PSY 242 - Research Methods II
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
bivariate correlation
association of two variables
operational definition
define the variable and how it will be measured (in order to replicate)
four types of variables
nominal (categorical)
ordinal (order; distance between varies)
interval (likert type scale)
ratio (true zero)
correlation coefficient (r value)
a value between -1 and 1
strength: close to -1 or 1 = close relationship
direction: positive, negative, or zero
pearson (r) for normal
spearman (rho) for skewed
0.1=small 0.3=med 0.5<=large
power
larger sample; lower power
statistical significant (p-value)
the probability that results are due to chance (p < 0.05 or 0.01 is typical) (reality)
type 1 or type 2 error
type 1 error: false positive (okay with 5%)
type 2 error: false negative (okay with 20%)
null hypothesis
no effect/no impact
effect size
the magnitude of effect
how meaningful/important the relationship is
how close the dots are to the line of best fit
generally effect size of 0.3 or higher is considered meaningful
ex. Cohen’s d
if the sample is too large, you risk an erroneous high effect size
confidence interval (CI)
a range of values that is likely to contain the true value of a population parameter
spurious association
variables that seem connected but are being influenced by a third variable
to establish causation, a study must satisfy:
covariance of cause and effect
are the variables related
temporal precedence
cause must come before effect
internal validity
is there an alternative variable
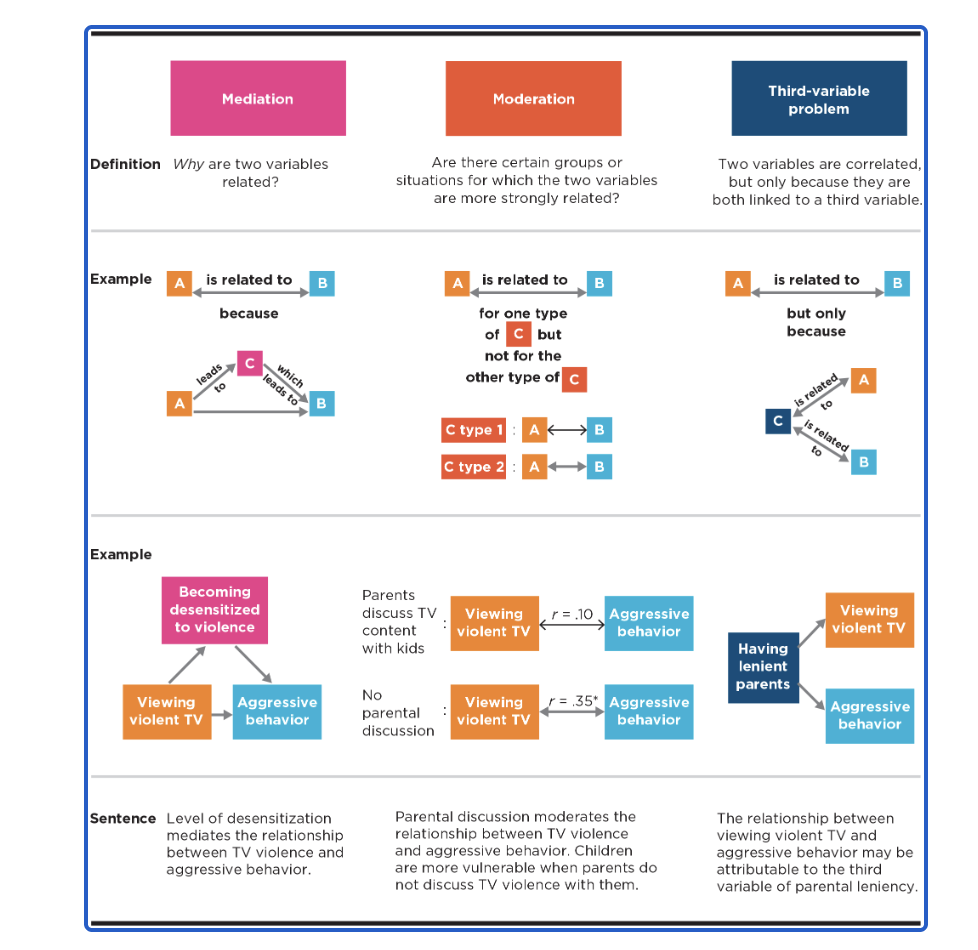
moderator vs mediator vs third-variable problem
third-variable problem
two variables are correlated only because they are linked to a third variable
moderator
strength/direction of relationship changes due to another variable
relationship does exist with or without mediator
beta would change in direction/ strength
mediator
