Lecture 2- Cells and Transport
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Plasma membran
a dynamic bilayer of phospholipids, with hydrophilic heads facing outward and hydrophobic tails inward. Cholesterol stabilizes membrane fluidity, while integral proteins span the bilayer for transport and signaling, and peripheral proteins attach to the surface for structural and signaling roles. Glycolipids and glycoproteins on the extracellular side aid in cell recognition and communication. This flexible structure allows molecules to move within it, maintaining the membrane's function and integrity.
Intracellular fluid
The water and dissolved substances that fill the inside of cells
Extracellular fluid
all the body's water that's not inside cells
Interstitial fluid
a clear, watery substance that fills the spaces between cells and tissues throughout the body
Diffusion
Nonpolar Lipid soluble, across membrane
Osmosis
Definition: Water across a semi-permeable membrane
Energy source: Chemical gradient
Example: Movement of H2O
Hypertonic solution
1.5% solute 98.5% solvent

Hypotonic solution
0.0% solute 100% solvent
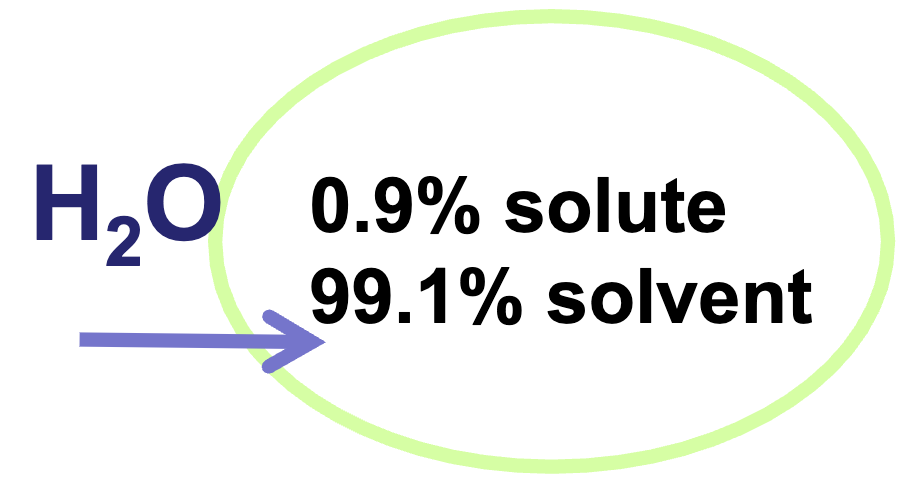
Isotonic solution
0.9% solute 99.1% solvent
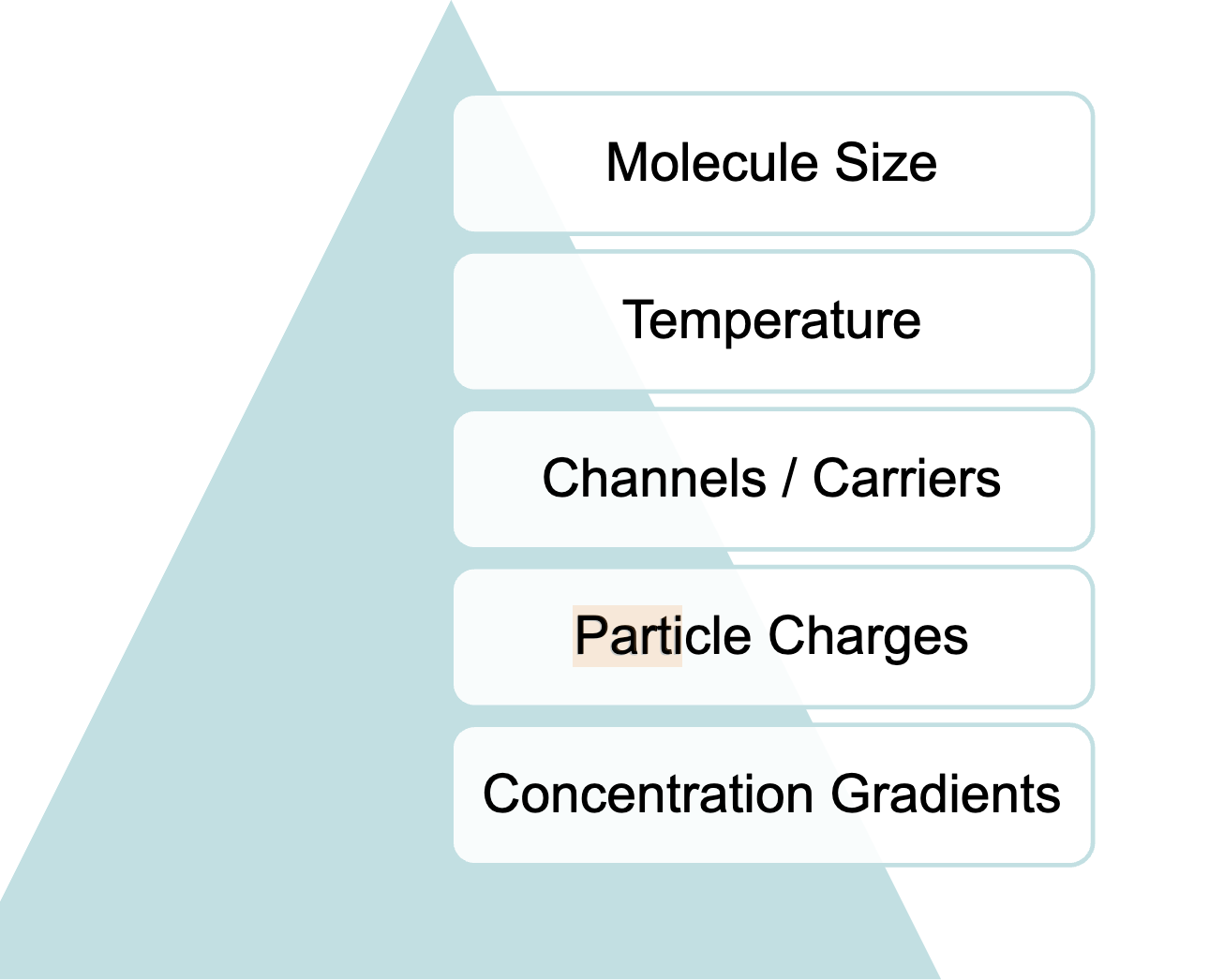
Five factors that affect the rate of transport of substances across cell membranes
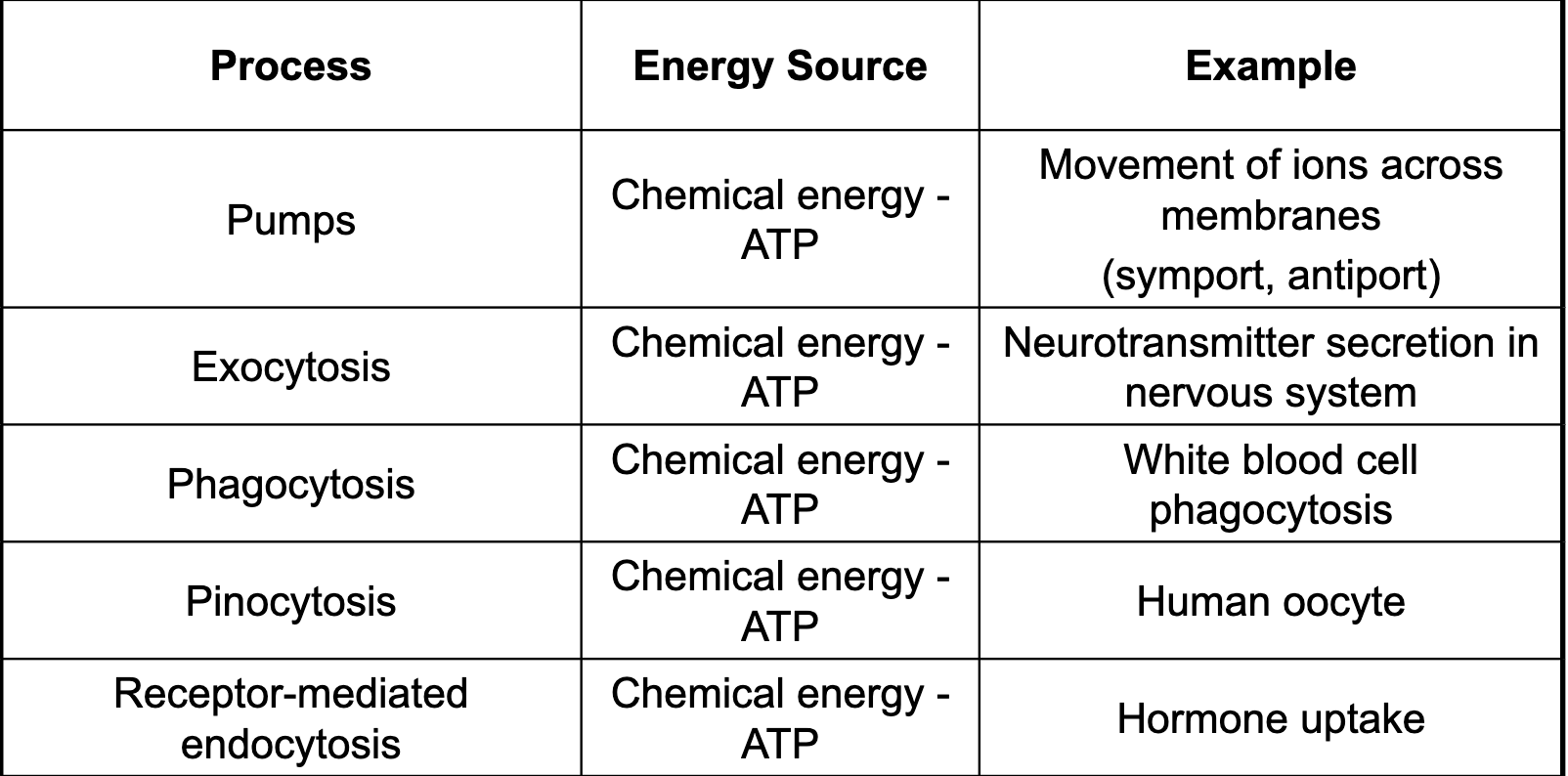
Active transport
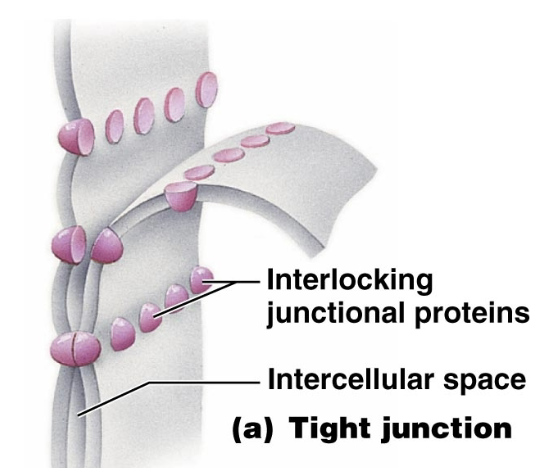
tight junctions
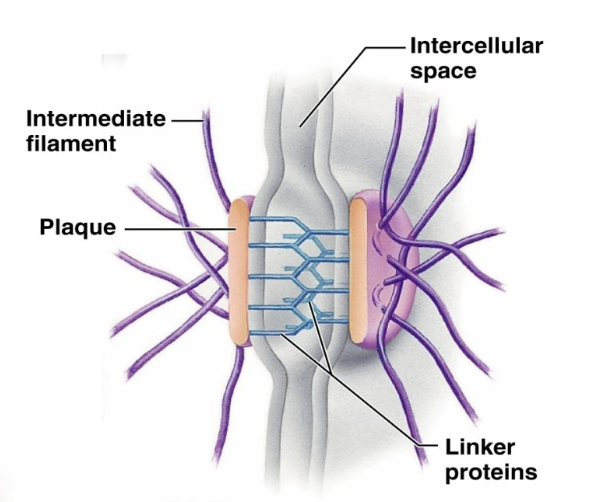
