9.1- Transport in the Xylem of Plants
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
1
New cards
What is transpiration?
- evaporation of water from plant leaves, stems or other above ground parts of the plant.
- it occurs mainly in the open stomata
- it has a cooling effect on the leaf and exerts a pull to move water from the roots into the leaves.
- it occurs mainly in the open stomata
- it has a cooling effect on the leaf and exerts a pull to move water from the roots into the leaves.
2
New cards
How much of the water absorbed by the stems/leaves through their roots is lost by transpiration?
95%
3
New cards
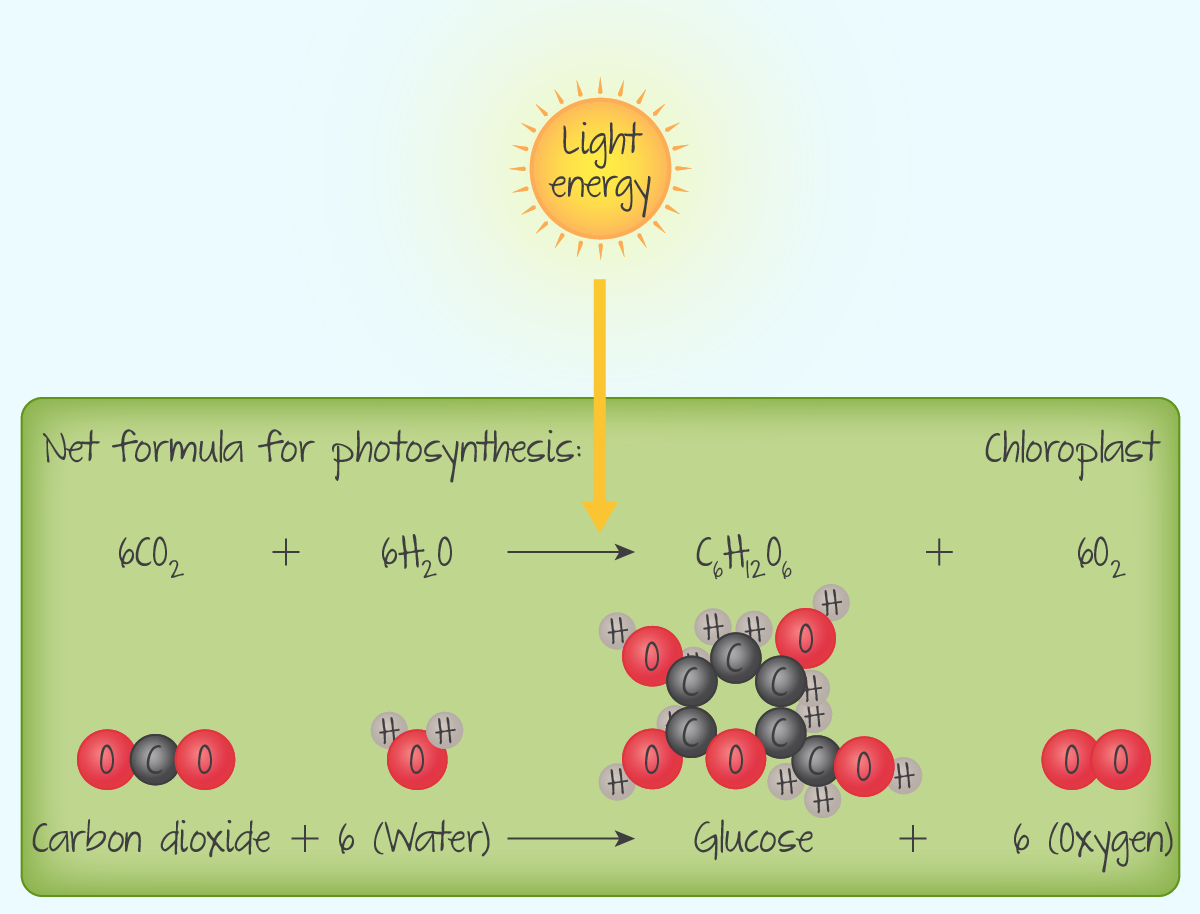
How does photosynthesis work?
- Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight and uses energy to convert CO2 and H2O into glucose(carbohydrate) and O2 (by product of carbohydrate synthesis).
- Mostly occurs during the day(when sunlight is available) and mostly occurs in leaves.
- Water reaches the cell through the xylem
- Mostly occurs during the day(when sunlight is available) and mostly occurs in leaves.
- Water reaches the cell through the xylem
4
New cards
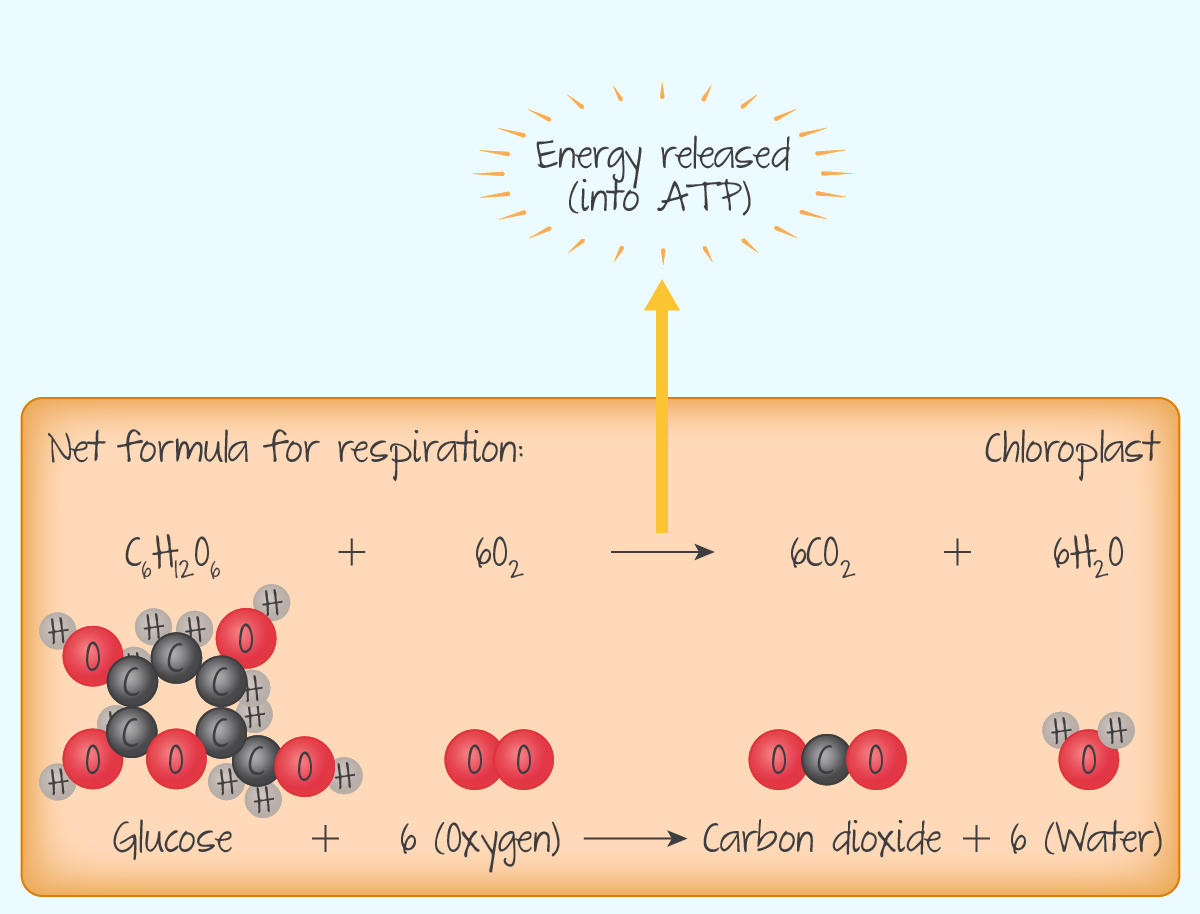
How does cellular respiration work in plants?
