7. history of European colonization: chapter 7: the twentieth century
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1. the first world war and its aftermath - war - peace 2. the interwar period 3. the second world war 4. decolonization 5. postcolonials
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
decisive contribution from the colonies in WWI
resources ex oil and metallic ores
troops
ca 1300000 Indians in the British army
ca 600000 northern africans in french army
flanders: first acquaintance with colonized individuals
british indian soldiers in flanders’ fields
fights in the colonies during WWI
conquest of german colonies
laying base for new colonies
WWI in the ottoman empire
the conquest of German colonies
1914: Asia and Oceania
Britain [new Zealand & Australia] & Japan (quickly reconquered)
1914: togo
1915: Kamerun and german southwest africa
belgian congolese force publique in kamerun
1914-18: german east africa (stayed german for longer time)
force publique, conquered 1916: Kigali, Usumbura & Tabora
ottoman empire
ottoman alliances
1760s-1910s: many wars with russia
ottomans protected by britain (common enemy)
but: alliance russia and britain in 1907 (triple entente)
august 1914: ottoman empire joins Triple Alliance
the triple entente’s interest
weakest link
vs the trenches at other fronts
oil in the Arabian/persian gulf
british
germans (ally ottoman empire): bagdadbahn (500 km short of completion in 1915)
fighting the ottoman empire (britain)
the defeat at gallipoli (april-dec 1915)
australian and new sealand army corps (ANZAC)
anzac day: 25 april
the mesopotanian campaign
1914 Basra, 1915-16 kut (wtihdrawal), 1917 bagdad
british troops mainly Indian
the arab revolt (1916-18) = brits gave support
T.E. Lawrence aids sharif hussein of mecca (hejaz)
conquest of jerusalem (1917) and Damascus (1918)
conflicting promises (allies to several groups)
1915: McMahon-Hussein correspondence
british high commissioner in egypt
prior to arab revolt to hussein: '“on behalf of british government, recognize and uphold independence of the arabs in all the regions within fronties proposed by sherif of Mecca (including “holy land”)”
==> independence of arab states as proposed by hussein
may 1916: sykes-picot agreement
british and french diplomat
divide west-asia after fall ottoman empire into (french and british zones of influence)
no obvious conflict with McMahon
trade zones and spheres of influence (not direct colonies)
Palestine: allied condominium
nov 1917: balfour declaration
british foreign secretary 1916-1919
“establishment in palestine of a national home for the jewish people” ==> promises national home for jews to zionist leaders
new war positions and need of US support
with respect for non-jews
protest from palestinians and zionists (did not go far enough)
league of nations mandates
jan 1918: wilson’s fourteen points
point 5: equal treatment between colonizer and colonized
point 14: formation of an association of nations
june 1919: mandate system
ruling the colonies of germany and ottoman empire
not seen as war booty, but responsible government on behalf of the league of nations
annual reports to a permanent commission in the league
THUS: international legitimization of colonialism
pariser vorortverträge
decisions about post-war fates:
versailles: germany
saint-germain: austria
neuilly: bulgaria
trianon: hungary
