Alkanes
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What are alkanes?
saturated hydrocarbons
What are saturated hydrocarbons?
hydrocarbons that only contain single carbon to carbon bonds
What is the general formula of an alkane?
CnH2n+2
What is the bond angle of straight chain hydrocarbons?
109.5
What is the polarity of alkanes?
Non-polar
- The electronegativities of carbon and hydrogen are so similar
- As a result, the only intermolecular forces between their molecules are weak van der Waals
What is the trend in boiling point in alkanes?
As chain length increases, the boiling point increases because there are stronger van der Waals forces
What is the effect of branching on alkane boiling points?
It lowers the boiling point as the molecules can't pack as closely together and have less surface contact, making the vdw forces not as effective.
What is the solubility of alkanes in water?
Insoluble as the hydrogen bonds between water molecules are stronger than the van der Waals forces between alkanes
How reactive are alkanes?
very unreactive
Which reactions can alkanes undergo?
Combustion and reaction with halogens
What is the reaction for the complete combustion of alkanes?
Alkane + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water
What is the reaction for the incomplete combustion of alkanes?
Alkane + Oxygen → Carbon monoxide/carbon + water
What is crude oil?
A mixture of hydrocarbons, mostly alkanes
How is crude oil formed?
over millions of years from the remains of ancient biomass
How is crude oil separated?
fractional distillation
What is a fraction in fractional distillation?
mixture of hydrocarbons with a similar chain length and boiling point range
What is the process of fractional distillation?
1. The crude oil is heated and the vapours are pumped into the bottom of a distillation column.
2. The vapours rise up the column, cooling as they do so.
3. Different hydrocarbons vapours condense to liquids a different point (when they reach a level which is at a temperature below their boiling point).
4. The liquids run out of the column along pipes.
Where are alkanes collected in the fractionating tower?
-Short chain hydrocarbons condense near the top
-longer chain hydrocarbons condense near the bottom
How is the high demand for short chain hydrocarbons met?
Cracking of large hydrocarbons to shorter ones
What are the conditions for thermal cracking?
High temperature (700-1200K) and High pressure 7000kPa.
What are the products of thermal cracking?
Alkanes and alkenes
What is the use of alkenes produced in thermal cracking?
Chemical Feedstock
What are the conditions for catalytic cracking?
-Lower temperatures (450°C)
-Moderate pressure
-Zeolite catalyst consisting of silicon dioxide and aluminium oxide
What are the products of catalytic cracking?
Branched alkanes, cycloalkanes and aromatic compounds
What is the advantage of catalytic cracking over thermal cracking?
Cheaper - due to lower pressure and temperature used
Saves time - Catalyst speeds up reaction
What determines how much energy is given out when an alkane is burnt?
The number of carbons in the hydrocarbon chain
How are nitrogen oxides formed from the combustion of hydrocarbons?
Reactions of nitrogen and oxygen in the air at high temperatures
What is the effect of nitrogen oxides?
React with water vapour to make acid rain and photochemical smog
How is sulfur dioxide formed from the combustion of hydrocarbons?
Combustion of fuels with sulfur impurities
What is the effect of sulfur dioxide?
acid rain and respiratory problems
What is the effect of carbon particles?
Cause global dimming and respiratory problems
How is sulfur dioxide removed from flue gas?
Using calcium oxide or calcium carbonate to produce calcium sulfite
What are the reactions for flue gas desulfurisation?
CaO + SO2 → CaSO3
CaCO3 + SO2 → CaSO3 + CO2
What are catalytic converters?
a device incorporated in the exhaust system of a motor vehicle, containing a catalyst for converting pollutant gases into less harmful ones.
How does a catalytic converter work?
As the polluting gases pass over the catalyst, they react with each other to form less harmful products
What is a free radical?