- the energy stored as carbohydrates during photosynthesis is released.
- occurs during both, day and night.
- occurs during both, day and night.
5
New cards
When does a plant need CO2 the most? and when does a plant need O2 the most?
During the day, the rate of photosynthesis in the leaves is generally much greater than the rate of respiration, so the leaves have a large net requirement of carbon dioxide. Plant leaves obtain carbon dioxide from the air.
6
New cards
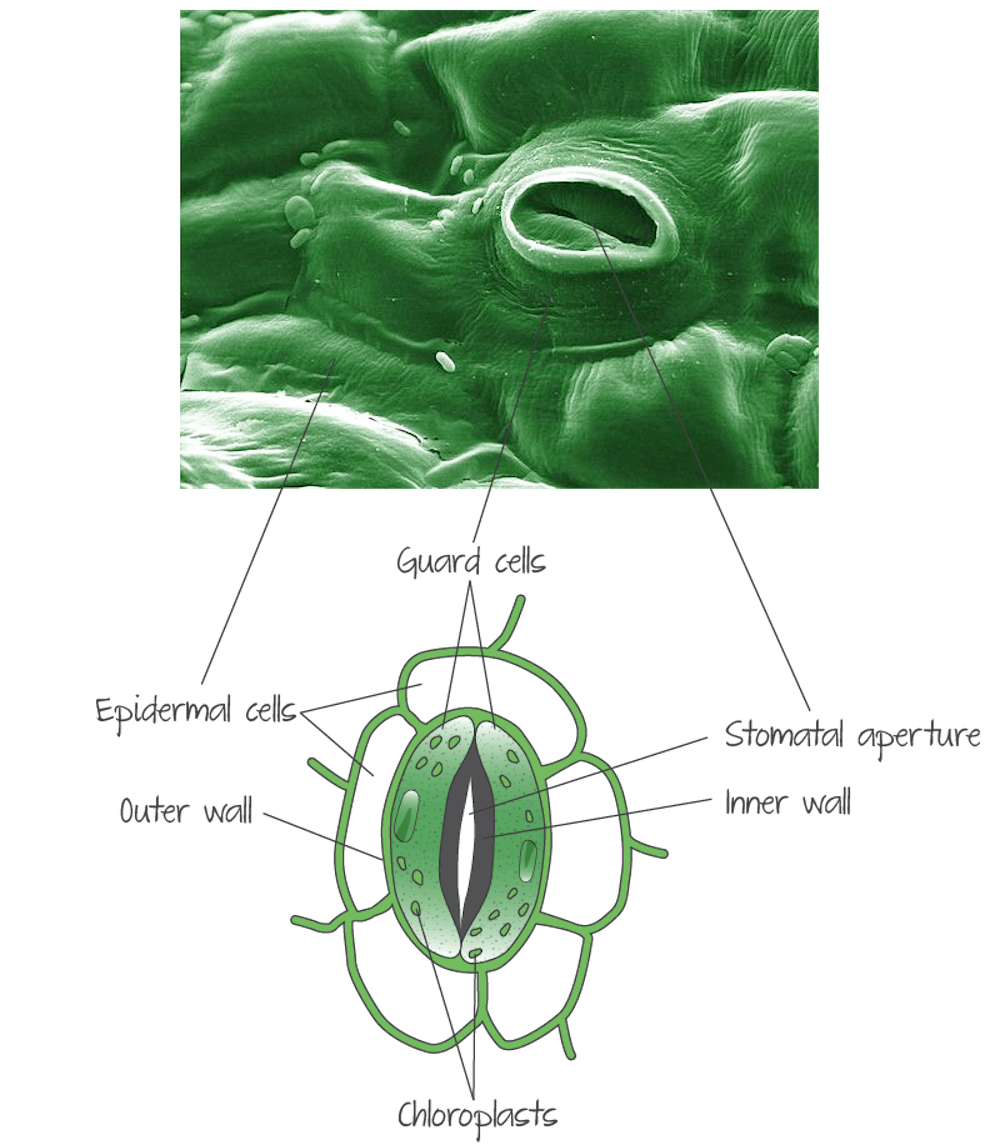
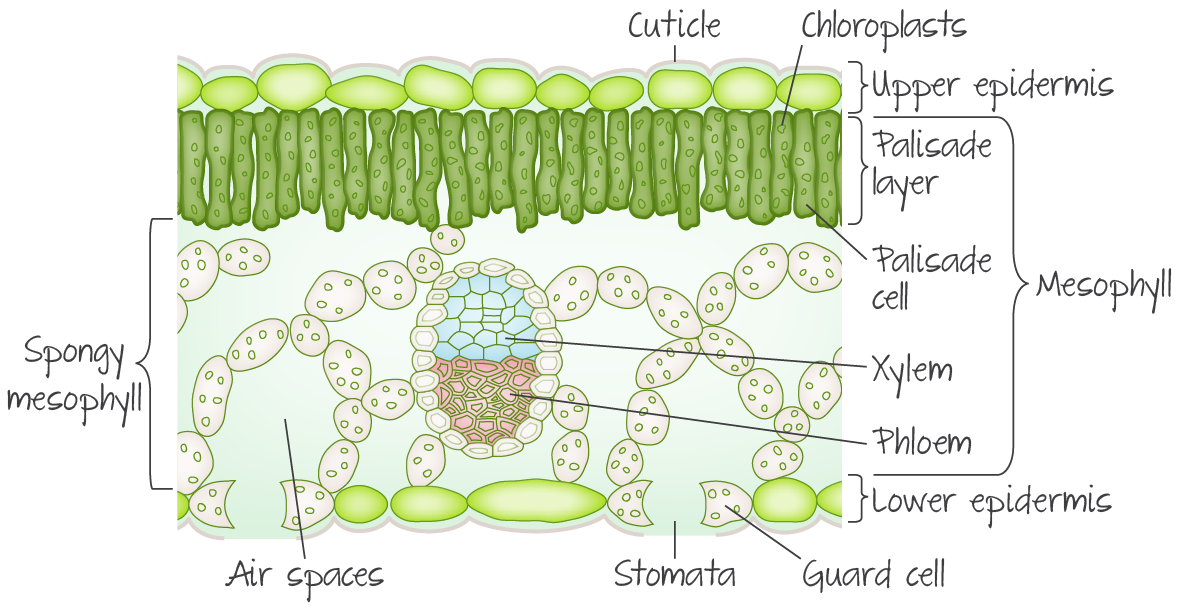
How does a leave carry gas exchange?
