Anatomy of the Ear Quiz
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
the ear contains three anatomical divisions, what are they?
External ear, middle ear, and the internal ear
external
pinna, auditory canal, ends at tympanic membrane and lined with cerminous (wax) glan
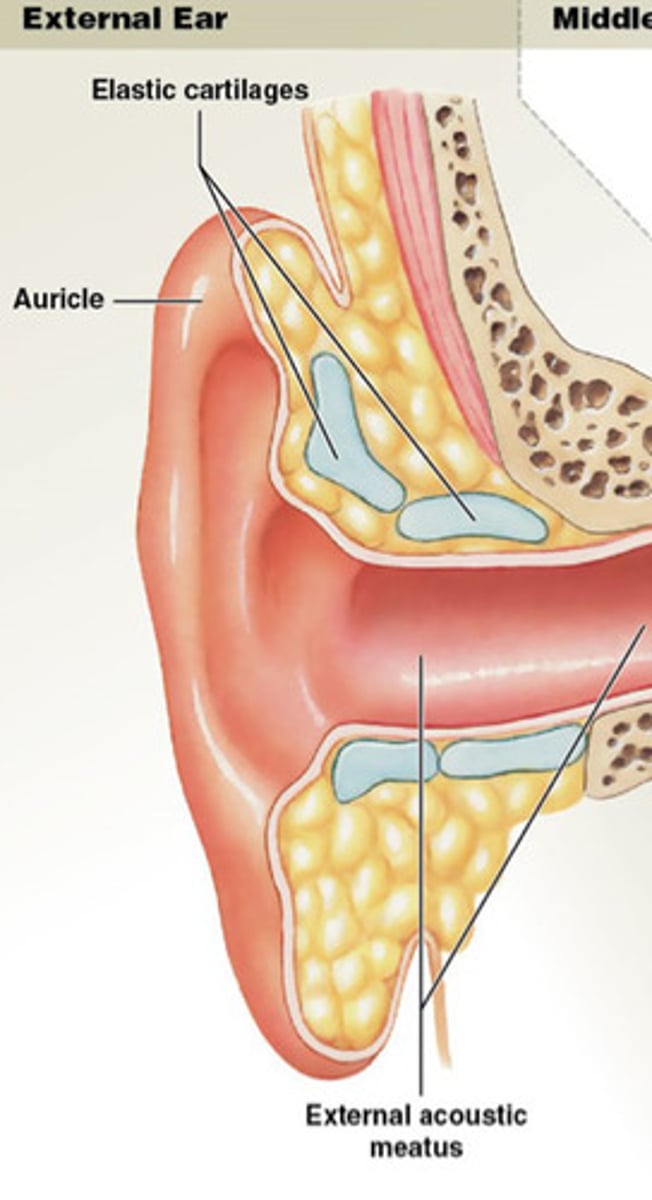
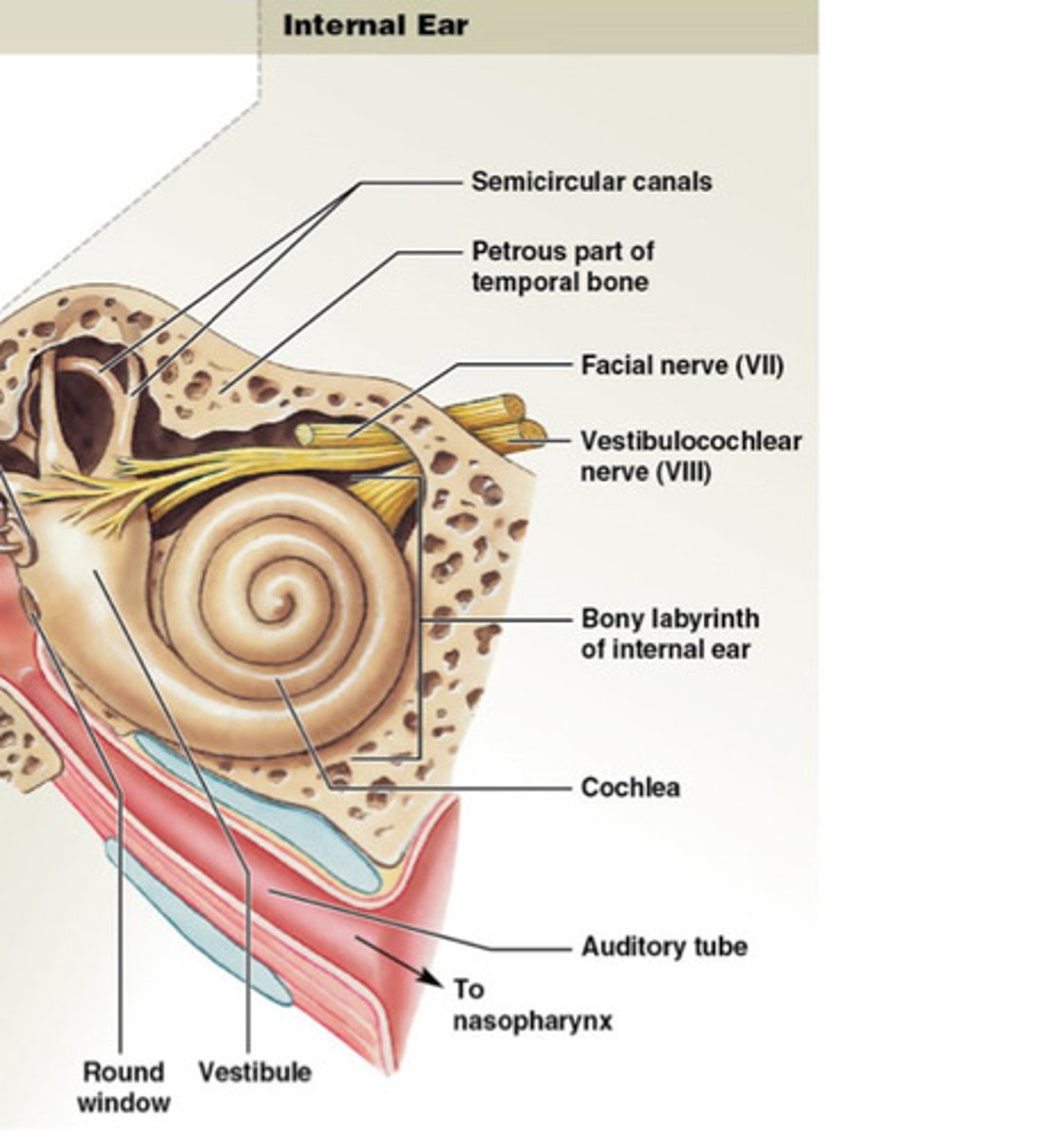
