Geometry Proofs
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Test on 11/13/25-
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
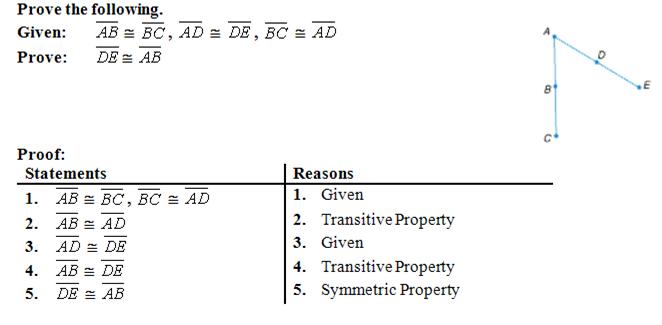
Transitive Property
If a=b, and b=c, then a=c
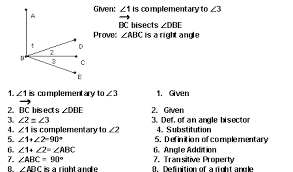
Substitution Property
If a=b, then (a) may be replaced by (b) an equation
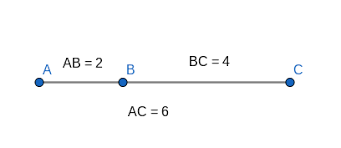
Segment Addition Postulate
If points a, b, and c are on the same line with b between a and c, then ab+bc=ac
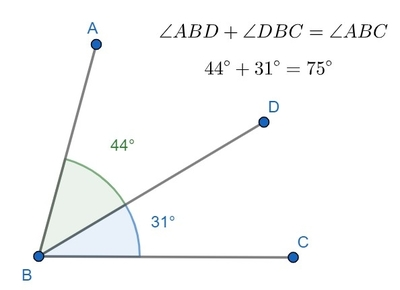
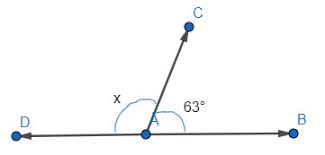
Angle Addition Postulate
To find one big angle, you can add the two smaller angles
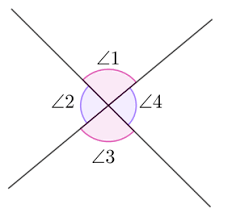
Vertical Angle theorem
if two angles are vertical angles, then they are congruent
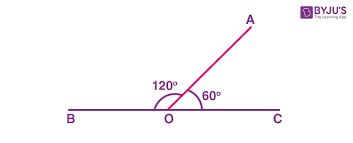
Supplementary Angles
Two angles that equal 180 degrees
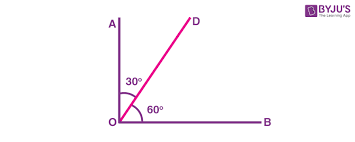
Complementary Angles
Two angles that equal 90 degrees
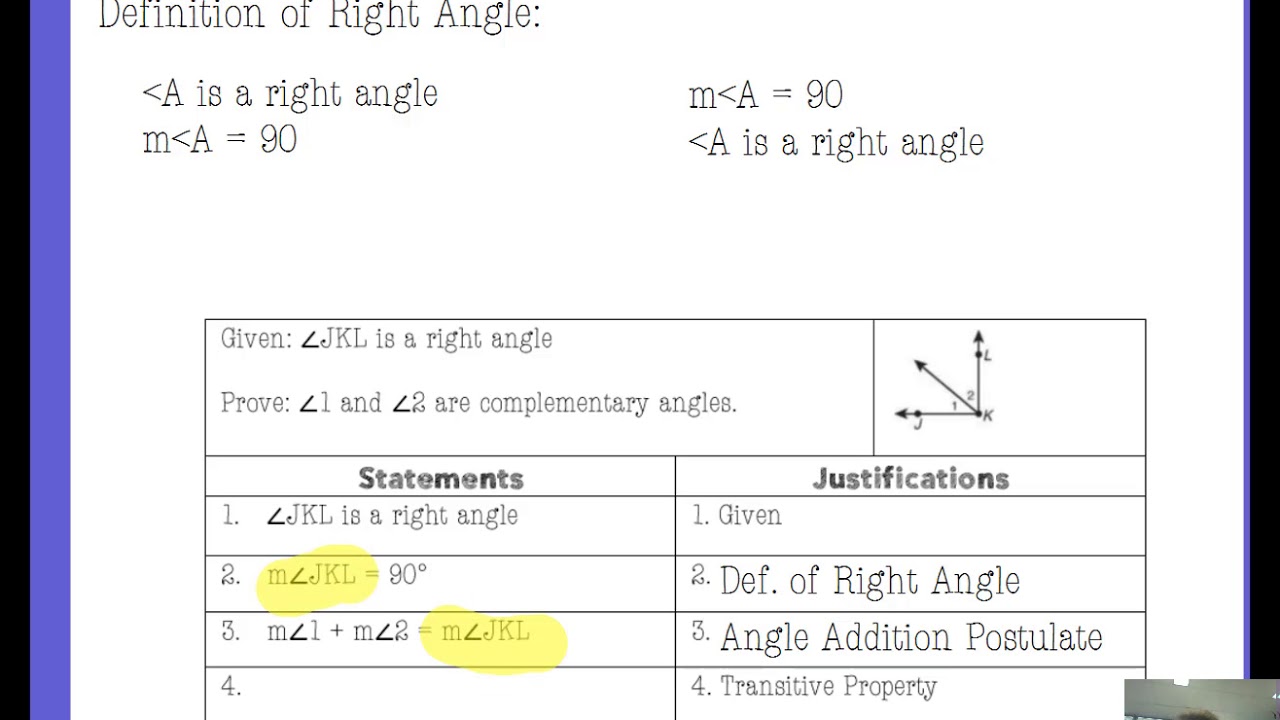
Definition of Right Angles
All right angles are congruent
Definition of linear points/ Linear Pair Theorem
The sum of the measure of a linear pair is 180 degrees- m<1+m<2=180 degrees
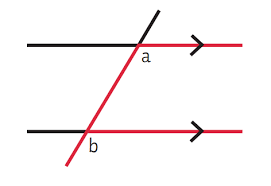
Corresponding Angles Theorem