A particle with an unpaired electron
When do free radicals form?
when a covalent bond splits equally giving one electron to each atom
How reactive are free radicals?
very reactive
How are free radicals represented?
with a dot to symbolize the odd electron
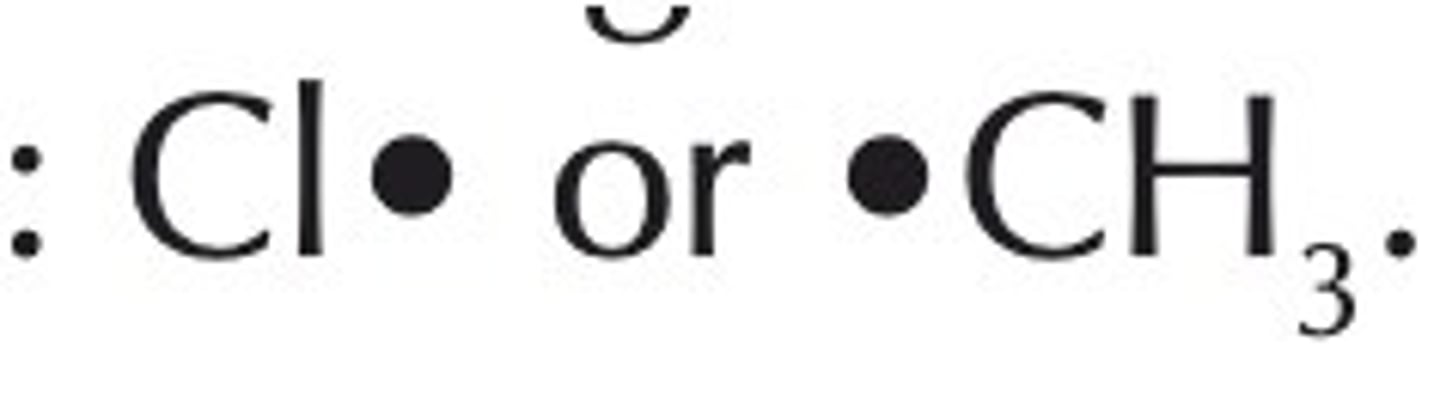
