AP World History Study Guide Unit 1-4
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Will continue updating (2024) You DON'T need to memorize everything, you only need to understand the content and context of each time period.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
How does the growth of long-distance trade appear?
interactions between new states and collapsing of Greek/Roman civilization
State
A territory politically organized under one government Ex) China, Japan, US
Religious Mysticism
focusing on mystical experience
Prayer, meditation, closer to their divine being
Buddhism
India, China, SE Asia, Japan
Siddhartha Gautama (Nepal, 563-483 BCE)
Rejected wealth & world possessions
all life is suffering from desire, can be freed from desire by following this path
Split into 2 versions
Impact: rejects caste system - appealed to those of lower rank
India: reabsorbed in Hinduism
China, Japan, Southeast Asia: Buddhism continued to thrive
Further: spread via trade routes
Theravada Buddhism
meditation, simplicity, Nirvana
Mahayana Buddhism
Spiritual comfort with greater spread
great ritual
Christianity
Jesus of Nazareth
teachings of devotion to God and love for others
was crucified
Believe Jesus is the Son of God - forgiveness of sins, everlasting life is achievable through him
World was created by God, but world has fallen from God
Believers should seek God and care for him and others
The final source of truth
Impact: compassion, grace through faith appealed to lower classes and women
Became most influential religion in Mediterranean basin by 3rd century
Became official religion of Roman Empire, then branching north and west
Connection with Roman Empire had profound impact on global culture
Confucianism
Founded by Confucius, educator and political advisor - thoughts and sayings
Deals with how to restore political and social order, not with philosophical or religious topics
5 fundamental relations build society and make it orderly - (1) ruler and subject, (2)
parent and child, (3) husband and wife, (4) older sibling and younger sibling. (5) friend and friend
Impact: Compatible with other religions, causing it to flourish Led to distinctive Chinese culture of tight-knit communities Stayed within Chinese culture
Hinduism
India
Belief in one supreme force called Brahma who created everything - gods are
manifestations of Brahma (Vishnu = preserver, Shiva = destroyer)
Goal of believer is to merge with Brahma - believe it takes multiple lives to
