Research Methods in Cell Biology
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
1
New cards
what kind of cell are bacteria?
prokaryotes
2
New cards
what kind of cells are yeasts?
eukaryotes
3
New cards
what cell line is 3T3?
fibroblast in mice
4
New cards
what cell line is HeLa?
epithelial cell in human (cervical cancer cells)
5
New cards
what cell line is 293?
kidney in human (transformed with adenovirus)
6
New cards
what cell line is CHO?
ovary in chinese hamster
7
New cards
what does growth of primary human cells look like?
grows fast in phase 1, remains constant in phase 2, decreases in phase 3
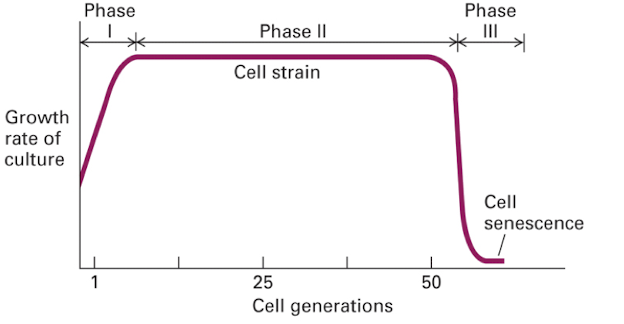
8
New cards
what does an immortalized mouse cell look like?
has a dip at around 30 days of initiation of culture
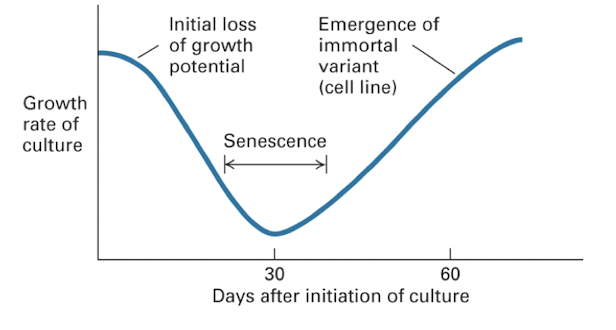
9
New cards
what separates different types of cells from each other?
fluorescence activated cell sorting
10
New cards
FACS
fluorescence activated cell sorting
11
New cards
what is done to cells in FACS to distinguish them?
stained with fluorescent dye
12
New cards
how many cells are in one drop in FACS?
one or less
13
New cards
what is an example of a cell separated by FACS?
T cells from white blood cells
14
New cards
will terminally differentiated cells divide more?
no
15
New cards
are embryonic cells differentiated or undifferentiated?
undifferentiated
16
New cards
what can embryonic stem cells be used for?
reproductive or therapeutic cloning
17
New cards
what is more useful reproductive or therapeutic cloning?
therapeutic cloning
18
New cards
what kind of tissue can totipotent ES cells make?
all tissues, including placental
19
New cards
what kind of tissue can pluripotent cells make?
all tissues except for placental
20
New cards
can pluripotent cells be used for reproductive cloning? why or why not?
no, because they cannot make placentas
21
New cards
what are hybridoma cell lines made for?
to make monoclonal antibodies
22
New cards
what is the purpose of using hybridoma cells?
to allow for a continuing source of anti-”X” antibody which would otherwise die in a culture by itself
23
New cards
what are monoclonal antibodies specific for?
one part of a molecule usually a protein
24
New cards
examples of monoclonal antibody usage
immunoaffinity chromatography, western blots, ELISAs, immunofluorescent staining, immunoprecipitations, immuno-gold labeling
25
New cards
how can small coated vesicles be purified?
binding of antibody for a vesicle protein and linkage to bacterial cells
26
New cards
what is used for visualizing cells?
microscopy
27
New cards
what are optical microscopes configures for?
bright-field, phase contrast, epifluoresence
28
New cards
how can live cells be visualized?
microscopy techniques that generate contrast by interference
29
New cards
what are the three methods of visualizing live cells?
bright field simple light, phase contrast in phase light canceling, nomarski/DIC polarized
30
New cards
what are double-label fluorescence microscopy used to visualize?
relative distribution of two proteins
31
New cards
deconvolution
out of focus fluorescence eliminated computationally
32
New cards
deconvolution fluorescence microscopy
yields high-resolution optical sections that can be reconstructed into one 3-D image
33
New cards
confocal microscopy
produces an in-focus optical section through thick cells
34
New cards
what does confocal microscopy eliminate?
light from out of focus planes
35
New cards
what can help explore the function of genes in cultured cells?
