GB1- Chapter 4
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
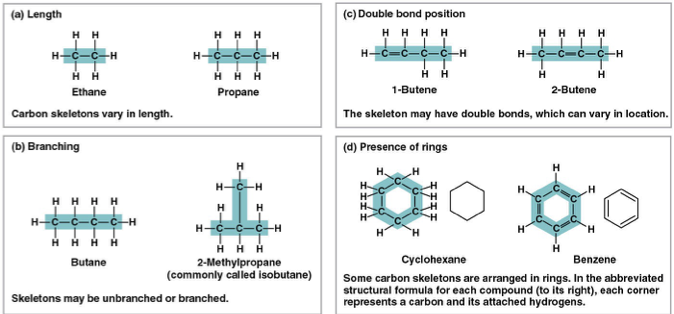
four ways carbon skeleton can vary
length
position of double bonds
branching
presence of rings
Hydrocarbons
organic molecules consisting only of hydrogen and carbons. hydrocarbons can undergo reactions that release a large amount of energy
fats
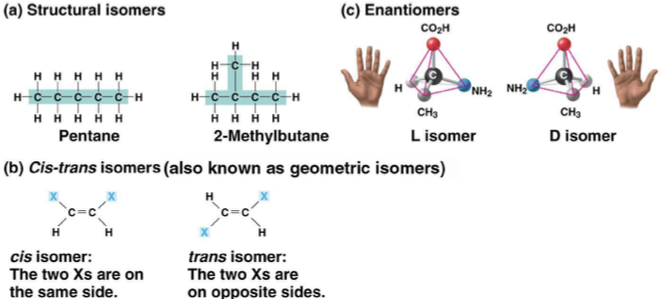
isomers
structural isomers
cis-trans isomers
enantiomers- important in pharmaceutical industry because they may have different effects, or only one of them are biologically active. organisms are sensitive to even subtle variaitons in molecules.
ex) Ibuprofen- S is effective/ R is not
Albuterol- R is effective/ S is not
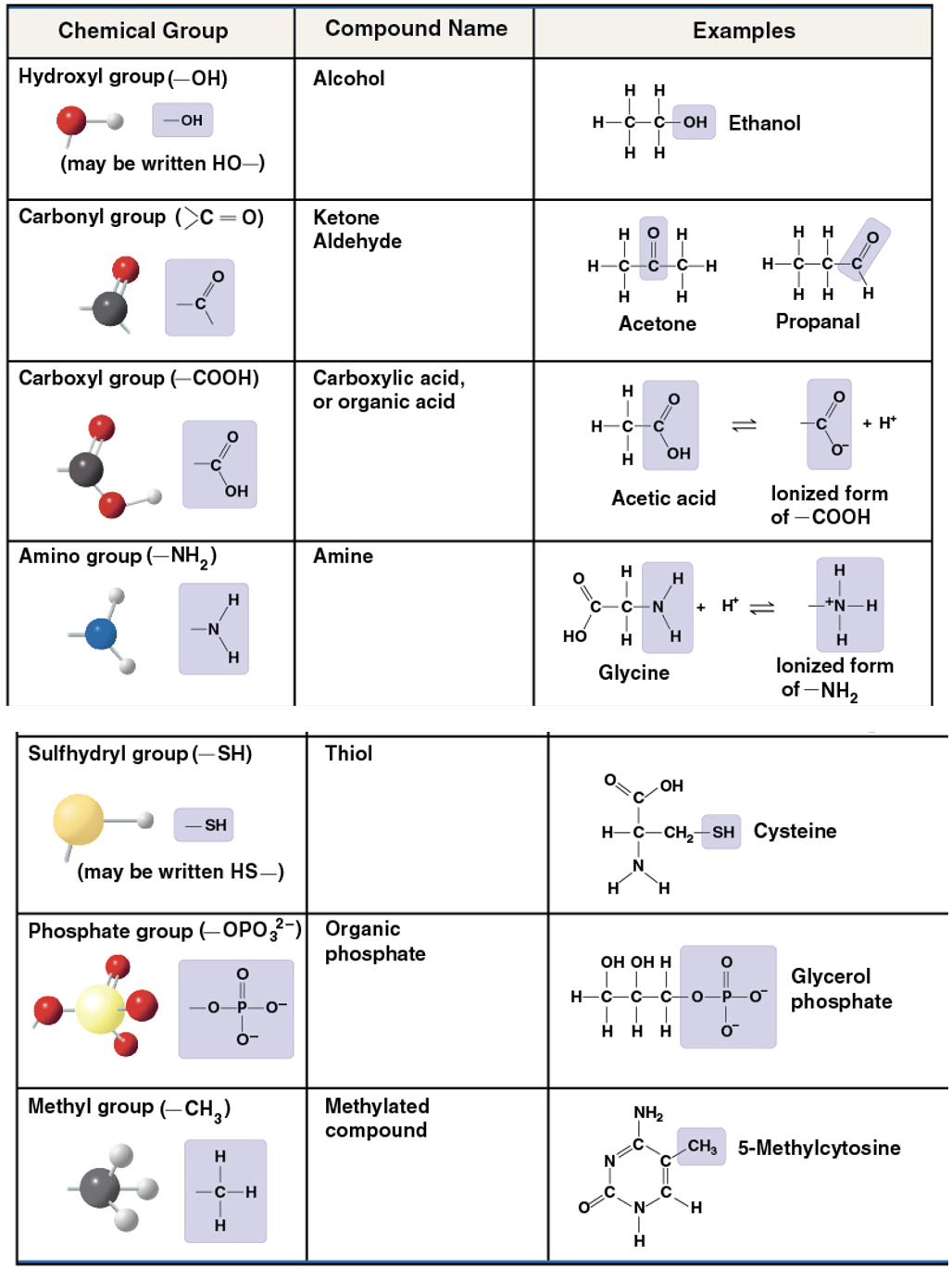
functional groups