accomplish and believers live to determine who they will be in their next life
Following the dharma (rules and obligations of your caste) will move you towards
Brahma - moksha is highest stake of being (internal peace and release of soul)
No sacred text - Vedas and Upanishads guide Hindus
Impact:
Religion and social caste system, which has prevented global acceptance of religion
Recently, Hindus are rebelling caste system
Spawned Buddhism
Islam
Cultures: caliphates (Islamic kingdoms), North Africa, central Asia, Europe
7th century - Muslims are the believers Allah presented words through prophet Muhammad, whose words were recorded in the Qur’an
Salvation is won through submission to God - 5 Pillars of Islam: (1) confession, (2) prayer 5 times a day, (3) charity, (4) fasting during Ramadan, (5) pilgrimage to Mecca
2 groups, Shia and Sunni, who disagreed who should succeed Muhammad
Sunni=
Abu Bakr
Caliph
Follows the Sunni Example
Shia=
Ali (Muhammad’s Nephew
Caliph = should be blood related
Twelve Shism
Imams
Judaism
God selected a group of holy people who should follow his laws and worship them
Unique relationship with God
World is for them to enjoy, free will - destiny of world is paradise
Hebrew Bible - Torah, miracles, laws, historical chronicles, poetry, prophecies
First of major monotheistic faiths
Sufism
Form of Islam that incorporated Hindu practices (meditation/yoga)
Abbasid Dynasty: Golden Age to Remember
Islamic Empire from 750-1258 CE - early mid-9th century golden age
Capital in Baghdad (modern-day Iraq)
Centre for arts and sciences - mathematics (Nasir al-Din al Tusi), medicine, writings (House of Wisdom library)
Built around trade - used receipt and bill system
Decline of Islamic Caliphates: Internal Rivalries and Mongol Invasions
Challenged by revolt of enslaved Turkish warriors, new Shia dynasty in Iran, Seljuk Turk
Sunni group, Persians, Europeans, Byzantines, and most importantly Mongols
Mongols overtook and destroyed Baghdad in 1258
Ottoman Turks would later reunite Egypt, Syria, and Arabia in new Islamic state until 1918
Mamluks: Egyptian group that defeated Mongols in Nazareth, helping preserve Islam in Near East
Christian non-Arab (Turkish) boys taken at a young age, trained to become govt officials, and converted to Islam
Middle Ages
fall of Rome before Renaissance - complicated time
Eastern Roman Empire became Byzantine Empire
Western Europe: collapsed entirely - Christianity remained strong
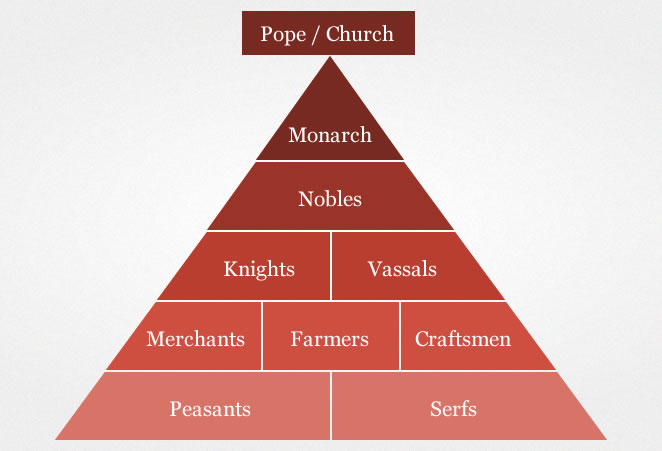
Feudalism
European hierarchy social system of Middle Ages
1) King:
power over whole kingdom
2) Nobles:
power over sections of kingdom
in exchange for loyalty to King & military service
3) Vassals:
lesser lords with sections of Noble land who could divide it further
estates were called fiefs or manors (self-sufficient)
4) Peasants/serfs:
worked the land
Had few rights or freedoms outside of manor
Skilled in trades
led to middle class emergence of craftsmen and merchants
Niccolo Machiavelli
wrote about how a ruler should maintain power - The Prince 1513
three-field system
3 fields for fall & spring, and 1 empty one for replenishing
Code of Chivalry
condemned betrayal and promoted mutual respect
Male dominated: women could not own land and land was passed down to eldest son (primogeniture), their education was limited to domestic skills
Germany (emergence of nation-states)
reigning family of emperorship died out, entering a period of interregnum (time between kings)
merchants and tradespeople became more powerful
England (emergence of nation-states)
English nobles rebelled against King John and forced him to sign the Magna Carta
reinstated the nobles, laid foundation for Parliament
Richard the Lion-hearted
Later divided into House of Lords (nobles and clergy - legal issues) and House of Commons (knights and wealth burghers - trade and taxation)
France (emergence of nation-states)
12th century, England began to occupy many parts of France which spurred revolts
Joan of Arc fought back English out of Orleans
Hundred Years’ War (1337-1453): unified France, leading to England’s withdrawal
Spain (emergence of nation-states)
Queen Isabella of Castile and Ferdinand of Aragon married to unite Spain in a single monarchy and forced all residents to convert to Christianity - Spanish Inquisition
Russia (emergence of nation-states)
taken over by Tartars (group of eastern Mongols) under Genghis Kahn in 1242 until
Russian prince Ivan III expanded his power in 1400s and became czar - Ivan the Terrible
became a ruthless ruler utilizing secret police in 1500s
Song Dynasty (960-1279)
Confucianism justified subordination of women - foot binding: women’s feet bound after
birth to keep them small
Neo-Confucianism: Buddhist ideas about soul, filial piety, maintenance of proper roles, loyalty to superiors
Champa Rice - caused an increase of population due to excess food supply

Ming Dynasty (1368-1644)
Religion: influenced by Nestorianism, Manichaeism, Zoroastrianism, Islam, and especially
Buddhism in two of its forms
Mahayana: peaceful and quiet existence apart from worldly values
