APUSH Ch 16 - Manifest Destiny and Its Legacy 1841–1848 Key Terms and People
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Tariff of 1842
Protective measure passed by Congressional Whigs, raising tariffs to pre-compromise tariff of 1833 rates. Also known as the “black tariff” due to its high 40% raised duties on imports; eventually, the unfavorable economic conditions sparked political backlash, leading to the response of the Walker Tariff.

Caroline
Diplomatic row between the United States and Britain. Developed after British troops set fire to an American steamer carrying supplies across the Niagara River to Canadian insurgents, during Canada's short-lived insurrection.

Creole
American ship captured by a group of rebelling Virginia slaves. The slaves successfully sought asylum in the Bahamas, raising fears among southern planters that the British West Indies would become a safe haven for runaway slaves.

Aroostook War
Series of clashes between American and Canadian lumberjacks in the disputed territory of northern Maine, resolved when a permanent boundary was agreed upon in 1842.

Manifest Destiny
Belief that the United States was destined by God to spread its "empire of liberty" across North America. Served as a justification for mid-nineteenth-century expansionism.

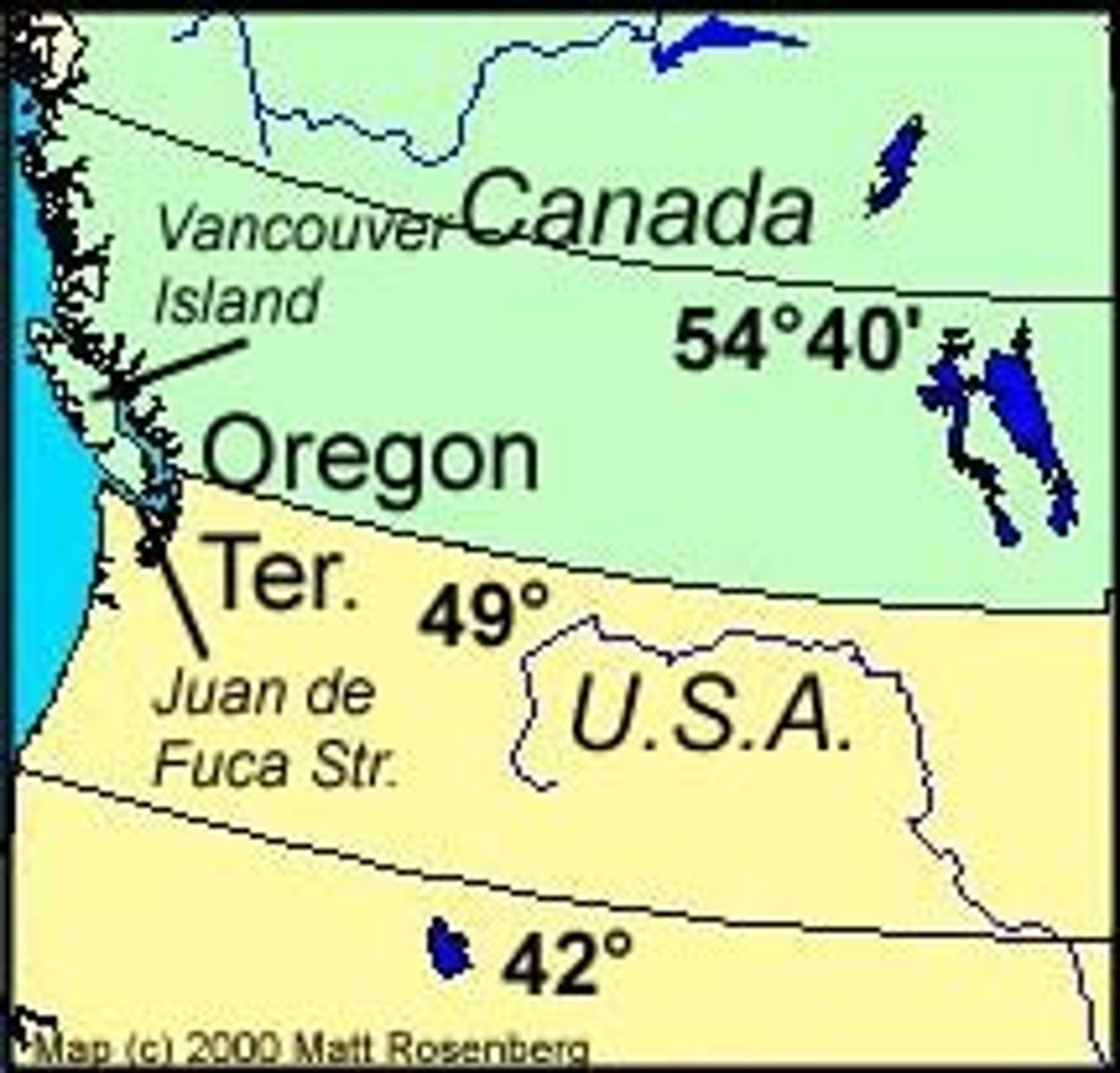
"Fifty-four forty or fight"
Slogan adopted by mid-nineteenth-century expansionists who advocated the occupation of Oregon Territory, jointly held by Britain and the United States. Though President Polk had pledged to seize all of Oregon, to 54°40', he settled on the forty-ninth parallel as a compromise with the British.
Liberty party
Antislavery party that ran candidates in the 1840 and 1844 elections before merging with the Free Soil party. Supporters of the Liberty party sought the eventual abolition of slavery, but in the short term hoped to halt the expansion of slavery into the territories and abolish the domestic slave trade.

