Autonomic - Sympathetic Nervous System
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Cholinergic Nicotinic Systems: Sites & Actions:
Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ)
- skeletal muscle effector site in SNS
- ACh released from myelinated nerves
- muscle contraction with stimulation
Sympathetic System Terminology:
Agonists (direct/indirect/mixed) are also known as:
sympathomimetic
adrenergic
Sympathetic System Terminology:
Antagonists (direct/indirect; reversible/irreversible) are also known as
- sympatholytic
- α-blockers
- β-blockers
Nicotine - a drug of addiction and also a poison. Explain.
- Addiction (mesolimbic stimulation, ANS) : arousal at low doses, calming at high doses
- Poison (2 cigarettes ground up, 40mg lethal dose): sweating, hypertension, decreased GI activity, arrhythmia, tachycardia, flaccid paralysis, convulsions, vomiting
How is norepinephrine synthesized?
Tyr: tyrosine hydroxylase → DOPA: DOPA decarboxylase → DA (dopamine)[into vesicle]: dopamine-β-hydroxylase → norepinephrine (NE): phenylehtanolamine N-methyl transferase → epinephrine (E)
What is the key regulating step in sympathetic system? and Why?
NET transporter
- picks up NE and moves it into cell
-NE is metabolized inside the cell
- drug target
Norepinephrine
principal NT, precursor to E
Dopamine
Secondary, also precursor to NE
Epinephrine
secondary or circulating, adrenal medulla
Vesicle storage is complexed with:
- ATP (co-transmitter)
- Chromagranin A (stabilization)
Ways of releasing NE
- Exocytosis (Ca2+) driven
- Inhibitory Feedback via α2 & DA2, mAChR (↓ cAMP)
- Stimulatory Feedback via β2, AII receptors (↑ cAMP)
Monoamine Oxidase (MAO-A*, MAO-B#)
location and action?
- neurons and effector sites
- oxidizes NE & other amines (domaine, serotonin, epinephrine) -> replaces amine with aldehyde
Catechol-O-methyl-transferase (COMT)
location and action?
- effector sites
- may act in series with MAO
- adds methyl group to OH on phenyl ring
Why are MAO and COMT drug targets?
- inhibit = prevent breakdown of NE, elevated [NE] in cell = more release of NE
- indirect agonist, stronger SNS output
What is the overall effect of α1 type receptors?
- ↑ IP3, DAG
- diagnostic procedures and decongestant
- contractions
What is an agonist and antagonist for α1 type receptors?
Agonist: Phenylephrine
Antagonist: Prazosin
Where can α1 type receptors be found and what is the resulting action?
- Pupillary dilator muscle: contraction leading to dilation and ↑IOP
- Lacrimal Gland - secretion
What is the overall effect of α2 type receptors?
- ↓ cAMP
What is an agonist and antagonist for α2 type receptors?
Agonist: Clonidine
Antagonist: Yohimbine
Where can α2 type receptors be found and what is the resulting action?
- Ciliary epithelium
- vesicle fusion inhibition leading to decreased aqueous humor production causing a decrease in IOP
What is the overall effect of β-adrenergic receptors?
- ↑ cAMP
- overall relaxation except in β1 receptors in the heart where HR increases
What is an agonist and antagonist for general β type receptors?
Agonist: isoproterenol
Antagonist: propranolol
Where can β2 type receptors be found and what is the resulting action?
- ciliary epithelium → increase in aqueous humor production → increase in IOP
What disease can highly selective β2 agonists be used to treat?
Asthma
- ↓ cAMP → relaxation in smooth muscle
What is ephedra used for and why is it bad?
- Chinese herbal medicine for treatment of asthma (bronchodilation) and as a dietary supplement (appetite suppressant)
Problem: lasts for hours; not metabolized and as a result ↑ NE levels at junctions
What is Meridia (sibutramine)? and Why is it so bad?
