Nasal drug delivery
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Why is the nasal cavity used as a drug delivery option?
easily accessible
Rich vascular plexus = topically administered drugs can rapidly achieve effective blood levels whilst avoiding IV
How is a good nasal drug delivery most effectively accomplished?
Accomplished by distributing drugs solutions as a mist of small droplets
Why are large droplets not favoured in nasal drug delivery?
Can aggregate and run off instead of being absorbed
Why is the nasal route a promising method of systemic delivery?
Easily accessed vascular bed
Why is nasal favoured in comparison to buccal/oral administration?
Nasal has a faster onset e.g., in pain, migraine and ED treatment
Drug won’t be destroyed by gastric acid + avoids first pass metabolism
Paediatric patients may refuse oral treatment but nasal may be enter
Buccal medicines require retention of dosage form on buccal areas and may not stay in contact/lower patient compliance
Why may children be more likely to prefer nasal administration?
Ease of access, non-invasive and lack of pain
What are the advantage of nasal drug delivery?
rapid onset of action
Simple administration - painless, convenient, easy
Reduced systemic side effects
Avoids first pass metabolism
Comparable to IV administration and better than Subcut/IM
What are the disadvantages of nasal drug delivery?
local metabolism
Limited number of medications that can be delivered via this route
Many formulations not adequately concentrated to achieve ideal dosing volumes - drug conc or frequency of dosing
Mucosal health impacts absorption - diseases can affect
What is the volume of the nasal cavity?
Around 20ml
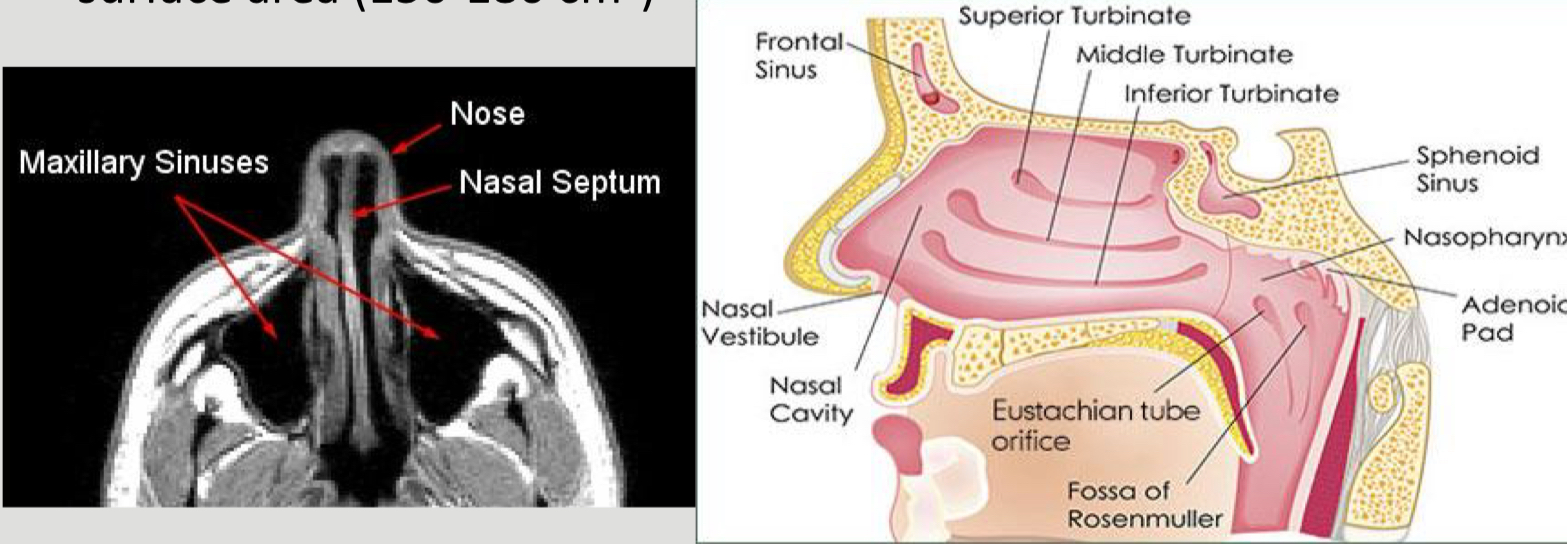
How does the nasal septum divide?
vertically
What is a nasal concha?
A long, narrow and curled bone shelf with protrudes into the breathing passage of the nose
What is a diagram showing the anatomy of the nasal cavity?
