Textiles Exam 2 Ciotti (CHS: 4 + 5) 🌱 🐑
Where are natural cellulose fibers derived from?
plant, animals, or minerals
What are the two types of manufactured fibers?
regenerated + synthetic
1/119
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Where are natural cellulose fibers derived from?
plant, animals, or minerals
What are the two types of manufactured fibers?
regenerated + synthetic
What is a regenerated fiber?
artificial fibres transformed from plant cellulose into yarn
What is a synthetic fiber?
man-made fibers, created through chemical processes from raw materials like petroleum, natural gas, or coal, and are not derived from natural sources like plants or animals
What fiber is most popular in the world?
Cotton !!!!
About Cotton:
Cotton's combination of properties makes it ideal for warm-weather apparel, activewear, work clothes, upholstery, draperies, area rugs, towels, and bedding! Cotton is also a major component of many blends in which manufactured fibers such as rayon or polyester are added to the fabric.
Manufactured characteristics of Cotton:
Extremely high moisture levels, Rain fall or irrigation, warm dry + long season during picking, Ginning, Toxic chemical with cotton and water usage, Cotton needs a long, hot growing season, Cotton grows worldwide.
Characteristics of Cotton:
Light weight, Durable, Breathable, Aborbs and releases fiber, Prone to discolor after wash, Always shrink, Wrinkles easily

About Flax:
Sustainable fiber, Linen, Oldest and strongest natural bast fibers, Durable, Breathable, Does not stretch, Insect resistance, Absorbs moisture, Cant dye or bleach

What is Kapok?
renewable natural plant fiber, often referred to as poor man silk, from south America late 19th century, 8 times lighter than cotton, soft and silky, water repellent, highly flammable, insulates sound, absorbs oil and dyes well, biodegradable

What is Coir?
coconut husks, doormats, thickest of all commercial natural fibers, India, ropes and cords, able to insulate heat, retains moisture, resistant to salt water damage, unable to insulate sound, very hard to dye

What is Ramie?
strong plant fiber similar to linen, china grass, strongest natural plant fiber, blend with cotton, polyester, wool, used in ancient Egypt, stiff and brittle, softens with age, hold garment shape well, withstands heat, antibacterial, dyes well, shrinks

What is Hemp?
sustainable textiles, blended with other fibers, coarse, 8000 bc, Middle Eastern civilization, UV resistant, mildew and insect resistant, very hard to dye,

What is Jute?
low cost, low maintenance, fast growing, most affordable fibers, originated in india, grown on farms for centuries, late1800s, durable, hold garment shape well, biodegradable

What is Abaca?
low cost, silk-like texture, extracted from the leaf by the trunk, close relative to the banana tree, dutch, ships, Philippines, lightweight, high elasticity, resistant to salt water damage, takes dye well

What is Sisal?
often used for ropes, strong coarse fiber, long fiber, leaves are beaten and separated tough from beaten, Mexico, pre Columbian times, durable, water resistant, insulate sound, takes dye well, biodegradable
What three fibers are apart of Seed Fibers?
Cotton, Kapok, Coir
What five fibers are apart of Bast Fibers?
Flax, Ramie, Hemp, Jute, Kenaf
What five fibers are apart of Leaf Fibers?
Pina, Sisal, Henequen, Ixle, Abaca
What are the Properties of Cellulose Fibers?
absorbent, greater wet strength than dry strength, good heat conductor, withstands high temperatures, low resiliency, lacks loft
What is Cotton Ginning?
removing the seeds from the cotton fibers
Longer fiber = …… quality
higher
What is used to determine the class of the cotton fiber?
High Volume Instrument (HVI)
What is the chemical composition of cotton?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
What is organic cotton?
produced following organic farming practices (no synthetic pesticides or fertilizers are used) for at least 3 years
What is Transition cotton?
produced on land where organic farming is practiced, but the 3-year minimum has not been met
What is Green cotton?
Cotton fabric that has been washed with mild natural-based soap but has not been bleached or treated with other chemicals, expect natural dyes
T or F? Cotton has better wet strength than dry strength
True
T or F? It is possible to see the twists in cotton under a microscope
True
T or F? Glucose is the basic monomer of cotton
True
T or F? Coir fibers come from coconut trees
True
T or F? Flax fibers are shorter than cotton fibers
False
What is Retting?
decomposing the pectin by bacteria rotting and loosen the fibers so that fibers can be removed from the stalk
What is unique to flax:
Flax does not lint, its a prestige fiber, and Fabric made from flax is called linen.
Environmental Impacts of Flax:
Flax has Less of an environmental impact than cotton, but Retting may cause environmental problems
Seed Fibers:
Seed fibers develop in the seedpod of the plant and In order to use the fiber, it must be separated from the seed.
T or F? Cotton can take place when growing season is short and cold
False
T or F? Flax is a seed fiber
False
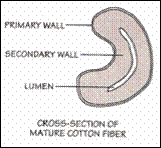
Physical structure of cotton:
Staple length is very important because it determines how the fiber is handled during the spinning process. The cotton fiber is made up of a cuticle, primary wall, secondary wall, and lumen.
Which is the oldest documented fibers?
flax
T or F? Flax has less of an environmental impact than cotton
True
T or F? Flax burns readily in a manner very similar to that of cotton
True
T or F? Pinal and sesal fall under leaf fibers.
True
What fiber is 8x stronger than Cotton?
Hemp
What is second to cotton when it comes to production?
Jute
What is considered the “golden fiber”?
Jute
Which fiber comes from a “banana tree”?
Abaca
What fiber is often referred to as old man’s silk?
Kapok
T or F? Cotton, when picked, is about 94% cellulose; in finished fabrics it is 99% cellulose.
True
What is the trademark symbol for cotton?
cotton incorporated
What fineness does cotton vary from?
16-20 micrometers
How many staple lengths is cotton?
19 staple lengths
How many grades are there of cotton?
39
T or F? Hemp and jute are usually used for industrial purposes
True