sèvres: ottoman empire
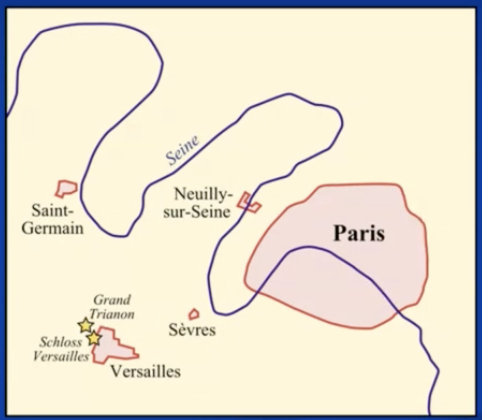
devision of the ottoman empire (sèvres)
mandates
british:
iraq (king faisal; 1932 independent)
transjordan (king abdullah; 1946 independent)
==> sons of sharif hussein
palestine (direct british rule)
french: syria and lebanon
loss of cilicia to turkey (Atatürk) => treaty of Lausanne 1923
others
Kuwait: british protectorate
Kingdom of Hijaz: 1925 to Saudi Arabia
Armenia: only the Armenian SSR
Kurdistan: divided
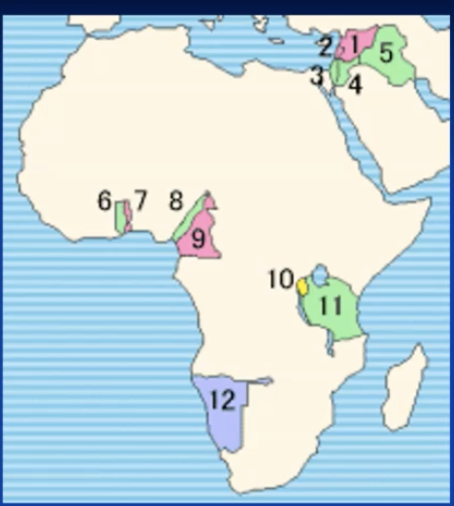
division of german colonies after WWI
France
largest parts togoland & camerun (incl Neukamerun)
great britain
rest of togoland and camerun
rest of german east africa
belgium
ruanda & urundi (only 1962 two different states)
1926: added to the administration of the Belgian Congo
colonies
south africa (britain): southwest africa (namibia)
Japan, australia & new-zealand: pacific islands
why colonial era experienced peak during inter-bellum period
colonies’ contribution to WWI
new colonies after WWI
mandates of the league of nations
Italy conquered Ethiopia (took revenge)
development of the colonies
immigration: more families and administrators
missionaries
infrastructure: railways, communication
economic specialization
cracks in colonialism
economic decline
priority: europe’s postwar recovery
great depression of 1929
more expenses due to growing democratization
loss of image
cruelty of the war (vs image of civilization)
cultural pessimism and self-criticism (Spengler)
fascism and nazism deriving from European culture
competition with US, Soviet Union and Japan
US and Philippines (1934: independent in 1946)
shrinking gaps between colonizer and colonized
colonized had better knowledge
education
more contact with Europe
better spread of ideas via colonial infrastructure
consequences
technological arreas (backwardness) shrink
ex rebellion (war) abd-el krim in morocco 1921-26
growing consciousness of abuse
forced labour, taxes,… due to colonials
answer colonized to developments and shrinking gaps
infiltration and collaboration
ex missionaries (indigenization of church), officials (felix éboué),…
group formation (to resist colonial system)
sub-nationalism (within colony): religion, ethnicity, age, gender
supra-nationalism: négritude (pan-african), panarabism, class (workers,…)
political parties
communist party of vietnam (Ho Chi Minh, 1925)
partai nasional indonesia (Sukarno 1927)
violence
strikes, insurrections
cracks in british empire
loss of position in türkiye, persia and china
loss of the white settlers’ colonies
ireland: independence in 1922
commonwealth with the white dominions
second declaration of balfour (1926)
statute of westminster (1931)
frustration in the arab world
egypt: revolution in 1919, independence in 1921
iraq: independence in 1932
Palestine & jewish immigration
growing problems in india
the egyptian revolution
Saad Zaghloul
demands egyptian independence at versailles
exiled by british —> protest in Egypt
1919: revolution
192: independence recognized by britain
Egypt became kingdom (sultan (fuad) —> king (fuad, farouk))
british kept control over sudan and suez
postwar
revolution/coup of 1952 (officers led by nasser) => monarchy abolished
1956: independence sudan and suez crisis (nasser)
Jews in Palestine
immigration
ca 400.000 jews between 1920 and 1945 (grew further after WWII)
development