Chan or Zen: meditation and appreciation of beauty
Feudal Japan (1192)
1. Emperor
2. Shogun (chief general)
3. Daimyo: owners of larger pieces of land, powerful samurai (like knights/lords)
Followed Code of Bushido
code of conduct - loyalty, courage, honour
4. Lesser samurai (like vassals)
5. Peasants and artisans
Women had little rights and esteem
Delhi Sultanate
Islamic invader kingdom in Delhi
Islam took over Northern India - clash between Islam monotheism and Hinduism polytheism
Islam rulership brought in colleges and farming improvements
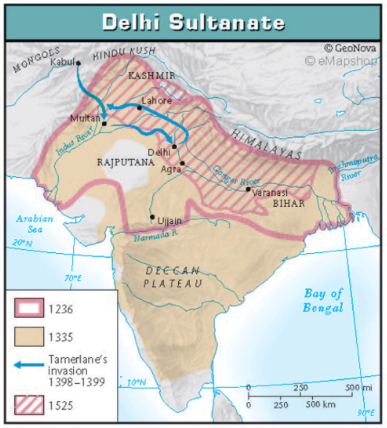
Rajput Kingdoms
several Hindu principalities that united to resist Muslim forces from 1191 until eventual takeover in 1527
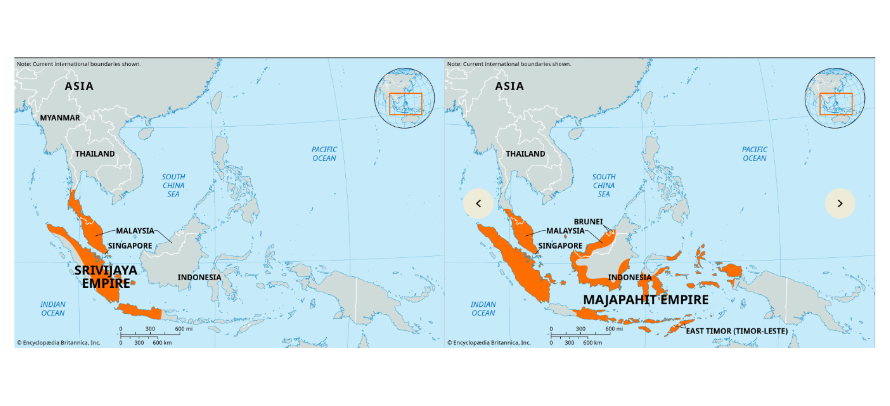
Srivijaya/Majahapit
trade empires that were made up of bureaucratic merchants (modern day indonesia)
Khmer Empire (9th-15th century)
Hindu Empire in modern day Cambodia, Laos, Thailand
Beliefs were carried through Indian Ocean trade network
Crafted the Angor Wat temple
Religion spread and established different states
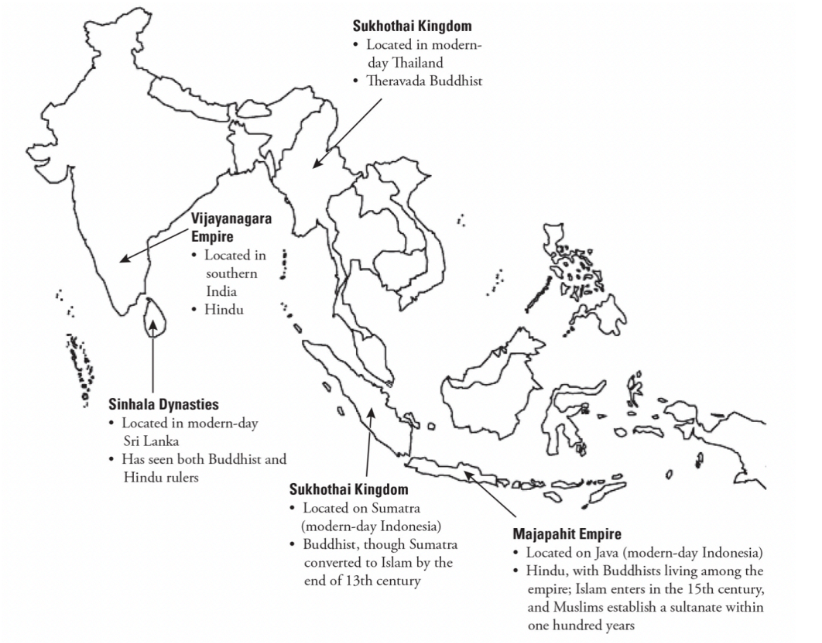
Vijayanagara Empire
formed from smaller Hindu Kingdoms to resist Islam
Bhakti Movement
Hinduism responding to monotheism (Islam brought belief in "one god" to India), more focused on individual Hindu Gods
Developments in Africa
Islamic Empire spread to North Africa in the 7th to 8th centuries - traveled through Sahara Desert and reached the wealthy sub-Saharan
An explosion of trade began
Hausa Kingdoms
off Niger River, series of state system kingdoms
Islam region, achieved economic stability and religious influence though long trade (salt and leather) - notably city of Kano
Political and economic downturn in 18th century due to internal wars
Aztecs
Arrived in Mexico in mid 1200s
Tenochtitlan: capital city (modern Mexico City)
Expansionist policy and professional, strict army
Empire of 12 million people with flourishing trade, many of people enslaved
Women were subordinate, but could inherit property
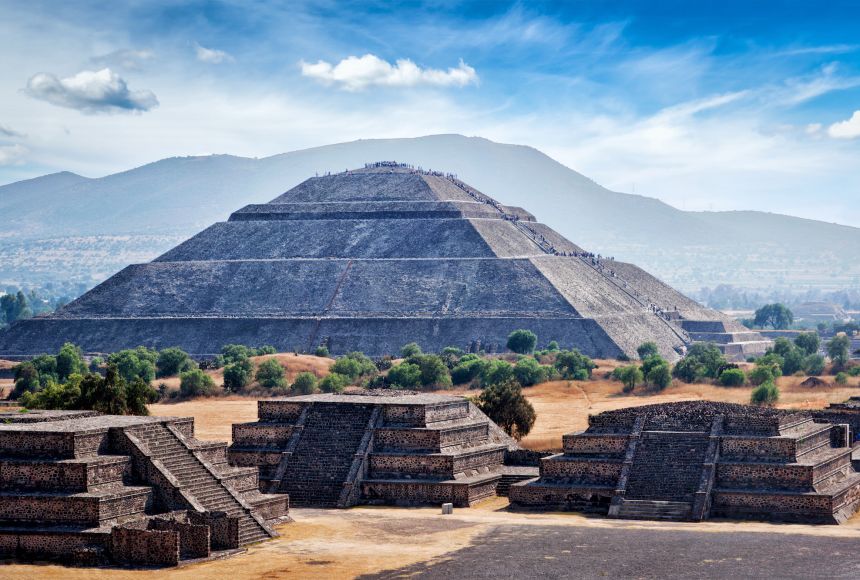

Inca
Andes Mountains in Peru
Expansionist - army, established bureaucracy, unified language, system of roads and tunnels
Many people were peasants
Capital of Cuzco had almost 300,000 people in late 1400s
Women were more important and could pass property to their daughters
Polytheistic religion with human sacrifice - Sun god was most important
People were mummified after death
Military was very important
Temple of the Sun and Machu Picchu architecture