Angora Goat:
a long warm fiber that was once used for kings, silk like high sheen, luxury fiber, diamond fiber, blended with others especially wool, tabet, and turkey, 16th century, 1800 US, 1960, most durable of all animal fibers, releases moisture, plant resistant, does not fade easily, biodegradable, younger goat can produce finer longer softer fabrics
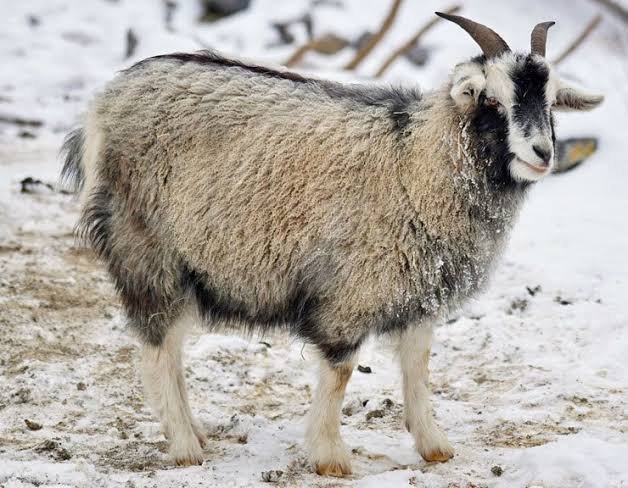