desmosomes
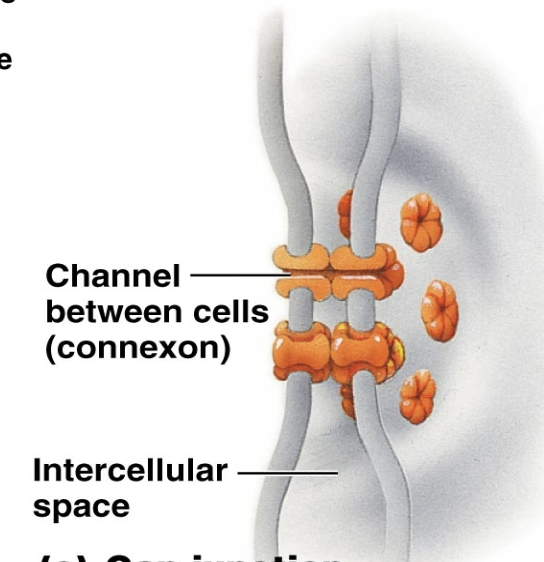
gap junctions
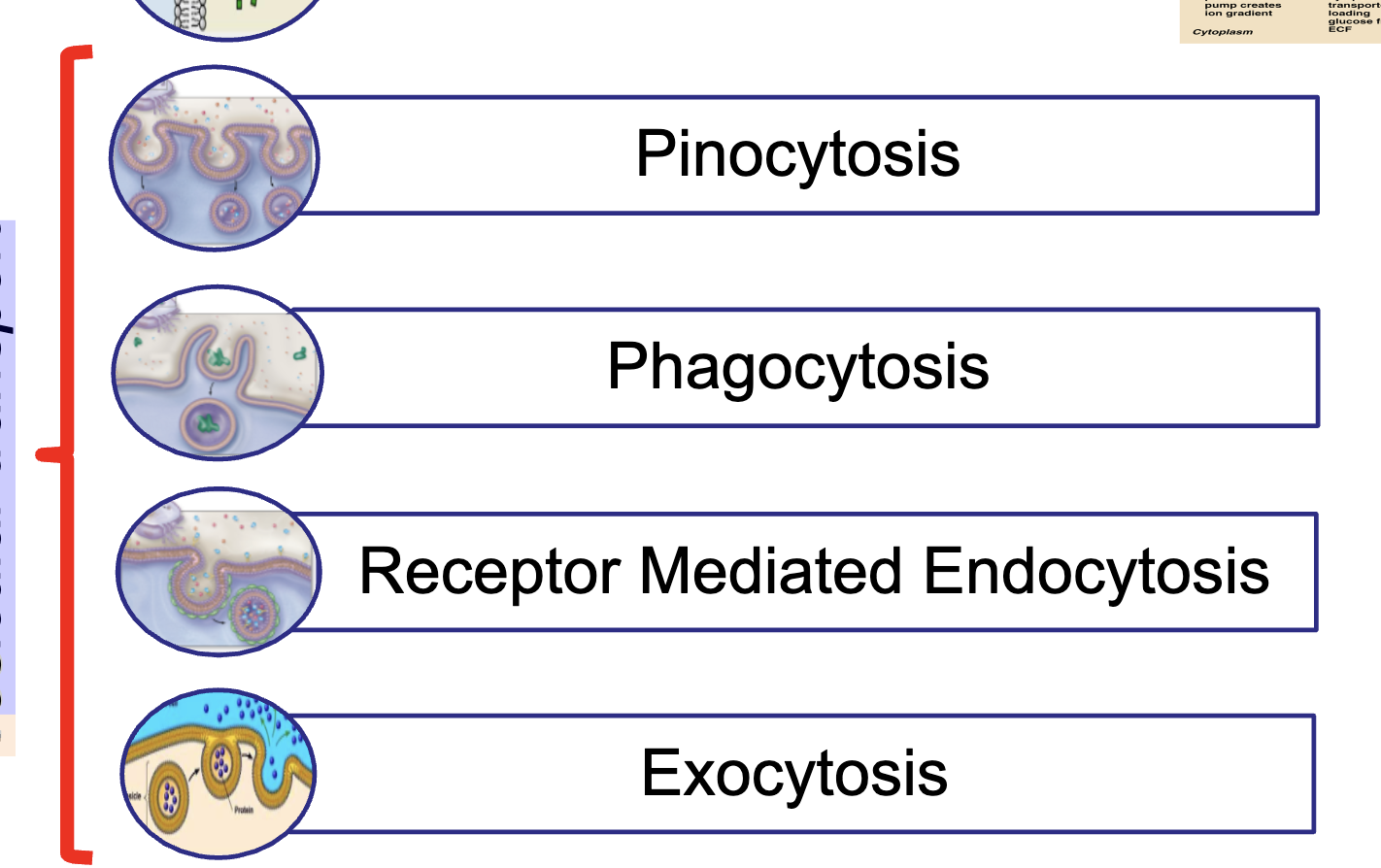
Vesicular transport
Facilitaed diffusion
Polar, Channels & Carriers
Energy source: Chemical gradient
Example: Movement of glucose into cells
Simple diffusion
Energy source: Chemical gradient
Example: Movement of O2 through membrane
Channels & Carriers
Channel proteins and carrier proteins are both transmembrane proteins that move substances across cell membranes