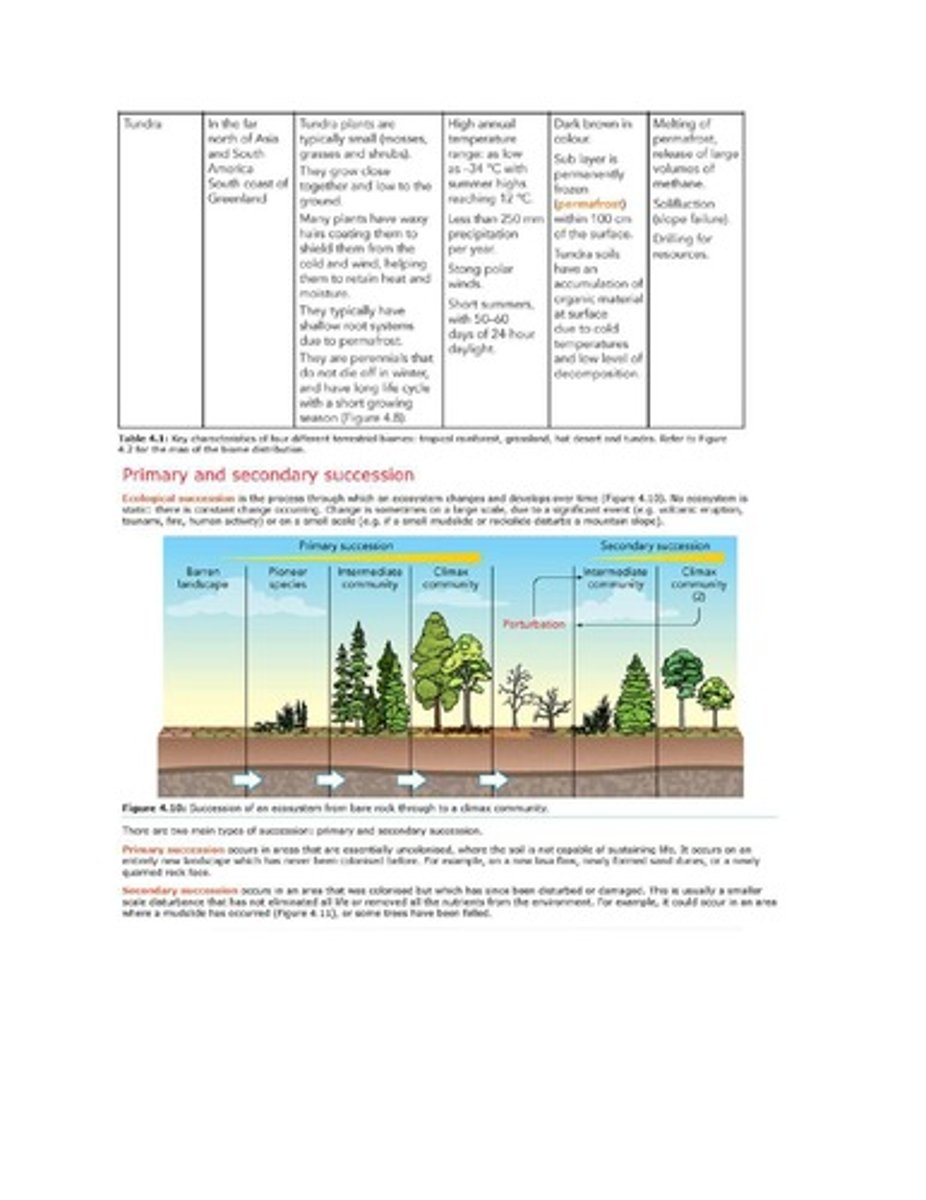
Primary Succession
Occurs on uncolonized, lifeless landscapes.
Secondary Succession
Occurs after disturbance in previously colonized areas.
Climax Community
Final, stable community in ecological succession.
Transpiration Rate
Rate of water vapor loss from plants.
Succulent
Plant with thick, fleshy tissues for water storage.
Waxy Cuticle
Layer on leaves reducing water loss.
Stomata
Small openings on leaves for gas exchange.
Root Systems
Structures anchoring plants and absorbing nutrients.
Vegetation
Plant life in a particular area.
Organic Material
Decomposed matter contributing to soil fertility.
Evaporation
Process of water turning into vapor.
Bark Thickness
Adaptation for fire protection in trees.
Temperature Range
Variation in temperature across different biomes.
Primary productivity
Rate of energy conversion into organic material.
Gross primary productivity (GPP)
Total energy captured by producers in an ecosystem.
Net primary productivity (NPP)
Energy stored by producers minus energy lost to respiration.
NPP formula
NPP = GPP - R, where R is respiration.
Ecosystem productivity
Rate of biomass production in an ecosystem.
Insolation
Solar radiation received by a specific area.
Biomass
Total mass of living organic material in an ecosystem.
Trophic levels
Hierarchical levels in an ecosystem based on energy flow.
Ecological pyramids
Diagrams representing energy, biomass, or individuals in trophic levels.
