To prepare a sample of soap by base hydrolysis/saponification
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Theory
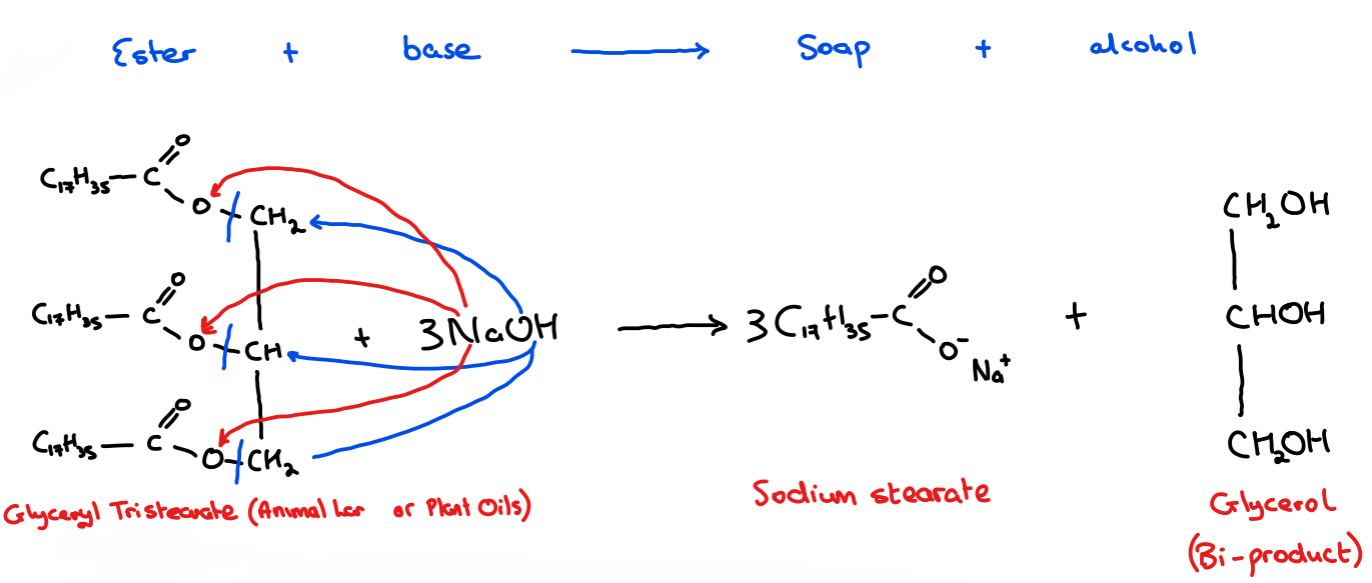
• Fats and oils found in animals and plants are naturally occurring esters.
• They can be reacted and refluxed with a base to produce a soap and alcohol
• Known as base hydrolysis/saponification
Example: Glyceryl tristearate, is an ester typically found in animal fats - if it is reacted and refluxed with the base sodium hydroxide, the soap sodium stearate and the alcohol glycerol are produced
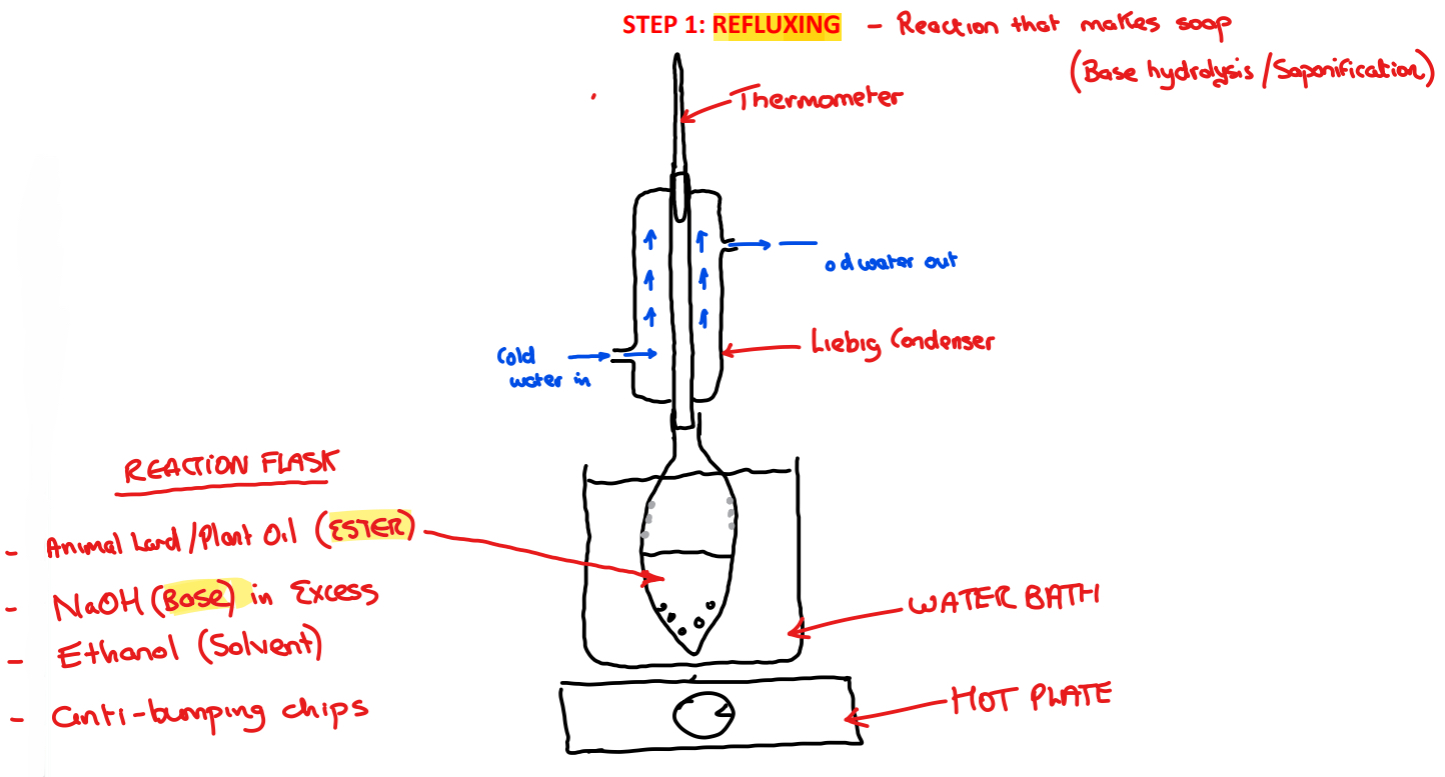
Procedure: step 1!
➢ Lard/plant oil is placed into the reaction flask, pellets of sodium hydroxide, ethanol and some anti-bumping chips are added
➢ The reactants are heated in the reaction flask using a hot plate and water bath and refluxed using a Liebig condenser for ̴30 minutes
