MCB EOT EXAM
1/470
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
471 Terms
Light Microscopy
Uses light to visualize live or fixed specimens.
Bright Field Microscopy
Observes live, unstained cells using light phase shifts.
Chromogenic Stains
Dyes used to enhance contrast in fixed specimens.
H & E Staining
Haematoxylin stains DNA blue/purple; eosin stains proteins pink.
Fluorescence Microscopy
Uses fluorescent dyes to visualize specific cell components.
MitoTracker
Fluorescent dye for labeling mitochondria in cells.
LysoTracker
Fluorescent dye for labeling lysosomes in cells.
Colocalisation
Presence of two fluorescent signals in the same area.
Immunofluorescence Microscopy
Combines antibodies with fluorescent tags for specific detection.

Direct Immunofluorescence
Fluorescently labeled primary antibody binds directly to target.
Indirect Immunofluorescence
Uses secondary antibodies for signal amplification.
Epitope
Antigenic determinant recognized by an antibody.
Myc Epitope
Specific epitope used for tagging proteins in studies.
Phase Contrast Microscopy
Enhances contrast using refracted and un-refracted light.
Differential Interference Contrast
Uses two light beams for enhanced contrast imaging.
Microtome
Instrument for slicing specimens into thin sections.
Paraformaldehyde
Common fixative used for preserving cellular structures.
Sensitivity in Immunofluorescence
Ability to detect low levels of target proteins.
Cost of Antibodies
Conjugated primary antibodies are more expensive than secondary.
Signal Amplification
Multiple secondary antibodies bind to enhance detection.
Cell Sorting Methods
Techniques for separating cells based on specific criteria.
Myc
A proto-oncogene acting as a transcription factor.
Epitope Tag
A peptide sequence added for antibody detection.
Recombinant DNA Technology
Method for introducing specific DNA sequences into organisms.
Permeabilization
Process to allow antibodies access to cells.
Fluorescence Microscope
Instrument for visualizing fluorescently tagged proteins.
Peroxisomes
Organelles involved in lipid metabolism and detoxification.
Cytoplasm
Fluid inside cells excluding organelles and nucleus.
PEX13
Peroxisomal membrane protein with cytoplasmic C-terminus.
Transfection
Introducing foreign DNA into eukaryotic cells.
Lipofection
DNA delivery method using lipid vesicles.
Electroporation
Technique using electric pulses to facilitate DNA entry.
Triton X-100
Detergent that permeabilizes all cellular membranes.
Digitonin
Detergent that selectively permeabilizes cholesterol-rich membranes.
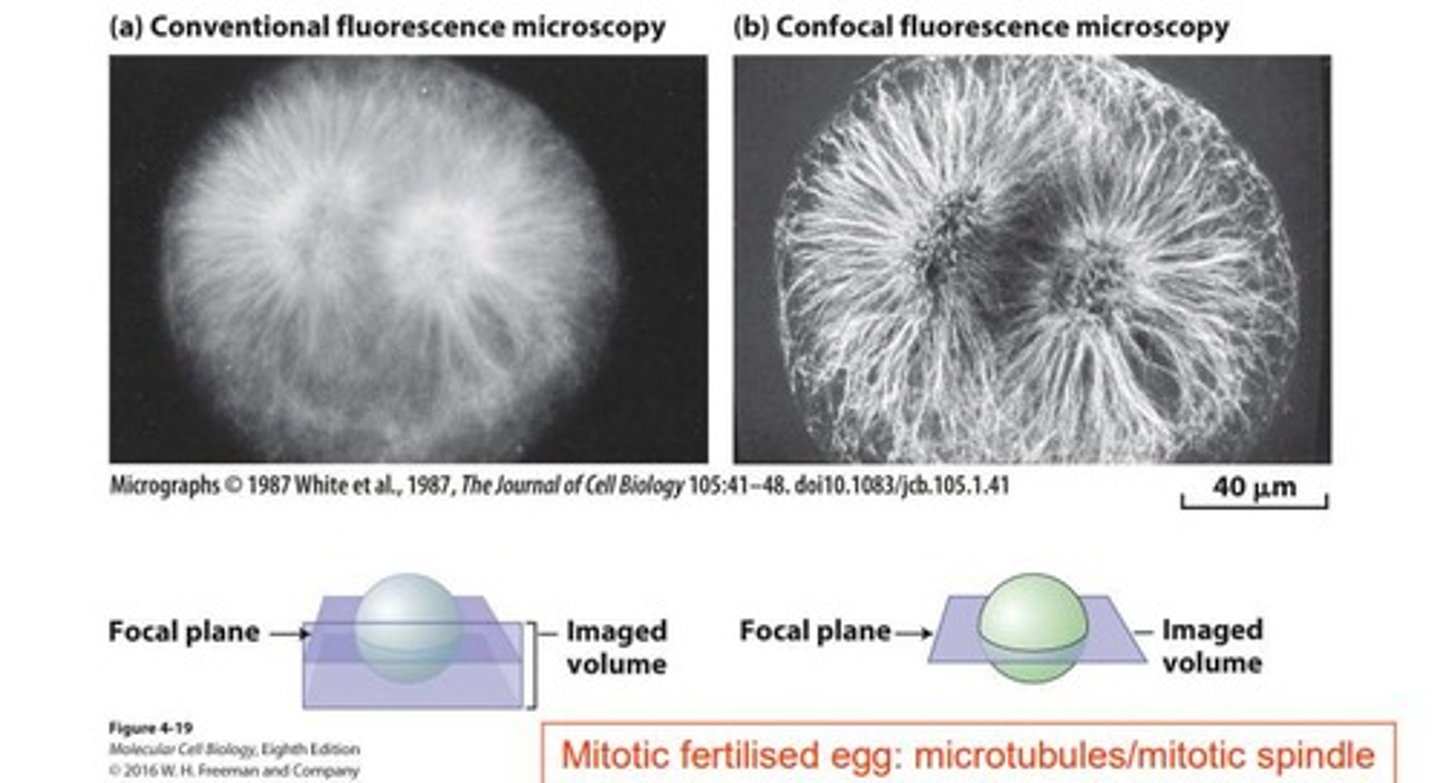
Confocal Microscopy
Technique for enhanced imaging using focused laser light.
