Sheep Brain Dissection/Responses to stimuli
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Frontal Lobe
Large lobe in cerebrum, front part of sheep brain
Executive functions
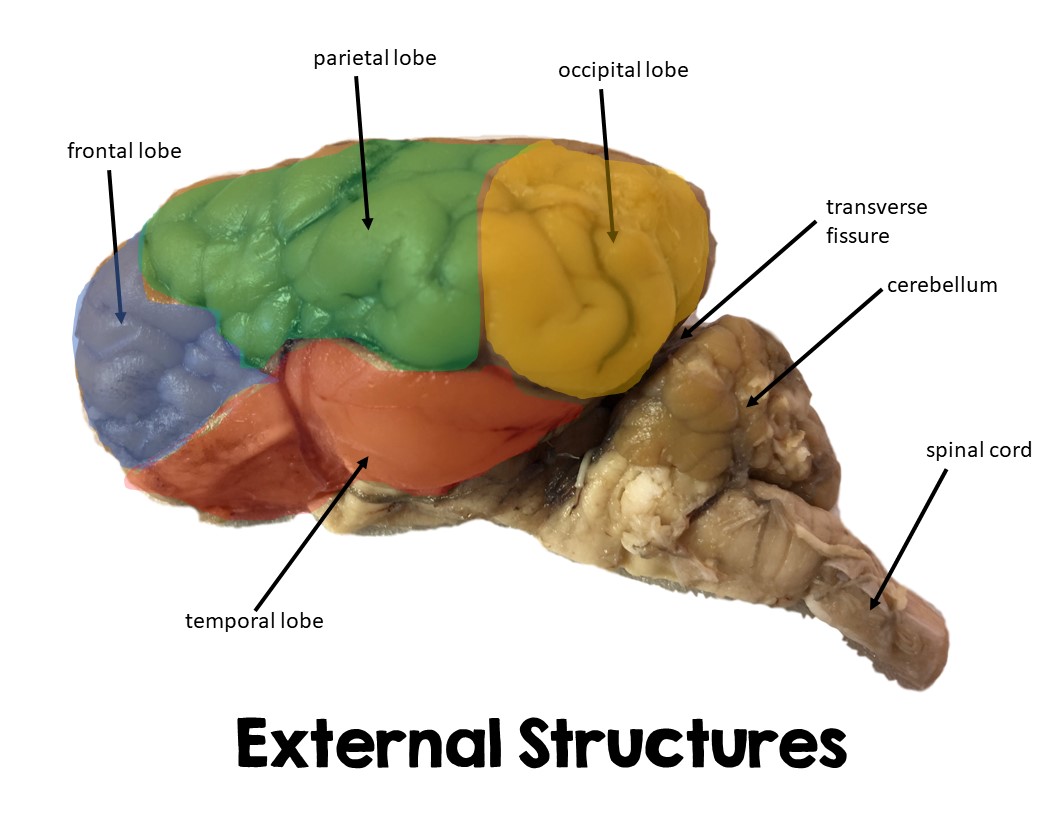
Parietal Lobe
Large part of upper middle brain, separated by frontal by central sulcus
Sensory
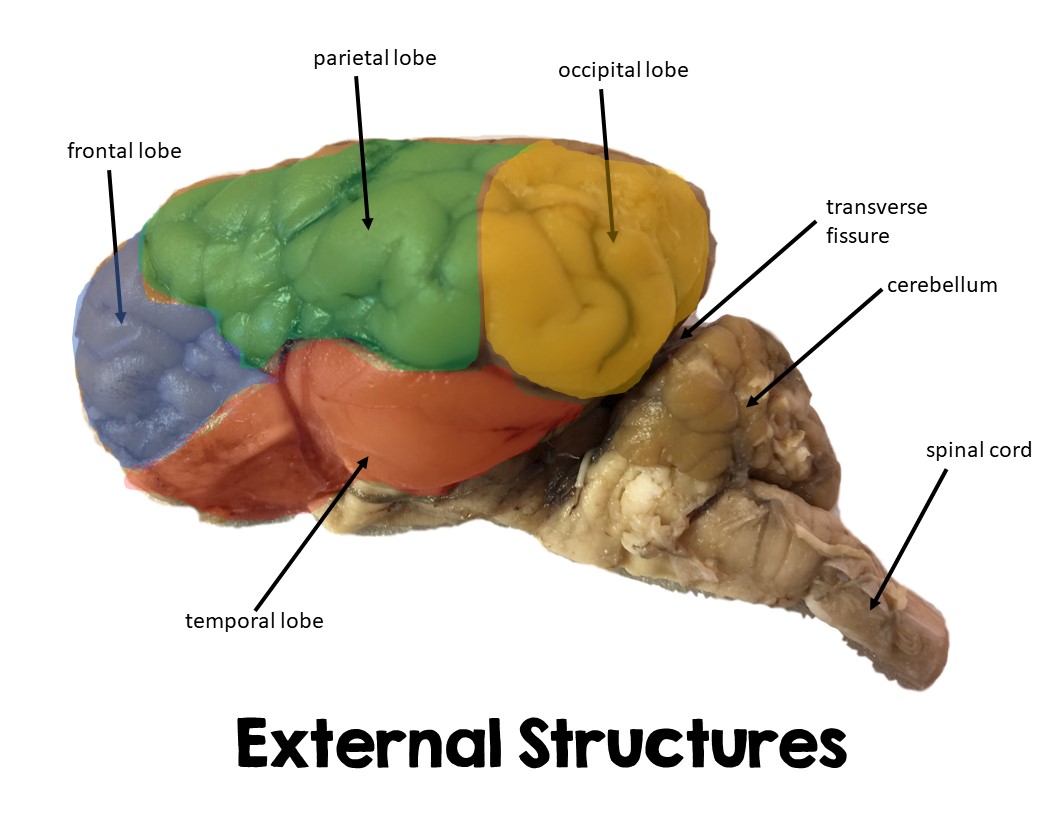
Occipital lobe
Portion of brain located posterior/in back
