Spinal Cord and Brainstem organization
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
segment
a cross section of the SC giving rise to a spinal nerve on each side
where do dorsal rootlets enter the SC
in the posterolateral sulcus on either side of the posterior surface of the SC
what do dorsal rootlets merge into
dorsal roots (sensory)
dorsal root ganglion (DRG)
collection of cell bodies of sensory nerves entering the SC
DRG location
just proximal to where the spinal nerve begins
ventral rootlets location
exit SC from the anterolateral sulcus on each side of the anterior surface of the SC
what do ventral rootlets merge into
ventral roots (motor)
what joins to form a spinal nerve
a dorsal and a ventral root
what nkind of nerves are spinal nerves
mixed (carry sensory and motor fibers)
how many segments are there in the human SC
31
how many cervical vertebrae
7
what many thoracic vertebrae
12
how many lumbar vertebrae
5
how many sacral vertebrae
5 (fused in adulthood)
how many coccygeal vertebrae
about 4 (fused in adulthood)
how many pairs of cervical spinal nerves
8
how many pairs of thoracic spinal nerves
12
how many pair of lumbar spinal nerves
5
how many pairs of sacral spinal nerves
5
how many pairs of coccygeal spinal nerves
1
groups of functionally or structurally related cell bodies in the CNS
nucleus
groups of functionally or structurally related cell bodies in the PNS
ganglion
groiups of parallel axons in the CNS
tracts
groups of parallel axons in the PNS
nerve
groups of several parallel tracts in the CNS
funiculus
group of axons connecting one side of the brain with the other
commissure
groups of functionally related cells that form a layer
layer, stratum
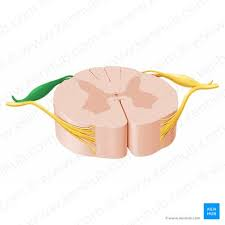
spinal nerve
dermatome
the area of skin innervated by a single spinal cord segment
C2 dermatome
back of head
T4 dermatome
nipple line
T10 dermatome
umbilicus
S5 dermatome
anal area
myotome def
group of muscles innervated by a single spinal cord segment
C5 myotome
elbow flexion
C6 myotome
wrist extension
C7 myotome
elbow extension
C8 myotome
finger flexion
T1 myotome
pinky abduction
L2 myotome
hip flexion
L3 myotome
knee extension
L4 myotome
ankle dorsiflexion
L5 myotome
long toe extension
S1 myotome
ankle plantarflexion
what does the cervical enlargement give rise to
spinal nerves for upper extremities
what does the lumbar enlargement give rise to
spinal nerves for lower extremities
conus medullaris
cone-shaped caudal end of SC located around vertebral level L1-L2
in the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral regions, where do spinal nerves exit
just below the vertebra of the same name
where do spinal nerves exit in the cervical region
just above the vertebra of the same name
where does the 8th spinal nerve exit
just aboce the 1st throacic vertebra
how do dorsal and ventral roots compensate for spinal nerves exiting at their respective interverebral foramina
become progressively longer proceeding from cervical to sacral levels
lumbar cistern location
enlarged subarachnoid space from end of SC at vertebral level L1-2 to end of dural sheath at vertebral level S2
what is the lumbar cistern filled with
CSF and cauda equina
clinical significance of lumbar cistern
safe for lumbar punctures
3 layers of meninges that cover and protect the SC
dura
arachnoid
pia mater
denticulate ligaments
lateral extensions f pia mater that span to arachnoid and then to the dura and help to suspend and laterally anchor SC
filum terminale
inferior extension of pia mater at conus medullaries aht is anchored caudally to the coccyx
spinal segment
cross-sectional area of SC supplied by a pair of spinal nerves
what does each spinal segment consist of
gray and white matter
gray matter of SC
central portion of SC; H shaped and can be divided into horns
whtie matter of SC
external portion of SC that surrounds gray matter; can be divided into funiculi, or columns
image 1
image 2
posterior intermediate sulcus
where in theSC is the posterior intermediate sulcus found
only at C and upper T levels
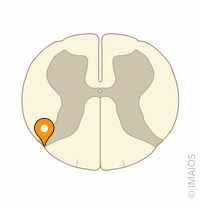
sulcus
posterolateral sulcus
image 3
central canal
anterior median fissure
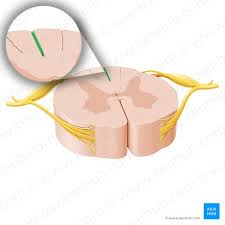
posterior median sulcus
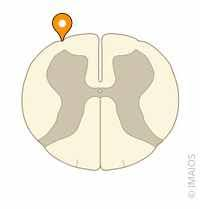
anterolateral sulcus
where do dorsal rootlets enter
posterolateral sulcus
where do ventral rootlets exit
anterolateral sulcus
central canal of the SC
extension of central canla from medulla; filled with CSF
what does the posterior horn receive
sensory input from dorsal roots
what does the posterior horn contain
mostly interneurons and projection neurons
2 primary parts of posterior horn
substantia gelatinosa
body
substantia gelatinosa of posterior horn
caps posterior horn; deals mostly with pain and temp information
body of posterior horn function
deals mostly with somatic and visceral sensory info
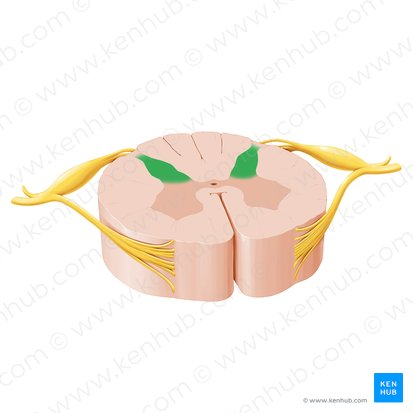
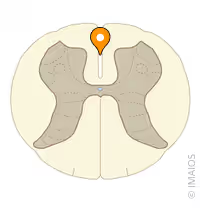
posterior horn
image 4
anterior horn
what does the anterior horn contain
cell bodies of motor neurons that supply skeletal muscle
two names for motor neurons that supply skeletal muscle
aplha or lower motor neurons
what type of lower motor neurons are more medial
clusters that innervate axial muscles
what type of lower motor neurons are more lateral
muscles of the limbs
location of intermediate gray matter
lies between anterior and posterior horns
consequence of location of intermediate gray matter
contains features of both anterior and posterior horns; also contains spinal preganglionic autonomic neurons
location of intermediolateral cell column
present in T1-L3
what does the intermediolateral cell column contain
sympathhetic nervous system neurons in teh pointy lateral horn
how do axons leave in teh intermediolater cell column
through ventral roots
what is the sacral parasympathetic nucleus
intermediate gray matter of S2-S4 with no distinctlateral horn
what does the sacral parasympathetic nucleus cotain
parasympathetic neuorns
how do axons leave the sacral parasympathetic nucleus
through ventral roots
what pathways does spinal white matter contain
both ascending and descending pathways
tracts def
bundles of axons that have the same origin, course, and termination
what is funiculus
collection of tracts
3 main funiculi of each half of the SC
posterior funiculus
lateral funiculus
anterior funiculus
where is the posterior funiculus located
between posterior median sulcus and posterior horn
two fiber tracts of posterior funiculus
fasciculus gracilis
fasciculus cuneatus
fasciculus gracilis relative location
more medial
fasciculus cuneatus relative location
more laterally in part of SC