How are halogenoalkanes formed from alkanes?
Free radical substitution reaction
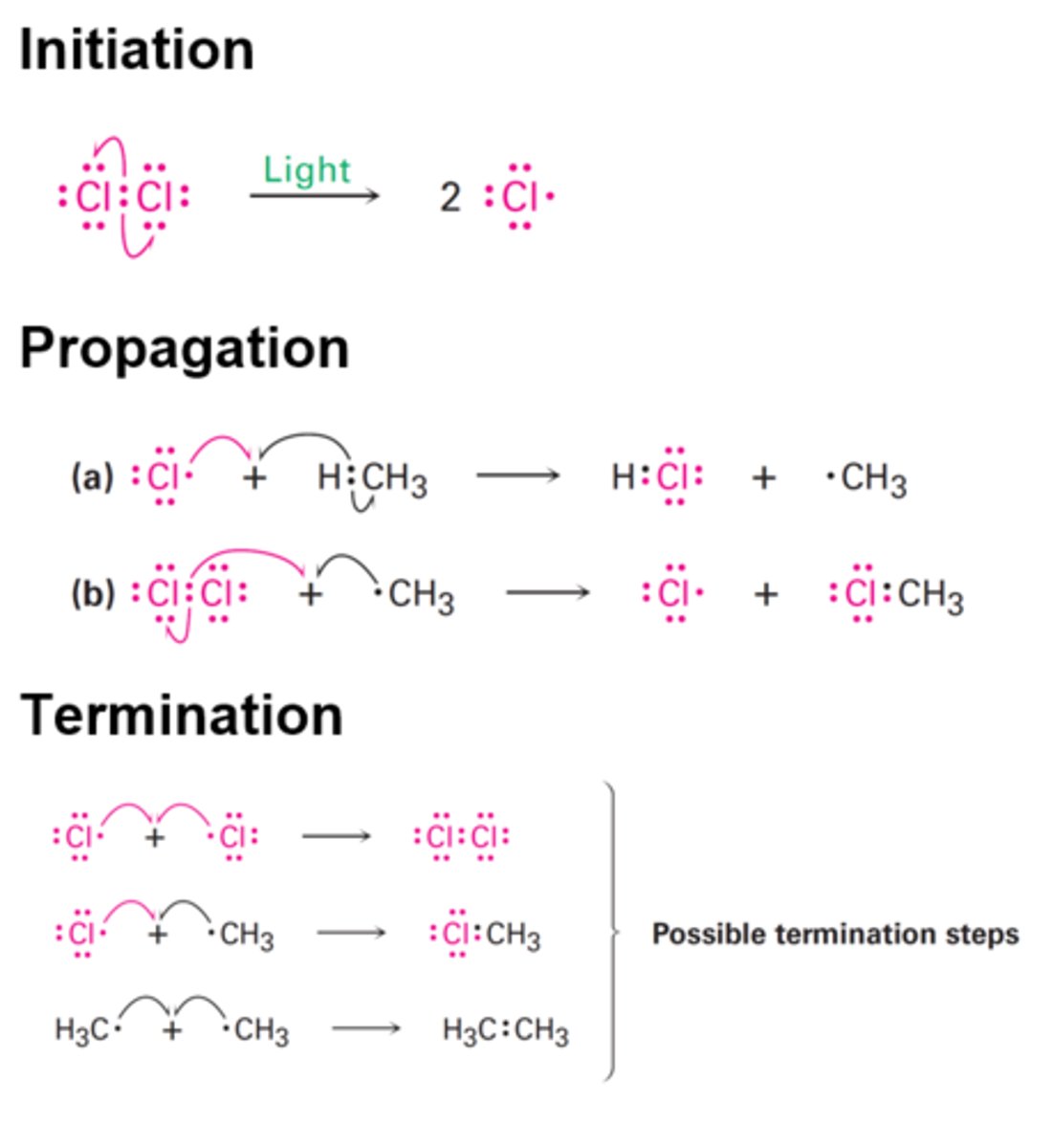
What are the three steps in free radical substitution?
1. Initiation
2. Propagation
3. Termination
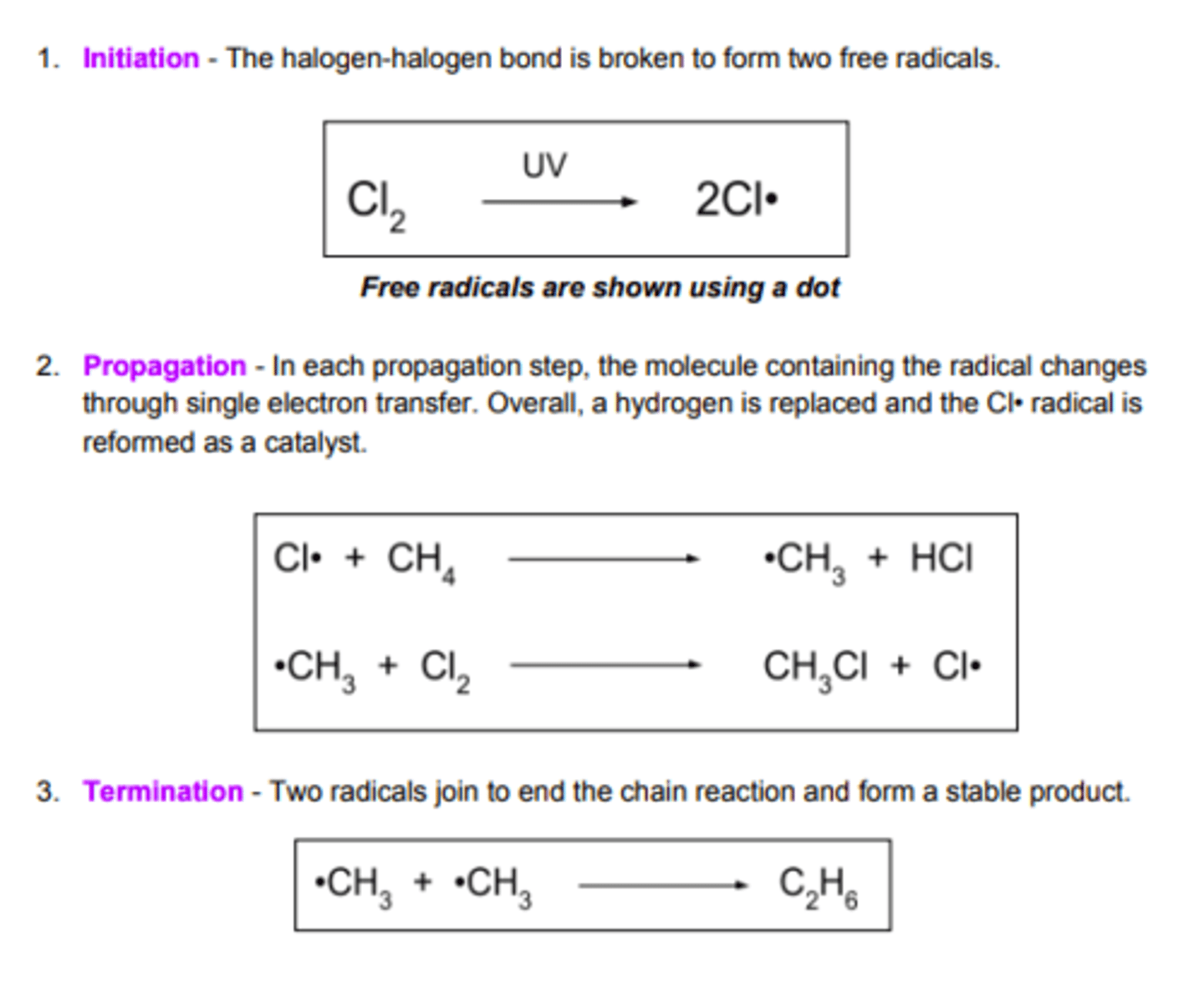