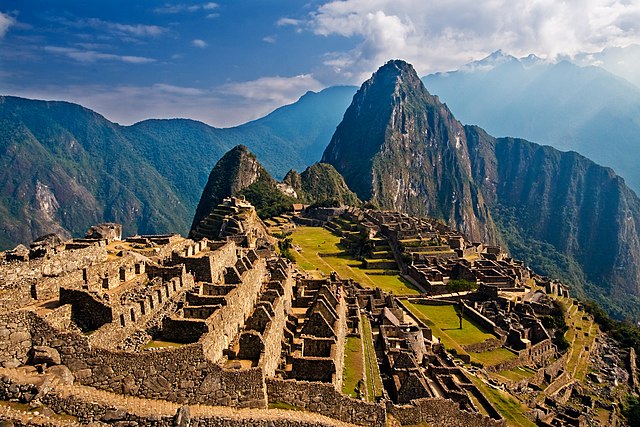

Mayan City-States and Mexica
used a "tribute system" to rule over other places that gave them payments in various forms
Cahokia
Mound-building civilization in N. America along the Mississippi River
Mesa Verde/Chaco Cultures
Southwestern tribes, predecessors of Hopi, Navajo, near 4 corners region of the US
Burghers
merchants emerging in towns that became politically powerful
Towns formed alliances
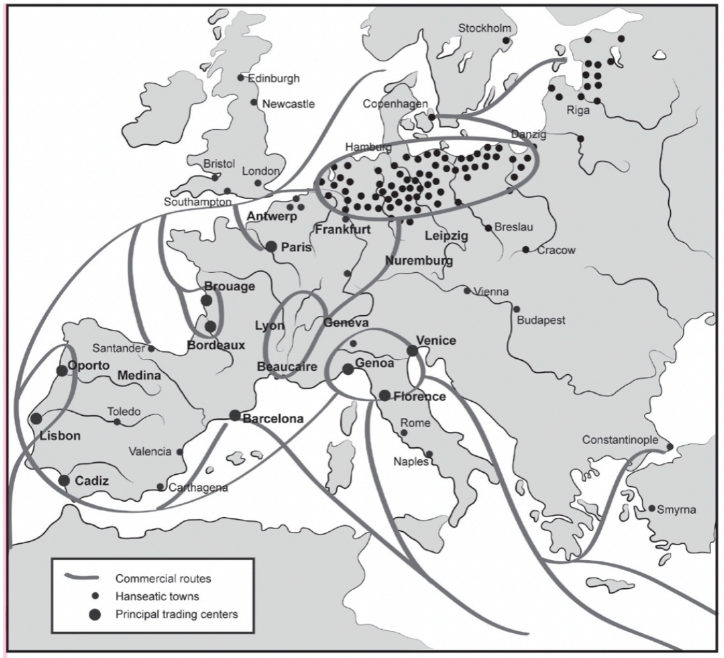
Hanseatic League (1358)
trade alliance though northern Europe to drive toward nationhood
increase social mobility and flexibility
Made up of over 100 cities
Created substantial middle class in northern Europe
Set precedent for large, European trading operations
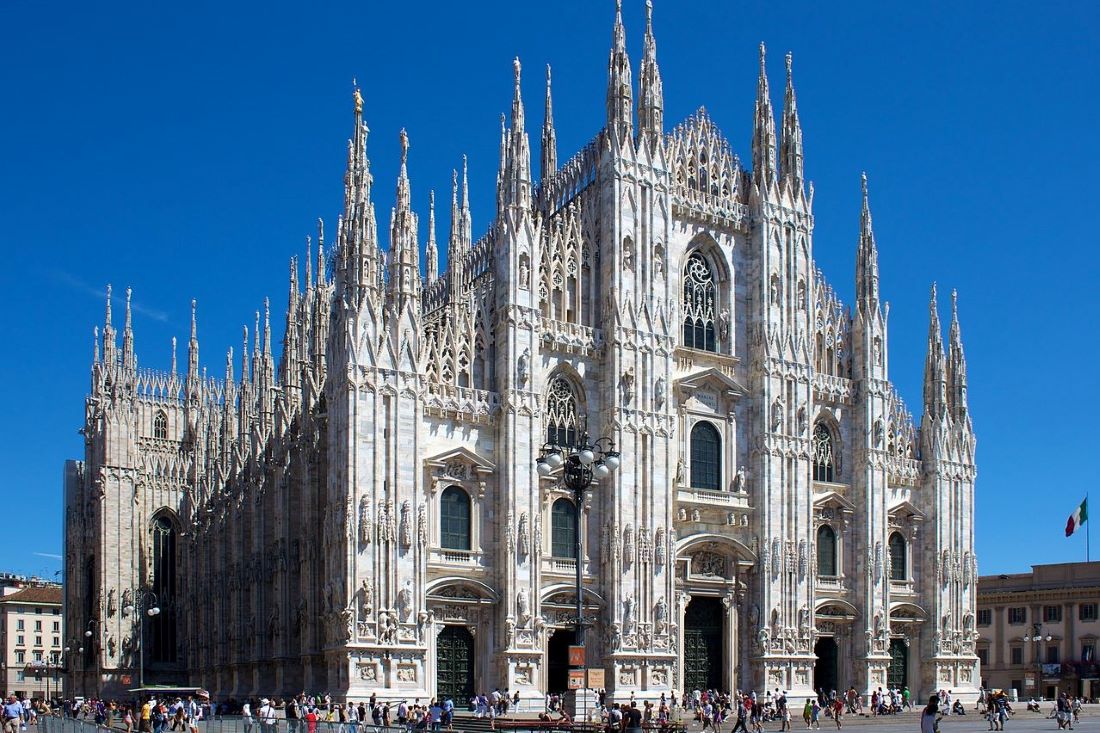
Romanesque to Gothic
especially reflected in cathedrals
Flying buttresses: tall windows and vaulted ceilings
Often had art and sculpture, music

Scholasticism
growth of education and knowledge
founding of universities for men; philosophy, law, medicine study; ideas of Muslims and Greeks
came in conflict with religion
Crusades (11-14th century)
military campaigns by European Christians to convert Muslims and non-Christians
combat religious questioning
Combat Heresies
religious practices/beliefs not conforming to traditional church doctrine
Pope Innocent III
issued strict decrees on church doctrine - frequently persecuted heretics and Jews
unsuccessful 4th crusade
Pope Gregory IX
Inquisition (formal interrogation and prosecution of perceived heretics with punishments like excommunication, torture, execution)
church often referred to as Universal Church or Church Militant
Thomas Aquinas (1225-1274)
Christian theologian who made advancements in Christian thought
faith and reason aren’t in conflict
Urbanization
Trade led to the growth of urban culture - cities usually were around trade routes
Silk Route cities were the most populous - Baghdad, Merv, Chang’an
Constantinople before 1400 and Paris and Italian city-states after 1400 were big European cities
Genghis Kahn
unified the tribes in Mongolia in the early 1200s to expand their authority over other societies
first invaded China in 1234
Mongol Empire
spanned from Pacific Ocean to Eastern Europe - spit into hordes after death of Genghis Kahn
ruthless warriors destroying cities but remained peaceful after settling into cities
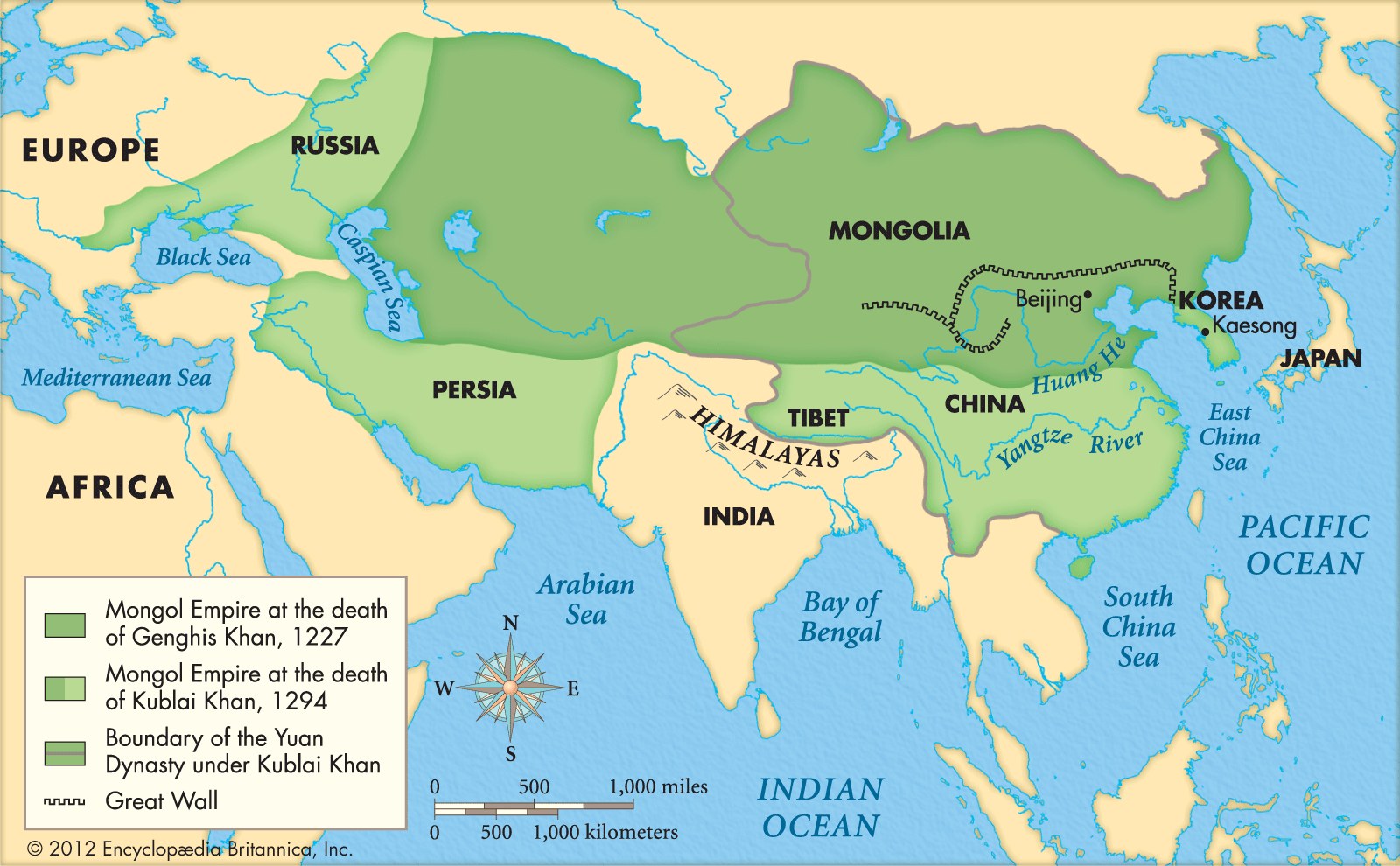
Golden Horde
conquered modern-day Russia
Kublai Khan
Genghis Kahn’s successor - ruled China