Leaves have special adaptations for gas exchange. One adaptation is stomata. Stomata are tiny pores, usually located on the underside of the leaf, whose opening and closing is controlled by two guard cells.Another adaptation for gas exchange is the lower tissue layer of the leaf known as spongy mesophyll, which provides the large surface area and moist surface necessary for gases to be exchanged
7
New cards
stomata diagram
8
New cards
spongy mesophyll diagram
9
New cards
How does diffusion help in the process of photosynthesis?
As the plant cells use up dissolved carbon dioxide in photosynthesis, the CO 2 concentration drops. Carbon dioxide from the air spaces between cells will dissolve and diffuse into the cell, moving from higher to lower concentration. When the concentration of carbon dioxide drops in the air within the leaf, there will be a net movement of carbon dioxide molecules into the leaf through the stomata, again by diffusion. Similarly, oxygen diffuses out of the leaf cells, into the internal air spaces, and out into the atmosphere through the (open) stomata.
10
New cards
Why is it important to lower the concentration of oxygen gas during photosynthesis?
It is important to lower the concentration of oxygen gas during photosynthesis, because it is a competitive inhibitor of a key enzyme, rubisco .
11
New cards
Why is transcription an inevitable consequence of gas exchange in a leaf?
Water vapour (H 2 O (g)) is also a gas, and will necessarily diffuse from the highly humid air spaces in the leaf to the areas of lower concentration in the atmosphere outside the leaf. Thus, the loss of water vapour (transpiration) is the inevitable consequence of gas exchange in the leaf.
12
New cards
How do plants use the stomata to limit their water loss in transcription? Explain how that impacts a plant.
- plants can close their stomata since 90% of water loss is through it(some is directly from outer epidermal cells).
- by doing this photosynthesis can't occur since CO2 can't come in.
- plants usually keep the stomata open during the day(for photosynthesis) and close in the night(to preserve water). Exceptions are plants with CAM metabolism to store CO2 at night and so they can do the opposite.
- evaporation of water cools down the plant that may overheat due to sunlight.
- by doing this photosynthesis can't occur since CO2 can't come in.
- plants usually keep the stomata open during the day(for photosynthesis) and close in the night(to preserve water). Exceptions are plants with CAM metabolism to store CO2 at night and so they can do the opposite.
- evaporation of water cools down the plant that may overheat due to sunlight.
13
New cards
What does the xylem do?
transports water from roots to leaves
14
New cards
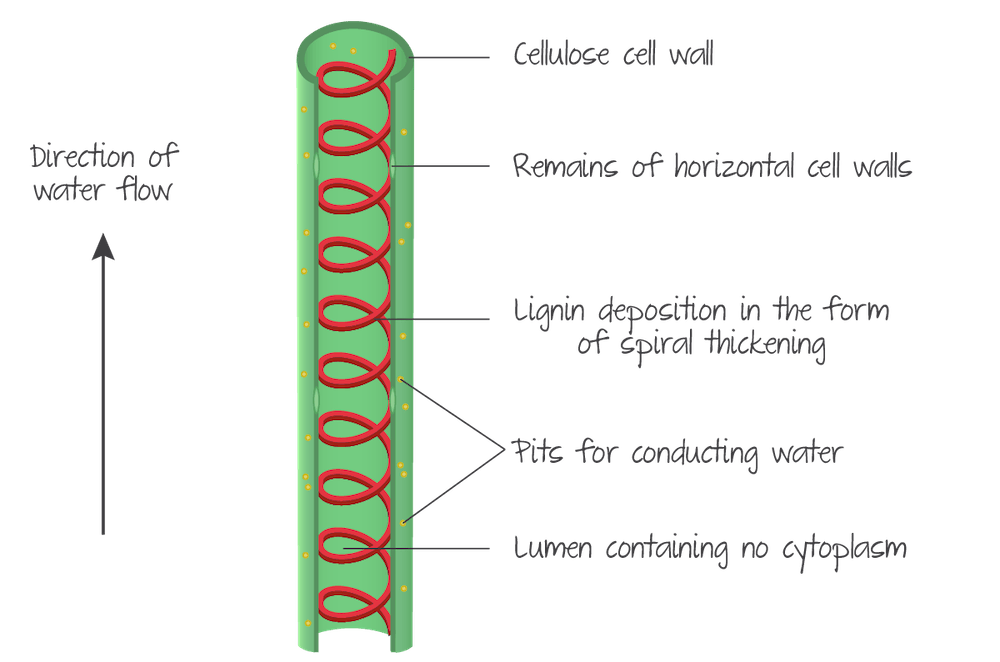
What is the structure of xylem like?
- long continuous hollow tubes.
- xylem is dead at maturity
- The cell membrane and internal structures break down and the horizontal cell walls also are partially or completely broken down.
- they
- xylem is dead at maturity
- The cell membrane and internal structures break down and the horizontal cell walls also are partially or completely broken down.