What is involved in initiation in free radical substitution?
Breaking halogen bond with UV light to form 2 free radicals
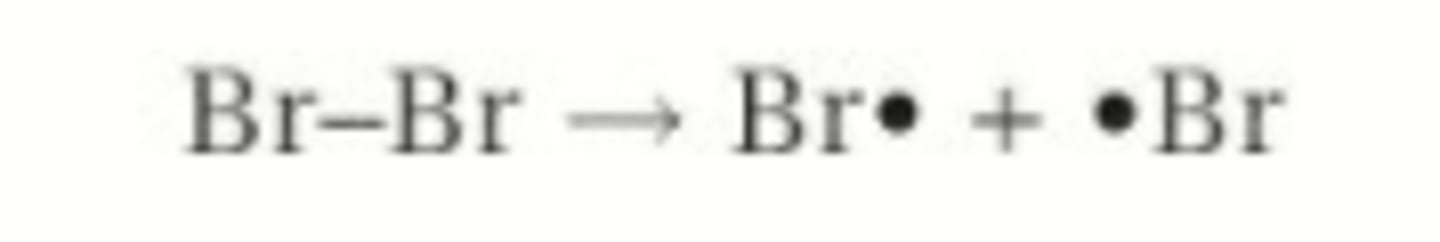
What is the general equation for initiation reactions?
X2 → 2X•
Why doesn't the carbon-hydrogen bond break under UV light?