components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions. The number and arrangement of functional groups give each molecule its unique properties.
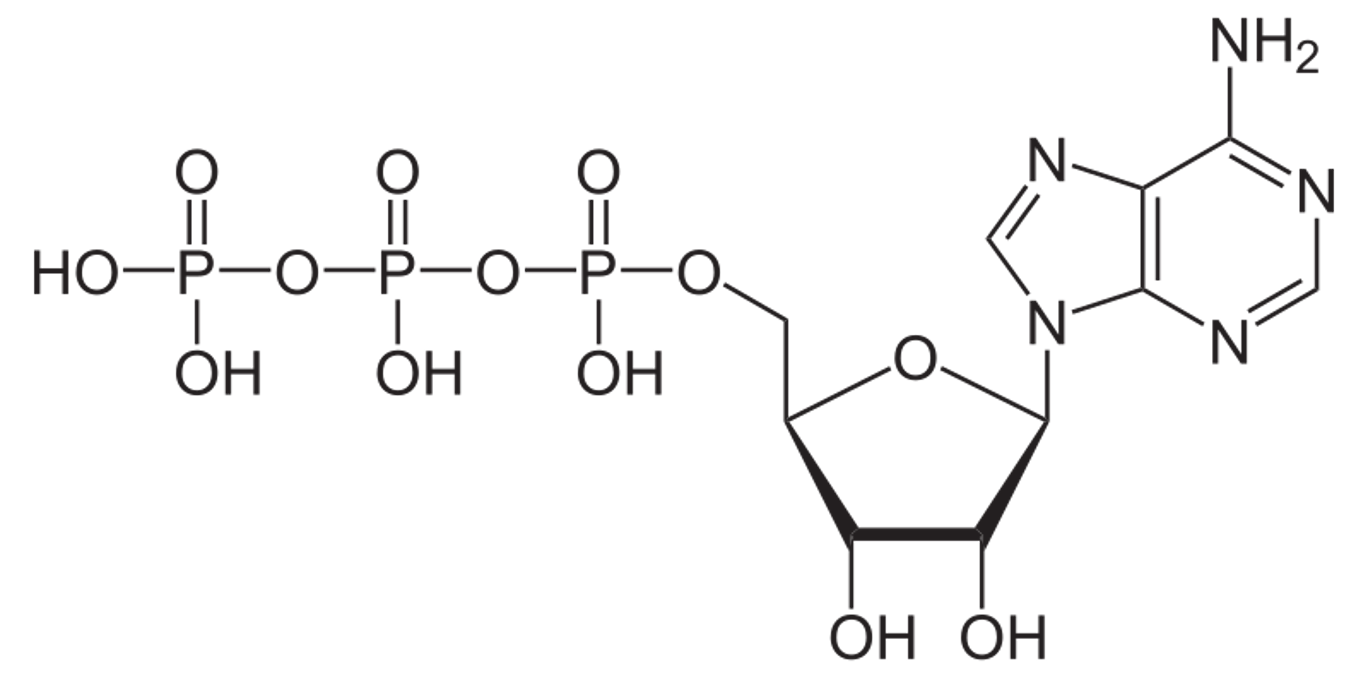
Adensoine triphosphate (ATP)
has the potential to react with water = release energy that can be used by the cell
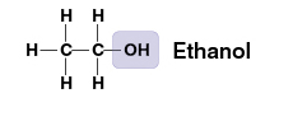
hydroxyl group
OH
compound name: alcohol
ex) Ethanol
polar- oxygen has strong electronegativity. dissolves in water
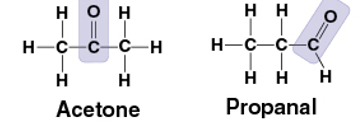
carbonyl group
C=O
compound name: Ketone- the carbonyl group is in the middle
ex) Acetone
Aldehyde- the carbonlyl group is at the end
ex) Propanal
polar- oxygen has high electronegativity
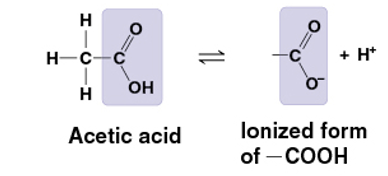
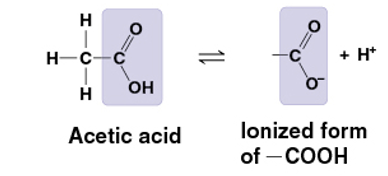
carboxyl group
COOH
carboxylic acid/ organic acid
pulls electrons away from hydrogen atom
H+ leaves as ion
acidic
Amino group
NH2
Compound Name: Amine
picks up H+ from the surrounding solution
acts as a base
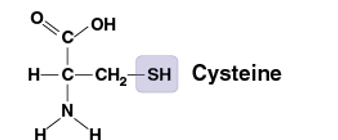
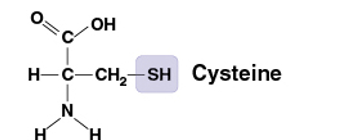
Sulfhydryl
SH
Compound name: Thiol
Two SH groups can react, forming a crosslink that stabilizes the structure of many proteins
Phosphate group
OPO3 2-
Compound name: Organic phosphate
oxygen attracts electrons and loses H+
acts as an acid
important in the transfer of energy between organic molecules
important in ATP
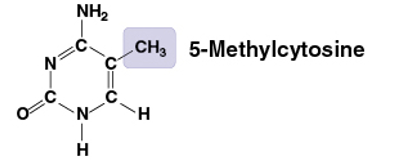
Methyl group
CH3
Compound name: Methylated compound
steriods
deriviatives of cholestrol with a common carbon skeleton
Estradiol- HO
Testosterone- =O and CH3