A and P TEST REVIEW MUSCULAR SYSTEM
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Muscles are organs that generate force to:
Cause all types of movement
Maintain posture and balance
Stabilize joints
muscles function to :
generate body heat.

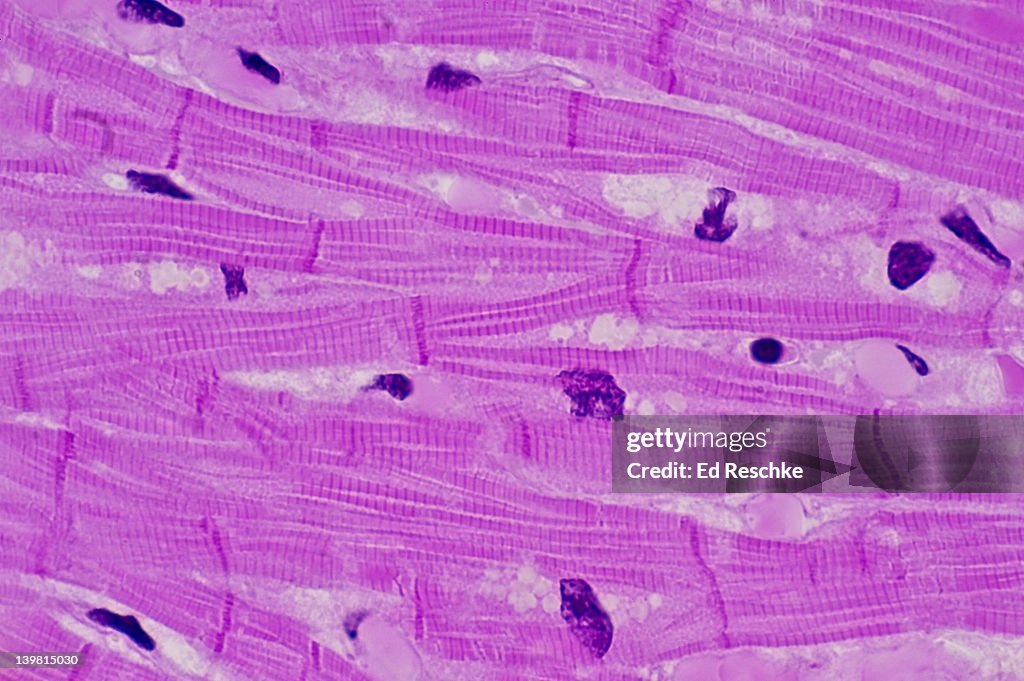
Skeletal Tissue
Location : Skeletal Muscle
Function : Movement of bones at joints, maintenance of posture
Striations : Present
Nucleus : Many nuclei
Special features : Well-developed transverse tubule system
Control : Voluntary
Contracts and relaxes rapidly when stimulated by a motor neuron
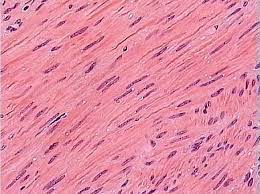
Smooth Tissue
Location : Walls of hollow viscera blood vessels
Function : Movement of viscera, peristalsis, vasoconstriction
Striations : Absent
Nucleus : Single
Features : Lacks transverse tubules
Control : Involuntary
Contracts and relaxes slowly; single unit type is self-exciting; rhythmic
Cardiac Tissue
Location : Wall of the heart
Function : Pumping action of the heart
Striations : Present
Nucleus : Single Nucleus
INTERCALATED DISCS
Features : Well-developed transverse tubule system; intercalated discs separating adjacent cells
Control : Involuntary
Network of cells contracts as a unit; self-exciting; rhythmic
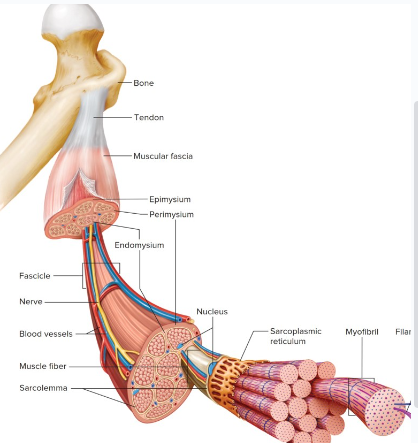
Sacrolemma
Cell membrane of a muscle fiber is the
Cytoplasm of a muscle cell is the ________; it contains many mitochondria and nuclei
sacroplasm
Sarcoplasm contains parallel _______, which are active in muscle contraction:
myofibrils
Thick filaments in myofibrils consist of the protein _______
Myosin
Thin filaments in myofibrils are mainly composed of the protein _____ but also contain troponin and tropomyosin
ACTIN
The organization of these filaments produces bands called _____
Striations
Skeletal muscle fibers contract only when stimulated by a __________
motor neuron
______ a synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber that it regulates
Neuromuscular junction
Each skeletal muscle fiber (cell) is functionally (not physically) connected to the axon of a motor neuron, creating a ________
synapse
Muscles are made of units called ______
MAIN = A small bundle of muscle fibers within a muscle
Fascicles
______ contains altering thick and thin filaments
Myofibrils
The outermost layer of connective tissue of a muscle is the ( Covers the entire muscle)
Epimysium
The thick myofibril filament of a sarcomere is composed of a protein
myosin
The muscle primarily responsible for a movement is the______
Prime Mover (AGONIST)
The neuron and the collection of muscle fibers it innervates is called a
Motor Unit
The functional contractile unit of a muscle fiber (cell) is a
Sarcomere
The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber (cell) is called the
Sarcolemma
STUDY THIS GRAPH FOR REAL
Sheet of dense connective tissue that separates individual muscle and helps hold them in position
Covers Skeletal muscle
MAIN = CONNECTIVE TISSUE LOCATED BETWEEN ADJACENT MSUCLE
FASCIA
Small bundle of skeletal muscle fibers
Fascicle
A nerve composed of axons (nerve fibers ) of a motor neruon
_____ stimulate muscle fiber to contract
Motor neuron
_____ that contain thick filaments (myosin) and thin (actin)
_____ play a fundamental role in muscle contraction = striations
Myofibrils
Within each myofibril there are repeating functional units called _______ BETWEEN THE TWO Z LINES
Sacromeres
Cordlike structures of connective tissues that attach MUSCLE TO BONE
Tendons
tissue that connects BONE TO BONE to keep the joint together
Ligaments
The immovable end of a skeletal muscle is it’s _______ (a fixed arch)
MAIN = THe _____ of a muscle is usually attached to a fixed location
ORIGIN
The MOVABLE end of a skeletal muscle is its _____
Insertion
_______ are muscle that OPPOSE a movement
Antagonist
Muscle that work together to assist movement
Synergists
WHen muscle contractions its insertion is ______ toward the orgin
PULLED
decrease in the angle between bones at a joint
Flextion
Increase in the angle between bones at a joint
Extension
Skeletal muscles are named according to any of these:
size
shape
location
action
number of attachments
direction of its fibers
______ filaments form cross bridges (linkages) with ______ filaments
Myosin , Actin