eye sensations
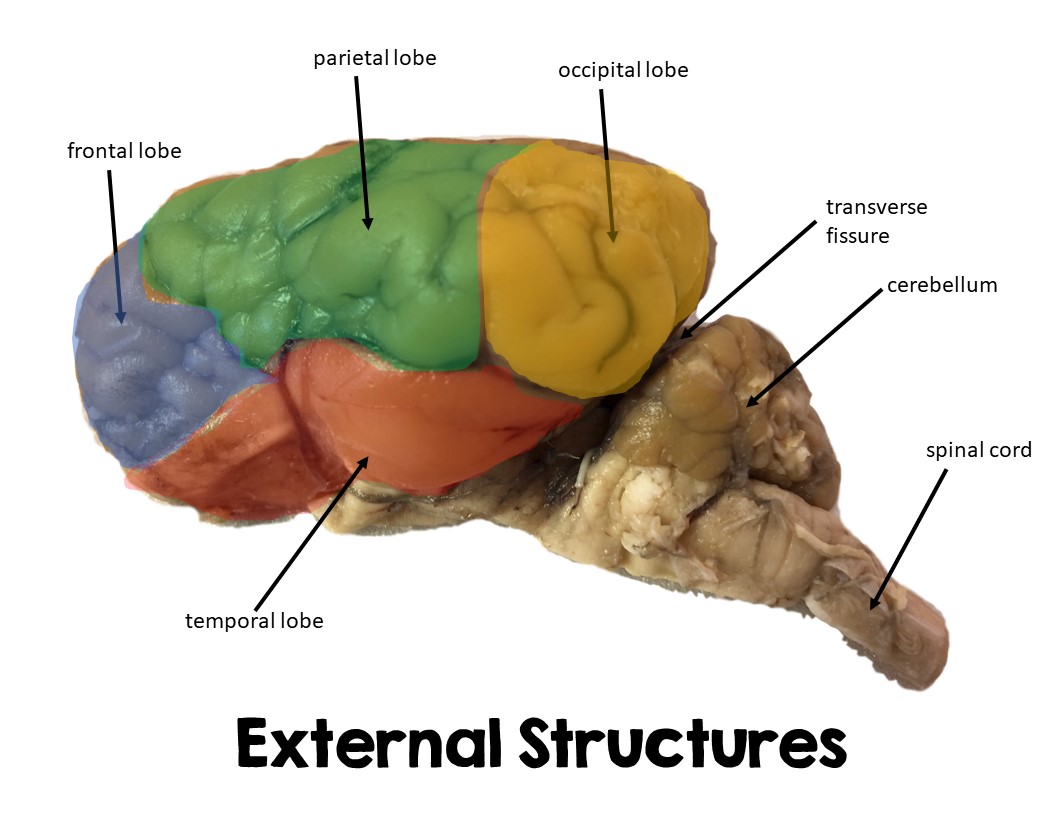
Temporal lobe
Bottom of brain directly above brainsteam/cerebellum
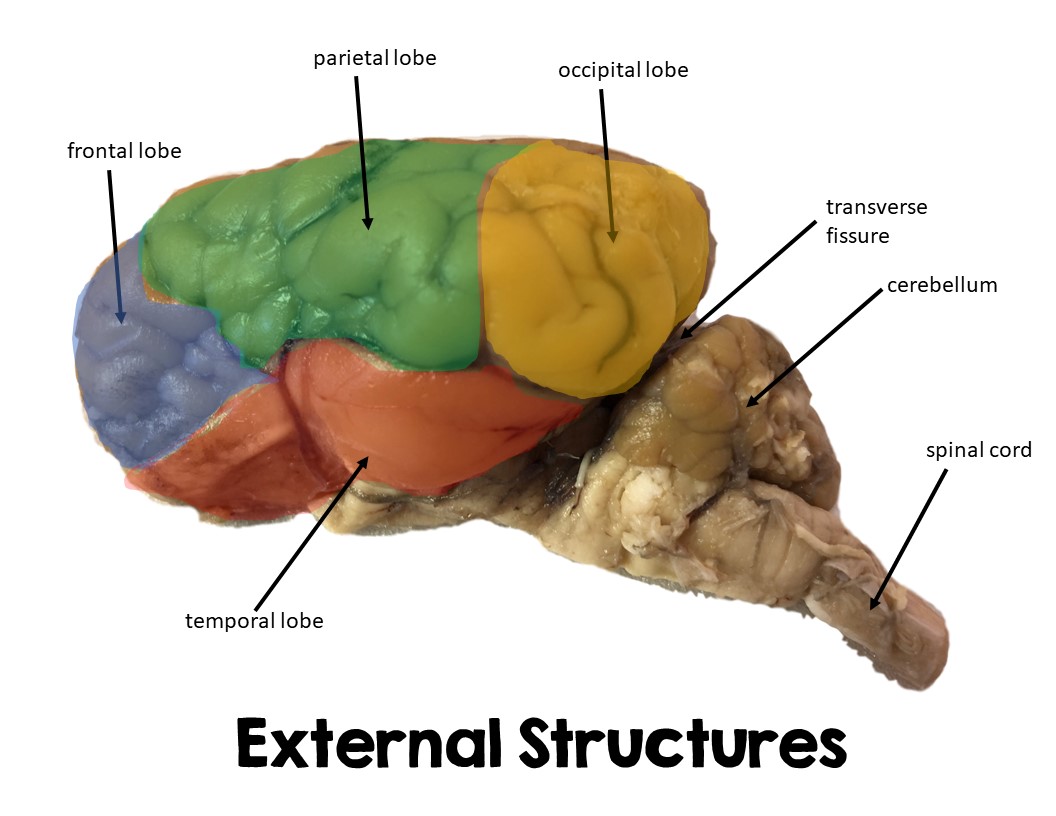
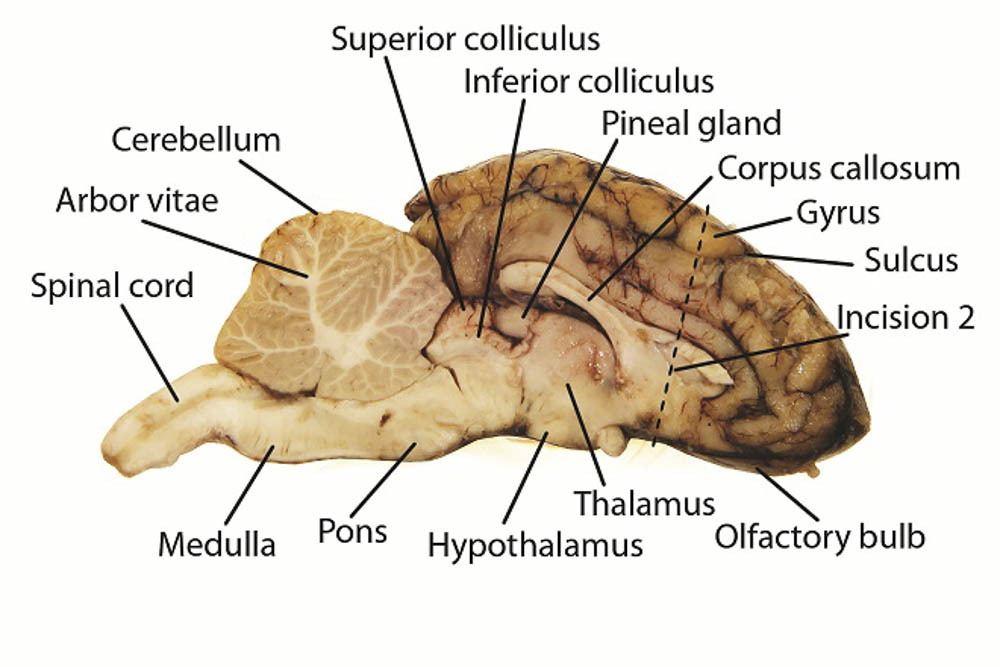
Cerebellum
Portion located posterior to cerebrum in sheep brain
Vermis
Central ridge of the cerebellum
Sulci
Grooves of the brain
Gyri
Ridges of the brain