- obesity drug; counterfeit weight loss product
- serotonin/norepinephrine uptake inhibitor (catecholamine transporter)
- increases serotonin level in brain and sympathetic tone, altering appetite (suppressing digestive activity) → flight or fight mode active for a long period of time
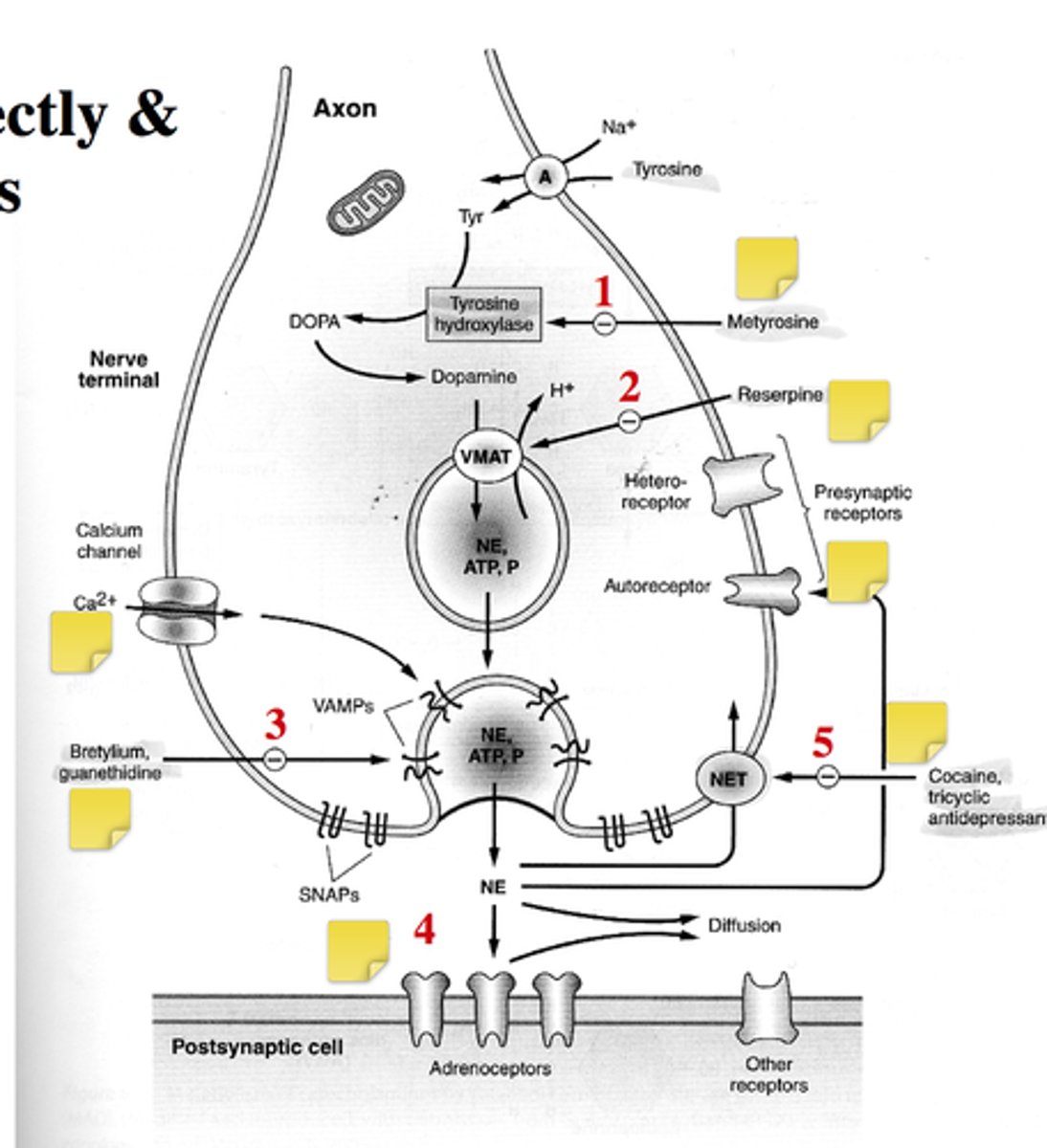
Possible Sites of Drug Interactions
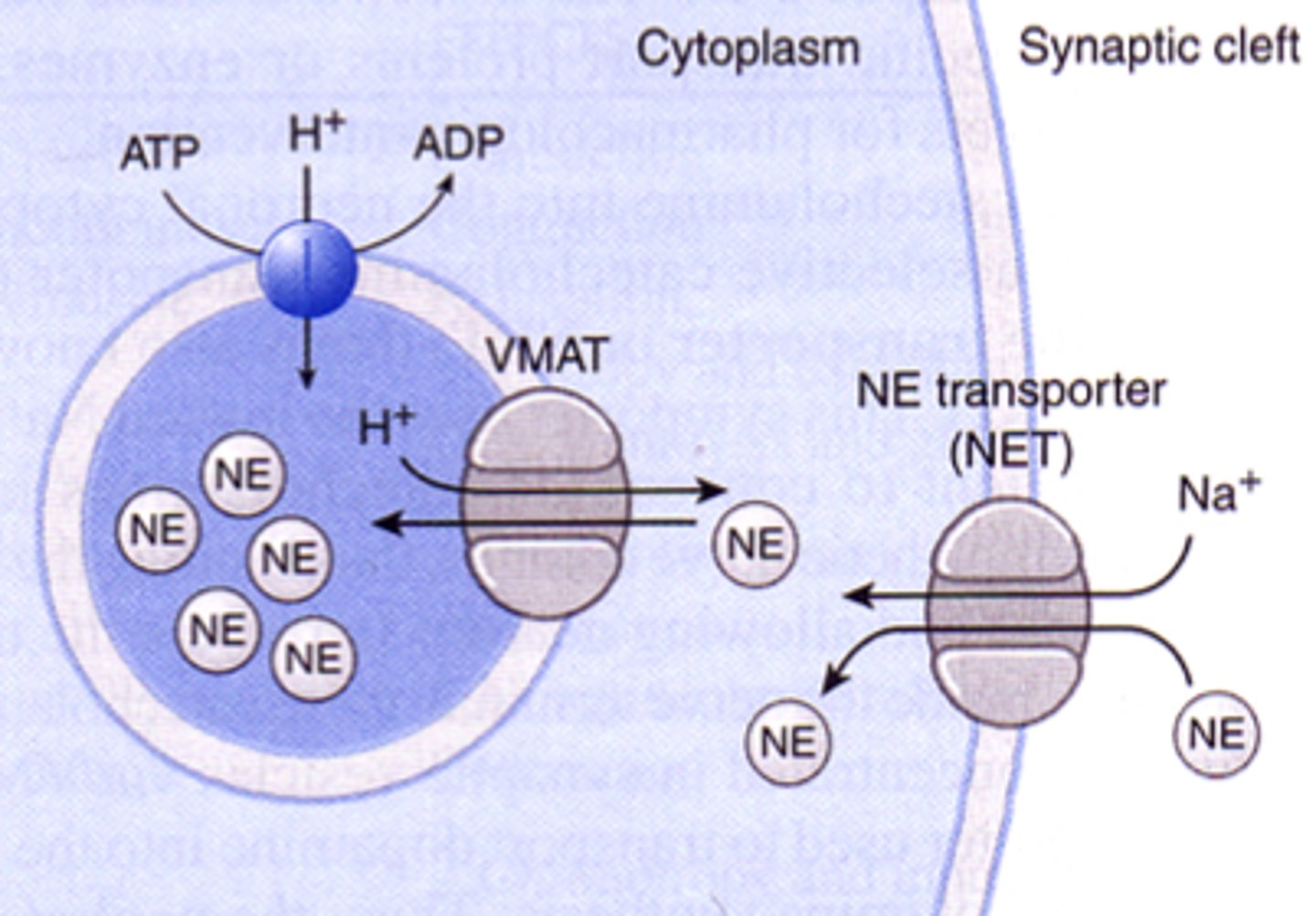
Normal uptake of NE from synaptic cleft
- NE uptaken by active transport (NET)
- NET co-transporter is Na+
- either metabolized or stored in vesicle by active transport (VMAT)
- VMAT co-transporter is H+; requires ATP to create H+ gradient
What are some indirect antagonists for sympathetic system?
- Metyrosine
- Reserpine
- Bretylium, guanethidine
- blocking calcium signals
How does metyrosine act as indirect antagonist?
- mimics the structure of tyrosine
- reduces amount of NE synthesis
How does reserpine act as indirect antagonist?
- prevents packing of NE into vesicles
- NET transporter is still active and NE still being uptaken, but it can't be packaged into the vesicles.
- Eventually the vesicles will have less and less [NE]
- neurons rely on recycling NE into the vesicles
- sympathetic activity ↓
