unit 3 study guide part 2
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
describe shape of s orbital
s orbitals have a spherical shape
describe shape of p orbtials
p orbitals have lobes (p orbitals look like to balls sticking together)
how many orbitals does the d sublevel have?
the d sublevel has 5
how many orbitals does the f sublevel have
the f sublevel has 7
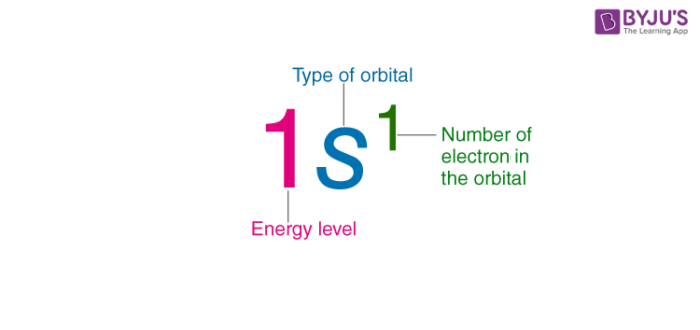
in an electron configuration what does the big number mean
it represents the energy level
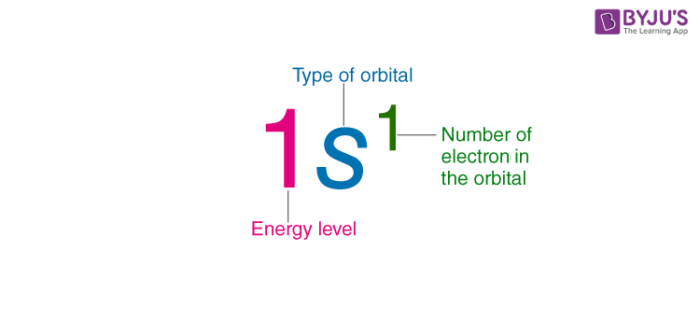
in an electron configuration what does the letter repersent
type of orbital/sub level
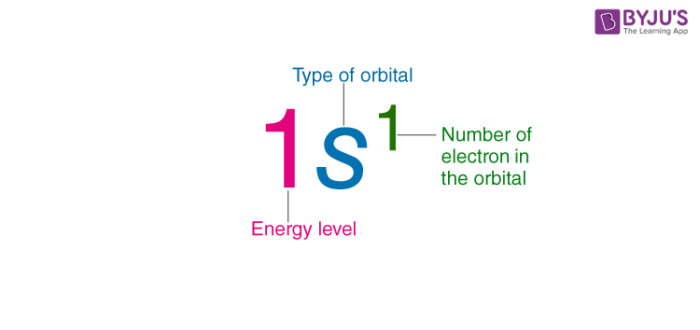
in an electron configuration what does the exponent repersent
it represents the amount of electrons
define periodic law
when elements are arranged in increasing atomic number there is a periodic repletion of their properties
what are the representative elements
all the metals and all the groups on the far left which don’t inculde the transition metals
define effective nuclear charge
the apparent charge a valence electron “feels” from the nucleus. to find out if an element will be smaller compared to the others do number of protons- number of core electrons if the answer is bigger then it’s smaller
define alkali metals
they have one valence electron, mostly solids , conduct electricity, malleable and very reactive.
define noble gases
mostly have 8 valence electrons, all gases, colorless, do nut conduct electricity, odorless, and very unreactive.
define alkaline earth metals
they are white, lustrous, and good conductors of electricity
define halogens
Halogens are a group of highly reactive nonmetals with seven valence electrons, known for their high electronegativity
describe how Mendeleev organized the periodic table
arranged elements by increasing atomic mass with similar properties. was able to predict the existence of some elements that had not been discovered.
describe how Mosely organized the periodic table
arranged the table by increasing atomic number (not atomic mass like Mendeleev) elements are in similar chemical families and corrected mendeleev’s mistakes.
describe coulomb’s law
describes variables that affect the force of attraction or repulsion between two charged particles
how does coulomb’s law apply to the periodic trends
a stronger force (due to a higher nuclear charge or smaller distance) leads to a smaller radius, higher ionization energy, higher electronegativity, and lower metal reactivity.
describe how nuclear charge can tell us if an atom is smaller or bigger compared to the other
an atom with more protons means that the attraction between the nucleus and electrons are stronger and thus making the distance smaller (we see this with nuclear charge’s equation)