RNAi screens in combination with microscopy
36
New cards
electron microscopy
images are formed from electrons that pass through a specimen or are scattered from a metal-coated specimen
37
New cards
how does transmission electron microscopy show fine features?
by looking at negatively stained samples
38
New cards
what makes surface details or small objects visible through transmission electron microscopy?
metal shadowing
39
New cards
what are gold particles coated with protein A used for?
detecting antibody bound protein by transmission electron microscopy
40
New cards
what are some examples of organelles viewed by transmission electron microscopes?
rough ER, clathrin coated pit, golgi complex
41
New cards
what are some examples of organelles viewed by transmission electron microscopy of thin sections?
structures in mitochondria and structures in chloroplasts
42
New cards
scanning electron microscope
carbon coated sample has electron beams scattered at an angle detected to produce a 3D image
43
New cards
what must cells be to be viewed under SEM?
dead and dehydrated
44
New cards
separating sub-cellular components
differential centrifugation is a common first step in fractionating a cell homogenate
45
New cards
how can a mixed organelles fraction be further separated?
equilibrium density-gradient centrifugation
46
New cards
low speed centrifuge
sediment cells out of solution
47
New cards
high speed centrifuge
purify nuclei, sediment bacteria, precipitates
48
New cards
ultra centrifuge
separate organelles and molecules
49
New cards
what is true of ultra centrifuges?
they are spun so fast that a vacuum must be created
50
New cards
what centrifuge speed pulls out whole cells of solution?
low speed
51
New cards
how are nuclei and cytoskeleton isolated in centrifugation?
cells are lysed then spun at low speeds
52
New cards
how is the supernatant isolated
spun at high speeds to isolate other organelles
53
New cards
what does low speed contain?
whole cells, nuclei, cytoskeletons
54
New cards
what does medium speed contain?
mitochondria, lysosomes, peroxisomes
55
New cards
what does high speed contain?
microsomes, small vesicles
56
New cards
what does very high speed contain?
ribosomes, viruses, large macromolecules
57
New cards
how are sucrose gradients used with ultra centrifuges?
separating molecules of different densities
58
New cards
column chromatography
separates molecules into fractions with eluent
59
New cards
what are the three types of beads used in column chromatography?
ion exchange, gel filtration, affinity chromatography
60
New cards
what does ion exchange separate?
charged molecules
61
New cards
what does gel filtration separate?
molecules by size
62
New cards
what does affinity chromatography separate?
specific molecules to antibodies or other molecule specific substrates crosslinked to the beads
63
New cards
what molecule is able to pass through size exclusion?
large unretarded molecule
64
New cards
what type of chromatography is considered the best?
affinity
65
New cards
sodium dodecyl sulfate
ionic detergent which denatures and coats proteins giving them a negative charge
66
New cards
beta mercaptoethanol
reducing agent that breaks disulfide bonds
67
New cards
what chemical tools help stabilize proteins?
sodium dodecyl sulfate and beta-mercaptoethanol
68
New cards
how are individual polypeptide components of a protein separated?
by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
69
New cards
what stain is used for SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis?
coomasie
70
New cards
what occurs in 2D polyacrylamide gel?
isoelectronic focusing
71
New cards
what occurs after isoelectronic focusing?
turned 90 degrees and separated by size in SDS page
72
New cards
can 2D acrylamide gel electrophoresis be combined with western bloting?
yes
73
New cards
what can mass spectrometry be used for?
identify proteins
74
New cards
what do fusion proteins do?
used for localization, purification or to look at protein-protein interaction
75
New cards
how are fusion proteins created?
different tags
76
New cards
western blot
identify protein from a preparative gel based on spot position
77
New cards
what is used for the yeast two hybrid technique?
BAIT and PREY
78
New cards
what does the yeast two-hybrid technique do?
detect protein-protein interactions
79
New cards
what is x-ray crystallography used for?
determining protein structure
80
New cards
what is NMR spec used for?
determining protein structure
81
New cards
restriction enzymes
restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific sequences/sites
82
New cards
what can restriction enzyme cut DNA be ligated to make?
new recombinant molecules
83
New cards
gel electrophoresis
separates molecules by size
84
New cards
acrylamide use
separates small molecules and single base-pair size differences
85
New cards
agarose use
large molecules, pulse field gels for whole chromosomes
86
New cards
probe
a single-stranded sequence of DNA or RNA used to search for its complementary sequence in a sample genome
87
New cards
genomic DNA library
inserts
88
New cards
cDNA library
a collection of cloned DNA sequences that are complementary to the mRNA that was extracted from an organism or tissue
89
New cards
polymerase chain reaction
amplifying large amounts of small pieces of DNA quickly in a test tube
90
New cards
PCR
polymerase chain reaction
91
New cards
the sequence of at least the ends of the DNA piece must be…
known to make oligonucleotide primers
92
New cards
first cycle of PCR
producing two double-stranded DNA molecules
93
New cards
second cycle of PCR
producing four double-stranded DNA molecules
94
New cards
third cycle of PCR
producing eight double stranded-DNA molecules
95
New cards
DNA fingerprint
technique used to determine paternity or to find a region linked to a genetic trait
96
New cards
what does a low percent of ddNTPs result in?
occasional termination
97
New cards
how are terminated DNA fragments separated?
by size
98
New cards
how are genes found?
by looking for open reading frames
99
New cards
ORF
open reading frames
100
New cards
what is the reading direction for sequence of both bottom and top DNA strand?
N terminus to C terminus