![<p>- prevents packing of NE into vesicles <br>- NET transporter is still active and NE still being uptaken, but it can't be packaged into the vesicles.<br>- Eventually the vesicles will have less and less [NE] <br>- neurons rely on recycling NE into the vesicles <br>- sympathetic activity ↓</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c59f59d1-e344-4bc0-a594-4f53f1553310.jpg)
How does bretrylium/guanethidine act as indirect antagonist?
- inhibits release of NE by reducing VAMPs and SNAPs
What are some indirect agonists acting on the sympathetic pathways?
- Cocaine, tricyclic antidepressants
How does cocaine act as a indirect agonist?
- blocks the NET transporter, increasing [NE] in the NMJ
![<p>- blocks the NET transporter, increasing [NE] in the NMJ</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bbd868b0-b117-4a95-97da-147d811c4b4f.jpg)
What are the acute effects of Ephedrine as an indirect sympathomimetic?
- Ephedrine taken up by cell and competes with NE → displace NE from vesicle → higher [NE] in cytosol → NE flows out of cell due to concentration gradient → increased [NE] in synaptic cleft → stimulatory effect (not as dramatic as cocaine)
![<p>- Ephedrine taken up by cell and competes with NE → displace NE from vesicle → higher [NE] in cytosol → NE flows out of cell due to concentration gradient → increased [NE] in synaptic cleft → stimulatory effect (not as dramatic as cocaine)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6a0fd476-2dfe-4bc2-be9e-07fe55bd672d.jpg)
What are the chronic effects of Ephedrine as an indirect sympathomimetic?