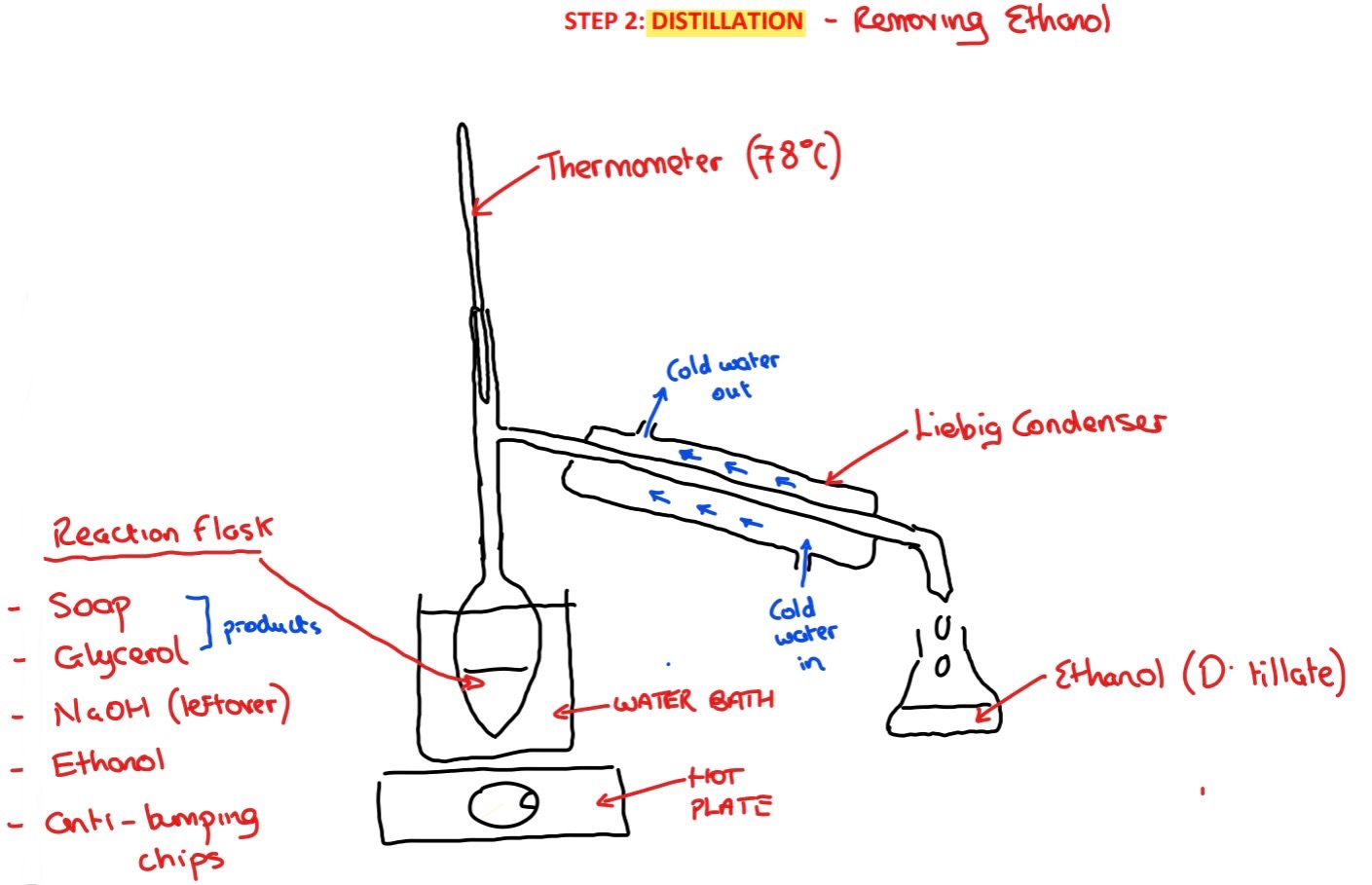
Procedure: step 2/
➢ The apparatus is rearranged to a distillation and the flask is heated using a hot plate and water bath to 78˚C to allow most of the ethanol to be distilled off
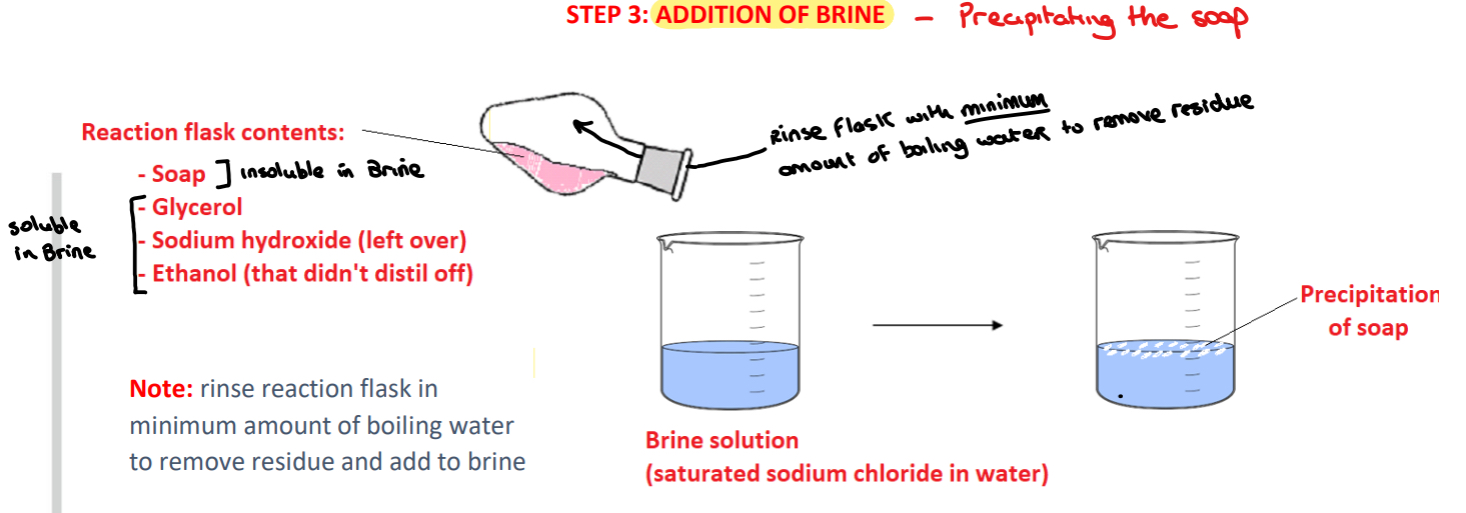
Procedure: step 3?
➢ The reaction mixture is poured from the hot reaction flask into a beaker of brine solution, rinsing the reaction flask with the minimum amount of boiling water to remove any residue remaining
➢ A solid material (soap) is observed precipitating out of solution when the mixture is added to the brine with the glycerol, ethanol and excess sodium hydroxide remaining dissolved in the brine
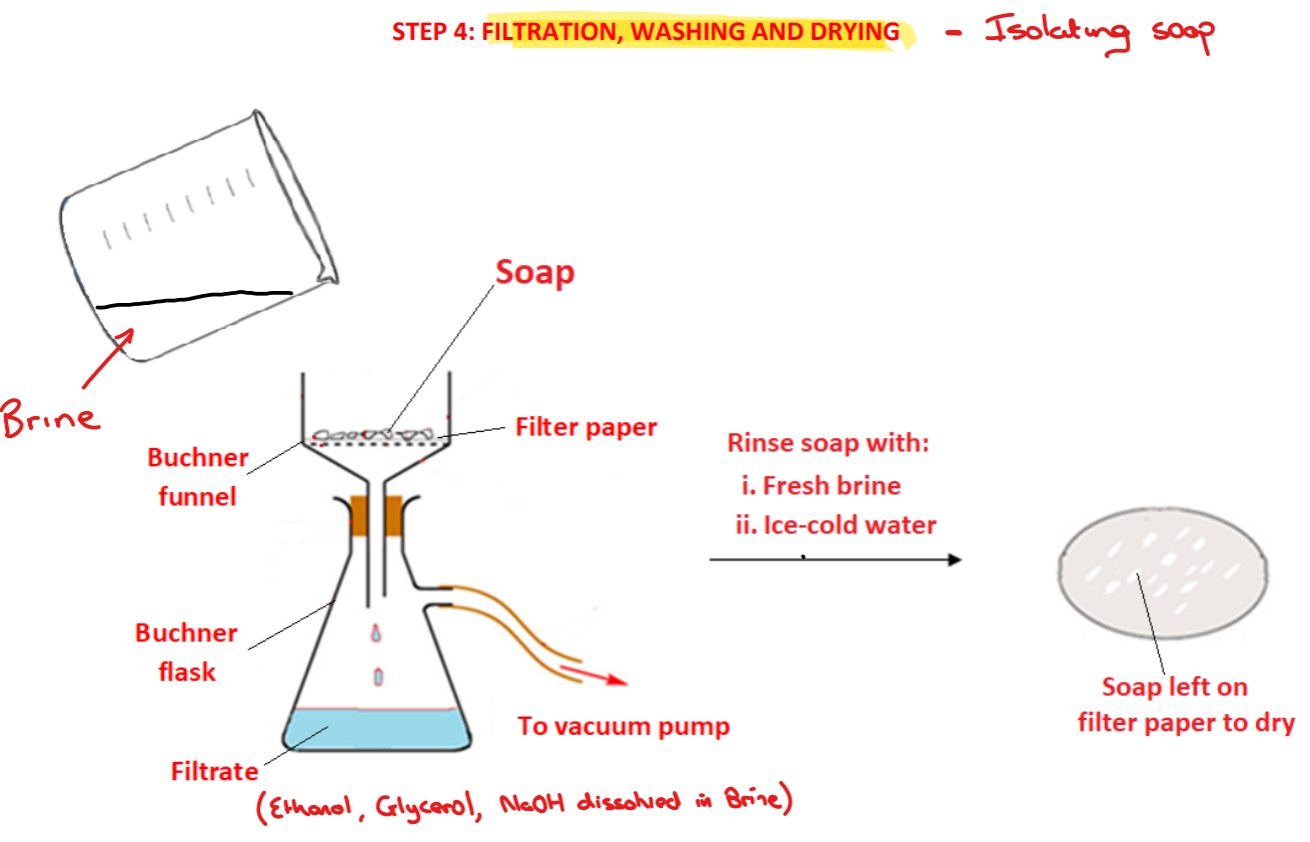
Procedure: step 4%
