Chapter 3 - Relational database modeling
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Relational database
A database that uses logic and shows the data as a group of tables
Relational schema
A big picture of the relational database model
Relation is a synonym for?
Relation table
Table
Column is a synonym for?
Attribute
Field
Row is a synonym for?
Tuple
Record
Relation
Its the table in the database that hold the rows and the columns(Holds all the information )
Requirements for a Relational table
All columns and rows must have a different name
values in the columns must have data from the same preset domain
in each row the columns values must be single valued from the preset domain
The columns need a primary key
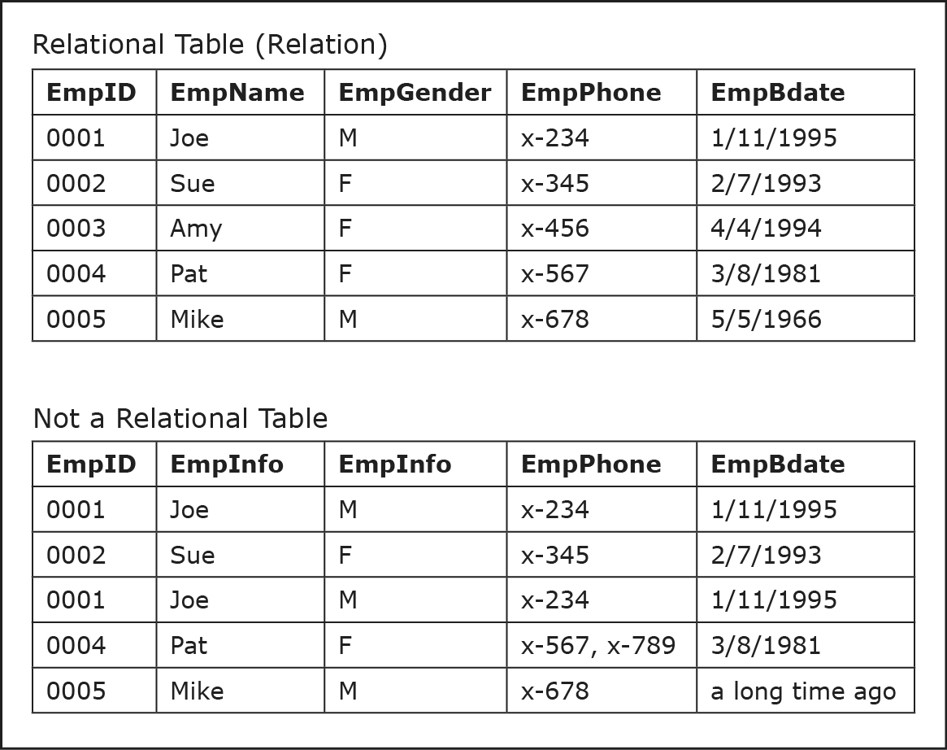
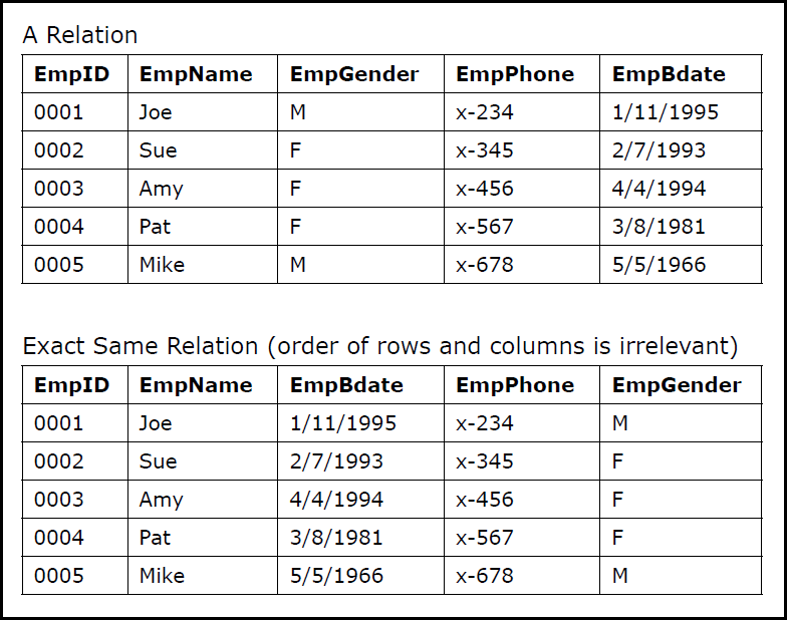
Do order of rows and columns matter
No they dont
Primary Key
Columns that have different and unique values for each row
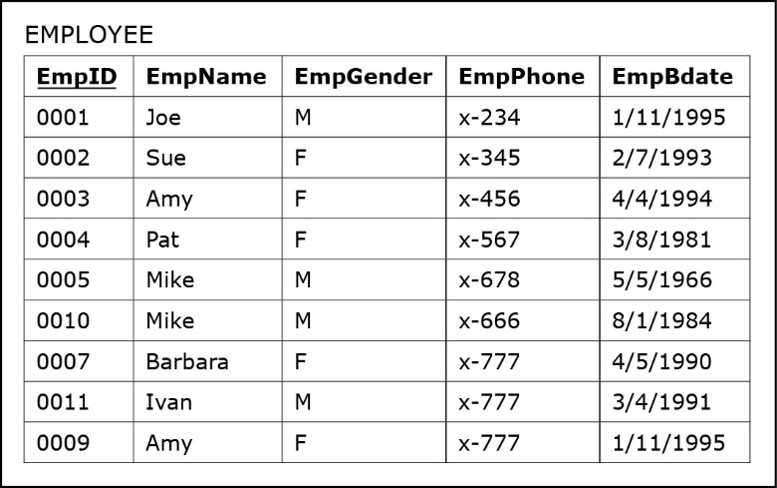
What must all tables have ____ and how is it shown ______?
A Primary key, with an underline
Mapping entity rules
Each entity becomes a relational table
each attribute becomes a column