actual cause (how/why)
relationship does not exist without mediator
beta would be n.s
regression model
internal/external validity
internal: study accurately shows association
external: can findings be generalized
construct/statistical validity
construct: study measures concepts accurately
statistical: data supports conclusions
multivariate research
involves more than two measured variables
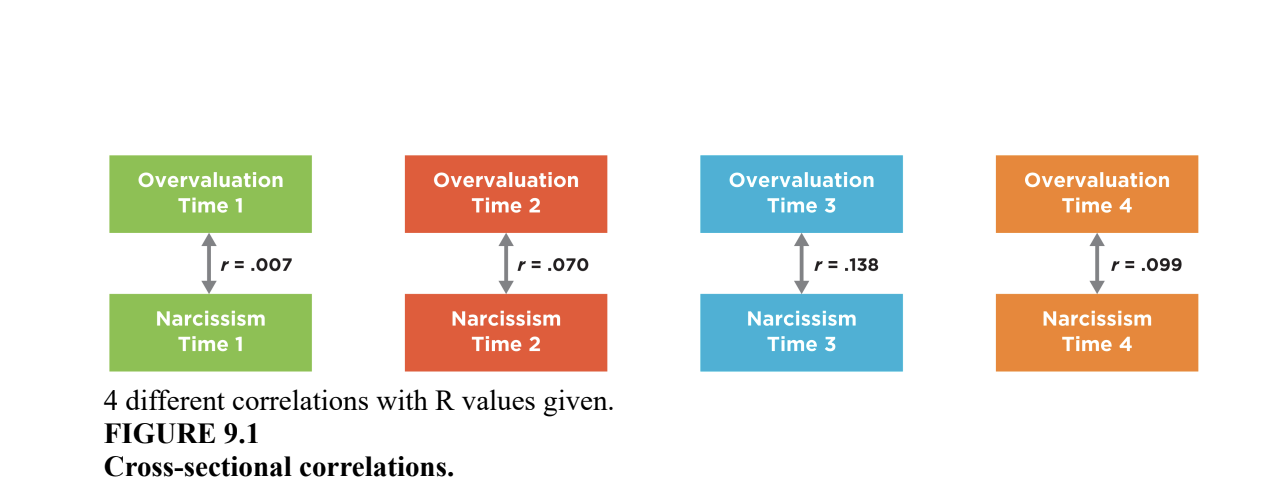
cross-sectional correlation
whether two variables, measured at the same point of time, are correlated
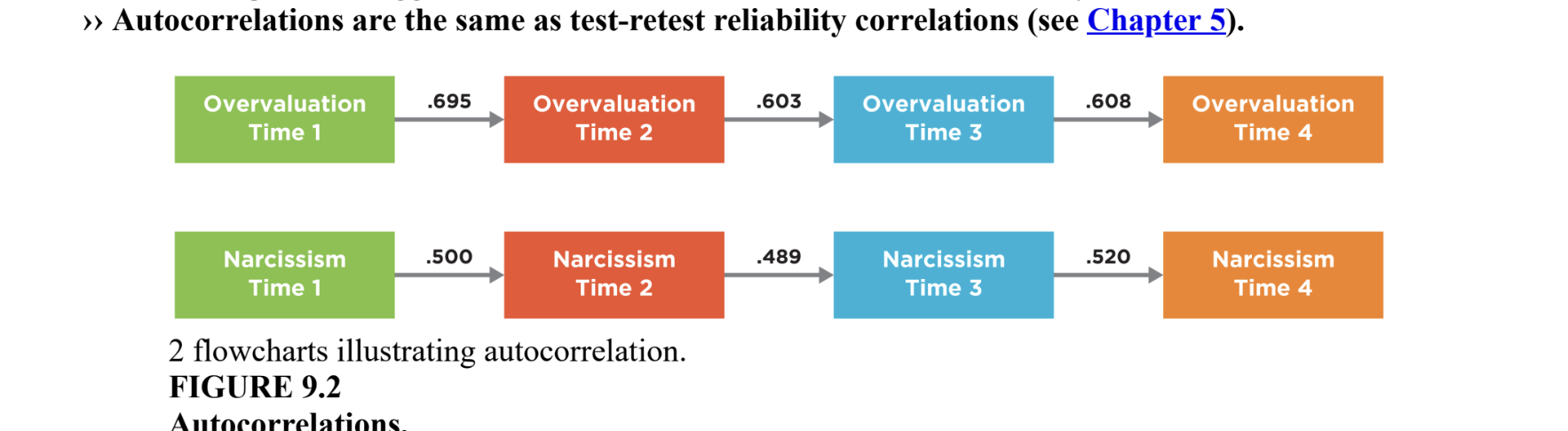
autocorrelation
determine the correlation of one variable with itself; measure at two different occasions
cross-lag correlation
earlier measure of one variable is correlated with the later measure of the other variable
show cause and effect
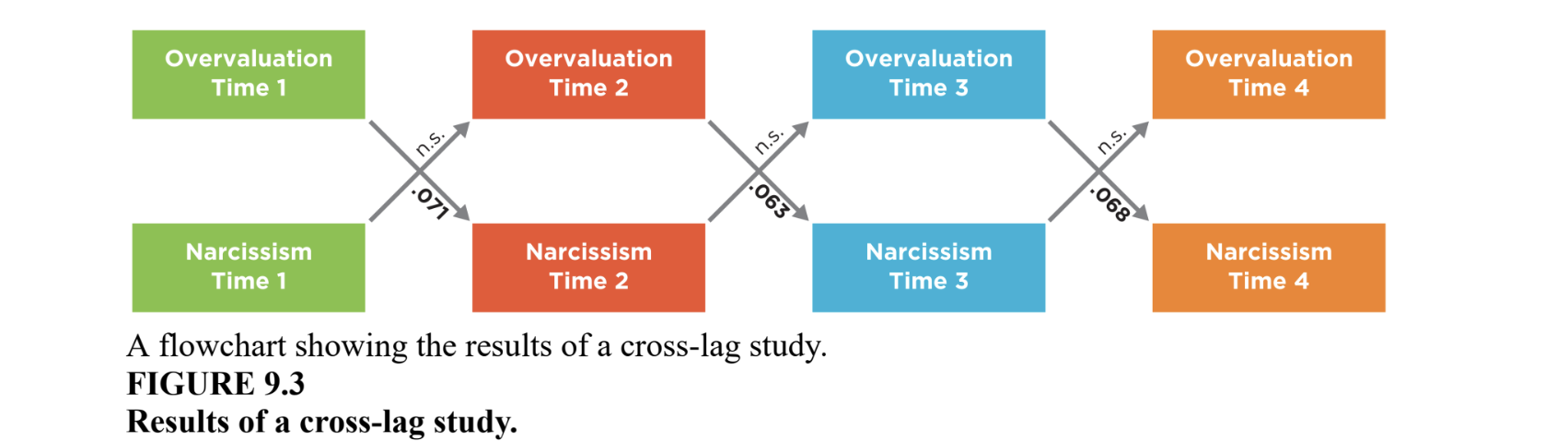
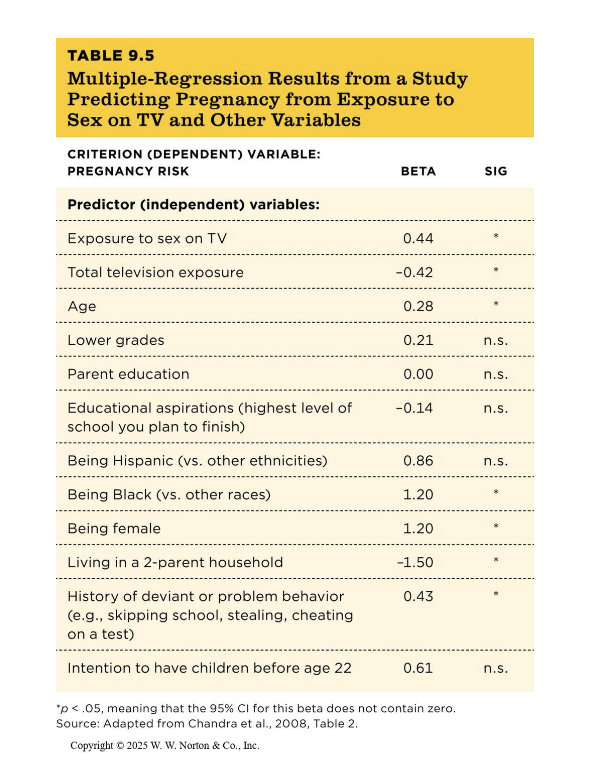
beta
used to test for third variables
beta close to zero = n.s.