➢ The soap is filtered using vacuum/suction filtration using filter paper, a Buchner funnel and a Buncher flask – the brine solution containing glycerol, ethanol and excess sodium hydroxide will pass through as the filtrate
➢ The soap is washed with fresh brine followed by ice cold water to remove any sodium hydroxide that may be still present
➢ The soap is left to air dry on the filter paper in a warm place or placed in a desiccator
Why is oil or lard used in this experiment?!
Oils or lard contain naturally occurring esters – hydrolysing these esters with a base will produce a soap
Why is sodium hydroxide added to the reaction flask?!
Hydrolysing an ester with a base will produce a soap – sodium hydroxide is the base used
Note: Potassium hydroxide could be used as the base
What is the difference between soap made with sodium hydroxide and soap made with potassium hydroxide?!
Soaps made with potassium hydroxide are milder than soaps made with sodium hydroxide
Why is excess base (sodium hydroxide) used?!
The base is used in excess to ensure ALL of the ester (lard/oil) reacts and is converted to soap – maximises the yield of soap obtained – the ester is the limiting reagent
Why is ethanol added to the reaction flask?!
Ethanol acts as a solvent for the oil or lard
Why are anti-bumping chips added to the reaction flask?!
Anti-bumping granules are added to allow boiling to take place more smoothly
Describe how the ester and base are reacted in this experiment!
The ester and base (oil/lard + sodium hydroxide) and the ethanol solvent are heated under reflux for 30 minutes - heated until they vapourised and are then cooled back to a liquid in the Liebig condenser and fall back into the reaction flask so they can completely react
Why is the reaction mixture refluxed?!*
1. Allows the reactants time to react to completion
2. Ensures no loss of the ethanol solvent as it is continuously condensed again
What type of reaction occurs during the reflux process?!
Saponification/Base hydrolysis
As the reaction proceeds, a coating is observed on the walls of the reaction flask. What is this coating?!
1. Soap that has formed
2. Lard/oil that has not been hydrolysed
Why is the reaction flask swirled from time to time under reflux?!
Swirling the reaction flask washes the coating from the walls of the flask back into the reaction mixture
Give a bi-product of the reflux reaction and give a use for this bi-product!
Bi-product: Glycerol
Use: Manufacture the explosive nitro-glycerine
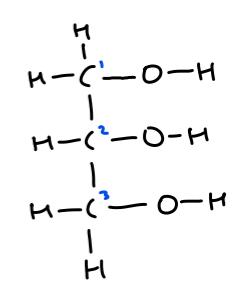
Give the IUPAC systematic name for this bi-product and draw its structural formula!