Central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
Lateral sulcus
separates the frontal and temporal lobes
Brainstem parts
Midbrain - top part of brain stem
Pons - middle brain stem
Medulla - posterior part of brainstem
Corpus callosum
Connects 2 hemispheres of brain
Lateral Ventricle
Contain CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) it is a cavity
One in right hemisphere, one in left
May need to remove septum pellucidum to view
Third ventricle
Top of brain stem
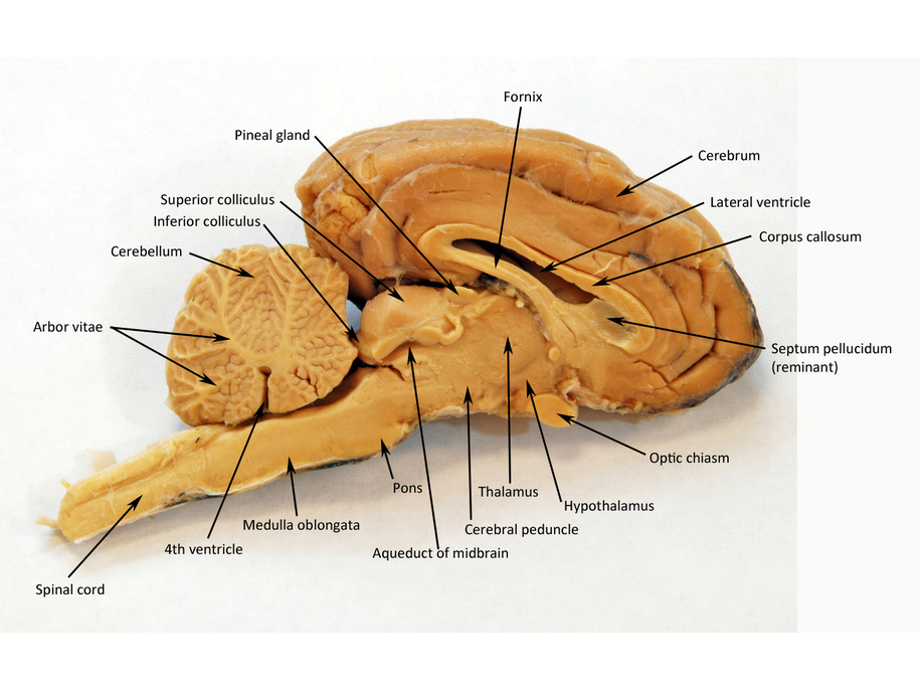
Fourth ventricle
Between cerebellum and brainstem
Cerebral aqueduct
Connects 3rd and 4th ventricles
Arbor vitae
In cerebellum, looks like a tree like structure “tree of life”
Thalamus
In forebrain, part of sensory and motor systems
Hypothalamus
end part of brainstem?
