DNA structure and replication
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Which bases are purines?
A & G
Which bases are pyramidines?
C, T, U
what is a purine structure
nitrogen 9- joins to another molecue - pic
what is a pyrimidine structure
nitrogen 1 - the region that connects to other parts
pic
What is a nucleoside?
Base + sugar
What is a nucleotide made of ?
nitrogenous base
pentoose sugar
1/2/3 phosphates
. What is a monophosphate nucleotide
Base + sugar + phosphate
what are 2 types of sugar in nuceloutides
ribose ( RNA)
deoxyribose (DNA)
what is the structure of ribose and deoxyribose

what is the structure of phosphate
pink
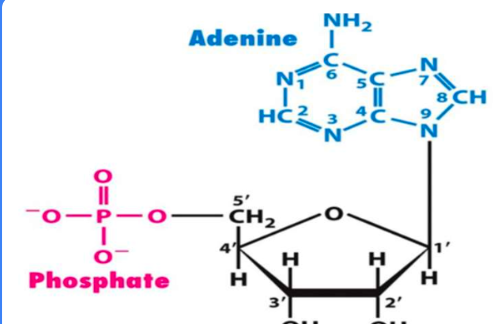
what are the bonds ( where known) and between what that makes the nucleotides
base + carbon 1 of sugar - join with glycosidic bond
phosphate + carbon 5 of sugar - phosphorylated with kinase
2 more phosphate join
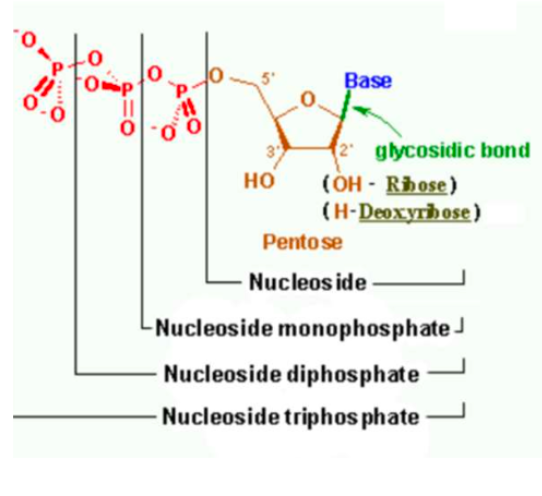
Which group forms the 5' end of a nucleotide and which group forms a 3' end?
5' - phosphate group
3' - hydroxyl group
how does Nucleic acid strands have polarity
its polarity in direction
5' is when carbon 5 of the last sugar on one side is bound to phosphate
3' is when carbon 3 of the last sugar on the other side is bound ot a hydroxyl group
Which bases bind to which via hydrogen bonding
A-T
C-G
How many H-bonds are there between A-T and C-G?
A-T: 2
C-G: 3
what direction is the hydrogen bond betwee the bases in comparision to the helix
perpindicular
What does anti-parallel binding of DNA mean
The 3' end of one strand is bound to the 5' end of the other.
What are the two grooves in the DNA double helix called
Major and minor groove
explain the structure of DNA overall
its made of repeating nucleotides
the nucleotides are joined with 5'3' phosphodiester bonds
hydrogen bonds between the bases makes a double strand
they make an antiparallel spin 5' and 3' are paired
the 2 chains coil making a double helix
is DNA a right or left helix
right - twist clockwise
how many nucleotides per turn on DNA
10
how long is one turn and whats the helix diameter
length: 3.4nm
diameter: 2nm
describe linear DNA and where is it found
double stranded
long
bound to protein to make chromatin
found in eukaryotes chromosomes
in nucleas
describe circular DNA and where is it found
single strand
super coiled ( the helix coils again)
in prokaryotes, makes nucleotied can have plasmids
found in plant chloroplast
eukaryotes mitchondria
what are chromosomes
chromotin- DNA and protein (histone) is packed into nuclosome then condensed into chormosomes, done by supercoiling
how and when was DNA discovered
between 1944 and 1952
expirements with bacteria and virus showign DNA was genetic material
what 2 sets of data where used to find out the structure of DNA
xray diffraction
base composition analysis of hydrolysed DNA samples
what is X ray diffraction
firing x rays on purified crystalised DNA showing its a helix structre
what is chargaffs rule
studying the base compotision in DNA
A - T and C- G had similar compositions in all organisms
What is the genome?
The entire set of genes in the chromosomes of an organism.
what are the 2 ways genetic info can be transfered
inheritence - passing gentic info from 1 cell to another through DNA replication DNA-DNA
expression - expressing the gentic info through protein synthesis DNA- RNA
highly conserved meaning
sequences for gene has few mutations between species as major change is harmful
What is the name of the temperature at which one half of the helical structure is lost?
Melting temperature (Tm)
Where does DNA replication take place?
Specialised regions of the nucleus with a cluster of proteins
overview of DNA replication
hydrogen bonds break the Double Strand unwinds
2 templates made
free nucleotides do complpementary base pairing
it twist to a helix
semi conservitive as it has one parental and one daughter strand
Why is the DNA double helix only unzipped a little bit at a time during DNA replication?
