US Economic Policy and Basics of Economics
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Economics
The study of how people seek to satisfy their needs and wants by making choices
Microeconomics
The study of the economic behavior and decision making of small units, such as individuals, families, and businesses.
Macroeconomics
The study of the behavior and decision making of entire economics.
Opportunity Cost
The most desirable alternative given up as a result of a decision.
Standard of Living
Level of economic prosperity.
Factors of Production
Land, labor, and capital; the three groups of resources that are used to make all goods and services.
Economic System
The method used by a society to produce and distribute goods and services.
Trade-off
An alternative we sacrifice when we make a decision.
Physical Capital
All human-made goods that are used to produce other goods and services; tools and buildings.
Human Capital
The skills and knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience.
Scarcity
Limited quantities of resources to meet unlimited wants.
Shortage
A situation in which a good or service is unavailable or a situation in which the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied, also known as excess demand.
Surplus
Situation in which the quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded; also known as excess supply.
Production Possibility Curve
A curve that shows alternative ways to use an economy's resources.

Production Possibility Frontier
The line on a production possibilities graph that shows the maximum possible output for a specific economy.
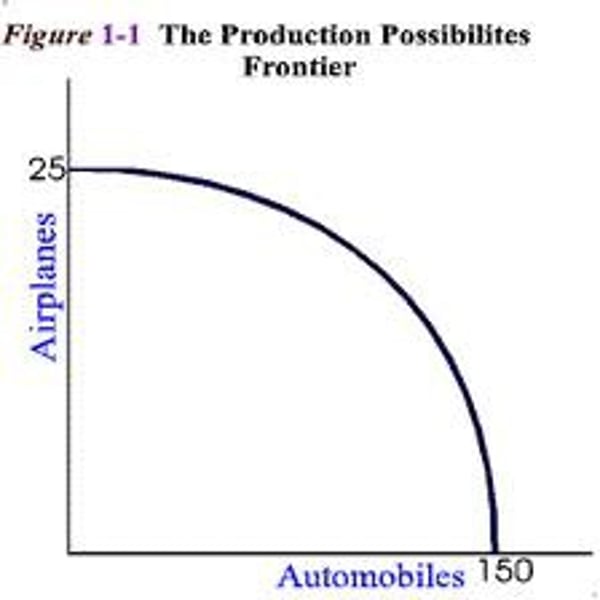
Efficiency
Using resources in such a way as to maximize the production of goods and services.
Underutilization
Using fewer resources than an economy is capable of using.
"Guns vs. Butter"
A phrase that refers to the trade-off that nations face when choosing whether to produce more or less military or consumer goods.
Marginal Utility
Satisfaction or usefulness obtained from acquiring one more unit of a product
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
The principle that as a consumer increases the consumption of a good or service, the marginal utility obtained from each additional unit of the good or service decreases.
Law of Diminishing Returns
The principle that, at some point, adding more of a variable input, such as labor, to the same amount of a fixed input, such as capital, will cause the marginal product of the variable input to decline
Firm
An organization that uses resources to produce a product, which it then sells.
Household
A person or a group of people living in the same residence.
Market Economy
Economic system in which decisions on production and consumption of goods and services are based on voluntary exchange in markets.
Command Economy
Economic system in which the central government makes all decisions on the production and consumption of goods and services.
Goods
Physical objects such as clothes or shoes
Services
Actions or activities one person performs for another.
Competition
The struggle among producers for the dollars of consumers; the rivalry among sellers to attract customers while lowering costs.
Adam Smith
Scottish economist who wrote the Wealth of Nations a precursor to modern Capitalism.
Specialization
The concentration the productive efforts of individuals and firms on a limited number of activities.
Free Enterprise
An economic system characterized by private or corporate ownership of capital goods; investments that are determined by private decision rather than by state control; and determined in a free market.
Consumer Sovereignty
The power of consumer to decide what gets produced
Demand
The desire to own something and the ability to pay for it.
Law of Demand
Economic law that states that consumers buy more of a good when its price decreases, and less when its price increases.
Substitution Effect
When consumers react to an increase in a good's price by consuming less of that good and more of other goods.
Income Effect
The change in consumption resulting from a change in real income.
Necessity
Anything that cannot be done without or that is greatly needed.
Complements
Two goods that are bought and used together.
Substitutes
Goods used in place of each other.
Elasticity of Demand
A measure of how consumers react to a change in price
Elasticity
Describes demand that is very sensitive to a change in price
Inelasticity
Describes demand that is not very sensitive to a change in price.
Supply
The amount of good available.
Law of Supply
Tendency of suppliers to offer more of a good at a higher price.
