Neurons and Synaptic Transmissions
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are neurones?
neurones are nerve cells
There are at least 100 billion neurones in the human nervous system
80% of neurones are located in the brain
* Provide the nervous system with it's primary means of communication
* Allow us to connect and communicate with our environment.
1. Dendrites - contain receptors, which receive signals
2. Cell body (soma) - includes the nucleus
3. Nucleus - contains the DNA of the cell
4. Axon - carries impulses away from the cell body, down the length of the neurone
5. Nodes of Ranvier - force electrical signals down the gaps along the axon
6. Myelin Sheath - membrane that covers and protects the axon. Aalso speeds up the electrical impulse
7. Schwann cell- maintains the PNS
8. Axon terminal buttons - communicate with the next neurone across the synapse and send the signal to another neurone, muscle or organ
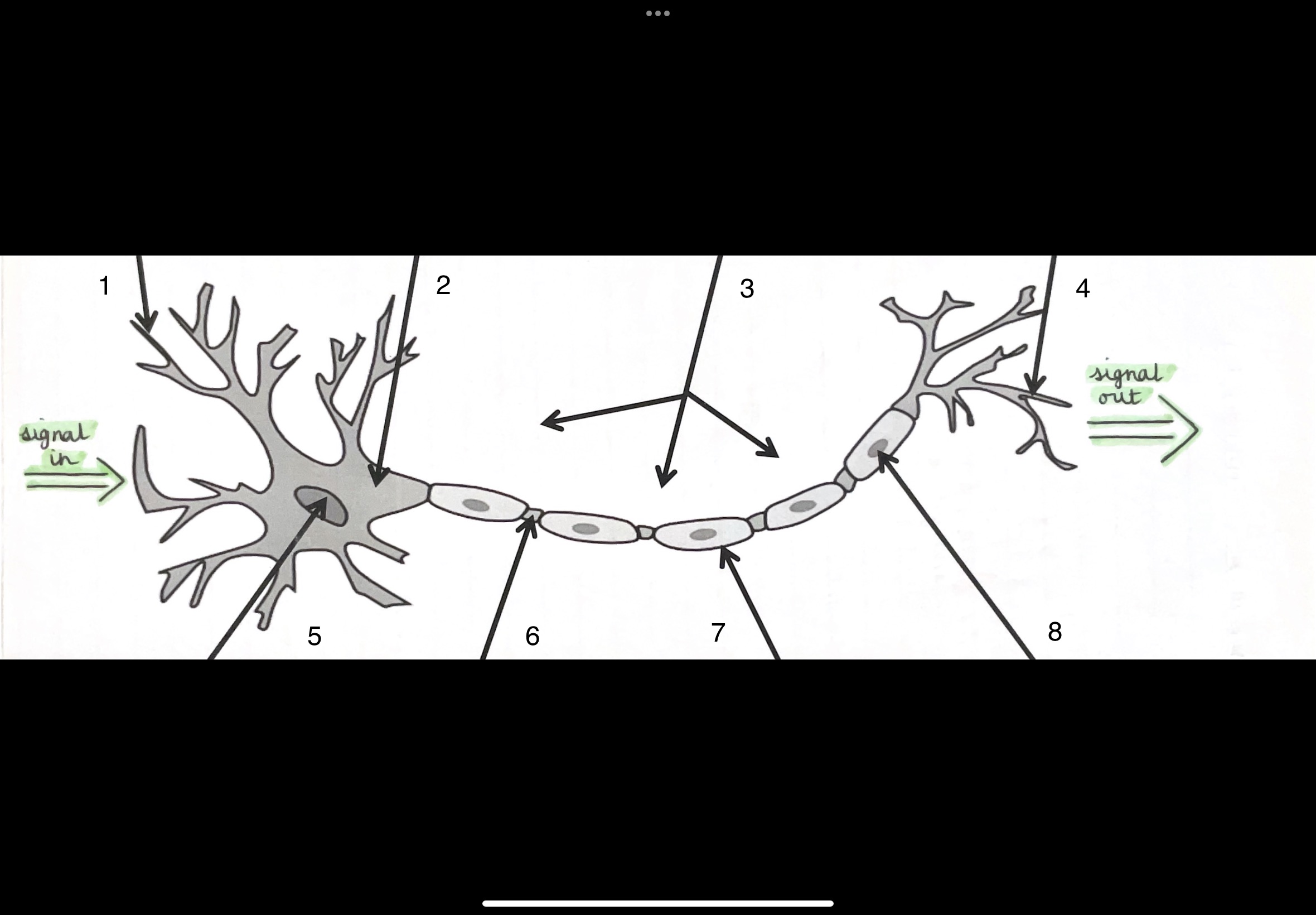
Label each part of the neurone:
dendrites
cell body (soma)
axon
axon terminals
nucleus
nodes of fancier
myelin sheath
Schwann cell
What are the differences between dendrites and axon terminal buttons?
Dendrites only contain receptors, so they can only receive signals
Axon terminal buttons do not have receptors and only have terminals, so therefore, they can only send/release impulses
What are motor neurones?