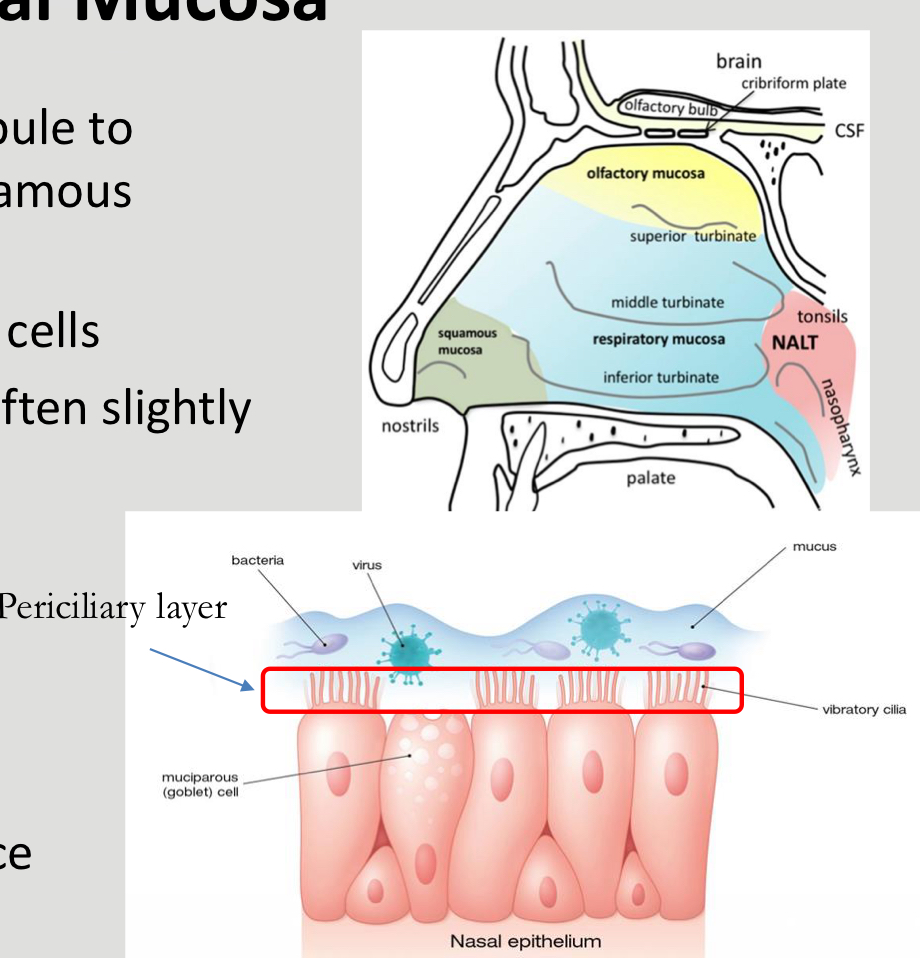
What does the anterior section in the nasal mucosa comprised of?
Squamous epithelium from vestibule to turbinates
What is the key role of the nasal mucosa?
Forms a layer covering the cells, Does not allow materials to penetrate and captures bacteria and large molecules and prevents from entering
What is the average pH of the nasal mucosa?
5.5-6 but higher in children
What is a diagram highlighting nasal mucosa?
What fraction of nasal mucosa cells are non ciliated?
1/3
What are the characteristics of nasal mucosa?
300 cilia per cell, size 5-100mm x0.1-0.3mm, 10Hz clearance and moves at 5-6mm/min
What are some examples of uses of nasal drug delivery for the local route?
Antihistamines, decongestants, corticosteroids, nasal infections
What is an example of a decongestant in local nasal drug delivery?
Ephedrine to relieve congestion of mucous membranes in acute sinusitis and hayfever
Why are corticosteroids used in local nasal drug delivery?
Reduce inflammation and suppress immune system
What is an example of a drug used for nasal infections?
Betnesol-N (betamethasone sodium 0.105% w/v + Neomycin sulphate 0.5% w/v) - colourless pale yellow liquid
How is betnesol-N administered?
2-3 drops instilled into each nostril 2 or 3 times daily
What can the side effects of Betnesol-N be?
Sneezing, changes in sense of smell and taste
What is an example of a systemic drug administered nasally?
Desmopressin to treat nocturnal enuresis/bedwetting
Why can nocturnal enuresis occur?
Deficiency in secretion of ADH during sleep
How does desmopressin work?
Raises night time levels of ADH and decreases urine production
Why is nasal administration favoured for desmopressin?
Faster absorption and onset of action faster than oral tablets
Why is Buserelin used for as a systemic nasal drug?
Treating prostate cancer and endometriosis
Why is buserelin administered nasally?
Ineffective via oral administration due to first pass metabolism in GIT
How is buserelin administered?
Nasal spray 3x per day
Whyat is galantamine used to treat?
Dementia
Why does galantamine use nasal route of administration?
Causes sickness when administered orally
mucociliary clearance slides
Mucociliary clearance
What local metabolism occurs in the nose?