cities (Tel aviv) and agriculture (kibbutz = collective farms)
jewish school system (exclusively for jews)
literacy rate: 86% among jews, 22% among arabs
seperate institutions (=> 2 nations)
assembly of representatives (later Knesset)
jewish national council
security service (later mossad)
Palestine under the british mandate
protest
1919 syrian national congress (about versailles)
1920 palestine riots (against zionism)
1936-39 Arab revolt
solutions
1939: White Paper (by British government)
favours independent Palestine governed by Arabs and Jews
1948: british disengagement and creation of Isreal
following holocaust
wars of 1948, 1956, 1967 and 1973 (conquests of land)
Intifada’s of 1985-93 and 2000-2005 (popular uprisings in palestine)
Gaza War of 2023-
India before Gandhi
representation
Indian National Congress (1885) = not to prepare Indian independence but wanted more representation indian elite in policy making British India
Muslim League (1906) = british supported muslim minority in India to weaken Indian national congress and other freedom fightsn (divide and rule) => led to the partition of India in india and pakistan
action
including violence ex in 1905 onwards
contribution in and disenchantment after WWI
promise of responsible government (out of racism, only for white settler colonies)
Dyer & Massacre of Amritsar (1919) => thousands of people killed
New measures: too little & too late
Mahatma Gandhi
1869-1948
Bio before 1915
India- UK (study) - India (lawyer) - south africa: 1893-1915
various strategies
1915: turned INC from elite party into mass party (crossed all of india by train and collected support)
1920-22 & 1930: non-violent boycott (satyagraha = insisting on the truth) => confront Brits with paradoxes of their own discourse => failed because Indians ended up using violence anyway
1924: constructive program (ashram)
early 1930s: round table conference in London (second satyagraha campaign)
1942: Quit India Movement
legacy
non-violence (ahimsa) = like Martin Luther King and Nelson Mandela
criticism of the European model (not only colonizers) = if entire world would adapt this system, it would be unsustainable
Japan WWII
1931-1937-1941: conquering parts of China (violent)
december 1937: The rape of Nanking (Nanjing)
pictures spread also in Europe => much fear
december 1941: United States
pearl harbour
Spring 1942: Japan conquers colonies in South-East Asia (European colonies)
because of fear of Europeans and European metropoles were in war with Germany
idea of Pan-asian liberation (represented by Japan) = welcomed with open arms
deliberate policy of offensing the white (taken into captivity, forced labour)
varying positions of ‘national’ leaders = some supported japan, others didn’t
1944 defeated by British India
1945 defeated by US (lost WWII, atom bombs)
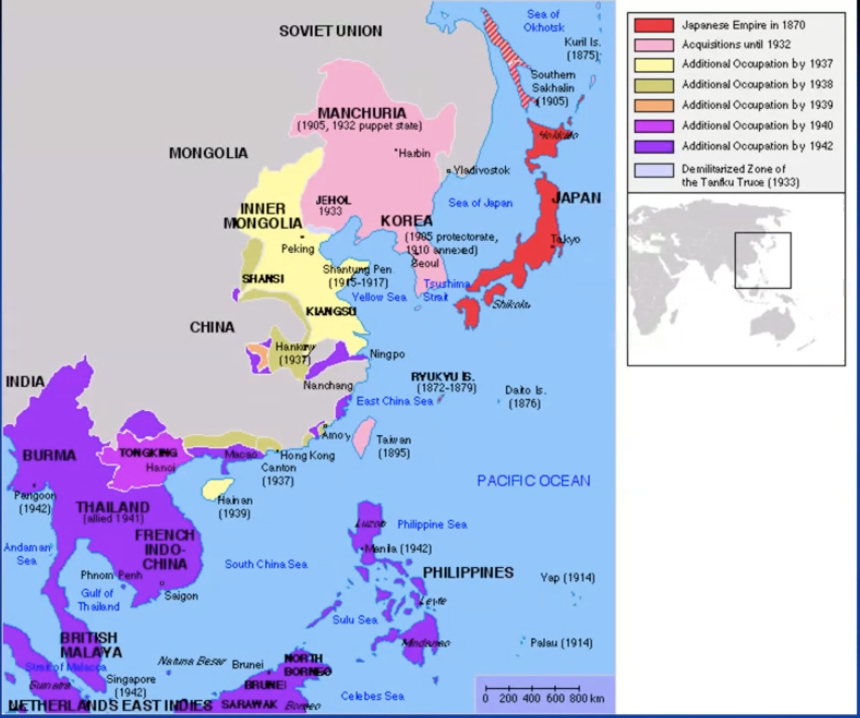
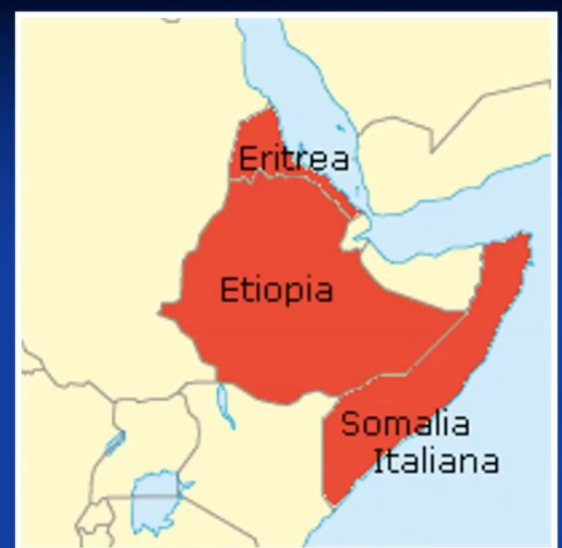
Italy colonies WWII
1935-36: Italy conquers Abyssinia (Mussolini)
decolonization immediately after WWII
ethiopia gains independence
eritrea joined with ethiopia
italian somaliland added to british somaliland (colony ruled by brits)
libya: 1945 UN administration, 1952 independent
NB: mandates of league of nations turned into UN trusteeships
after the decolonization: bloody conflicts
1970s in the Horn: Mengistu, Ogaden War,…
1993: Eritrea independent after decades of civil war (after collapse mengistu regime)