inner ear
Cochlea, vestiblue, bony chambers, sensory organs for hearing balance, filled with perilymph, membrane labyrinth filled with endolymph (thick liquid).
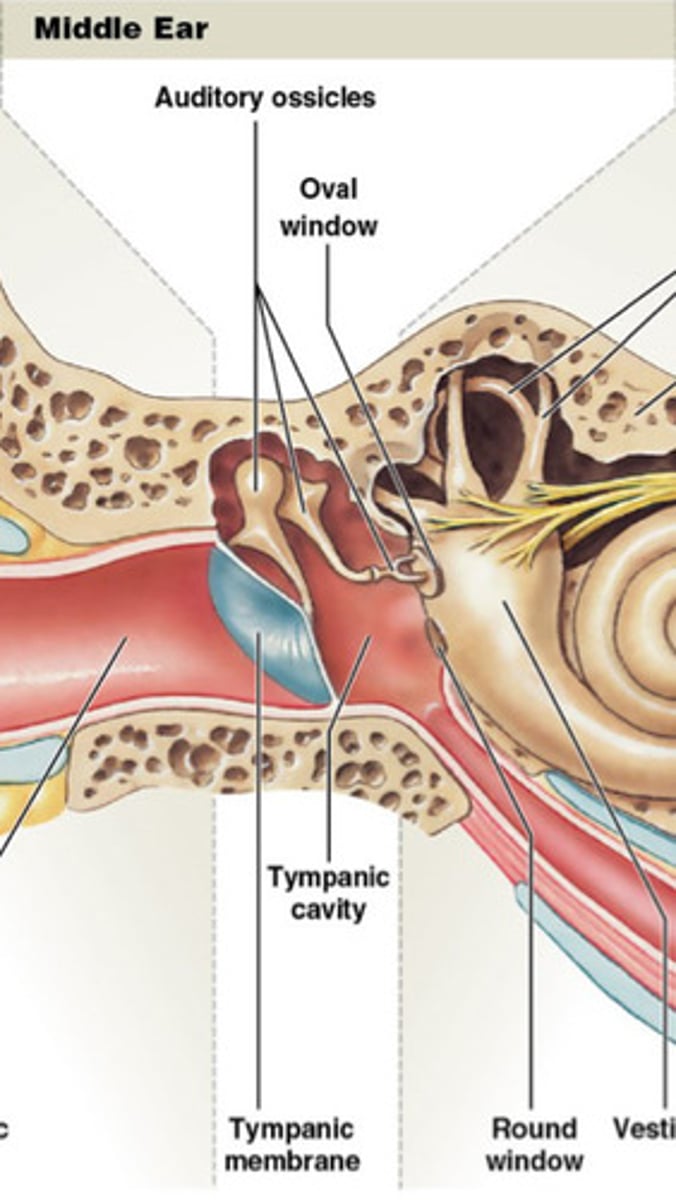
middle/ tympanic cavity
Air filled cavity, 2 tubes with inner ear, auditory to middle ear, allows for equal pressure while yawing and swallowing.