Unique attribute is the primary key
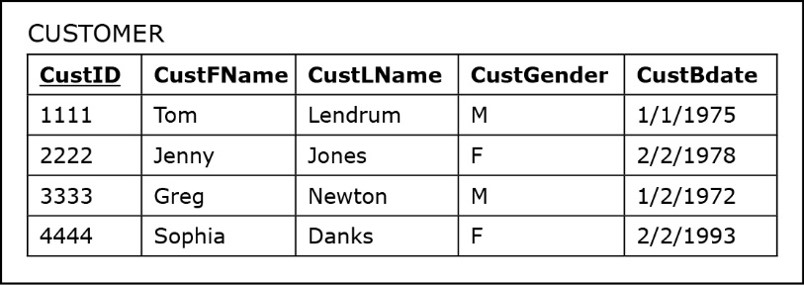
Mapping entity rules (Composite Attributes)
Each attribute that makes the composite is mapped in the table
In the backend the composite is not mapped
in the front end the composite is mapped for the users
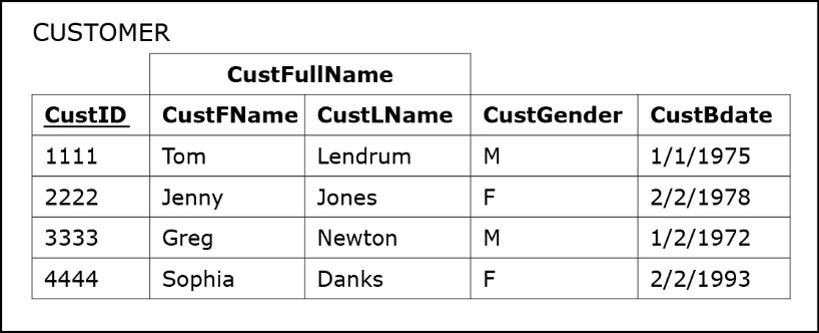
Composite primary key
Is a combination of multiple columns to make the primary key and is shown with underlining
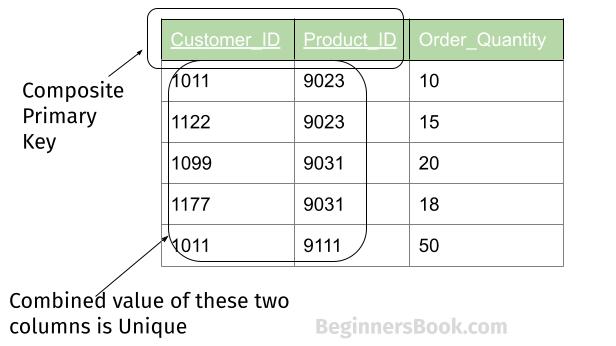
unique composite attribute
The same mappings as a composite primary key
Optional attributes mapping
Each row does not need a value
Entity integrity constraints
does not allow for any row value in the primary row column to have an empty value
Foreign key
A column in the table that refers to the primary key in another table
Foreign keys have ______ that point to _____
Lines ; corresponding primary keys
How are foreign keys used
To represent different types of relationships
Bridge table
Created when mapping a many to many relationship and has to foreign keys that match tables primary keys that represent the two entities
Many to many relationships mappings need a ___?