Walker Tariff
Revenue-enhancing measure that lowered tariffs from 1842 levels, thereby fueling trade and increasing Treasury receipts.

spot resolutions
Measures introduced by Illinois congressman Abraham Lincoln, questioning President James K. Polk's justification for war with Mexico. Lincoln requested that Polk clarify precisely where Mexican forces had attacked American troops.

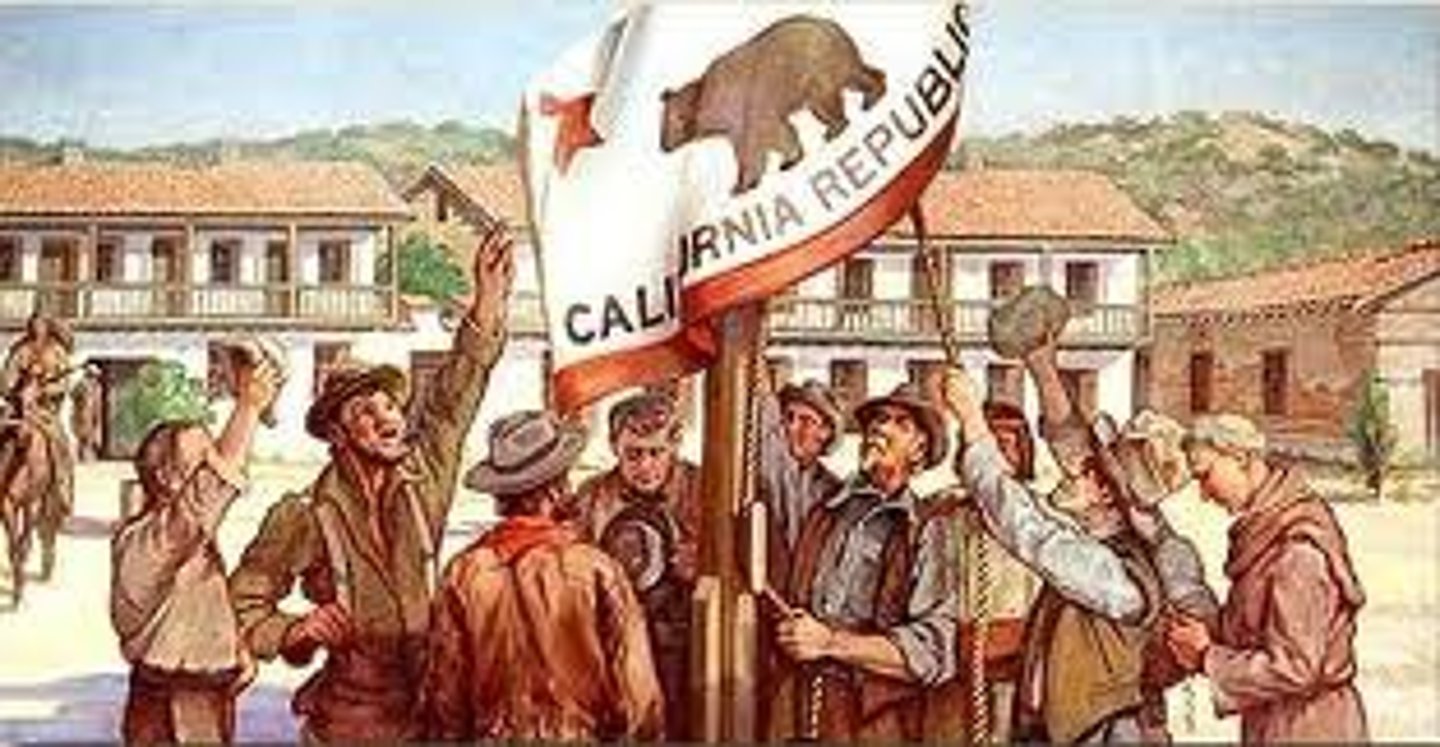
California Bear Flag Republic
Short-lived California republic, established by local American settlers who revolted against Mexico. Once news of the war with Mexico reached the Americans, they abandoned the Republic in favor of joining the United States.