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
Microscope for observing internal structures at high resolution.
Diaminobenzidine (DAB)
Substrate oxidized to visualize peroxisomes in microscopy.
Scanning Electron Microscope
Microscope for viewing surfaces of unsectioned specimens.
C-terminus
End of a protein with a free carboxyl group.
Localization
Determining the specific location of proteins in cells.
Antibody Access
Ability of antibodies to bind to target proteins.
Green Dots
Indicate localization of PEX13-myc in microscopy.
Confocal Aperture
Pinhole that allows light from a specific plane.
Electron Density
Variation in electron scattering used in electron microscopy.
Protein Sorting Pathways
Two main routes for directing proteins to destinations.
Protein Sorting
Directs proteins to correct cellular compartments.
Targeting Signal
Short peptide guiding proteins to locations.
Specific Receptor
Recognizes and binds targeting signals.
Translocon
Channel for proteins to traverse membranes.
Cytosolic Ribosomes
Site of protein translation in cytoplasm.
Co-translational Translocation
Translation and translocation occur simultaneously.
Post-translational Translocation
Translation completes before translocation occurs.
Nuclear Pore Complex (NPC)
Large structure facilitating nuclear protein transport.
FG Nucleoporins
Proteins forming a gel-like matrix in NPC.
Nuclear Localization Signals (NLS)
Signals directing proteins to the nucleus.
GTPase Cycle
Molecular switch regulating protein interactions.
Importin Pathway
Mechanism for nuclear import of proteins.
Mitochondrial Targeting Sequences (MTS)
Signals directing proteins to mitochondria.
Translocase of Outer Membrane (TOM)
Complex facilitating mitochondrial outer membrane translocation.
Translocase of Inner Membrane (TIM)
Complex facilitating mitochondrial inner membrane translocation.
Energy Requirement
Energy needed for protein translocation processes.
Chaperones
Assist in proper folding of precursor proteins.
Nuclear Transport Factor 2 (NTF2)
Recycles Ran protein back into the nucleus.
Ribosome Attachment
Ribosomes bind to ER for co-translational translocation.
Sorting Defects
Errors in protein sorting causing diseases.
Precursor Proteins
Proteins synthesized in cytoplasm for organelle import.
Membrane Bound Translation
Translation occurs on ribosomes attached to membranes.
Hydrophobic Gel-like Matrix
Regulates transport through the NPC channel.
TOM
Translocase of Outer Membrane for mitochondrial proteins.
TIM
Translocase of Inner Membrane for mitochondrial proteins.
Proton motive force
H^+ gradient driving mitochondrial protein import.
ATP
Energy source for chaperone function in import.
MTS
Matrix Targeting Sequence for mitochondrial proteins.
Sub-mitochondrial compartments
Different mitochondrial locations for protein targeting.
PTS1
Type 1 peroxisome targeting signal, tripeptide SKL.
Pex5
Cytosolic receptor for PTS1 signal.
PTS2
Type 2 peroxisome targeting signal near N-terminus.
Pex7
Receptor for PTS2 signal in peroxisomal import.
Pex19
Receptor for importing peroxisomal membrane proteins.
PMP70
Example of a peroxisomal membrane protein.