Propane -1,2,3 triol
Why is the ethanol then distilled off after reflux?/
Distilling the ethanol off makes it easier to isolate the soap and maximises its yield – some soap would remain dissolved in the ethanol and it would not be precipitated
What is a suitable heating method for first refluxing the reaction mixture and then distilling off the ethanol. Justify the suitability of this heating method/
• A hot plate and a water bath are used for the reflux and distillation procedures
• Allows for gentle heating where the temperature can be easily controlled
What is brine? Why is the reaction mixture added to a saturated brine solution??
• Brine is a saturated solution of sodium chloride (salt) in water.
• The soap does not dissolve in salt solution and is precipitated out of solution while other substances (glycerol, sodium hydroxide, ethanol) remain dissolved
Why is a minimum amount of hot water used to remove residue from the flask??
Using a minimum amount of hot water maximises the amount of soap that will be precipitated.
Why is the reaction mixture then filtered?% *
• The reaction mixture is filtered to isolate the insoluble soap in the filter paper
• The glycerol, ethanol, sodium hydroxide will pass through dissolved in the brine solution into the Buchner flask in the filtrate
Why is vacuum filtration performed in preference to gravity filtration?%
a) To speed up the filtration process – faster than using regular filter paper
b) To help dry the soap
What two substances is the soap washed with after the filtration and why?%
i. Fresh salt solution (brine) - dissolves and removes any sodium hydroxide that may be present with the soap – sodium hydroxide causes burns
ii. Ice-cold water – To wash off the brine. The water is ice-cold to avoid any soap dissolving maximising its yield
How is the soap left to dry overnight?%
The soap is placed on filter paper and left to air dry in a warm place
Outline a test that is performed on the prepared soap%
The soap is added to a test tube of de-ionised water (soft water) and shaken
Result: The presence of a lather proves that the substance is soap
Note: If the soap is added to a hard water sample, it will be more difficult to form a lather
Example: river water
Outline two safety precautions taken in this experiment%
1) Wear googles and gloves – sodium hydroxide causes burns
2) Take care when dealing with hot flasks during the reflux and distillation stages – keep them in a water bath to prevent overheating
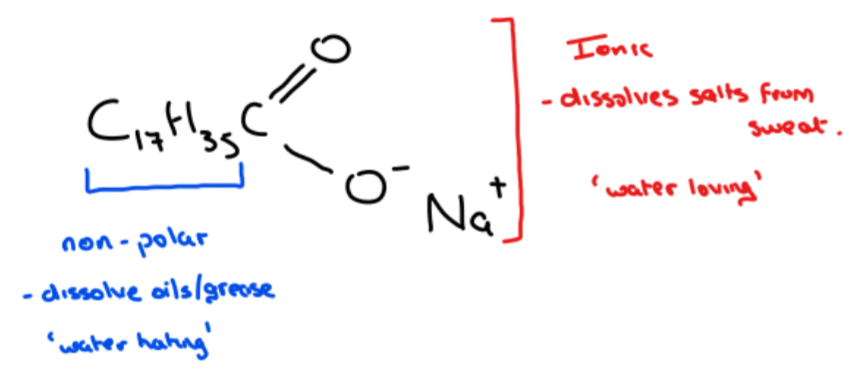
Explain with reference to its structure, how a soap such as sodium stearate can dissolve both oils and salts in sweat from the skin/Explain why one end of a soap molecule is described as water loving (hydrophilic) and one end is described as water hating (hydrophobic)%
• Soap consists of a non-polar hydrocarbon portion (C17H35) that dissolves non-polar substances such as oils and grease – water hating part
• Soap also consists of an ionic portion ( - COO – Na+) that dissolves salts from sweats and causes the soap to dissolve in water – water loving part
Example: Sodium stearate
Soap can be produced using vegetable and animal fats. What is the principal chemical
difference between vegetable and animal fats?%
• Vegetable fats are unsaturated (contain double bonds between some of the carbons)
• Animal fats are saturated (contain only single bonds between carbons)