Bridge table
One to one relationship mappings
One table will have a foreign key which is a primary key from another table
You can choose which table gets the foreign key but choose the mandatory one
Referential integrity constraints
In each foreign key the value in the rows either matches with one of the primary keys table or the space is empty
Referential integrity constraints lines
lines that point from the foreign key to the matching primary key
Granularity of the table
Describes what is shown in the table by one row
Relational database constraint?
is a bunch of rules that help keep the cohesiveness among the different tables that are being created. It makes sure that all tables follow the same rules
What are the business rules?
rules set by a business on its data, including field specifications, relationships, and actions like creating, updating, and deleting data.
Candidate Keys
Many unique attributes
Mapping candidate keys
One is chosen to be the primary key and the rest are mapped as regular attributes
Mapping multivalued attribute
Create a separate table with the name as the primary key
The foreign key is the name of the original base entity
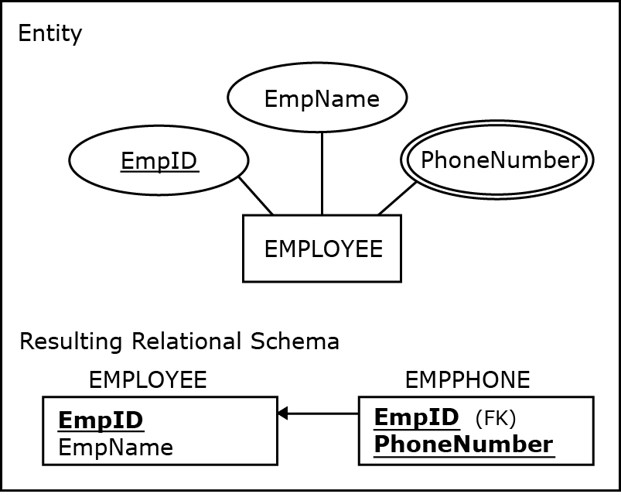
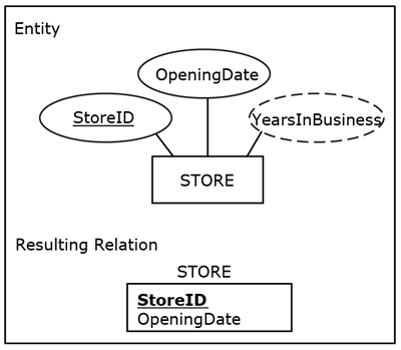
Mapping derived attributes
Are not shown in the relational table abut is shown in the end application
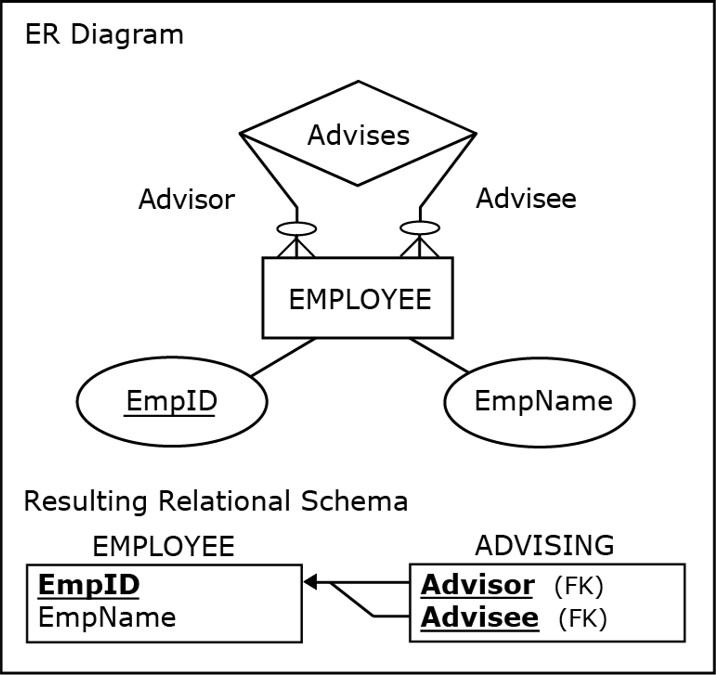
Mapping unary relationship
Is mapped like a binary relationship
contains a foreign key which the relationship name
Unary M:M
Create a bridge table for the relationship name
The two foreign keys are the names of the relationship lines