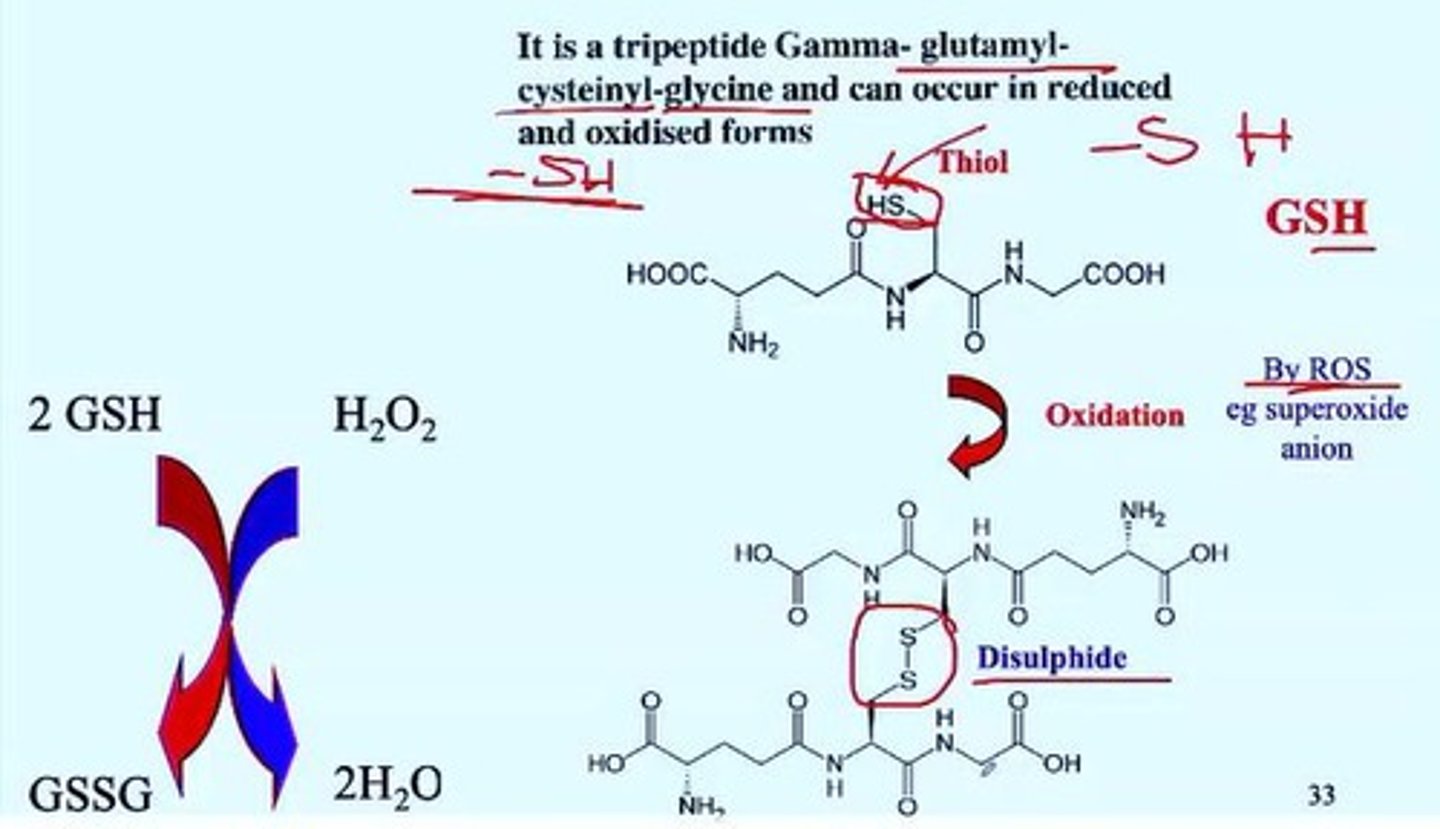
Catalase
Most abundant peroxisomal matrix protein, reduces H2O2.
Pex11
Protein required for peroxisome proliferation.
mPTS
Peroxisomal membrane targeting signal for Class I PMPs.
Pex3
Membrane anchor protein for cargo-loaded Pex19.
Zellweger syndrome
Disorder from mutations in PEX genes affecting peroxisomes.
Hyperoxaluria Type 1
Peroxisomal disorder due to protein mistargeting.
AGT
Alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase, normally sorted to peroxisomes.
Ubiquitination
Process marking Pex5 for extraction from membrane.
Pex14 and Pex13
Docking complex for Pex5 at peroxisomal membrane.
Peroxisomal ghosts
Large, empty peroxisomes due to defective import.
AGT Loss
Causes calcium oxalate excretion and kidney stones.
Peroxisomal Import
Involves folded proteins and translocon.
Cytosolic Receptor
Importin facilitates protein import into peroxisomes.
Secretory Pathway
Involves ER, Golgi, lysosomes, and plasma membrane.
Signal Sequence
Directs protein to the endoplasmic reticulum.
Amino Acid Length
Signal sequences are 16-30 amino acids long.
Positive Amino Acids
Located near the N-terminus of signal sequences.
Hydrophobic Residues
Bind signal recognition particle during protein targeting.
Signal Peptidase
Cleaves signal peptide from precursor proteins.
Glycosylation
N-linked glycosylation is dolichol-mediated.