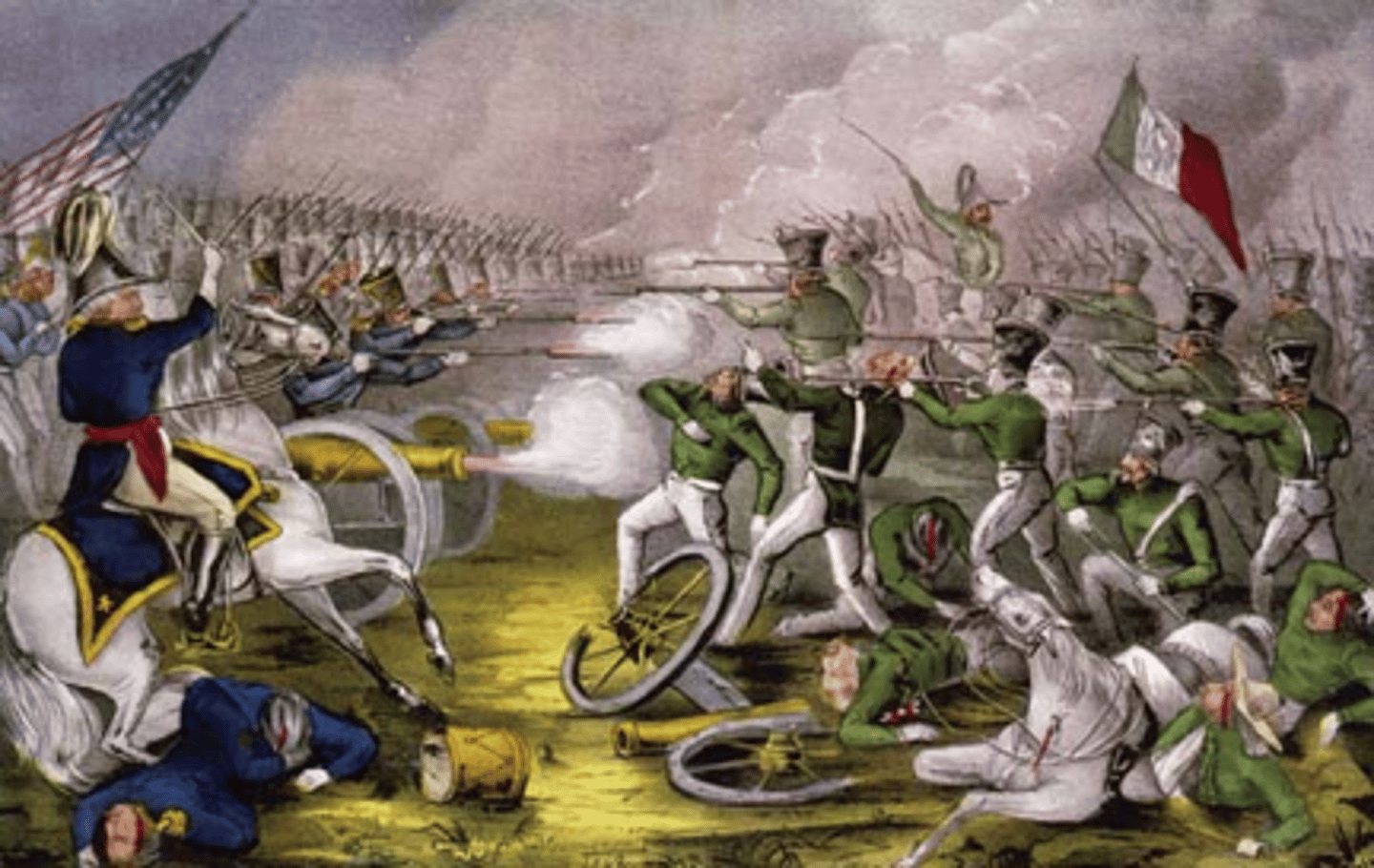
Battle of Buena Vista
Key American victory against Mexican forces in the Mexican War. Elevated General Zachary Taylor to national prominence and helped secure his success in the 1848 presidential election.

Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
Ended the war with Mexico. Mexico agreed to cede territory reaching northwest from Texas to Oregon in exchange for $18.25 million in cash and assumed debts.
Conscience Whigs
Northern Whigs who opposed slavery on moral grounds. Conscience Whigs sought to prevent the annexation of Texas as a slave state, fearing that the new slave territory would only serve to buttress the southern "slave power."

Wilmot Proviso
Amendment that sought to prohibit slavery from territories acquired from Mexico. Introduced by Pennsylvania congressman David Wilmot, the failed amendment ratcheted up tensions between North and South over the issue of slavery.

John Tyler (1790-1862)
Tenth president of the United States. A Whig in name only, Tyler opposed central tenets of the Whig platform, including tariffs, internal improvements, and a national bank.
James K. Polk (1795-1849)
Eleventh president of the United States. A North Carolina Democrat, largely unknown on the national stage, Polk campaigned on a platform of American expansion, advocating the annexation of Texas and the "reoccupation" of Oregon. As president, Polk provoked war with Mexico, which added vast tracts of land to the United States but led to a bitter sectional conflict over the expansion of slavery into newly acquired territories.

Stephen W. Kearny (1794-1848)
American officer during the Mexican War who led a detachment of troops into New Mexico and captured Santa Fe.
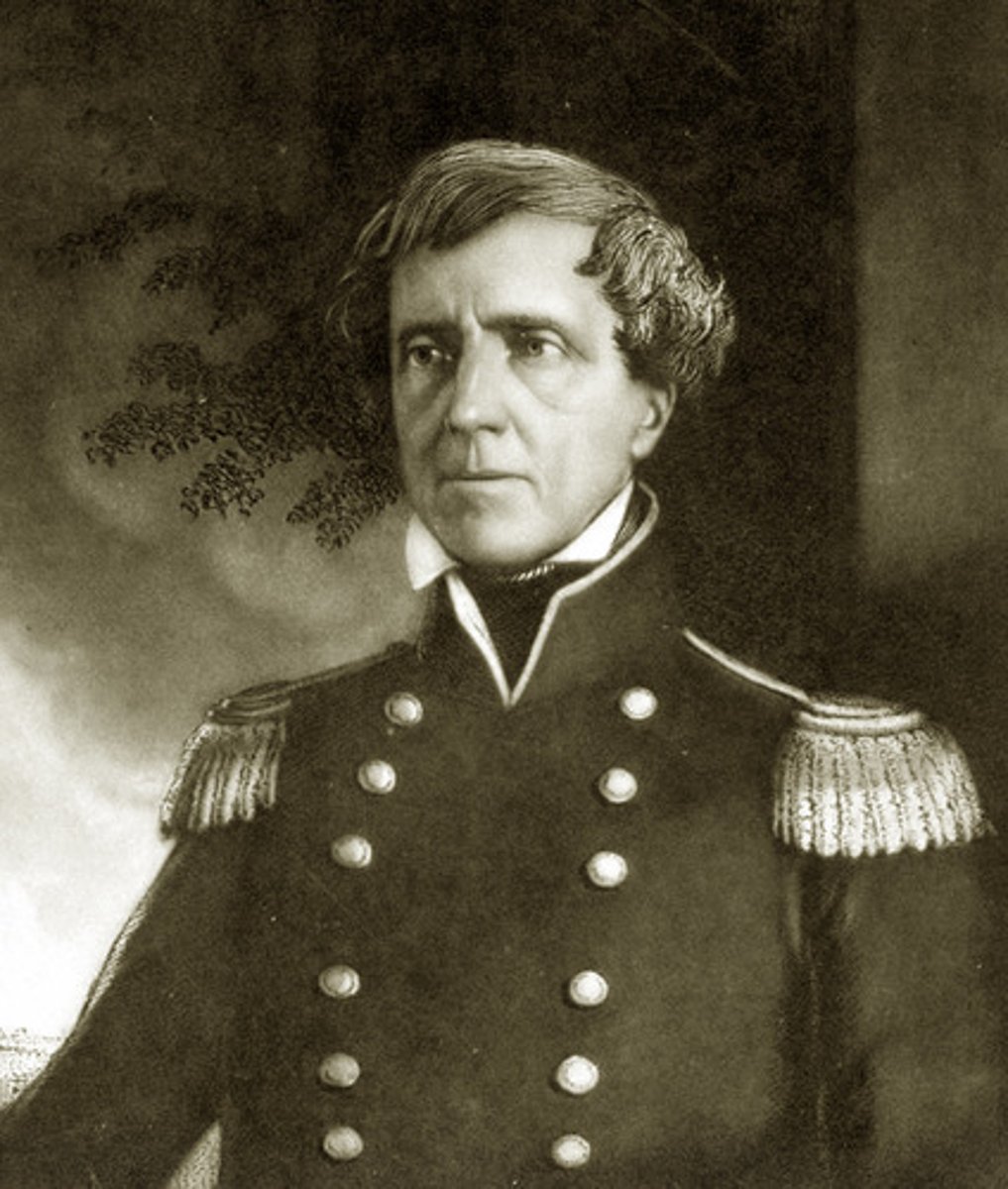