somalia (independent in 1960): chaos from 1990s
causes of decolonization
a normal stage of development
technical catch-up by the colonies
radicalization and inspiration through education
confrontation with the metropole’s discrimination
war (WWII)
economic weakening of Western Europe
new, ‘anti-imperialist’ world leaders: US & SU, UN
ideological dimension: antifascism and antiracism
atlantic charter (aug 1941): self-determination (britain and US)
observation effect
domino from asia to africa
geography of decolonization
interwar and WWII: Middle east/west-asia
egypt & Iraq: interwar period
Lebanon, Syria & Jordan: de facto during WWII
Israel: 1948
1947: south and southeast asia
1947: independence India and pakistan
1945-49: dutch east indies (indonesia) = first to claim independence but dutch did not immediately accept
1946-1954: first/french indochina war
1954: northern africa
1957/1960: sub-saharan africa
India after WWII
growing Muslim-Hindu violence = about what British India should look like => 2 nations theory
Hindu side: Jawaharlal Nehru, Muslim side: Mohammed Ali Jinnah = founding father Pakistan
Churchill (imperialist) lost elections => Labour PM Attlee: political solution
jan 1947: Brits promised independence in july 1948
spring 1947: Brits promised independence a year earlier in august 1947 => growing violence and Britain did not want to be responsible
partition: India and (West- and East-) Pakistan
Radcliffe Border Commission: public on 14 aug
ethnic cleansing in Punjab and Bengal (divided between Pakistan and India)
10M-15M refugees; 1M casualties
Hindu’s in west-punjab or east-bengal and muslims in east punjab or west bengal
Maharaja of Kashmir does not want to take side (wanted to become independent)
hindu raja, but three quarters of population is muslim
had choice between being conquered by pakistan or joining india => chose india
1947 Pakistan invasion, 1949 cease-fire
wars in 1947-49, 1965, 1971 (Bangladesh) & 1999 => kashmir still not solved today
other British colonies in South Asia independence
1948: Ceylon (Sri Lanka)
conflict between Sinhalese majority and Tamil minority (2 ethnic groups)=> only ended in 21st c
1948: Birma (Myanmar)
Initially democracy, from 1962 military junta
democracy temporarily returned with AUng San Suu Kyi but she is “dethroned” in 2021
Malaya remains British colony
1948: federation of Malaya
without crown colonies Singapore, British Borneo,…
1948-1960: ‘Malayan Emergency’
= anti-British National Liberation War (should be seen within cold war) => much amnesia
1957: Malaya independent
1963: federation of Malaysia (with Borneo & Singapore)
1965: secession Singapore
Brunei stays British protectorate until 1984 = very rich
the decolonization of the Dutch Indies
17 aug 1945: Sukarno asserts independence
two dutch military actions (1947 and 1949)
KNIL (100.000 soldiers) = royal dutch indian army
95.000 dutch soldiers to East Indies to fight indonesian freedom fighters
5000 Dutch soldiers died, 150.000 indonesian casualties
different names
Netherlands: ‘politionele actie’
indonesia ‘agresi militer belanda’ (dutch military agression)
huge research program amsterdam university on decolonization indonesia => acknowledge extreme violence
27 dec 1949: dutch recognize independence
Sukarno remains president
dragging problems after independence indonesia