- they
15
New cards
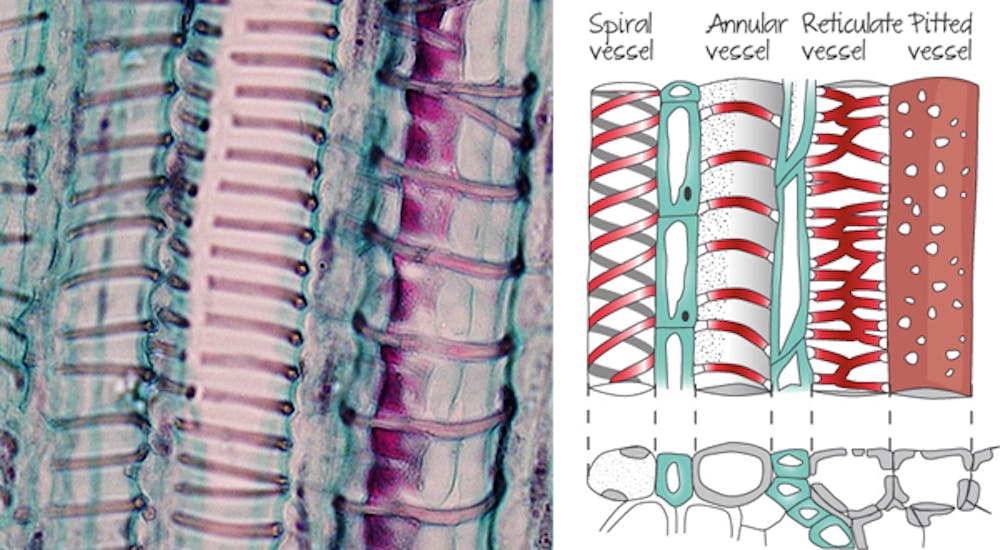
What is lignin?
- it is a complex polymer that binds with cellulose to provide strength and rigidity to the cell walls.
- the woody tissue made from lignified xylem can support tall plants
- Lignin also allows the xylem vessels to withstand the forces involved in transpiration without collapsing.
- Lignin can be deposited throughout the cell walls or as rings or spirals inside the xylem vessels.
- the woody tissue made from lignified xylem can support tall plants
- Lignin also allows the xylem vessels to withstand the forces involved in transpiration without collapsing.
- Lignin can be deposited throughout the cell walls or as rings or spirals inside the xylem vessels.
16
New cards
diagram of lignin structure in xylem
17
New cards
diagram of xylem
18
New cards
How does the fact that mesophyll cells are hydrophilic help move water up the xylem?
The cellulose in mesophyll cell walls is hydrophilic and water adheres(water sticks to other things cuz its polar) to it, creating a film of water on the surface of the cells. When water vapour diffuses out of the stomata, the internal air spaces of the leaf become less humid. Water then evaporates from the moist mesophyll cell walls into the air spaces.
19
New cards
How does the fact that water is cohesive impact the water flow in xylem?
When a water molecule evaporates from the cell wall it exerts a pulling force, or suction, on water molecules within the cell. This is because water is cohesive(h-bonds that attract water molecules to eachother) The tension caused by the pull of evaporating water molecules draws water from the xylem into the leaf cells. The transpiration pull begins with water molecules evaporating from the cell wall into the air spaces of the leaf and is transmitted through the column of water in each xylem vessel.
20
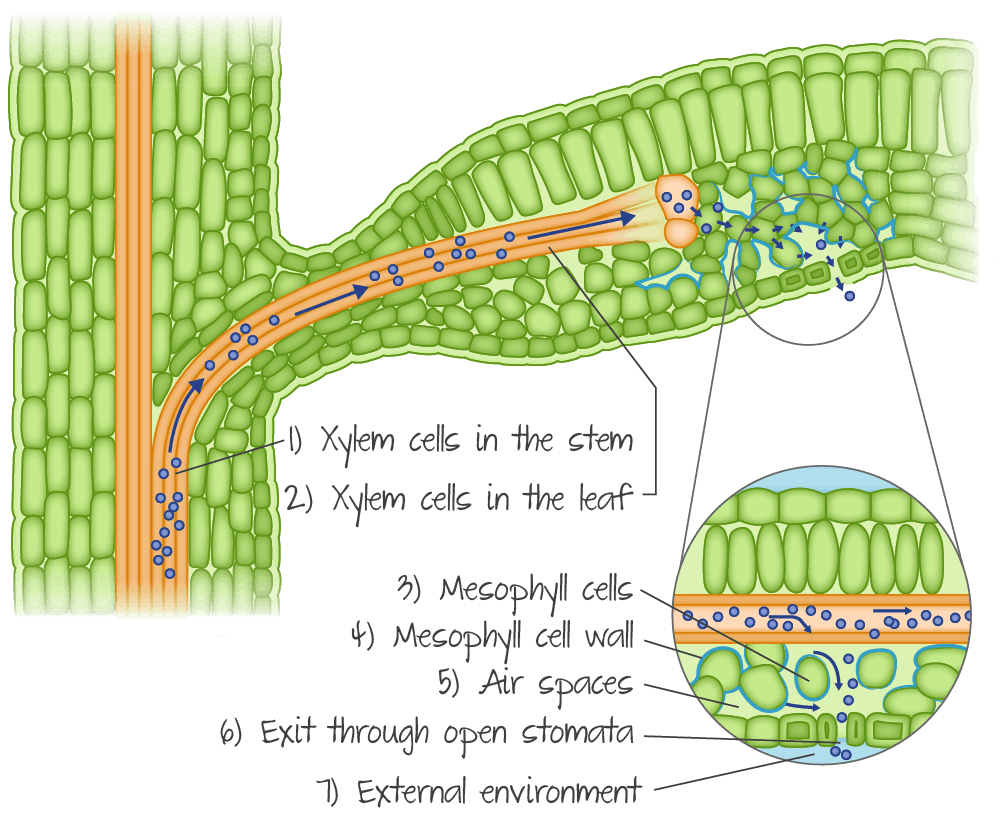
New cards
diagram of transpiration pull
Transpiration pull is similar to the way suction (low pressure) draws a column of liquid up a drinking straw.
21
New cards
Why do plants have root hairs?
- Some root cells have extensions called root hairs that greatly increase the surface area available for absorption.
- so that plants can absorb mineral ions like nitrate and potassium for growth and metabolism.
- so that plants can absorb mineral ions like nitrate and potassium for growth and metabolism.