_____ (neurotransmitter ACh) released the end of a motor neuron stimulates a skeletal muscle fiber at the _________ (nerve connecting with muscle )
Acetylcholine , Nueromuscular junction
the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release
calcium ions
______ breaks down acetylcholine on the receptors
Acetylocholinesterase
Downward,
plantar flextion
Upward
Dorsiflextion
moving a body part away from the midline
Abduction - arm go up and down
moving a body part toward the midline
Adduction
The arm and leg go foward
Flexion
the leg and arm go backward
extenstion
Palm upward
Supination
Palm downward
Pronation
Muscle contraction involves several events, that result in the shortening of _______, and the pulling of the muscle against its attachments
SARCOMERES
_____________is the neurotransmitter for skeletal muscle fiber contraction at the neuromuscular junctions
Acetylcholine
Upon receipt of the muscle impulse, the _______ releases its _____ to the cytosol of the muscle fiber
sarcoplasmic reticulum , stored calcium
Acetylcholinesterase decomposes acetylcholine, and the muscle fiber membrane is no longer stimulated.
Calcium ions are actively transported into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
ATP breaks cross-bridge linkages between actin and myosin filaments without breakdown of the ATP itself.
Breakdown of ATP “cocks” the myosin heads.
Troponin and tropomyosin molecules block the interaction between myosin and actin filaments.
The muscle fiber remains relaxed, yet ready, until stimulated again.
MUSCLE RELAXTION
impulse travels down motor neuron, release of acetylcholine into neuromuscular junction, release of calcium ions into muscle fiber, binding sites on actin are exposed, myosin forms cross-linking, thin filaments are pulled toward the center of sarcomere.
MUSCLE CONTRACTION
Energy for muscle fiber contraction and relaxation comes from molecules of __________ (IMPORTANT)
ATP
___________is present to initially regenerate ATP from ADP and phosphate, as it also contains high energy bonds.
CREATINE PHOSPHATE
_______is a complete breakdown of glucose; it is ______ (requires oxygen) and occurs in the mitochondria, myoglobin
Aerobic respiration
____ occurs in the absence of oxygen faster reaction but produces less ATP leads to lactic acid formation
Anaerobic respiration
Pathway : Aerobic
Waste : Carbon dioxide is exhaled
Blood flow provided sufficient oxygen
Low to moderate intensity:
Oxygen supply is not sufficient <
Anaerobic respiration
Lactic acid accumulates FATIGUE
High intensity
A muscle exercised strenuously for a prolonged period may have a decreased ability to contract a condition called ________-
When a muscle loses its ability to contract during strenuous exercise, it is referred to as______
FATIGUE
Make up majority of muscle fibers
Rapid movements, reach maximum force quickly, fatigue quickly
Large diameter
Few mitochondria, store glycogen; anaerobic metabolism
Powerful contractions, but best for short-term activities
White Meat
Fast fibers:
Small diameter
Takes longer to reach peak tension, but resistant to fatigue
Provide prolonged contraction
Many mitochondria and capillaries; aerobic metabolism
Slow fibers:
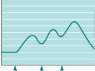
the force of individual twitches combine by the process of
SUMMATION.
the minimum stimulus required to generate a impulse through the muscle fiber, release calcium ions, activate cross-bridges, and contract the muscle.
Threshold Stimulus
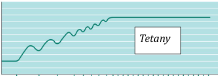
frequency of stimulation is very high and the sustained contraction lacks any relaxation, it is called a
TETANY
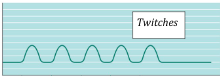
_______ consists of a cycle of contraction and relaxation.
TWITCHES
An increase in the number of activated motor units
RECRUITMENT
Summation + recruitment together can produce a _______of increasing strength.
sustained contraction
Strain
tear in the muscle and or tendons that attach muscle to bone
Muscular Dystrophy = Genetic Condition
inherited condition in which muscles waste away.
caused by abnormal genes unable to control muscled development and function
Myasthenia Gravis
AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE causing weakening of voluntary muscles