John C. Frémont (1813-1890)
Explorer who helped overthrow the Mexican government in California after the outbreak of war with Mexico. He later ran for president as the Republican nominee in 1856 but lost the election to Democratic candidate James Buchanan.
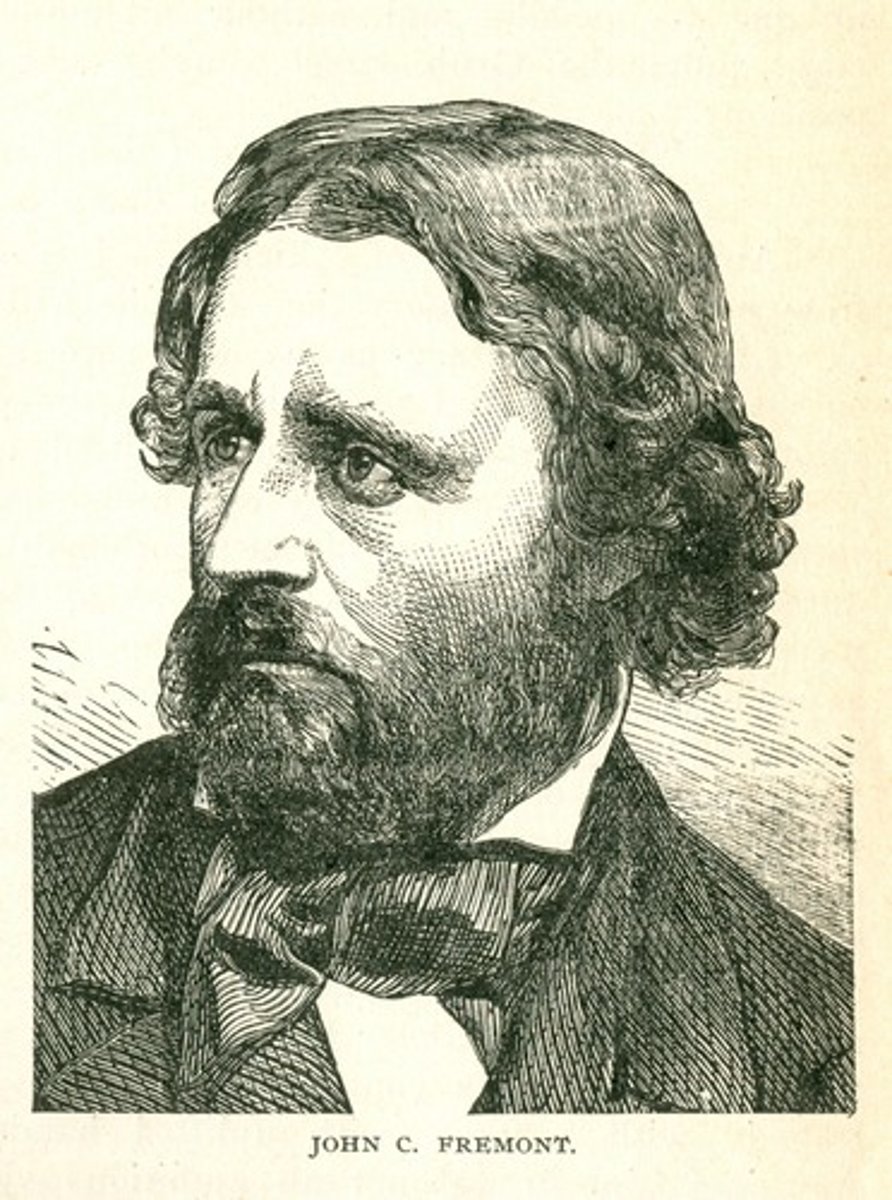

