Cellular Respiration & Metabolic Pathways: Key Concepts for Biology
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What process produces most of the ATP during cellular respiration?
The movement of protons across a membrane that drives ATP synthase.
What is the primary purpose of fermentation pathways in eukaryotes?
To regenerate NAD+ to allow glycolysis to continue.
How are metabolic pathways characterized?
They consist of a series of reactions, each catalyzed by a different enzyme.
What does it mean that glycolysis has an investment and payoff phase?
It initially requires ATP but returns more later.
Where does glycolysis occur in a typical eukaryotic cell?
In the cytoplasm.
How does glycolysis produce ATP?
Through substrate-level phosphorylation.
What do muscle tissues produce from pyruvate during anaerobic conditions?
Lactate.
What is the role of oxygen in the electron transport chain?
It is reduced to form water.
After the citric acid cycle, most usable energy from glucose is in the form of what?
NADH.
Under which conditions would yeast grow faster, anaerobic or aerobic?
Aerobic conditions — Higher yield of ATP from glucose oxidation.
What is the primary role of oxygen supplied by breathing?
To act as an acceptor in the electron transport chain.
In glycolysis and cellular respiration, what is oxidized and what is reduced?
Glucose is oxidized and oxygen is reduced.
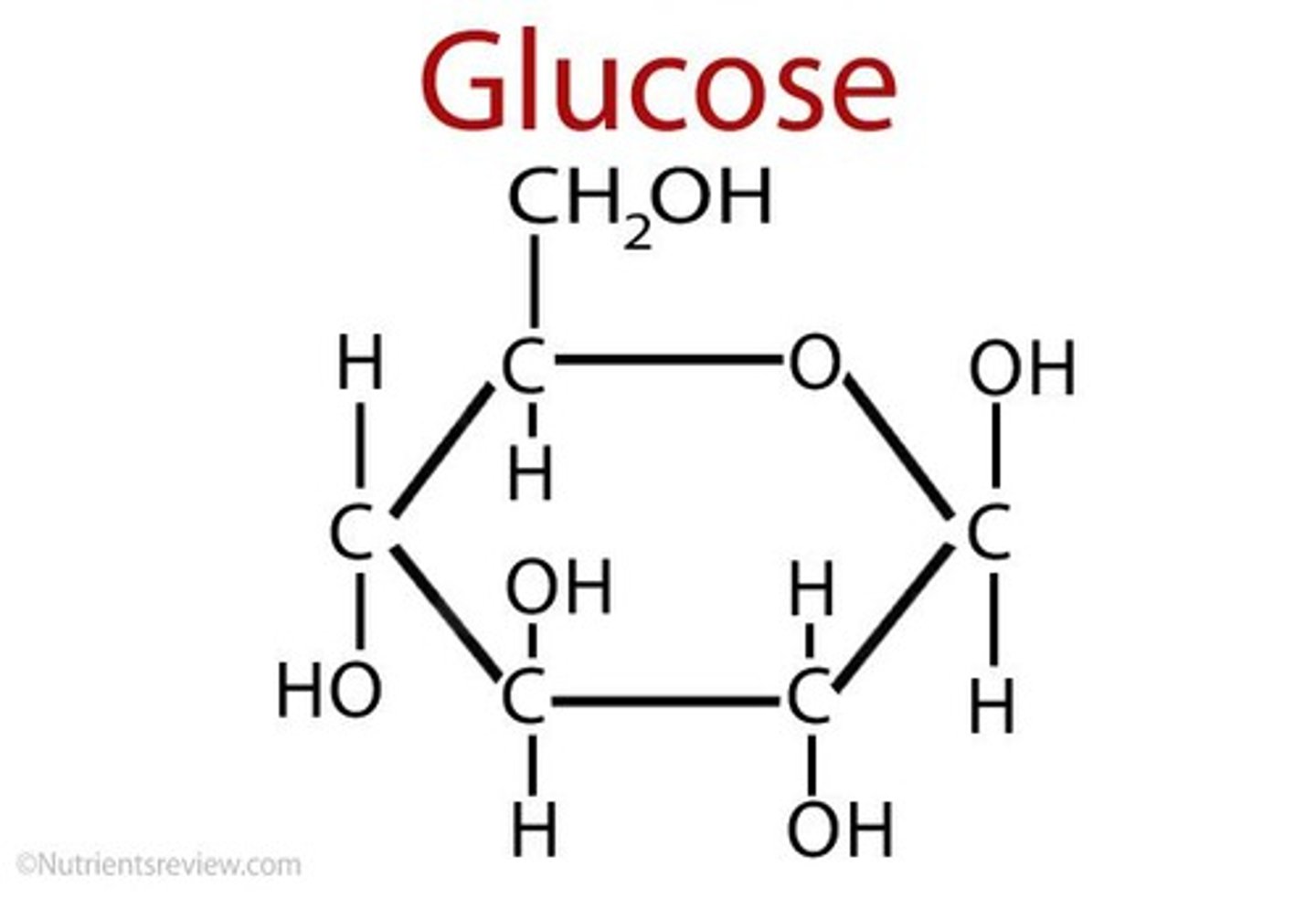
Which metabolic pathway is common to both fermentation and cellular respiration?
Glycolysis.
What occurs during the energy payoff phase of glycolysis?
ATP and NADH are produced.
Most electrons removed from glucose during cellular respiration are used for what?
Producing a proton gradient for ATP synthesis in the mitochondria.
What step occurs in preparing pyruvate to enter the citric acid cycle?
Pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA.
What happens to pyruvate during its conversion to acetyl-CoA?
Pyruvate is oxidized and decarboxylated, and the removed electrons are used to reduce NAD+ to NADH.
Why is ATP important in biological systems?
Hydrolysis of ATP is coupled to endergonic reactions, allowing it to drive various cellular processes.
What is the main product of lactic acid fermentation?
Lactic acid fermentation produces lactate.
What does alcohol fermentation produce?
Alcohol fermentation produces ethanol.
What is the purpose of pumping protons (H+) across the inner mitochondrial membrane?
It contributes to a proton gradient that can drive unfavorable reactions forward.
What is the relationship between anabolic and catabolic pathways?
Anabolic pathways synthesize more complex organic molecules using the energy derived from catabolic pathways.
How many molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2) are released during the complete aerobic respiration of one glucose molecule?
6 molecules of CO2 are released.
What type of gradient is primarily created by the pumping of protons out of the mitochondrial matrix?
An electrical gradient.
What does the chemiosmotic theory for ATP synthesis propose?
The proton gradient created by the electron transport chain is used to make ATP.
How is a small amount of ATP produced in glycolysis?
By the transfer of a phosphate group to ADP through substrate-level phosphorylation.
What process allows ATP to be considered a renewable resource?
ATP can be regenerated by the addition of a phosphate group to ADP.
What occurs in an exergonic reaction?
An exergonic reaction releases free energy.
What is the result of an endergonic reaction?
An endergonic reaction requires free energy.
What happens as electrons move along an electron transport chain?
They release energy that is used to pump protons across a membrane.
Which statement correctly describes aerobic cellular respiration?
In eukaryotes, glycolysis and the Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle occur in separate compartments.