AGRI 22 - Poultry Breeding and Hatching
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Breed
Established group of birds having same
general appearances, weight and common
characteristics.
Variety
It is a sub-division of a breed, distinguished
either by a color pattern, shape, comb type or feather
pattern. For Example : Single Comb Leghorn, Rose
Comb Leghorn
Strain
A group of birds within a variety that has been
bred by one person or firm for some time and has
more or less uniform characteristics and capabilities.
Chromosomes
A structure containing a complete strand of
DNA. Function in the transmission of
hereditary material from one generation to the next.
Typically come in pairs, with one set donated
from the mother and one from the father. Humans have 23 pairs . Chickens have 39 pairs.
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism.
Phenotype
The observable physical or biochemical
characteristics of an organism resulting from its genotype.
Examples of aspects of a chicken's _______ include body
shape, feather color, eye color, comb type, and so on.
Dominant factors
A gene that can express itself in the
homozygous state or the heterozygous
state is referred to as a ____ _____
Recessive factor
A gene that can express itself only in the
homozygous state is referred to as a ____ ____
Asiatic
Mediterranean
English
American
Standard classification of poultry breeds
Based on Origin
Meat
Egg
Dual
Fancy
Fighting
Standard classification of poultry breeds
Based on Utilization
Meat type
lay less eggs and heavy in body weight
Egg type
Lay big eggs and are not heavy in body weight
Dual purpose
lay more egg and heavy in body weight
Inbreeding
breeding for increased homozygosity
It is defined as mating between individuals which are more closely related to each other than the
average relationship between all individuals in a
population.
Outbreeding
breeding for increased heterozygosity
This is the opposite of inbreeding in the sense that the relationship of the individuals which are mated is less close than the average relationship within the population.
Close inbreeding
Mating between sibs and parents and progeny. Full sib mating and back crossing of the progeny to the younger of the parents are often practiced.
Strain formation
Developing a small group of animals within a breed and variety with a special character in view. This is a mild form of inbreeding. For example Babcock strain of Single Comb White Leghorn developed to lay heavier eggs.
Line breeding
This is inbreeding with an ancestral line and is the most
intensive form of back-crossing.
Four-way cross
What type of Cross
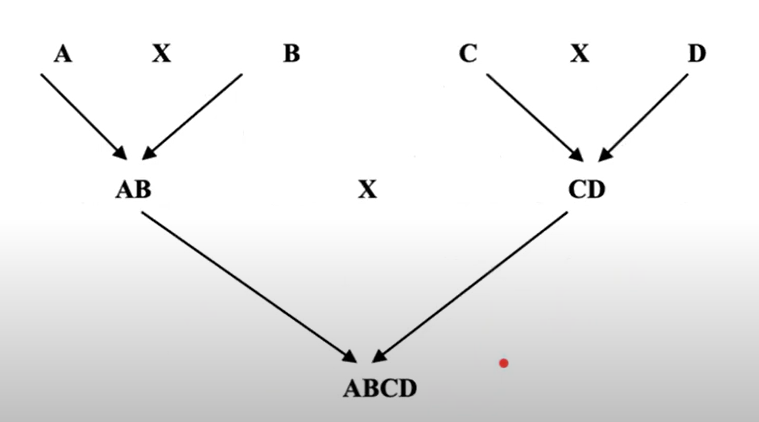
Upgrading
Different breed types have been crossed to produce the local
or native breeds of farm animals so as to combine desirable
traits from many sources.
Itik Pinass (IP)
A genetically superior breeder duck called _______ was
developed in a project conducted by the Philippine Council for
Agriculture, Aquatic and Natural Resources Research and
Development of the Department of Science and Technology
(DOST-PCAARRD) and the National Swine and Poultry Research and
Development Center of the Bureau of Animal Industry (BAI-NSPRDC).
Pateros duck
IP was a product of continuous selection and breeding of the
traditional _________
Mating
is defined as the pairing of a male and a female for
the purpose of reproduction or production of young ones.
Hatchery
responsible for the incubation
and hatching of chicks from fertile eggs
obtained from broiler breeders.
38C
Eggs initially need a very controlled heat input to
maintain the optimum temperature of ___,
because the embryo is microscopic in size.
18
As the embryo grows in size (especially after __
days), it produces more heat than it requires and
may even need cooling.
60 to 80%
Moisture levels of __ __% Relative Humidity
(increasing during the incubation period) are
important to stop excess moisture loss from the
egg contents through the porous egg shell and
membranes.
True
Lower relative humidity for ostrich eggs because it is thicker than chicken and eggs (true or false)
Turning of Eggs
To improve embryonic development.
Turned by tilting the trays at an angle of 45
deg.on each side.
Done 4-6 times within the day.
Candling
To determine if an egg is fertilized or not.
Determine the soundness and quality of
eggs.
Day 4-5, Day 12-13 and Day 18 of incubation
Hen-day egg production

Hen-housed egg production

Mortality Rate

Fertility Rate
Measurement of the
efficiency of the
BREEDER FARM &
HATCHERY

Hatchability Rate
Measurement of the
efficiency of the
BREEDER FARM &
HATCHERY

Hatch of fertile
Measurement of the
efficiency of the
HATCHERY
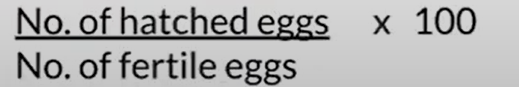
Embryonic Mortality Rate

Hatching eggs recovery rate