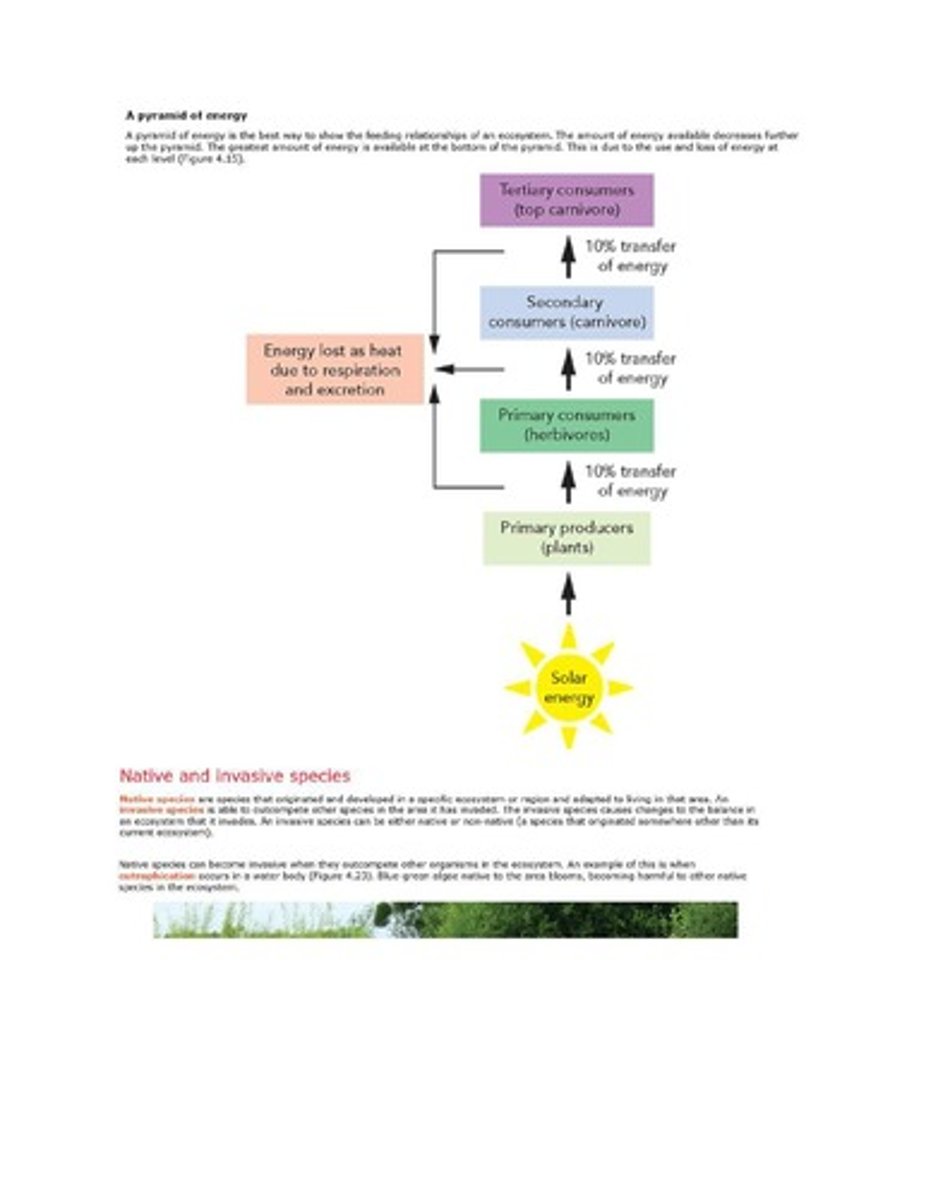
Pyramid of energy
Shows energy availability decreases up the trophic levels.
Energy transfer efficiency
Typically 10% of energy is transferred between levels.
Native species
Species that originated and adapted to a specific ecosystem.
Invasive species
Species that outcompete natives, disrupting ecosystem balance.
Cultural eutrophication
Nutrient enrichment causing harmful algal blooms in water bodies.
Biodiversity conservation
Protecting variety of species and ecosystems globally.
Food security
Dependence on natural resources for food production.
Dry organic matter
Amount of organic material measured in grams.
Tropical forest productivity
Approximately 2000 g/m²/year in biomass production.
Desert productivity
Less than 100 g/m²/year in biomass production.
Factors affecting productivity
Sunlight and water availability influence ecosystem productivity.
Respiration (R)
Energy used by organisms for metabolic processes.
Energy loss
Energy lost as heat during respiration and excretion.
Producers
Organisms that convert solar energy into biomass.
Biodiversity conservation
Protection of diverse biological species and ecosystems.
Soil fertility
Ability of soil to sustain plant growth.
Nutrient recycling
Process of reusing nutrients in ecosystems.
Pest regulation
Control of pest populations through natural mechanisms.
Soil erosion prevention
Methods to protect soil from being worn away.
Pollination
Transfer of pollen for plant reproduction.
Economic growth
Increase in the production of goods and services.
Poverty reduction
Strategies to decrease the number of people living in poverty.
Natural resources
Materials provided by nature for human use.
Conflict over resources
Disputes arising from scarcity or mismanagement.
Climate change mitigation
Efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Storm surge reduction
Lessening of storm-induced sea level rise effects.
Medicinal plants
Plants used for their healing properties.
Pharmaceutical development
Creation of medicines from natural substances.
Genetic diversity
Variety of genes within a species.
Species adaptation
Ability of species to adjust to environmental changes.
Ecological security
Stability and balance of ecosystems.
Food webs
Interconnected food chains in an ecosystem.
Cultural value
Importance of biodiversity in cultural practices.
Recreational value
Benefits of biodiversity for leisure and tourism.
Eco-tourism
Tourism focused on conservation and sustainability.
Legislation for biodiversity
Laws aimed at protecting biological diversity.
Global treaties
International agreements to manage natural resources.
Biodiversity
Variety of life in ecosystems, crucial for stability.
Endangered Species Act
US law prohibiting harm to endangered species.
American Bald Eagle
Protected species under US law, symbol of freedom.
CITES
International treaty to protect endangered species globally.
IWC
Commission focused on whale conservation and management.
African Black Rhino
Species reduced to 2400 by 1995 due to poaching.
Sustainable Harvesting
Resource use ensuring future supply without ecosystem harm.
Fynbos Ecosystem
South African biome with diverse plant uses.