Winfield Scott (1786-1866)
Military officer and presidential candidate, Scott first made a name for himself as a hero of the War of 1812. During the war with Mexico, he led the American campaign against Mexico City, overcoming tremendous handicaps to lead his men to victory. He later made an unsuccessful bid for the presidency in 1852 as the Whig candidate.
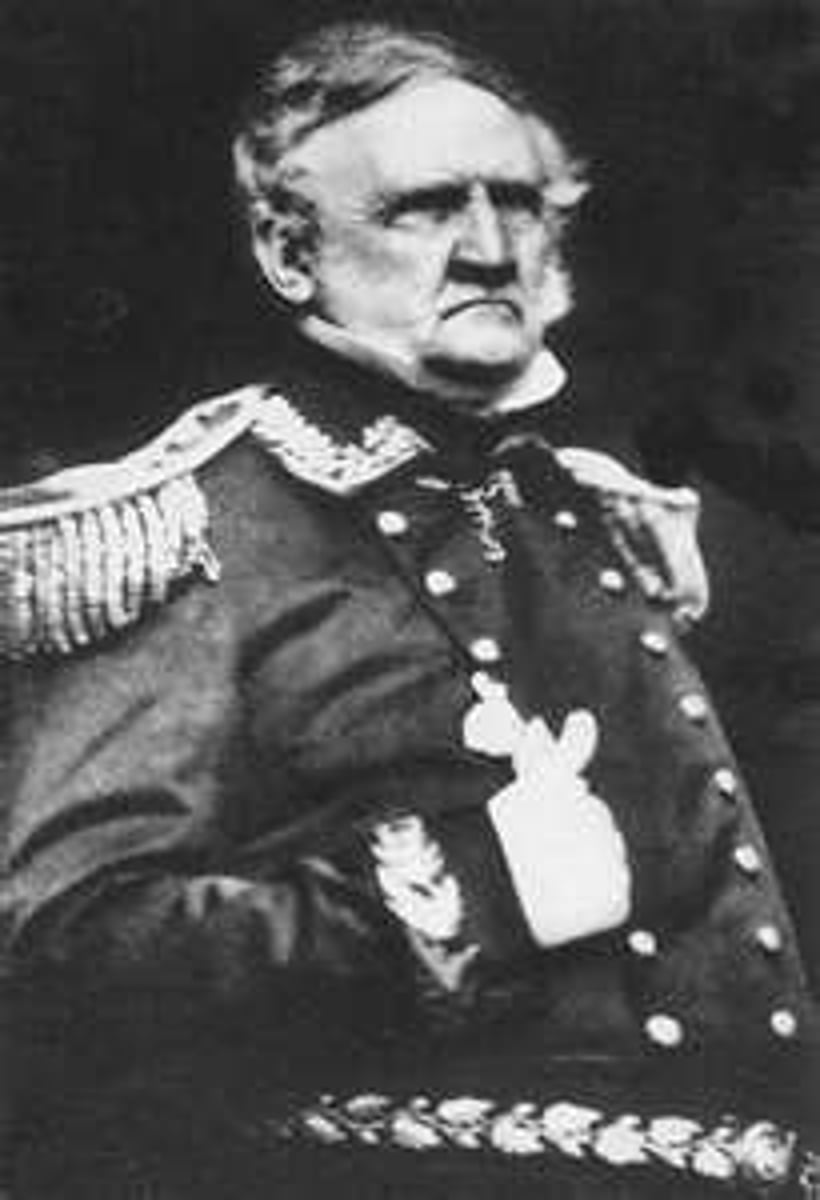