- accumulation of NE in cytosol will lead to it being metabolized
- since Ephedrine displaced NE from vesicle, no new release of NE and overtime [NE] ↓ in the cleft → going from good highs to low. becomes inhibitory chronically
![<p>- accumulation of NE in cytosol will lead to it being metabolized <br>- since Ephedrine displaced NE from vesicle, no new release of NE and overtime [NE] ↓ in the cleft → going from good highs to low. becomes inhibitory chronically</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/49aca492-d3a1-45fe-89ba-b035ebe7dc13.jpg)
What are some other drugs that causes displacement from vesicles?
- Amphetamine
- Hydroxyamphetamine
- Tyramine
- Ephedrine
- Pseudoephedrine (highly effective decongestant)
- Methylphenidate (ADHD) [increases NE, serotonin, DA in brain]
Why is the sale of pseudoephedrine being restricted?
Precursor for synthesizing meth
What is tyramine?
- found in fermented foods (ex. cheese) catecholamine release, MAO inhibitors
- substrate for enzyme, enhancing effect of MAO inhibitor → net effect increase NE levels
- if pts are on MAO inhibitors, ↑ NE in cleft, with cheese, ↑↑NE in cleft
Neuronal effects on recycling
- Cocaine (topical anesthetic & drug of abuse)
- net effect = increase level of NE, DA, Serotonin (5HT), at neurojunctions
- Amphetamine (drug of abuse)
- inhibit uptake of NE, DA, 5HT
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TADs)
- desipramine
- imipramine
Extraneuronal effects on recycling
- corticosteroids
- ↓ rate of NE degradation = ↑ NE in cleft
- phenoxybenzamine (irreversible α-antagonist)
- ↑ NE in neurojunction
MAO inhibitors effect on metabolism
- depression, targeting mainly 5HT/DA.
- phenelzine: irreversible
- amphetamine
- clorgyline (MAO-A)
- selegiline (MAO-B)
PDE inhibitors effect on metabolism
- act on 2nd messengers: cAMP (also adenosine receptor antagonist)
- methylxanthines (caffein, theophylline)
- Caffeine ↑ cAMP by preventing breakdown of cAMP by PDE → more awake
COMT inhibitor effects on metabolism
- used for parkinson's disease
- entacapone
- trying to ↑ levels of 5HT/DA in system
Sildenafil (Viagra) also inhibits a PDE. How is it different from xanthines?
uses the cGMP pathway instead of cAMP
Directly acting α1 agonists we should know [[used for decongestant and mydriatics]]
phenylephrine
naphazoline
oxymetazoline
tetrahydrozoline
Directly acting α1 antagonist to recognize
prazosin
doxazosin
tetrazosin
Directly acting α2 agonists we should know [[used for glaucomarrrr]] ((↓ cAMP → ↓ AH → ↓ IOP))
aproclonidine
brimonidine
Directly acting α2 antagonist to recognize
yohimbine
Directly acting α1/α2 agonists to recognize
methoxamine
Directly acting α1/α2 antagonists to know [[reverse mydriasis]]
thymoxamine
dapiprazole
Directly acting β1 agonist to recognize
dobutamine
Directly acting β1 antagonist to know [[application for glaucomarrrr]] ((↓ cAMP → ↓ AH → ↓ IOP))
betaxolol
carteolol
Directly acting β2 agonists to know [[application for asthma, bronchodilator]] (↑ cAMP → bronchodilation but also ↑ heart contraction)
salbutamol
salmeterol
Directly acting β1/β2 agonist to know
ephedrine
Directly acting β1/β2 antagonist to know [[application for glaucomarrr]]
metipranolol
timolol
levobunolol
Would you give timolol to a patient with asthma, why or why not?
No because 80% of timolol is cleared systemically, blocking β1/β2 will make asthma worse.
Likely side effects of antagonists (peripheral, central/vascular)
α-blockers
• Orthostatic hypotension
• Tachycardia
• Vertigo
• Sexual dysfunction
β-blockers
• Drowsiness
• Fatigue
• Bradycardia • Hypotension
Likely side effects of agonists
adrenergic
• Cardiac arrhythmias
• Headache
• Hyperactivity
• Insomnia
• Nausea • Tremors
All drugs have more than one action
- phenyl: 10x-20x dose for diagnostic than you would give for decongestant action, don't want to give to someone with heart problems.
- E equally potent for β1/β2, NE less effect on bronchodilation, greater effect on heart
- anaphylactic shock → E binds to all receptors equally → epi-pen
- isoproterenol very potent for asthma, but increases HR as well