22
New cards
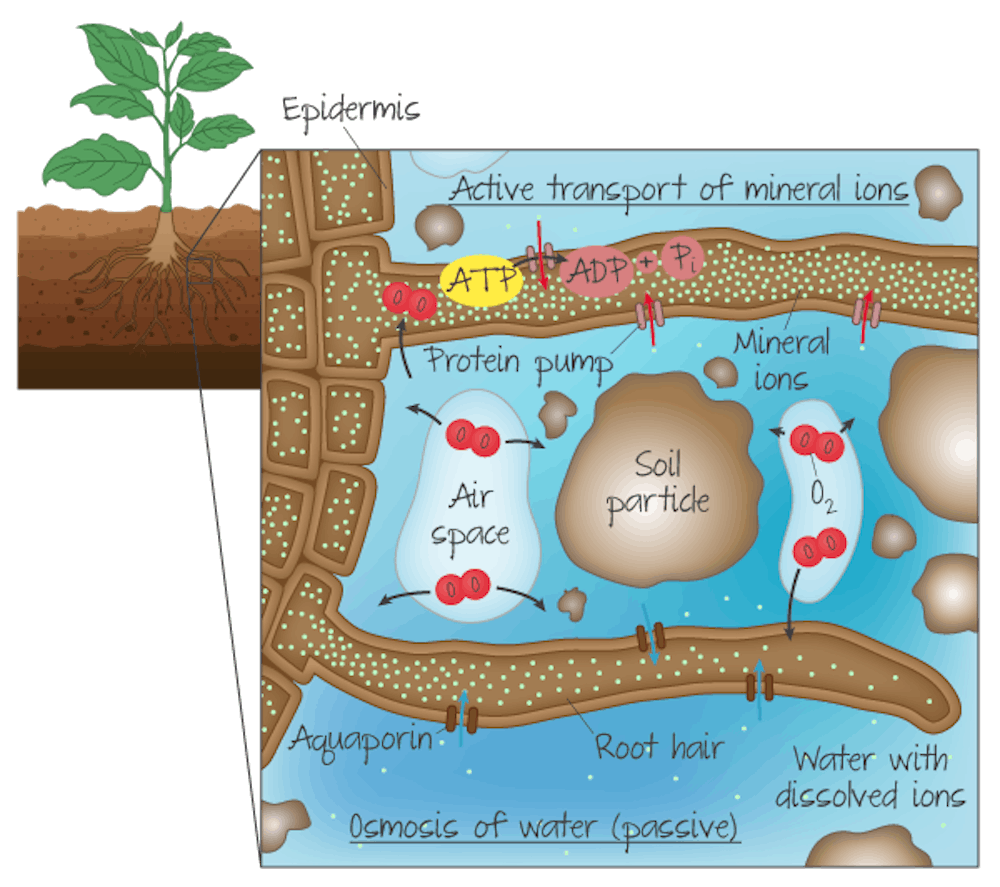
How do root hairs transport mineral ions?
- The plasma membrane of root hairs has many protein pumps that actively transport mineral ions from the surrounding water into the cytoplasm of the cell against the concentration gradient.
- This process requires energy stored in ATP molecules. Due to the high demand for ATP, root hairs have a high rate of cellular respiration, many mitochondria, and a high demand for oxygen gas.
- The oxygen is dissolved from air pockets in the soil into the surrounding water and from there diffuses into the root cells.
- This process requires energy stored in ATP molecules. Due to the high demand for ATP, root hairs have a high rate of cellular respiration, many mitochondria, and a high demand for oxygen gas.
- The oxygen is dissolved from air pockets in the soil into the surrounding water and from there diffuses into the root cells.
23
New cards
diagram of active transport in root hairs
24
New cards
How does water move through root cells(after getting in from root hairs) into the xylem?
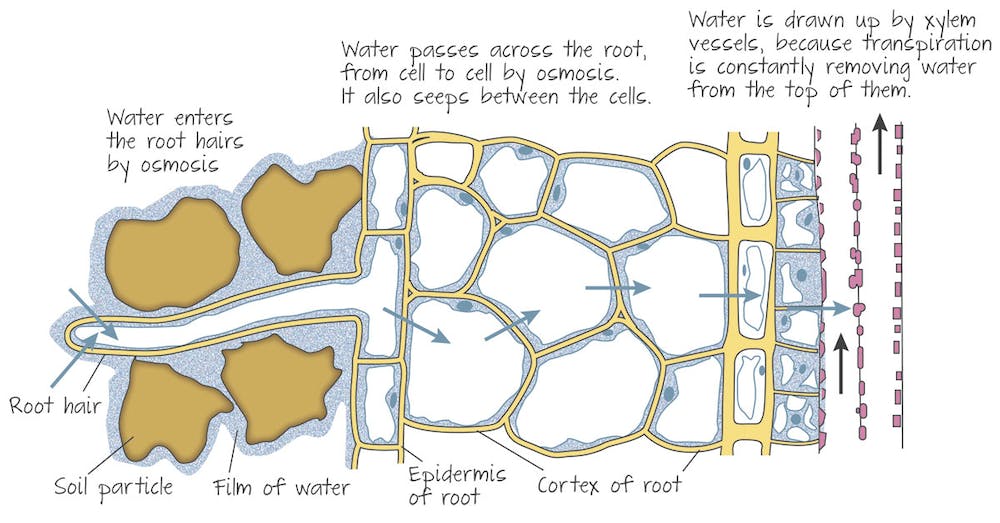
25
New cards
What is water potential?