When a transversal intersects two parallel lines, the corresponding angles formed are congruent (equal in measure).
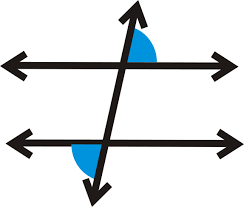
Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the pairs of alternate exterior angles are congruent (equal in measure)
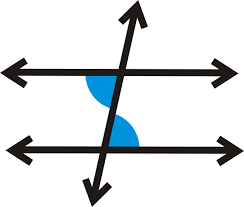
Alternate Interior Angles Theorem
When two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, the pairs of alternate interior angles are congruent (equal in measure)
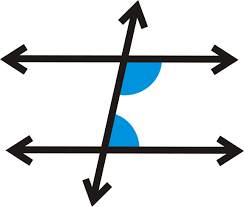
Same Side Interior Angle Theorem
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the same side interior angles are supplementary.
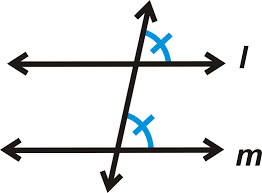
Converse of the Corresponding Angle Theorem
If the angles in corresponding positions are equal, the lines must be parallel.
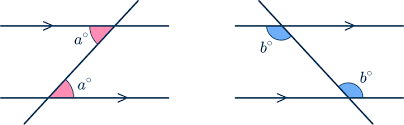
Converse of the Alternate Interior Angles Theorem
if two lines are intersected by a transversal forming congruent alternate interior angles, then the lines must be parallel.
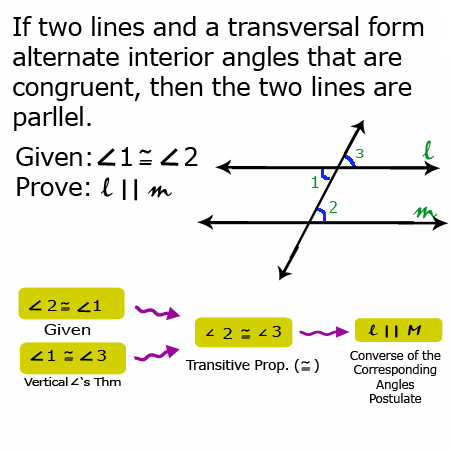
Converse of the Same Side-Interior Angles Theorem
If two lines are cut by a transversal and the same side interior angles are supplementary, then the lines must be parallel
Converse of the Alternate Exterior Angle Theorem