Dutch New Guinea (west of papua)
Dutch remain ‘to protect Melanesian population’
1962-63: Indonesia takes over after UN intervention
South Moluccans (like sikhs in british india)
fought with the dutch against the indonesian freedom fighters
independence war 1950-1966
KNIL soldiers to the Netherlands (Westerbork)
1975-78: train and school hostages (2nd generation) = schools and trains hijacked by moluccans
East Timor
1974: Portuguese withdrawal
1975: indonesian invasion
2002: independence
french retreat from indochina
1945: vietminh (hanoi) declared independence
1946: French troops returned to Indochina
French defeat
independence Laos (1949) and Cambodia (1953)
1954 French troops surrendered at Dien Bien Phu
1954: geneva conference: division
North vietnam: vietminh (communist)
south vietnam: republic => quite weak
1965-73: american protection of south vietnam (from communist powers of north vietnam) = Vietnam war
1975: south vietnam surrenders (painful defeat americans)
1976: (united) socialist republic of vietnam
the algerian war
algerian resistance (had already resisted colonization since beginning)
political parties in interwar period
May 1945: Sétif rising and French suppression (about 300 pieds noirs killed) = French took revenge with severe violence
insurrection of 1 november 1954 (Geneva)
Front de Libération Nationale (FLN) = algerian freedom fighters
french occupied with indochina => answered uprising with war
war (1954-1962)
fierce stance of the pieds-noirs
500.000 french troops vs guerilla
cruelty and violence = greater amount of European settlers in Algeria
300.000 algerians and 21.000 Europeans killed
the suez crisis
1956
facts
Nasser nationalizes the Suez canal
britain france and Israel attack on egypt (29 oct)
furious US reaction
not informed about operation by Brits, french and israeli
colonialism fosters third world’s sympathy with Soviet Union => US wanted to avoid this
attack diverts attention from hungarian crisis
cease-fire (6 nov) and retreat => Suez canal became egyptian
significance
anachronistic colonial arrogance = Brits and French still determined to show power in Africa
to some: trigger of african decolonization => algerian war had already broken out before
french colonial disengagement
Morocco and Tunesia gain independence in 1956
france cannot handle three fronts
fifth republic (sept-nov 1958)
may 1958: de gaulle to pieds-noirs: ‘je vous ai compris’ = promised to fight back in algeria
in power: negotiations with FLN
violent reactions against decolonization
paris massacre of 1961 (maurice papon) = police shot at pro-algerian demonstrants
terrorism: organisation de l’armée secrète (OAS) = attacks on de gaulle
decolonization
14 sub-saharan colonies 1960 (referendums in 1958)
Algeria: Evian Accords (1962)
Sub-Saharan africa
Britain: first
1957 Ghana, 1960 Nigeria, 1961 TAnganyika
France: peaceful
Belgium: quick
Portugal: last
1961-1974: wars (heaviest in Guinea-Bissau)
1974: carnation revolution and decolonization
1974: independence Guinea-Bissau
1975: independence Angola & Mozambique
next decades: civil wars (especially Angola)
Kwame Nkrumah
1909-1972
1935-47 in US
1947 back to Gold Coast
1949 leader Ghana independence moement
1957-66 first president Ghana
advocate of Pan-Africanism
Pariticipant of the Non Alignment Movement (NAM)
Julius Nyerere
1922-1999
1954 cofounder Tanganyika African National Union