Water potential, which is a measure of water's tendency to move in a particular direction, brings all of these effects together. Pure water has a water potential of 0.0 MPa (megapascals, a unit of pressure), with all other values being negative. Water always moves toward the value that is more negative
26
New cards
summarie overall movement of water in a plant
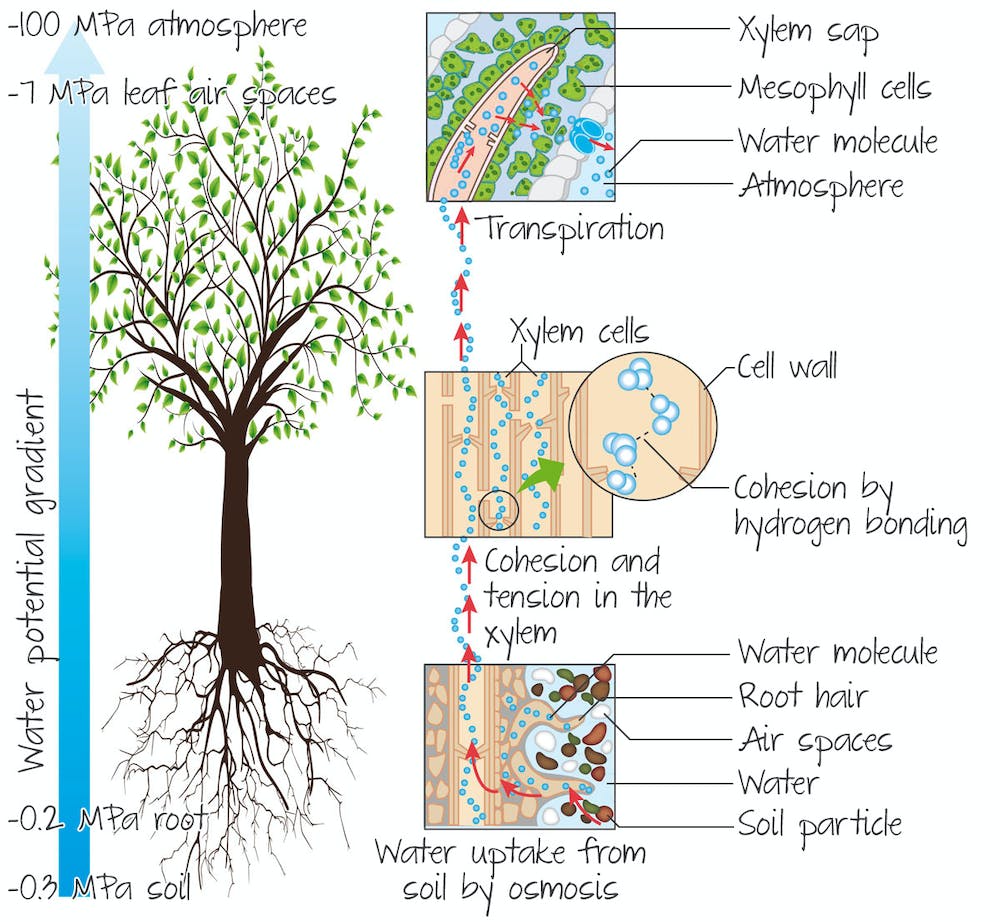
27
New cards
What are xerophytes?
- Xerophytes are plants that have adapted to live in conditions where liquid water is difficult to obtain, such as deserts, areas with seasonal drought, or areas like the Arctic when the soil water is frozen.
- Their adaptations help to conserve the little water plants acquire
- Their adaptations help to conserve the little water plants acquire
28
New cards
Name 10 xerophytic adaptations and their uses part 1
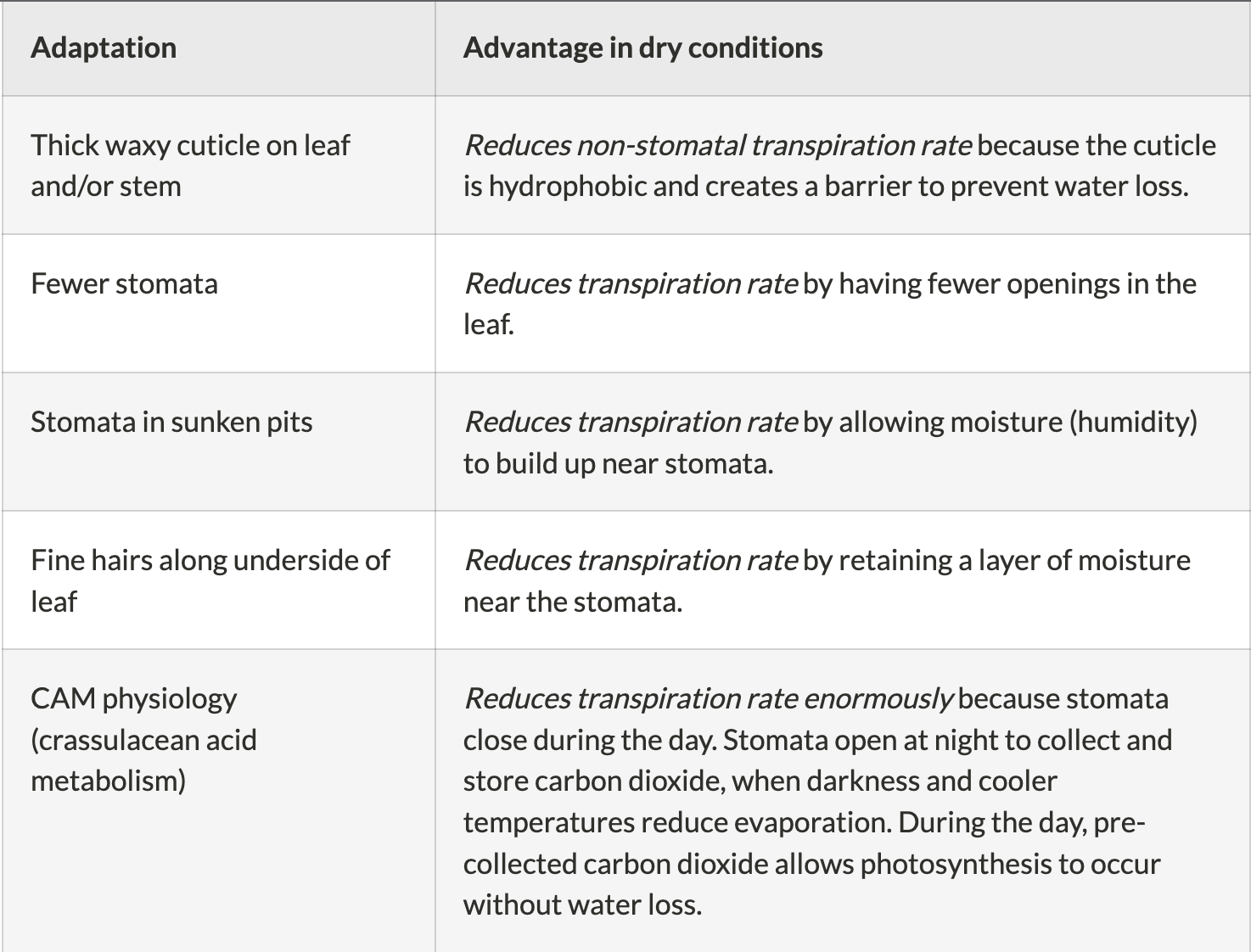
29
New cards
Name 10 xerophytic adaptations and their uses part 2
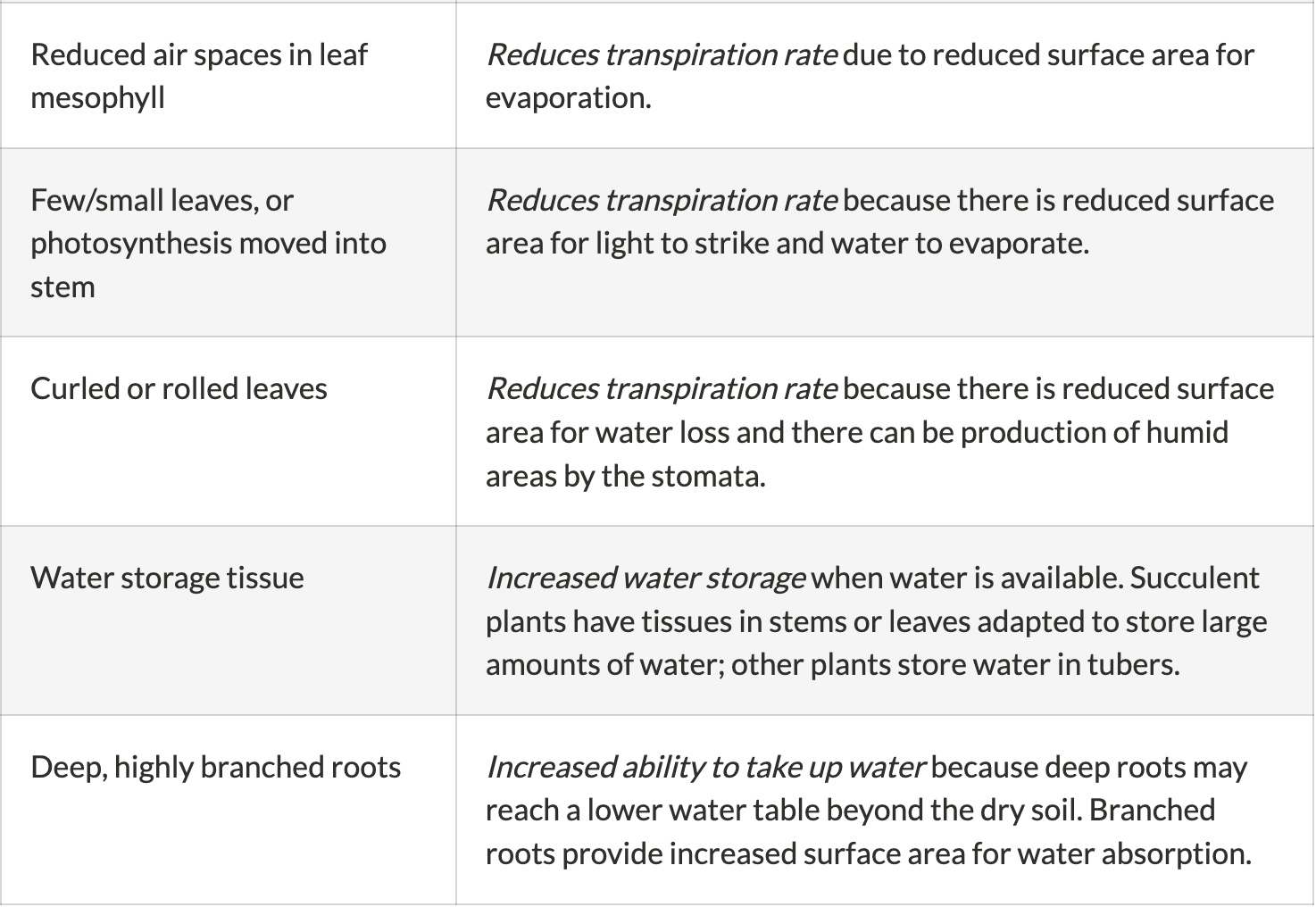
30
New cards
give 2 examples of xerophytes