Elasticity of Supply
A measure of the way the quantity supplied reacts to a change in price.
Marginal Cost
The cost of producing one more units of a good.
Subsidy
A government payment that supports a business or market.
Increasing Marginal Returns
A level of production in which the marginal product of labor increases as the number of workers increase.
Diminishing Marginal Returns
A level of production in which the marginal product of labor decreases as the number of workers increase,.
Point of Equilibrium
The point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal.
Price Floor
A minimum price for a good or service.
Price Ceiling
A maximum price that can be legally charged for a good or service.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total value of all final goods and services produced in a particular economy; the dollar value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders in a given year.
Business Cycle
A period of macroeconomic expansion followed by a period of contraction.
Public Sector
The part of the economy that involves the transactions of the government.
Private Sector
The part of the economy that involves the transactions of individuals and businesses.
Liquidity
The ability to be used as, or directly converted to, cash.
Fiscal Policy Tools
Policy that affects the economy by making changes in government spending and tax rates. The key players are the President and Congress. The two types of policy is Expansionary (Government Spending goes up and tax rates go down) and Contractionary (Government spending goes down and tax rates go up) policy.
Fiscal Year
A 12-month pd, October through Septmeber, for planning the federal budget
Keynesianism
The belief that government must manage the economy by spending more money when in a recession and cutting spending when there is inflation
Supply-siders
The belief that lower taxes and fewer regulations will stimulate the economy.
Monetarism
The belief that inflation occurs when too much money is chasing too few goods.
Monetary Policy Tools
Policy that controls the money supply and interest rates, mainly through the Federal Reserve System. The can have reserve requirements, discount rates and open market activities. The types of policy are expansionary(reduce unemployment [increase money supply]) and contractionary (reduce inflation [decrease money supply]).
Council of Economic Advisors (CEA)
A group of three respected economists that could advice the President on Economic policy.
Office of Management and Budget (OMB)
Government office that manages the federal budget.
Congressional Budget Office (CBO)
Government Agency that provides economic data to Congress.
Ways and Means Committee
A permanent committee of the United States House of Representatives that makes recommendations to the House on all bills that would raise revenue
Appropriation Committees
Committees of Congress that decide which of the programs passed by the authorization committees will actually be funded
Budget Committees
One committee in each house of Congress that supervises a comprehensive budget review process
Budget
A document that states tax collection, spending levels, and the allocation of spending among purposes.
Budget Resolution
A congressional decision that states the maximum amount of money the government should spend.
Budget Reconciliation
The process by which congressional committees are held to the spending targets specified in the budget resolution. During this process, the House and Senate Budget Committees combine the budgetary changes from all the legislative committees into an omnibus reconciliation bill to be approved by Congress.
Continuing Resolution
When Congress cannot reach agreement and pass appropriations bills, these resolutions allow agencies to spend at the level of the previous year.
Omnibus Spending Bill
An omnibus spending bill is a type of bill in the United States that packages many of the smaller regular appropriations bills into one larger single bill that could be passed with only one vote in each house.
Income Tax
Tax paid to the state, federal, and local governments based on income earned over the past year.
Excise Tax
A tax on the production or sale of a good.
Debt
Something, typically money, that is owed or due
Deficit
The result of when the government in one year spends more money than it takes in from taxes.
Revenues
The financial resources of the government. The individual income tax and Social Security tax are two major sources of the federal government's revenue.
Expenditures
Federal spending of revenues. Major areas of such spending are social services and the military.
Appropriations Bill
A bill that sets money aside for specific spending.
Discretionary Spending
Spending Category about which government planners can make choices.
Mandatory spending
Spending on certain programs that is mandated, or required, by existing law.
Entitlements
Social welfare program that people are "entitled" to if they meet certain eligibility requirements.
Federal Reserve System
The country's central banking system, which is responsible for the nation's monetary policy by regulating the supply of money and interest rates
Open Market Activites
They include the buying and selling of government securities to alter the supply of money and is one of the most used monetary policy tools/
Discount Rate
Rate the Federal Reserve charges for loans to commercial banks.
Budget and Accounting Act of 1921
Gave the president authority to prepare an annual budget and submit it to Congress for approval. Also created the OMB and GAO.
Marginalism
An examination of the additional benefits of an activity compared to the additional costs of that activity.
Congressional Budget Act of 1974
Act that established the congressional budgetary process by laying out a plan for congressional action on the annual budget resolution, appropriations, reconciliation, and any other revenue bills. Must be approved by the House of Representatives and Senate and created CBO. IT prevented the impoundment of money so a portion of it is called the Budget Impoundment and Control Act.