It needs more energy than available in UV light
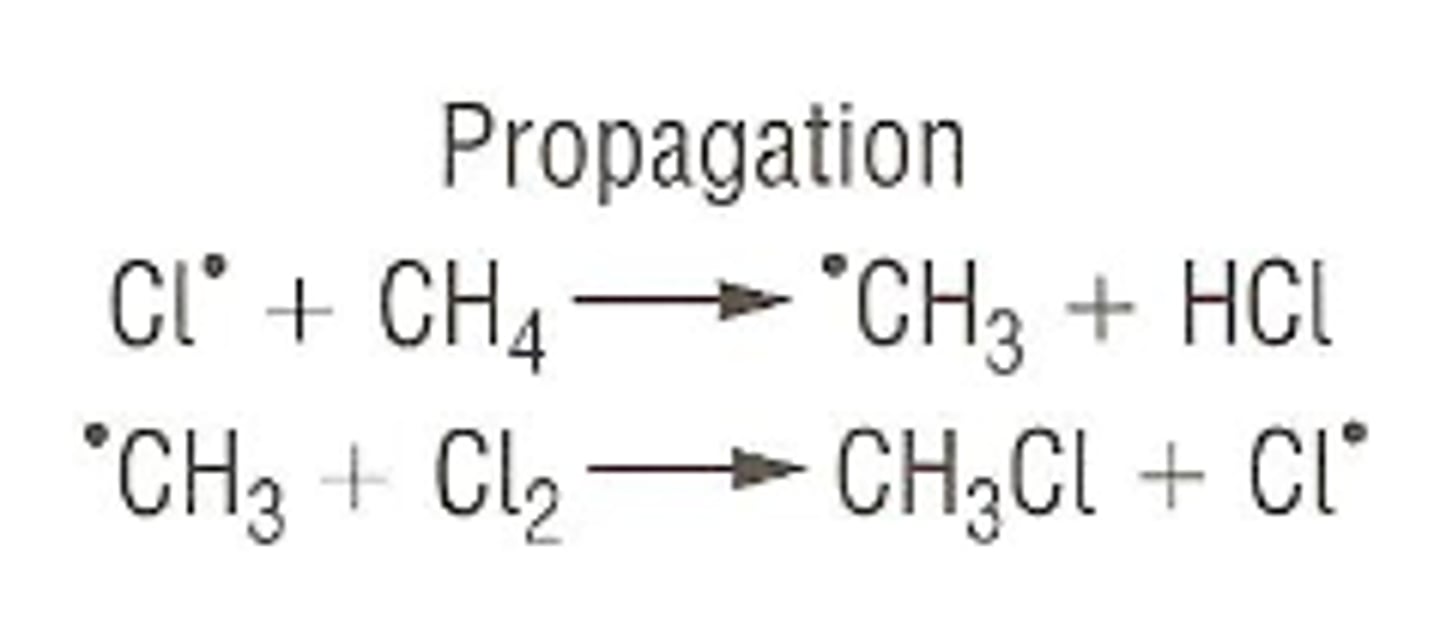
What occurs in propagation reactions?
Chain part of the reaction where products are formed but free radical remains
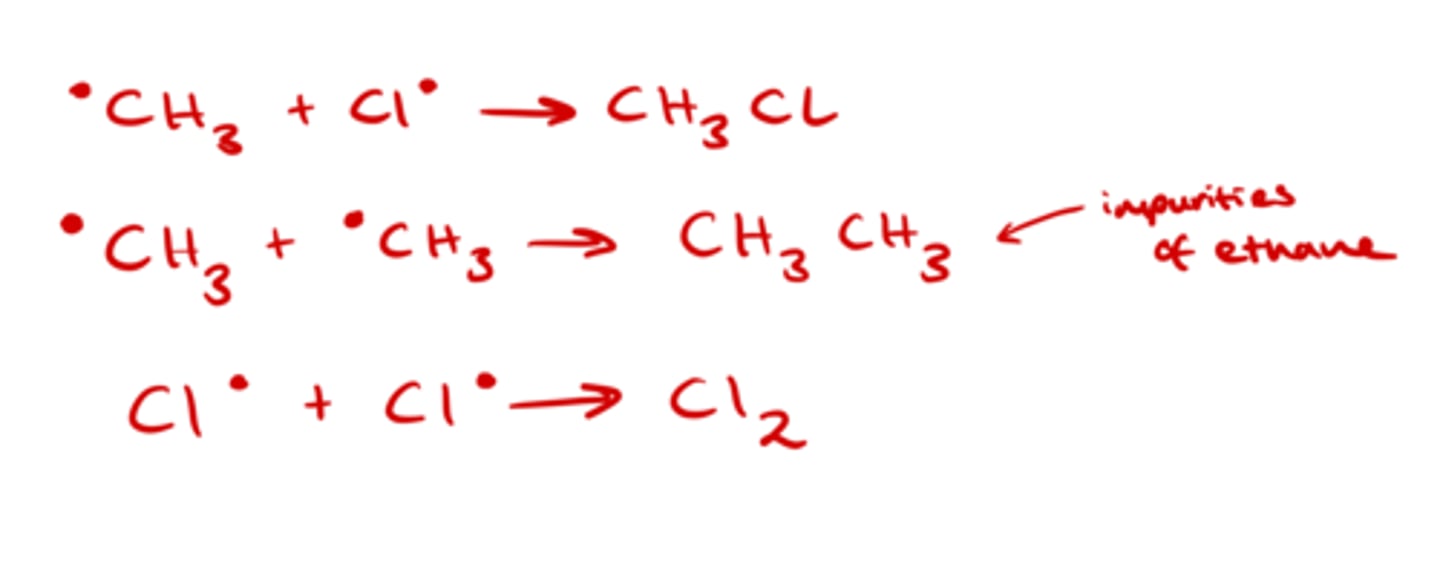
What happens in termination reactions?