Cashmere Goat:
soft fine fiber, luxurious wool, low in shine, rare production, 13th century, 19th century popular, silky and fine, drapes well, retains warmth, weaker than wool and mohair, pilling, absorbs moisture like wool, flame resistant, takes dye well
Camel:
worn by desert travelers to protect from heat, tents, carpets, coats, and suits first in the fashion industry, lightweight, smooth, excellent insulating, more sensitive to chemicals than wool, take natural dyes well
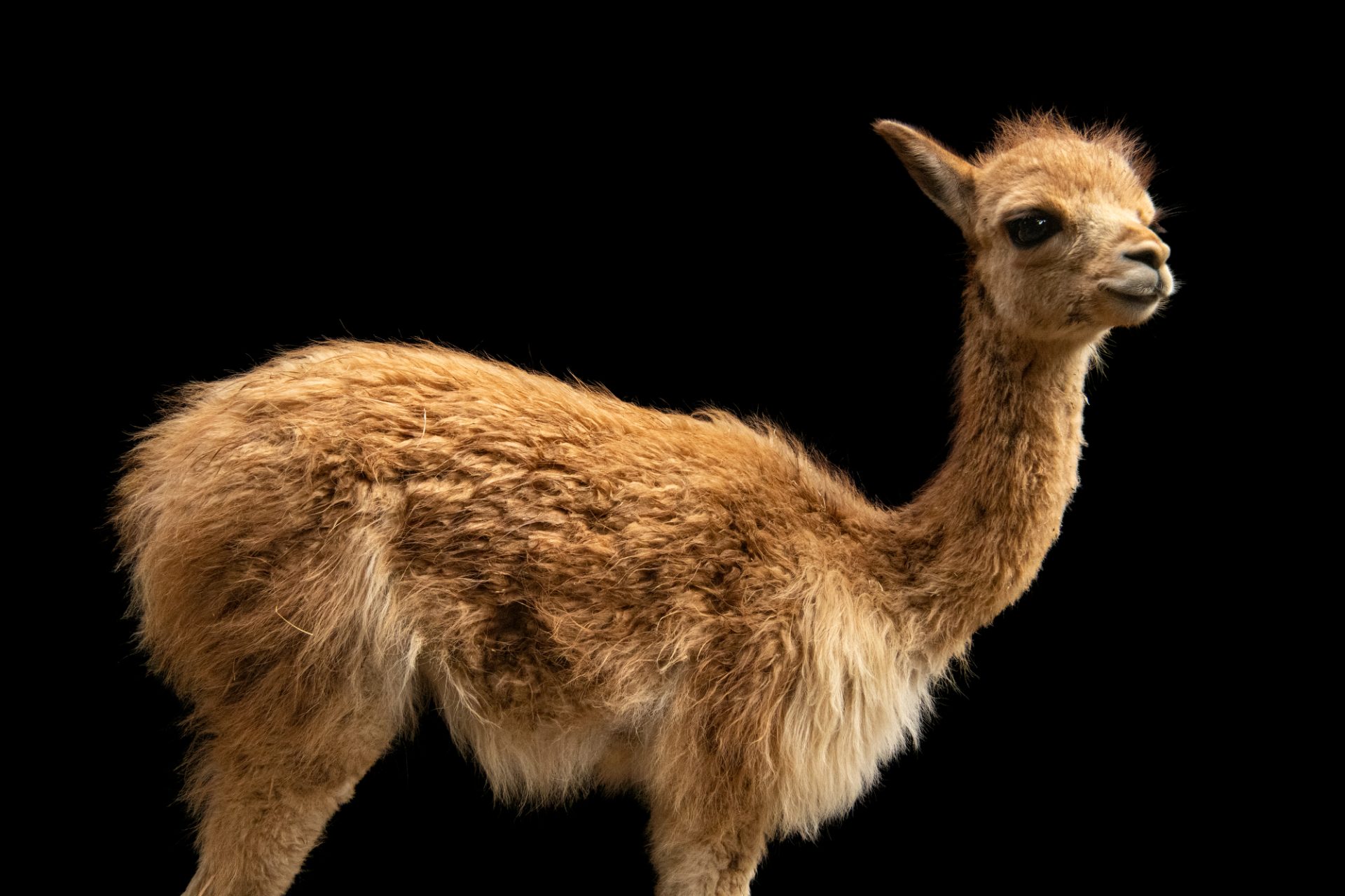
Llama:
less fine and soft than alpaca, south America, native to Andes mountains, Peruvians, lightweight, soft and fine, durable, difficult to process, weaken under sunlights, shrinks easily
Alpaca:
softer than cashmere, light fine, warm, rare, blended with silk and mohair, andes mountains, durable, 3-5 times warmer than wool!!!!!! Breathable, flame resistant, takes dye well

Vicuna:
rare and delicate fiber, fiber of the gods, softer and more delicate than cashmere, retains warmth, no pill, dries quickly, flame resistant, easily damaged when dyed, biodegradable
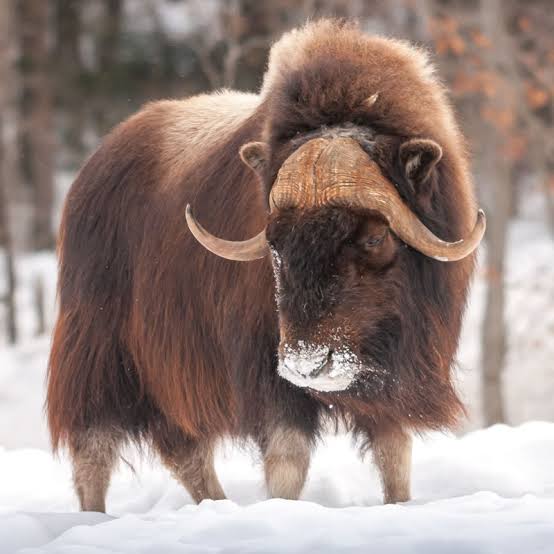