Cytochrome P450s, dehydrogenases, hydroxylases, carboxylesterases, carbonic anhydrase and glutathione transferase
What enzymes may affect peptide drugs administered nasally?
Proteolytic enzymes
What can poor nasal absorption of a drug be attributed to?
Physiochemical properties of the drug limiting transport across nasal membrane
Reduced retention time in nasal cavity due to mucociliary clearance
Biotransformation by the enzymes in the nasal mucosa
What should you use in terms of concentration and volume to maximise bioavailability?
Most concentrated form/lowest volume of medication available - ideal volume is 0,25-0.30mL per nostril
What does a low volume allow for bioavailability?
Reduces runoff but allows maximum mucosal coverage
How can you double the absorptive surface area in nasal drug delivery?
Use both nostrils
Which drug formulation can you use to maximise surface average coverage in nasal administration?
Atomized spray
What patient factors should you beware of in nasal administration?
Localised issues in the nose e.g., bleeding, high mucous production
What physiochemical factors can affect nasal absorption?
lipophilicity/hydrophilicity, molecular weight
PH and ionisation
Solubility
Rate of dissolution
Particle/droplet size
How can local pH be controlled in the nose?
Formulation
Why do you need to consider pH when considering physiochemical factors affect nasal absorption?
Disturb integrity of mucous layer and can change ionisation of molecules
What is the pH at the mucosal surface in the nose?
7.39
What is the pH of mucus in the nose?
5.5-6.5
What factors can affect solubility in nasal absorption?
Prodrugs, choice of salt form, use of appropriate excipients
What affects how far the drug particle goes in the nasal cavities as well as what it does when deposited?
Size, shape and density of particulate material
What is the ideal particle size to ensure particles are deposited in the nasal mucosa?
10-20um
What particle size can pass through the nasal cavity and are deposited in the lungs?
2um or smaller
What will drugs do if introduced as soluble particles in nasal absorption?
Readily pass into nasal lining secretions and absorbed into blood
What formulation considerations should be thought about when improving nasal administration?
control of nasal pH
Maintain toxicity
Choice of vehicle/viscosity
Inclusion of antioxidants and preservatives/shelf life
Why may you want to increase viscosity in nasal administration?
Increases retention/nasal residence time by applying polymers
Why may glycerol be added to improve nasal administration?
Reduces or minimises irritation to the nasal mucosa
What are the requirements of an ideal absorption enhancer?
rapidly-acting with a transient and reversible effect on nasal epithelium
Not absorbed systemically
Non-toxic, non-irritant and non-allergenic
Doesn’t permit entry of dangerous environmental material
Compatible with drugs and other excipients in the formulation
Safe for chronic use - dependant on condition being treated
What are some examples of absorption enhancers?
Surfactants, phosphatidylcholines, cyclodextrins
What are the negative effects of using surfactants as absorption enhancers?
Cause permanent damage and loss of cells
What are the negative effects of phosphatidylcholines?
Disrupts cell membranes as they are similar to naturally occurring cell membrane compounds
What are the properties of cyclodextrins?
Polar outer surfaces and less polar inner surfaces
What is interception in drug deposition?
When the drug travels so close to a surface of the airway passages
What is impaction in drug deposition?
Fast-moving turbulent flow of large particles/droplets of size 0.5-1um and change direction of air flow
Where do particles larger than 10um in diameter get deposited?
In nose and throat and cannot penetrate the lower tissues of respiratory tract
What does particle sedimentation depend on?
Air flow velocity, gravitational forces and air resistance
What is the Stokes law equation?
Smaller the particle = more vigorous the movement
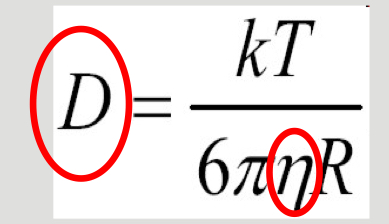
interception and electrostatic precipitation slide
What are some examples of nasal formulations?
Liquids/nasal drops, squeezed bottles/atomised fluids and metered dose pumps
What are some properties of liquid formulations in nasal drug delivery?
Aqueous drug solutions generally, simple and cheap to develop, may require preservatives, can be soothing to nasal mucosa, usually given as nasal drops or unit dose packs
What can be irritating to nasal mucosa in liquid formulations in the nose?
Preservatives
Why can nasal drops be disadvantageous?
Can be inaccurate and lose liquid
What are squeezed bottles for nasal administration?
Partially atomised spray of liquid, sprayed directly into anterior part of cavity
What is an advantage of a squeezed bottles as a nasal drug delivery route?
Large surface coverage of nasal mucosa
What is a disadvantage of squeezed bottles as a route of nasal administration?
technique dependant
What are some advantages of metered dose pumps?
Offer greater control, pre-determined volume of 25-200ul, formulator has larger degree of control over deposition
What can metered dose pumps deliver?
Solutions, suspensions and emulsions