To prevent mutations
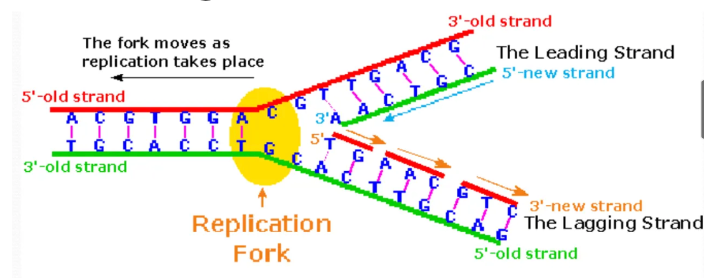
what is a replication fork
the point on the double helix where the new strands are being formed, there are 2 sides to the strand

Which direction does DNA synthesis occur?
5' to 3' end
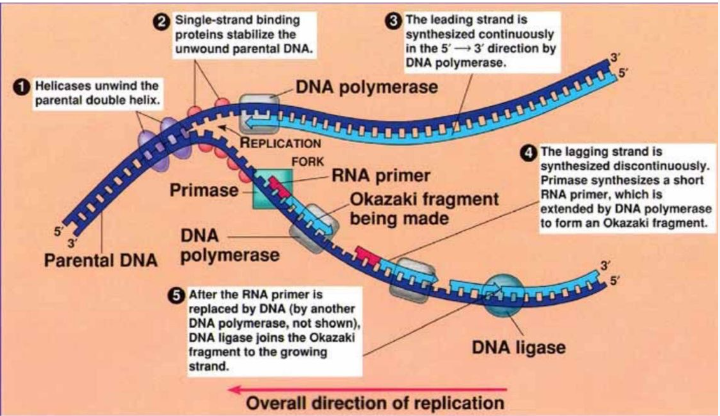
What does helicase do?
Unwinds DNA into 2 strands by breaking hydrogen bonds between the bases
rWhat does topoisomerase do?
Releases supercoils in DNA - when the DNA double helix spins on itself
What are single strand binding proteins? (SSBs)
Tetramers ( protein made of 4 subunits) that bind to single stranded DNA so it cannot bind to another strand and remakign the helix during DNA replication
What is primase?
An RNA polymerase that makes short RNA primers.
What is a primer?
A short nucleic acid sequence that provides a starting point for DNA synthesis.
can DNA polymerease start its own strand
no, it needs primers
What does DNA polymerase do
Synthesises DNA by adding nucleotides to sugar-phosphate backbone. It has proof-reading ability.
What does the sliding clamp do?
It helps DNA polymerase hold onto the strand its copying.
What does RNaseH do?
Removes RNA primers after the DNA polymerisation is finished extending the fragment
What does DNA ligase do?
Forms phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides to form a long strand.
Which strand in the replication fork is replicated continuously?
Leading strand
Which strand in the replication fork is replicated discontinuously
Lagging strand
What are the names of the short fragments produced in the lagging strand during DNA replication
Okazaki fragments
how are the 2 chains on the replication fork replicate simultanously
dna polymerease works from 5'-3' but one strand is 3' to 5' direction
so there is discountious replication in the lagging strand with fragmented nucleotides
pic
what happens to the gaps between the okazaki fragemnts
each okazaki fragemnt has primers which are removed
free nucleotides join
DNA ligase makes phosphodiester bonds joining them
how mnay mistakes does DNA polymerease III make
1 mistake for every million nucleotides
how is a new daughter strand made after the template strand is exposed
Single Strand Binding proteins (SSB) bind to the single stranded DNA to stop the two strands from annealing
the enzyme primase, synthesis RNA primers that bind to the strand
DNA polymerease adds complementary nucleoties (dNTPS) startign from 5'-3' makign the lagging and leading strands
1 pyrophosphate ( 2 phosphates) is released per dNTPS that joined
DNA polymerease uses exonuclease activity to proof reading frm 3' to 5' to make sure its correct nucleotides
after DNA synthesis the RNA is removed
what are telomeres
Telomeres: tandem repeats (GGGTTA in humans) at chromosome ends
Functions:
Prevent chromosome fusion
Solve DNA replication end problem → telomerase adds repeats so important DNA isn’t lost during division
What is random assortment of maternal and paternal chromosomes?
During metaphase there is random assortment if their chromosomes which help with genetic variation
simple explination of the stages of the cell cycle
G0- when the cell isnt dividing
G1- growth, cell gets ready to synthesise DNA
S- DNA replication, its synthesised
G2- contunued growth, proteins made for mitosis
M - mitosis
summary
all definitions
primase: RNA polymerase that makes short RNA primers.melting temperature: temp when hald of the helican structure is lost
SSB: stop the 2 strands from annealing
RNA primers: bind to start of dna so that dna polymerease can work
DNA polymerase: add the nuclotides, uses exonucleas activity to proof read
dNTPS: nucleotides
okazaki fragment: short pieces of nucleotides on the lagging strand
DNA ligase: make phsophodiester bonds between nucleotides
helicase: unzips the 2 strands
RNaseH: remove RNA primers
slding clamp: helos dna polymerease hold onot the strand its copying
topisomerase: make a supercoil
nucleotide: sugar phsophate base
nucleoside: sugar base