Muscox/Qiviuto:
are underwool, lightweight, fine, spun into pure yarn, blended with moreno, production is limited, north America and Greenland, overhunted, soft, durable, 8x warmer than wool, dryer than wool, takes dye well, odorless, does not shrink or felt
Angora Rabbit:
fluffy feel, flexible hair, blended with other wools, lightweight, soft and silky, very thin and fine, retains warmth, hard to dye, absorbs and releases moisture
Which protein fiber is 3-5 times warmer than wool?
Alpaca
Wool:
Winter fiber commonly used in suits and knit fibers, 200 breeds available, crimp and wavy, oldest domestic animal, spring or early summer, treated with chemicals, bleaching, weaker than cotto nand flax. Strength decreases when wet, hold shape well, absorbs moisture than cotton, irritant to skin, shrinks, biodegradable,
Silk:
Oldest known lucury fiber, Moth catipillars, queen of fabrics, Only natural filament !!!!, Soft shiny and smooth, 5000 years, Silk was a currency
Which is the only natural filament fiber?
Silk
T or F? flax fibers are shorter than cotton
False
T or F? Natural cellulose has better wet strength than dry strength
true
What is the structure of silk?
Triangular cross section with rounded corners
What does Wool look like under a microscope?
scales that are visible along the edge
What is Spider Silk?
spiders of the Nephila and Araneus families: exceptional strength, elasticity, and biodegradability
What is the diameter of wool fiber?
varies from 10-50 micrometers
What cross-linked protein is wool?
keratin
How is wool produced?
Wool is produced in about 100 countries ranging from small family-owned farms to large-scale commercial operations.
What is Virgin wool?
wool that has never been processed
What is wool?
new wool or wool fibers reclaimed from knit scraps, broken thread, and noils
What is recycled wool?
scraps of new woven or felted fabrics that are garnetted (shredded)
What is shoddy wool?
comes from old apparel and rags that are cleaned, sorted, and shredded
What is the most important use of wool?
adult apparel
What is the protein of silk called?
fibroin
Is silk or wool easier to identify through a microscope?
Wool
What are the two groups in an amino acid?
amino group + carboxyl group
proteins are composed of …..
amino acids
Properties of Protein Fibers:
Resiliency: resist wrinkles, wrinkles hang out, fabrics hold shape
Hygroscopic: comfortable in cool damp climates, moisture prevents brittleness in carpets
Weaker when wet: handle carfeully in wash, wool loses 40% of strength, silk loses about 15%
Specific Gravity: fabrics feel lighter than. cellulose fabrics of same thickness
Harmed by Alkali: use neutral or slightly acid soap or detergent, perspiration weakens fibers
Harmed by oxidising agents: chlorine bleaches damage fibers, sunlight causes white fabrics to turn yellow
Harmed by dry heat: wool becomes harsh, brittle, and scorches easily (use steam), white wool and white silk yellow
Flame resistant: does not burn easily, self-extinguish, odor of burning hair, forms a black crushable ash
What is Merino wool?
Merino wool is the most valuable wool, which is 3 to 5 inches long and very fine, and 43% of “merino” wool comes from Australia
Where is U.S fine wool produced in?
Texas + california
About Crimp:
Crimp refers to the natural wave or curl in fibers that contributes to the texture and bulk of textiles. It affects properties like cohesiveness and resiliency, with wet conditions reducing its effectiveness. Related to cohesiveness, elasticity, resiliency and loft.
How much % of wool is used in the US
Only 0.7% of all fibers used in the U.S. is wool
Sustainability of wool:
although wool can be viewed as a renewable resource, it is not produced without any impact on the environment
What is the production of cultivated silk called?
Sericulture is the production of cultivated silk. Created by Bombyx mori moth
What is Chemical Composition and Molecular structure of silk?
The protein in silk is fibroin, with 15 amino acids in polypeptide chains With reactive amino (NH2) and carboxyl (COOH) groups
Uses of Silk:
drape, luster, texture
What two ways does silk come in?
cultivated ( filament), wild (spun)
Wool vs Silk (amino acids)
There are more types of amino acids in wool than in silk! (Amino acids in wool have large side groups), Wool is bulkier and less compact + Wool has better resiliency, Wool is more prone to insect damage
Where is the most wool produced?
Australia = 27.4%
What is Raw wool?
Raw wool is Newly removed wool. It Contains 30% to 70% by weight of impurities (sand, dirt, grease, dried sweat).
What happens in the grading and sorting part of the wool making process?
Wool is sorted by, thickness, long to short, scratchy, color, and location from the sheep
what do you do in the washing or scouring part of the wool process?
you remove greases. the greases are then used in cosmetics, soaps, and creams
What happens in the carbonizing process?
remove particles of grass, burrs, and other plant material to get scoured wool
Care of Wool:
Dry cleaning is recommended, If necessary, hand wash using warm water; avoid agitation; squeeze gently; air dry, No chlorine bleach; no alkali detergent, Be cleaned before storage