Two free radicals react together to form a molecule with no unpaired electrons
What are the conditions needed for the formation of a free radical chlorine atom?
Presence of UV light
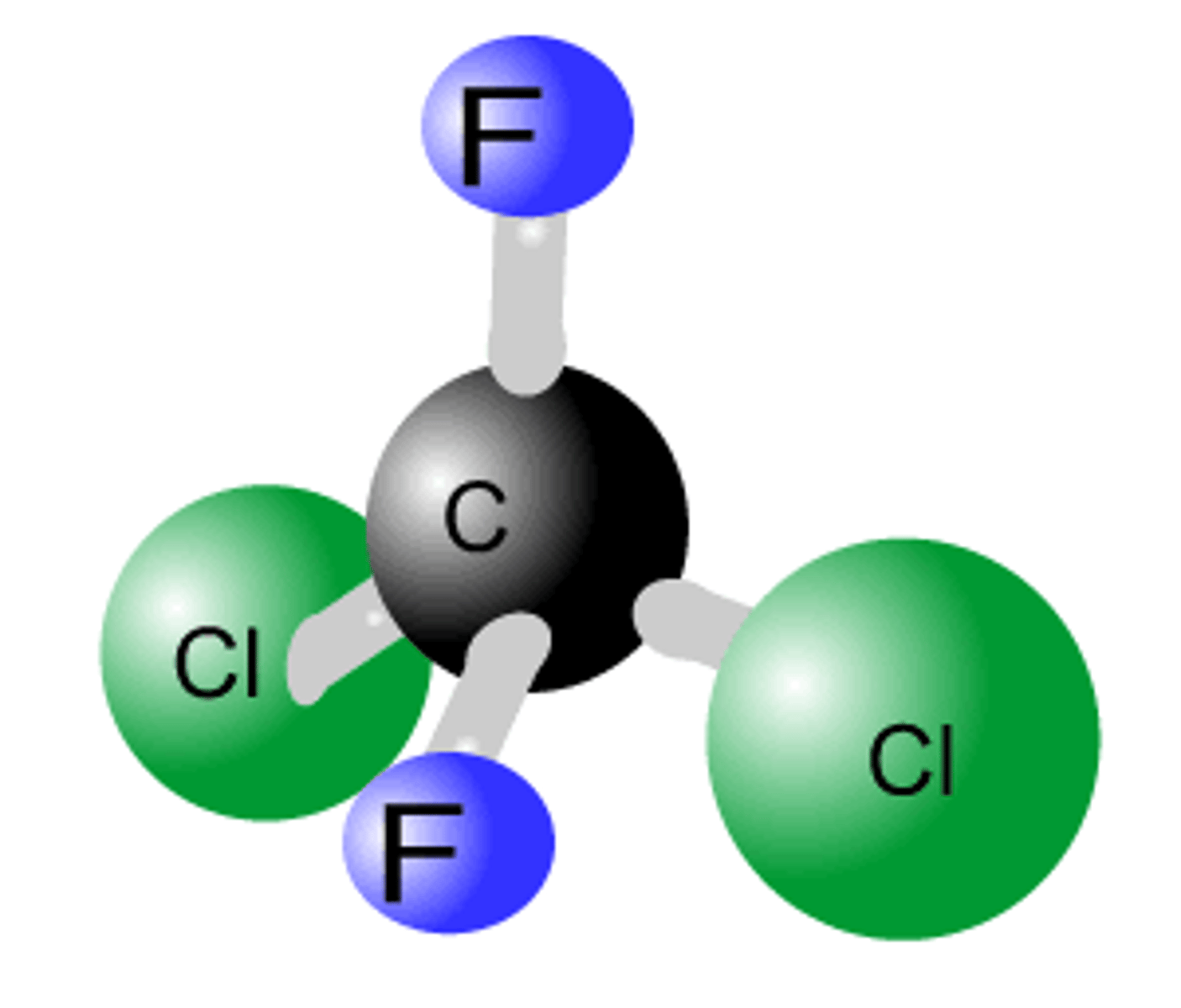
What are chlorofluorocarbons?