Nicholas P. Trist (1800-1874)
American diplomat who negotiated the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848, which ended the Mexican War and through which the United States acquired a vast amount of territory from Mexico.
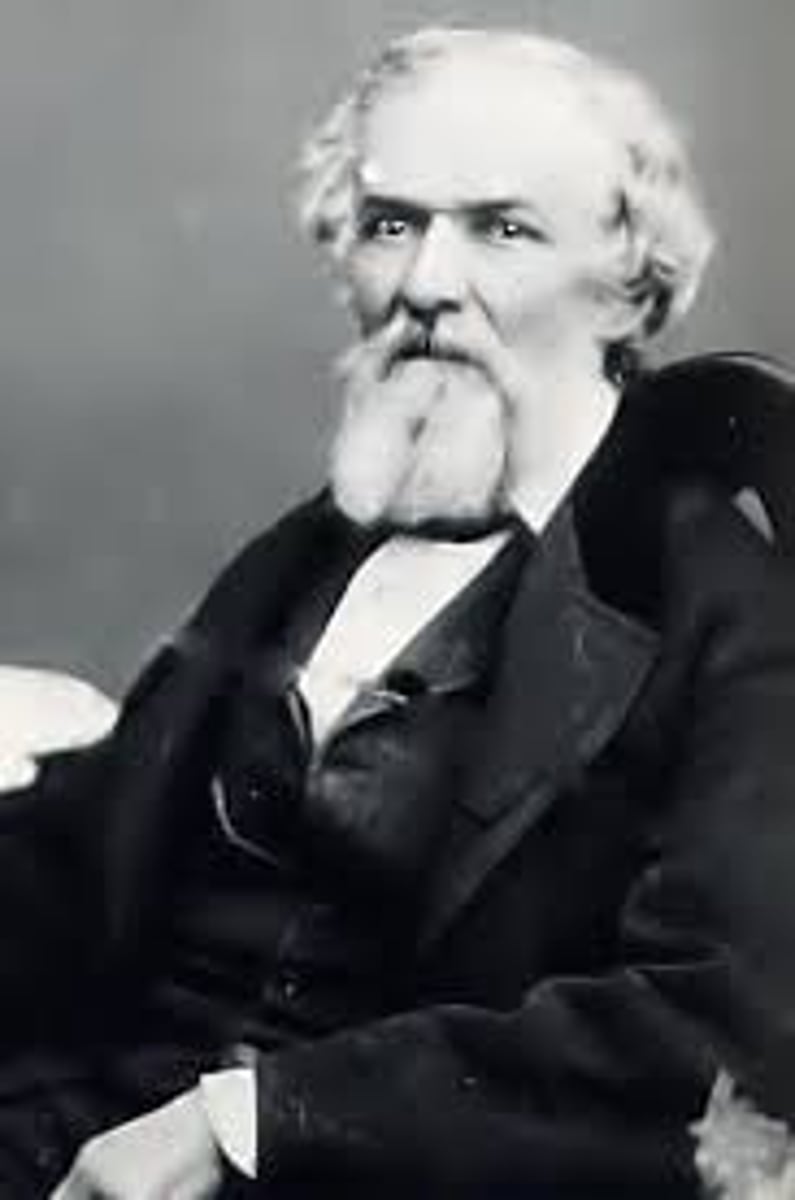

David Wilmot (1814-1868)
Pennsylvania congressman best known for his "Wilmot Proviso," a failed amendment that would have prohibited slavery from any of the territories acquired from Mexico. He later went on to help organize the Free Soil and Republican parties, supporting Abraham Lincoln in 1860.