The auricle also known as the pinna has what function?
Surrounds and protects external acoustic meatus
Also provides directional sensitivity
What does the tympanic membrane do? (Eardrum)
It is a thin, semi transparent sheet at the end of the external acoustic meatus.
This structure separates external ear from middle ear.
What are ceremonious glands? What do the produce?
They are glands along the external acoustic meatus that secrete a waxy material
What three bones make up the auditory ossicles?
malleus, incus, stapes (hammer, anvil, stirrup)
organs of Hearing
organ of corti (within cochlea)
Mechs of Hearing Process
Receptors (hair cells) on the basilar membrane (gel-like tectorial membrane is cpable of bending hair cells)
Cochlear nerve attached to the hair cells transmit nerve impulse to auditory cortex on the temporal lobe
Vibrations from sound waves move tectorial membrane
Hair cells are bent by the membrane
An action potential starts int he cochlear nerve
Hear “in stereo”
Continued stimulation → adaptation
Deafness Conduction
Conduction: interference with sound vibrations, earwax build-up, fused ossicles, ruptured eardrum→ hearing aid
Deafness Sensorineural
Degradtion of receptor cells on the organ of corti, cochlear nerve and beurons of the auditory cortex, loud music
ear receptores
mechanoreceptors
What do the auditory ossicles do?
auditory ossicles conduct vibration to the internal ear
What do the tensor tympani and stapedius do?
Protect the ear from very loud noises
tensor tympani
Pulls on malleus and stiffens the tympanic membrane
Stapedius
Reduces movement of stapes at the oval window
What does the bony labyrinth do?
Surrounds and protects membranous labyrinth
What flows between the two labyrinths?
perilymph
What flows within membranous labyrinth?
Endolymph
The round window is..
Thin, membranous partition that separates perilymph from air spaces of the middle ear
Hair cells are
Sensory receptors if the internal ear, they provide information about direction about direction and strength of the mechanical stimuli.
The maculae are
Oval structures where hair cells cluster, consist of the macula of utricle and the macula of saccule
What does the macula of utricle do?
Senses horizontal movement
What does the macula of saccule do?
Senses verticals movement
The process of hearing is
- Sound waves are converted into mechanical movements by vibration of tympanic membrane
- auditory ossicles conduct vibrations to internal ear
- vibrations are converted to pressure waves in fluid, these are detected by hair cells on cochlear duct
- information is sent to auditory cortex of brain
Stereocilia of the cochlea hair cells project into..
Tectorial membrane
Organs of equilibrium
vestibule, semecircular canal
Static equilibrium
Maculae- receptrs in vestibule, report on the position of the head while not moving, up or down. Orolithic membrane sends position of the head via vestibular nerve.
Anatomy of Maculae
Hair cells are embedded on the otolithic membrane, otoliths (tiny stones) float in gel around hairs, movement casses otoliths to bend the hair cells.
Dynamic equilibrium
receptors found in semi circullar canals, respond to angular or rotary movement. Receptor region: cristia ampullaris (tuft of hair cellsO, Cupula (geletan cap) covers the hair cells and stimulates the hair cells by dragging against stationary endolymph, and an impulse is sent to the cerebelum.
Doll’s eye reflex
compensate for disturbance in balance reflex using the sensory receptors within the vestibule and semicircular canals.