95% CI contains zero = n.s.
criterion vs predictor variables
criterion variable = dependent variable (ex. pregnancy risk)
predictor variable(s) = independent variable (ex. socioeconomic status, age, etc.)
pattern and parsimony
pattern: evidence from multiple studies points to the same direction (evidence of replication)
parsimony: simplest explanation with the fewest assumptions (preferred)
in a proper experiment there is:
1 manipulated variable (independent)
1 measured variable (dependent)
one-time occurrence
control group, placebo group, and experimental group
experiments can determine causality because…
covariance (comparison)
temporal precedence (IV before DV)
internal validity (no confounds)
design confound
mistake in designing independent variable
selection effect
systemic difference between groups
participants pick groups
random assignment/matching reduces selection effect/individual differences
order effect
exposure to one level of the IV influences the next level (practice, fatigue, carryover effects)
systemic vs unsystematic variability
systemic variability: consistent variation
unsystematic variability: random variation
independent-group designs
different groups of participants given different levels of the IV
posttest only
pretest/posttest
within-groups design
each person is presented with all levels of IV
each person is own control
repeated-measures design
subject measured more than once
concurrent-measures design
subjects exposed to different levels of IV at the same time
counterbalancing
presenting the levels of the IV to participants in different sequences
latin square
ensuring every condition appears in each position at least once
partial counterbalancing
demand characteristic
a cue that leads participants to guess a study’s hypotheses or goals
manipulation check
an extra dependent variable that can be inserted into an experiment to ensure the manipulation worked
pilot study
a study using a separate group of participants completed before/after the study of primary interest to confirm the effectiveness of the manipulations
maturation threat
definition: observed change emerges more/less spontaneously
prevention: control/comparison group
history threat
definition: external/historical factor affects most members of the group
prevention: careful timing, control group
regression threat
definition: extreme measures moving closer to the mean
prevention: random assignment, multiple baseline measures
attrition threat
definition: participants dropping out of study
prevention: analyze patterns, track attrition, more participants
testing threat
definition: effects of taking the test more than once
prevention: alternative forms, control group
instrumentation threat
definition: measuring instrument changes
prevention: consistency, training, calibration
selection-history threat
an outside event or factor systematically affects participants
selection-attrition threat
participants in only one group experience attrition
observer bias
definition: researchers’ expectations influence their interpretation of the results
prevention: double-blind study, masked study
demand characteristics
participants guessing what the study is about and changing their behavior in the expected direction
placebo effect
improvement after treatment because recipients believe they are receiving a valid treatment
double-blind study
both participants and researchers do not know who is in treatment and comparison group
null effect
independent variable did not make much difference
ceiling effect
scores cluster at high end
floor effect
scores cluster at low end
measurement error
factors that can randomly inflate/deflate scores
situation noise
definition: distractions in the environment
prevention: control lab conditions
power
likelihood a study will yield a statistically significant result when the IV really has an effect
interaction
original IV affects a level of the other IV
intersecting lines = crossover interaction
moving away slowly = spreading interaction
factorial design
two or more IVs
participant variable
selected variables (not manipulated)
ex. age, gender, ethnicity
main effect
overall effect of one IV on DV
average
independent-groups factorial design
IVs = independent groups
ex: 2×2 = 4 groups
within-groups factorial design
all participants receive all combinations
mixed factorial design
IV #1: independent-groups design
IV #2: within-groups design
quasi-experiment
researchers do not have full experimental control (also called natural experiments)
quasi-independent variable
a variable that resembles an IV but the researcher does not have control over it
small n-design
a lot of information from a small sample size (information from special case studies)
stable-baseline design
researcher observing behavior for an extended baseline period before implementing an intervention/treatment
multiple-baseline design
staggering the introduction of an intervention/treatment across a variety of individuals, times, or situations to rule out alternative explanations
reversal design
observing a problem behavior with and without treatment, taking treatment away and seeing whether behavior returns or not
direct replication
replicate the original experiment as closely as possible
conceptual replication
explore the same research question using different procedures
replication-plus-extension
researchers replicating an original experiment and adding variables/conditions to test additional questions
scientific literature
series of related studies
meta-analysis
mathematically averaging the results of all the studies
file drawer problem
meta-analysis overestimating the true size of an effect
HARKing
hypothesizing after results are known
p-hacking
attempting questionable data analysis techniques in order to obtain a p-value under 0.05 (can lead to nonreplicable results)
open science/data/materials
disclosing data, hypotheses, materials, measures, and manipulations openly
theory-testing mode
a researcher’s intent for a study
universality assumption
an explicit/implicit belief by researchers that all participants would act the same
ecological validity
the extent to which manipulations in a study are similar to real-world contexts
experimental realism
the extent to which a lab experiment is designed so that participants experience authentic emotions, motivations, and behaviors