Halogenoalkane molecules in which all hydrogen atoms are replaced by chlorine and fluorine atoms
What is the ozone layer and why is it important?
The ozone layer is composed of ozone (O3) molecules that absorb harmful ultraviolet light.
How does the ozone layer form?
- The oxygen molecules split by UV radiation to form oxygen free radicals
- The oxygen radicals react to form ozone
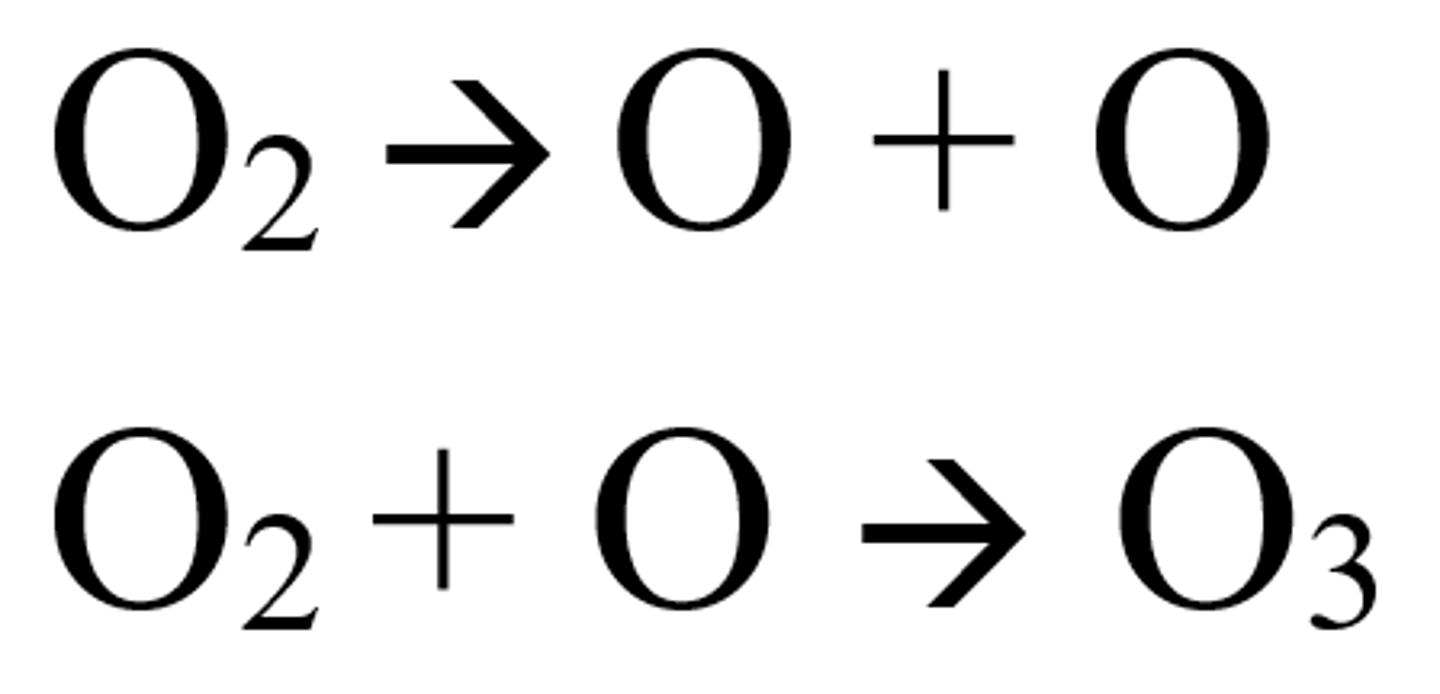
How do CFCs deplete the ozone layer?
- CFC molecules are broken down by UV to create chlorine free radicals.
- Chlorine atoms react with ozone atoms.
- Chlorine atoms regenerated so can react with more ozone molecules.

What is the equation for ozone depletion?
Cl• + O3 → ClO• + O2
ClO• + O3 → 2O2 + Cl•

What is the role of chlorine free radicals in ozone depletion?
Acts as a catalyst
Why don't carbon-fluorine bonds break in chlorofluorocarbons?
They are stronger than carbon-chlorine bonds