Didn’t really have a set culture - didn’t enforce religion or way of life on conquered nations, but did make any cultural advancements
Timur Lang
Mongol leader who took over India and destroyed everything - grew Islam in the nation
If any residents of society the Mongols took over resisted, they would immediately kill them, so most had no choice but to give in - they were ruthless fighters, organized and mobile
Great diffusers of culture
Prevented Russia from culturally developing
World trade, cultural diffusion, global awareness grew as they spread through Europe, the Middle East, and Asia
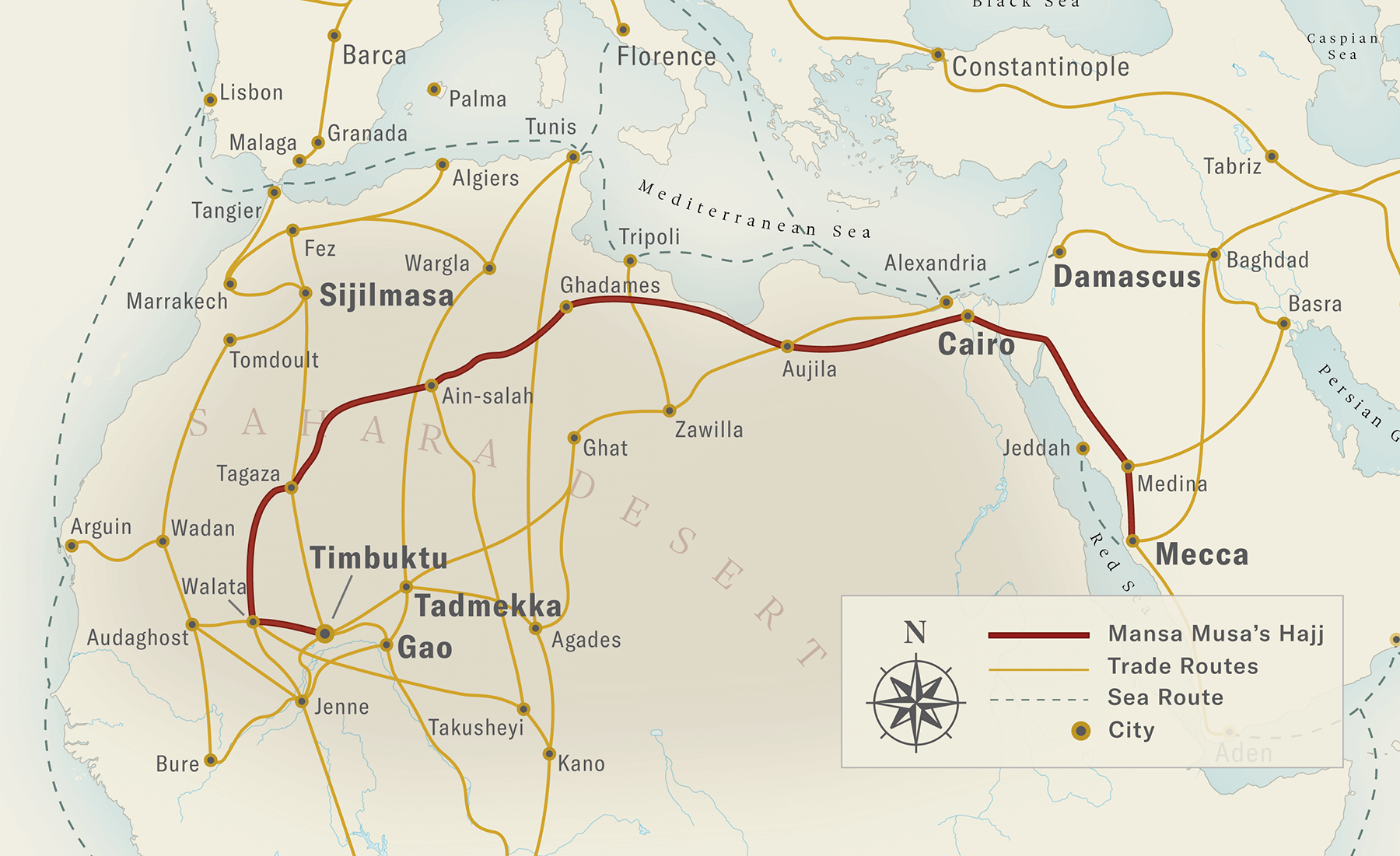
Mali and Songhai
Mali had a lot of gold that Islamic traders were interested in
Mansa Musa
Malian ruler who built the capital of Timbuktu and expended the kingdom beyond Ghana
Richest man
Hajj to Mecca (religious pilgrimage)
Sonni Ali
Songhai ruler that conquered region of west Africa in 15th century
became a major cultural centre until 1600
Song Dynasty: Chinese Technology
bureaucratic system built on merit and civil service examination creating a lot of loyal government workers, improved transportation and communication and business practices
Concentrated on creating an industrial society
improved literacy with printed books which increased productivity and growth
Civil Exam
Trade Networks and Cultural Diffusion
Trade exploded from 1200-1450
Improved with better transportation and monetary systems
Cultural diffusion - spread religions, languages, literature, art, idea, disease, plague
Main Global Trade Routes
1. The Hanseatic League
2. The Silk Road
3. The land routes of the Mongols
4. Trade between China and Japan
5. Trade between India and Persia
6. The Trans-Saharan trade routes between west Africa and the Islamic Empire
Bubonic Plague
started in Asia in the 14th century and carried by merchants
killed about 1/3 population
Indian Ocean Trade
Dominated by Persians and Arabs - western India to Persian Gulf to eastern Africa
Great Zimbabwe: trading empire in Africa from 11th to 15th centuries
Silk Road
China to Mediterranean cultures in early days of Roman Empire and from 1200 to 1600
Cultural exchange through travelers stopping at trade towns - Kashgar, Samarkand
Silk, porcelain, paper, religion, food, military technologies
Sailors marrying local women created cultural intermixing
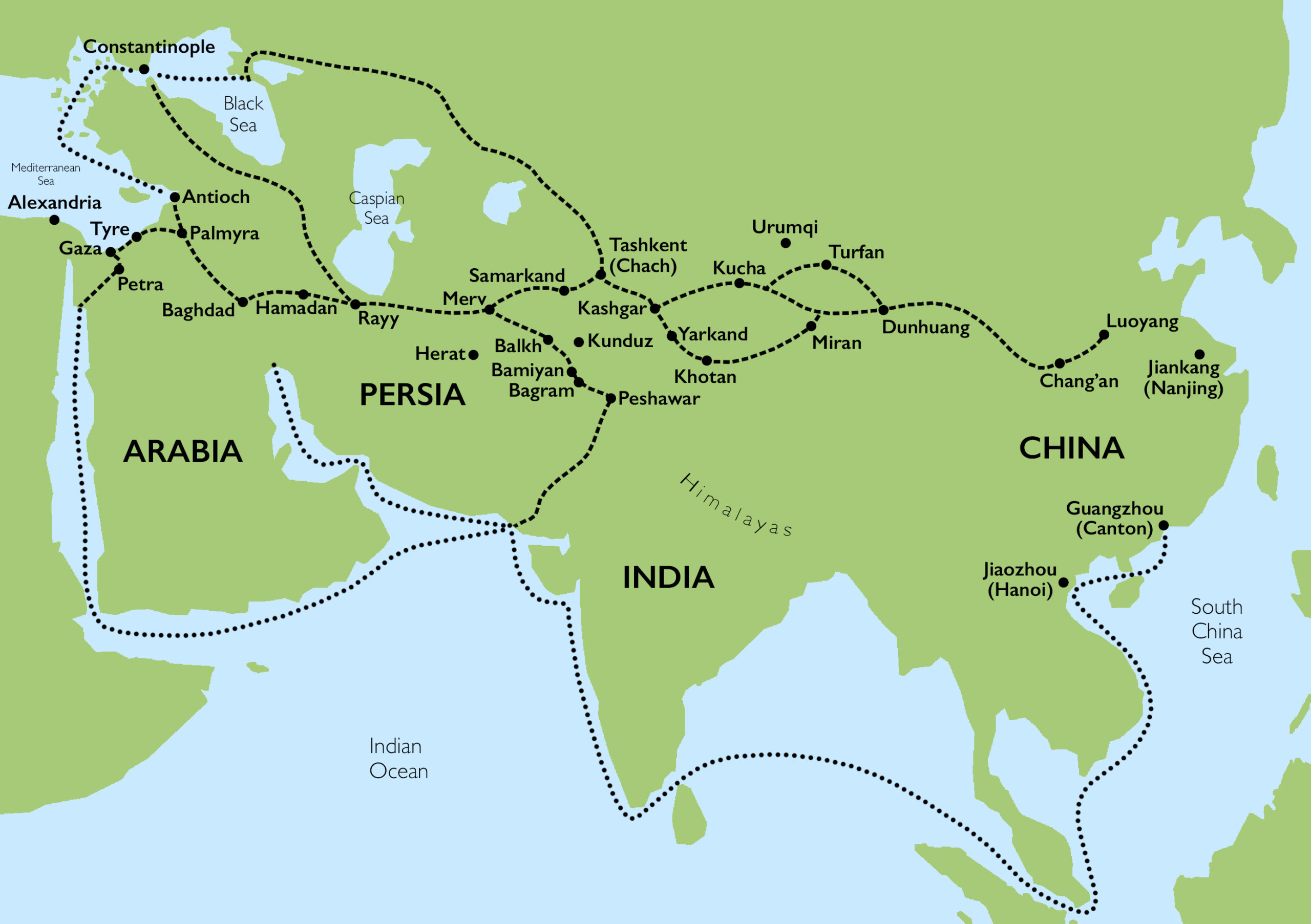
Ibn Battuta
Islamic traveler, through Islamic world to India to China
The Renaissance
people moved to the cities and an influx of money was experienced