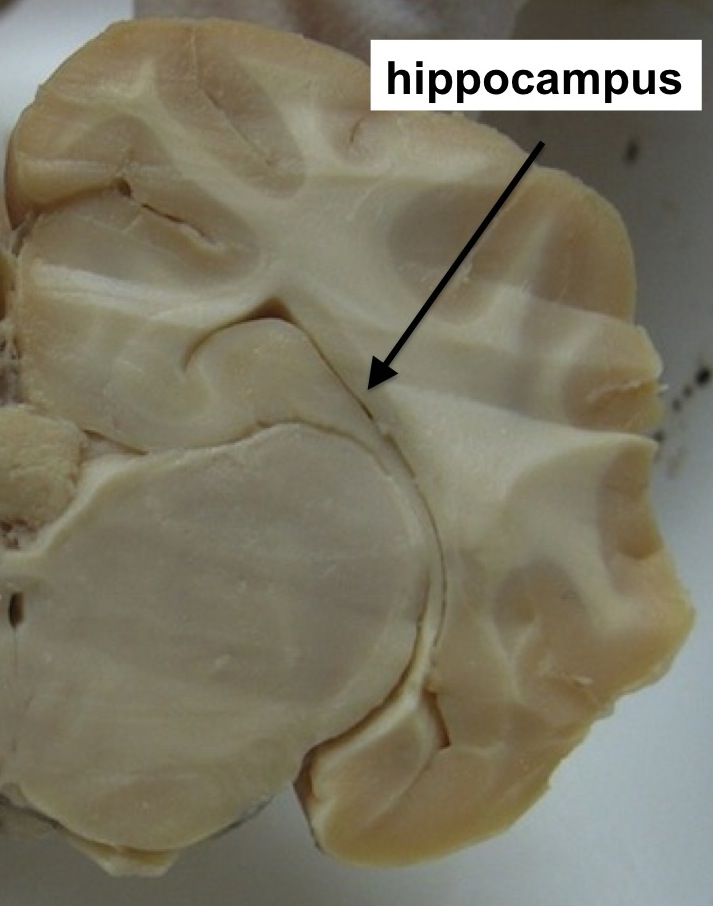
Hippocampus
Grey matter - Outside of brain
White matter - within inside
Sensory neurons
Used to convert electrical signals sent to CNS
Motor neurons
integrated in brain and response is sent through them
Mechanoreceptors
Touch, pressure, motion, stretch on the skin
Chemoreceptors
Chemicals dissolved in bodily fluids
Electromagnetic receptors
responsive to light
Thermoreceptors
Detects heat
Detects hot and cold temp (cold and hot bucket)
Nociceptors
Detects physical pain (relay signals to and from other parts of body
Elbow in water to see if referred pain relays to fingertips
Homunculus brain
shows the amount of mechanoreceptors found on different parts of the body
more receptors = increased sensitivity
Hearing receptors
Cochlea has ciliated hair cells that are receptors for auditory signals
CN VIII (vestibulocochlear nerve) damage causes hearing loss
Weber & Rinne tests - tests lateralization (one side louder)
Otolithls
Present in both chambers to detect movement
Referred pain
Occurs when the pain signals are sent to parts of the body that are unharmed
Elbow in water to see if referred pain relays to fingertips
Odorants
Thousands of these, what scents are detected by
Chemoreception of olfaction (smell)
Tastant
chemical that stimulates sensory receptor cells
Five tastants: sweet, salty, sour, bitter, umami
Photoreception of vision
Ciliary muscles used to help focus
Rods and cones - Rods are low light, cone is RGB and bright levels
Myopia
People can not see far away without lasses/contacts
ipsilateral eye
eye being exposed during consensual reflex
contralateral eye
eye not being exposed to light in consensual reflex
Optic chiasm
axons of optic nerves converge here, enter opposite sides of brain
lateral geniculate nuclei
axons enter in here, travel to primary visual cortex in cerebellum for information and production of images
Ciliary muscles
these contract while suspensory ligaments relax during near vision
Afterimage test
Eyes become sensitized or fatigued from extended staring at image
Blindspot test
optic disc → lacks photoreceptors and blind spot forms where no light detected
Chemoreception of gustation
Taste test depicting different parts of your tongue’s ability to detect taste
Chemoreception of olfaction
Test smelling different unknowns to test olfactory receptors ability
Mechanoreception of equilibrium
2 chambers in inner ear - utricle and saccule (maintain balance)
otoliths - calcium carbonate particles covering hair cells signifying movements
Cupula - gelatinous substance which moves to detect motion
Hearing loss
Conductive - interference with sound in outer/middle ear
Sensorineural - damage of inner ear
Tactile distribution/localization
mechanoreception of tactile stimuli,
different regions of body have different sensitivites