Motor neurones carry signals from the Central Nervous System and send them to muscles, glands and organs
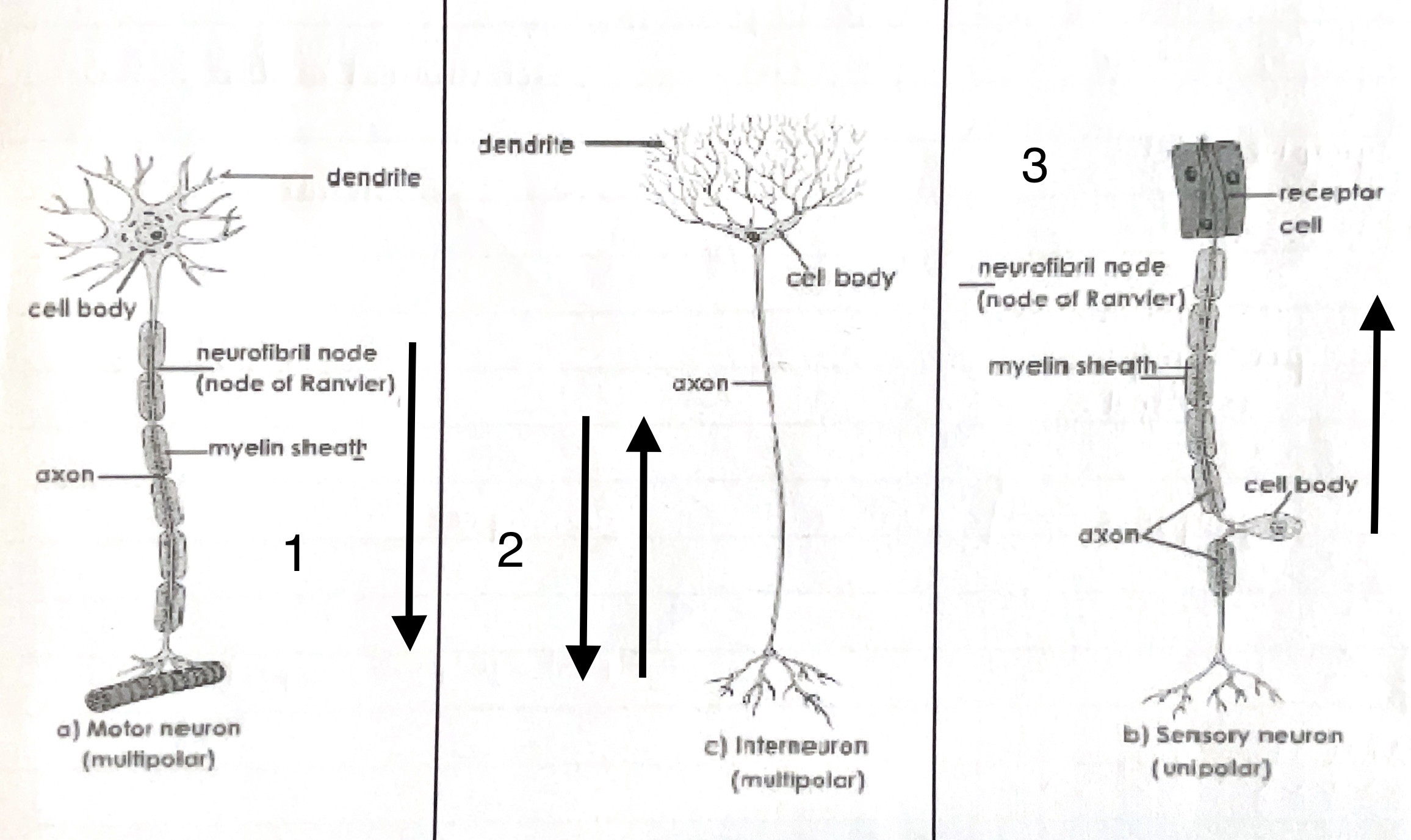
Identify the different neurons:
motor neuron
relay (interconnecting neuron)
sensory neuron
Name the parts of the synapse
synaptic vesicles
axon terminal buttons
neurotransmitters
pre-synaptic terminal
synapse/synaptic gap
dendrites
receptor
post-synaptic receptor site
What are the 3 stages of synaptic transmission?
Pre-synaptic transmission
The synapse
Post-synaptic transmission
What activates the neutron?
when a neurone is in a resting state, the inside of the cell is negatively charged compared to the outside.
when a neurone is activated by a stimulus, the inside of the cell becomes positively charged for a split second, causing an action potential to occur
this causes an electrical impulse that travels down the axon towards the pre-synaptic terminal
What is excitatory transmission?
neurotransmitters have either an excitatory or inhibitory effect on the neighbouring neurones.
excitatory transmission occurs when a neurotransmitter increases the positive charge of the post-synaptic neurone.
this increases the likelihood that the neurone will fire and pass on the electrical response.
What is inhibitory transmission?
this occurs when a neurotransmitter increases the negative charge of the post-synaptic neurone.
this then decreases the likelihood that the neurone will fire and pass on the electrical response.
What is summation?
excitatory and inhibitory influences are summed and must reach a certain threshold in order for the action potential of the post-synaptic neurone to be triggered.
if the net effect of the neurotransmitters is inhibitory then the post-synaptic neurone is less likely to fire
it is more likely to fire if the net effect is excitatory
Excitation vs inhibition stimuli