a lot of money went to studying the past
trade increase
Humanism
focus on personal accomplishment, happiness, and life on earth instead of living for the goal of salvation
Afterlife remained dominant in the Catholic Church
Medici family
Extremely rich patrons of art in Italy
Patrons of Michelangelo & Brunelleschi
Renaissance Artists
Leonardo da Vinci, Donatello, Michelangelo, Rafael
Printing Press
made books easy to produce and affordable, and accessible to everyone
led to more literate people
Johannes Gutenberg md-1400s invented it
Protestant Reformation
Catholic Church, one of the most powerful organizations in the Middle Ages
power in politics and society - undisputed authority
Church capitalized off its followers with indulgences: purchased to reduce time in purgatory
Nobles and peasants began getting increasingly frustrated by the church’s exploitation and corrupt nature
Martin Luther
German monk who published his list of complaints against the church (95 Theses)
proposed salvation was given directly through God, not through the church, which significantly reduced the church’s influence
Pope Leo X
excommunicated Luther when he refused to recount his idea
Christianity split
Luther’s ideas led to many others to come forward
Lutherans
Luther’s followers - separated from Catholic Church
Calvinism
John Calvin: predestination - only a few people would be saved by God, great influence in Scotland and France
Church of England/Anglican Church
pope refused to annul King Henry VIII’s marriage to Catherine of Aragon because an heir wasn’t produced
he declared himself the head of religious affairs
Jesuits
Ignatius Loyola: prayer and good works leads to salvation
Catholic Reformation (16th century)
Catholic church attempts to remedy some of their controversies and regains some of its credibility
still wanted authority and control
Council of Trent: reinstated pope authority, punished heretics, reestablished Latin as only language in worship
Caused wars
Scientific Revolution
Expanded education led to world discoveries
Copernican Revolution:
Nicolaus Copernicus - discovered earth and other celestial bodies revolved around the sun and the earth rotated on its axis
Galileo
built off Copernicus’s theories and proved them - forced to recant by the Catholic Church and put under house arrest
Scientific Method
shift from reasoning being most reliable means of scientific meaning to scientific method (theory, documentation, repetition, others experimenting)
Newton
Natural Laws