1960 prime minister and 1962 president (till retirement 1985) Tanganyika/Tanzania
1967-: ujamaa (familyhood): african socialism
economic decline and systematic corruption
British acceptance independence africa
1960: Nigeria, Somalia
1961: Tanganyika (1964 Tanzania)
1962: Uganda
1963: Kenya
1964: Northern Rhodesia (Zambia) & Malawi
1965: Gambia
1966: Bechuanaland (Botswana) & Lesotho
1968: Swaziland
1980: Southern Rhodesia (Zimbabwe)
==> all different dates (not know)
British declarations of independence Asia
Mlaya (1957), Borneo & Singapore (1963)
(south-) Yemen
north yemen: 1918 independent
south yemen (Aden): British leave in 1967
after lost war against communist insurrectionists
1990: unification North and South Yemen
Cyprus: 1960 independent
Makarios, enosis and the Turkish invasion of 1974
Brudei (petrol and gas): 1984 independent
Hong Kong: 1997 to China
British’ mess
more democratic but also more divided colonies
Palestine, Kashmir,…
secessions
Nigeria: Biafra War (1967-1970) (Igbo ethnical group)
Sudan: south sudan, darfur,…
white vs black
Kenya: Mau Mau uprising (1952-60)
south africa: Apartheid 1948-90
namibia: occupied by south africa until 1990
the Mau Mau uprising
anti-colonial rebellion
large white presence owned the (very fertile) land
increasing african population
rebellion and guerilla war
first european victim shot in 1952
rebel leader dedan KImathi arrested in 1956
dirty war and fierce repression
detention programme
villagisation programme
capital punishment: more than 1000 hanged
at least 20.000 Mau Mau militants killed
heritage of colonialism
general
politics: states, borders, systems
culture: religions, languages, identities
francophonie, commonwealth,…
psychology: feeling of inferiority
power: the west vs the rest
globalization and the place of Europe
particular
politics: the cold war
economy: neocolonialism?
societies: development aid
people: migration
the cold war
the appeal of communism
soviet union
Mao’s China
communism in the third world (fidel castro, che guevara, ho chi minh)
the non aligned movement = did not want to choose either west or communist block
the bandung conference of 1955: to share ideas, form a front (India, Ghana, Egypt, jugoslavia)
US interventionism
support of dictatorships around the world (afraid of ‘red danger’ => american support of Mobutu Congo (cleptocracy)
neocolonialism
new economies
state directed economy
nationalization and loans
dependency theory
economy based on export of raw materials
neoliberalism
1970s: growing debts at IMF and World Bank
1980s: growing interference
1989: washington consensus: standard reform package => counties who wanted loans, very neoliberal
1995: World Trade Organization
2001-: Doha Development Round
development aid
colonial era
missionaries for colonies
NGO’s for European issues
1960s: mushrooming of NGOs
episcopacy, missionaries, pillars, ‘vierde pijler’
1970s: tiersmondism (committed)
1980s: humanitarian aid (professional or popular)
artsen zonder grenzen
band aid & USA for Africa
umbrella organizations
11.11.11
migration
France & Britain
ex British Nationality Act 1948
right of all british subjects to enter Britain (six categories)
migration waves in the 1950s
—> majority of immigrants from the colonies
Netherlands
1M on 16M has colonial roots
Portugal
150.000 postcolonial immigrants
begium?
20.000 congolese in 1990