1. The saguaro cactus- has a thick waxy cuticle on the stem. It has one tap root plus a highly branched surface root system to collect water during infrequent rains, which it then stores in the stem for later use. It has a very reduced surface area with photosynthesis moved into the stem. Leaves are reduced to spines that protect the stem from herbivores and intense sunlight. The saguaro also uses CAM photosynthesis, so its stomata are closed during the day.
2. Marram grass- dapted to grow on sand dunes. It has a thick outer cuticle, rolled shape, a few stomata, and hair-like structures to reduce transpiration.
2. Marram grass- dapted to grow on sand dunes. It has a thick outer cuticle, rolled shape, a few stomata, and hair-like structures to reduce transpiration.
31
New cards
What are halophytes?
- plants that have adapted to grow in areas with high salinity, such as along an ocean shoreline or in certain swamps and marshes.
- usually establish a higher concentration of ions in the roots than in the surrounding area to draw water in by osmosis. Areas of high salinity make this difficult since the ion concentration outside the plant is very high.
- usually establish a higher concentration of ions in the roots than in the surrounding area to draw water in by osmosis. Areas of high salinity make this difficult since the ion concentration outside the plant is very high.
32
New cards
name 6 halophyte adaptations
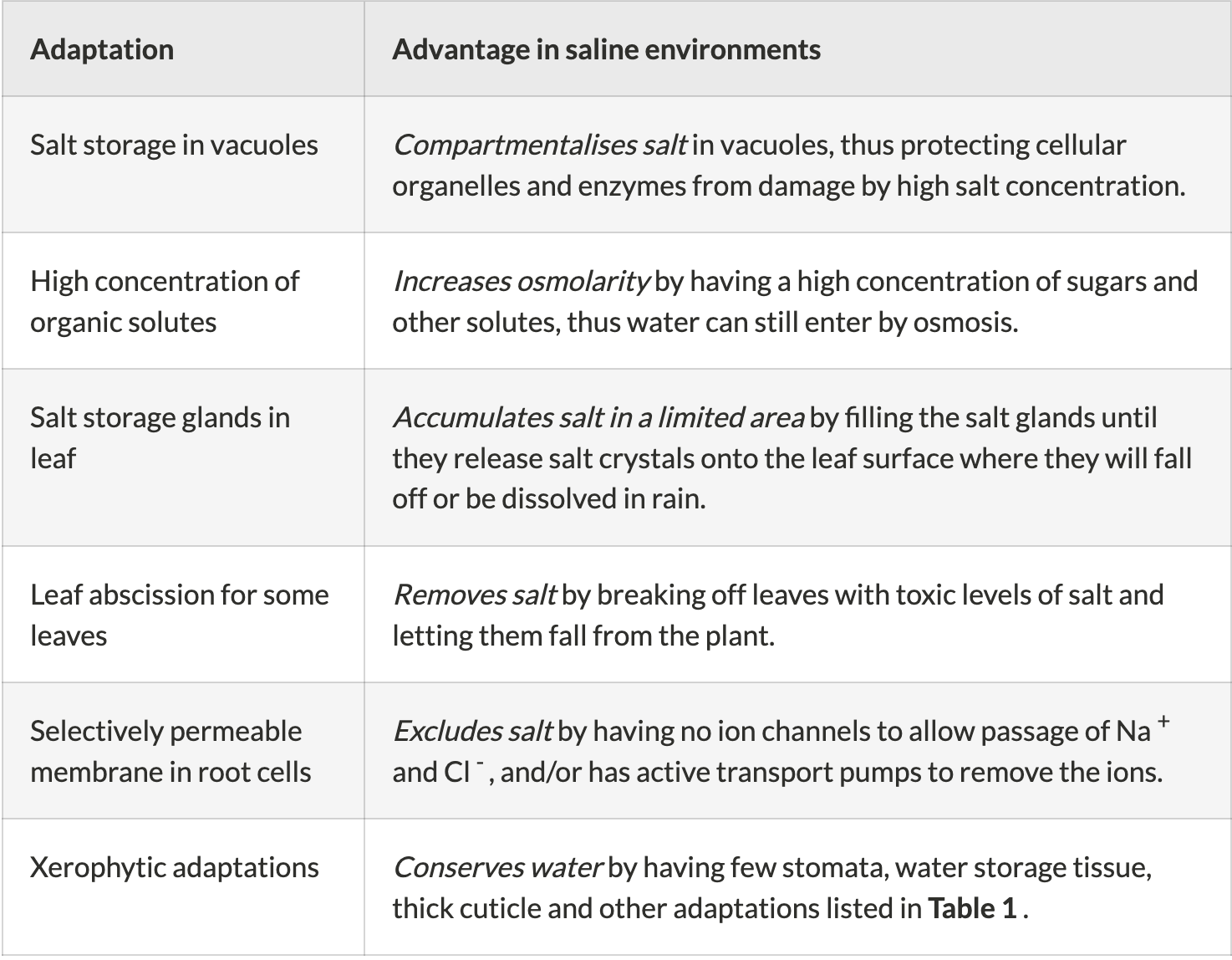
33
New cards
give an example of 1 halophyte
Mangrove trees - rey mangrove leaves have salt glands that excrete salt crystals. Red mangroves have root cell membranes that mostly exclude salt ions, and they also store salt in vacuoles that keep the cell turgid while protecting the cellular mechanisms from salt damage.
34
New cards
Name 4 internal factors that affect transpiration rates.
- Root to shoot ratio
- Surface area of leaves
- Number of stomata per unit leaf area
- Leaf structure, for example, the presence of hair or thick waxy cuticle.
- Surface area of leaves
- Number of stomata per unit leaf area
- Leaf structure, for example, the presence of hair or thick waxy cuticle.
35
New cards
name 5 external factors that affect the rate of transpiration
+Water availability.
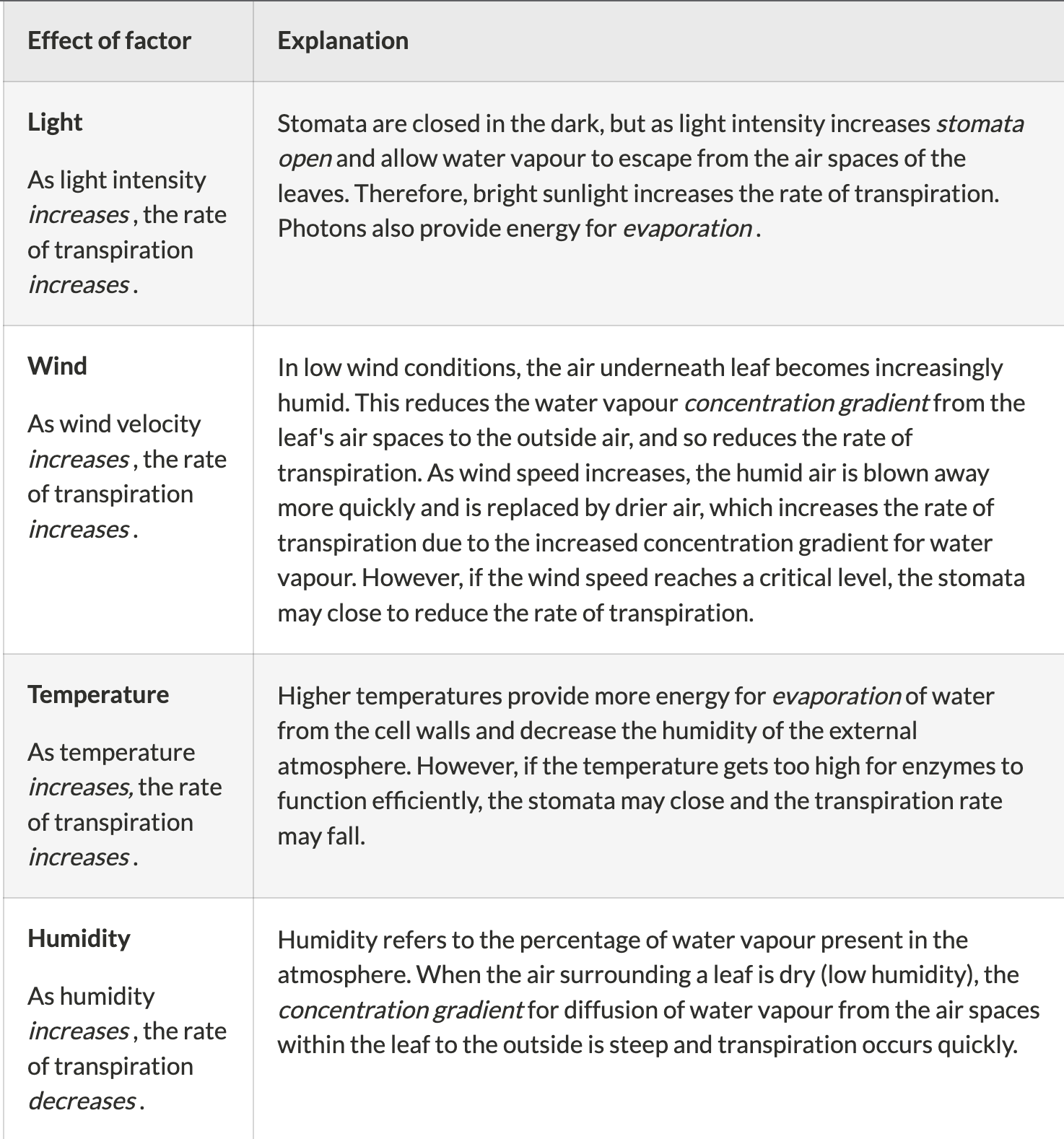
36
New cards
there are potometers.