Led to Industrial Revolution, and many rejecting the church - atheists (believe no god exists), deists (believe God exists, but is passive)
Deism: became popular in 1700s - God created the earth but doesn’t interfere in its workings
Rene Descartes- Rationalism
All truth comes from reason and logic
Spain and Portugal
Spain became very powerful, supporting exploration, expansion of Spanish language and culture, and having a large naval fleet
Portugal focused on dominating costal Africa, Indian Ocean, Spice Islands - lost control to Dutch and British
England
Elizabethan Age (1558-1603): expansion, exploration, colonization in New World - golden age
Muscovy Company: first joint-stock company - British East India Company
Petition of Rights (limiting taxes and forbidding
unlawful imprisonment)
Oliver Cromwell - dictator
Habeas Corpus Act: prevents people from arrests without due process
Glorious Revolution
English Bill of Rights (1689)
France
Unified and centralized under strong monarchy after Hundred Years’ War (1337-1453)
bureaucratic class
War of Spanish Succession (1701-1714)
Germany/Holy Roman Empire
Holy Empire was in present day Austria/Germany - weak due to the mixed dynamics, rulership, and religion of the surrounding area
Russia
Overthrown by Mongols late 15th century
Ivan III refused to pay tribute to Mongols and declared them free from their rule
Ivan IV (Ivan the Terrible): strong leader feared by many - executing people who were threats to his power
Time of Troubles (1604 to 1613): killing those who tried to rise to the throne
Gunpowder Empires
Land-based
Used gunpowder to expand
Ethnically different from their subjects (Safavids-Shi’a, Ottomans-Sunni, both are Muslim)(Qing- Han subjects, Manchu leader)
Ottoman Empire (Gunpowder Empire)
Eventually invaded Constantinople in 1453 and ended Byzantine Empire (Constantinople now named Istanbul)
Istanbul center of Islamic civilization
Jannissaries
Warriors trained after being converted through Devshirme
Devshirme
Collecting young boys (NOT Muslim) from families (Balkans) and turning them into bureaucrats
Safavid Empire (Gunpowder Empire)
Shah Ismail
Bureacrat
A govt. official who carries out the will of the govt./govt. leader
Mughal Empire (Gunpowder Empire)
Babur: Mongol leader who invaded northern India
Akbar: succeeded Babur
Hindus and Muslims lived side by side in a golden age of art and thought - under Shah Jahan, the Taj Mahal was built
Aurangzeb: emperor who ended religious toleration and waged wars to conquer rest of India
- Hindus were persecuted
Africa
Swahili-