Physics Exam 2
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
What state of motion did Aristotle attribute to Earth?
Natural motion
What did Galileo discover in his legendary experiment on the Leaning Tower of Pisa?
He found that objects of various weight, when released at the same time, fell together and hit the ground at the same time.
Is inertia the reason for moving objects maintaining motion or the name given to this property?
It's the name given to the property of objects resisting a change in their motion
What type of path does a moving object follow in the absence of force?
A straight horizontal path.
Why do we say that force is a vector quantity?
Because force has both magnitude and direction
What is the net force on a bag pulled down by gravity with a force of 18 newtons and pulled upward by a rope with a force of 18 newtons?
Zero
State the equilibrium rule for forces in symbolic notation
∑F=0
When you stand at rest on a bathroom scale, how does your weight compare with the support force by the scale?
It is equal. The force downward is supported by the scale spring and the scale spring pushes back on you as much as you are pushing down on it, and that is how it reads your weight.
What is the net force on an object in either static or dynamic equilibrium?
Nf= 0
What concept was not understood in the 16th century when people couldn't conceive of a moving earth?
The concept of inertia wasn't understood.
Rank the net forces on the blocks from least to most in the four situations A, B, C, and D.
A)10N to the left 5N to the right
B) 7N to the left 3N to the right
C) 12N to the left 4N to the right
D) 3N to the left 3N to the right
DBAC
Was it Galileo or Newton who first proposed the concept of inertia?
Galileo
A space probe may be carried by a rocket into outer space. What keeps the probe moving after the rocket no longer pushes it?
Inertia
Which of the following are scalar quantities, which are vector quantities, and which are neither? Force, Age, Acceleration, Temperature
Vector, Scalar, Vector, Vector
If the strong man in the preceding exercise exerts a downward force of 800N on the rope, how much upward force is exerted on the back?
800N
How many significant forces act on a book at rest on a table? Identify the forces
Two. The downward force (gravity), and the upward force (support force). There is zero net force since it is at equilibrium.
Two people each pull with a force of 300N on a rope in a tug-of-war. What is the net force of the rope? How much force is exerted on each person by the rope?
Net force is 0. Force exerted on each person is 300N
Suppose that you're in a moving car and the motor stops running. You step on the breaks and slow the car to half speed. If you release your foot from the breaks, will the car speed up a bit, or will it continue at half speed and slow due to friction?
It will continue at half speed and slow due to friction because of the law of inertia
Consider the normal force on a book at rest on a tabletop. If the table is tilted so that the surface forms an inclined plane, will the magnitude of the normal force change? If so, how?
The magnitude changes, it becomes less.
What class of motion, natural or violent, did Aristotle attribute to motion of the Moon?
Natural
What relationship between the Sun and Earth did Copernicus formulate?
Copernicus stated that Earth circles the Sun
What did Galileo discover about moving bodies and force in experiments with inclined planes?
Downward slope-speed increases
Upward slope-speed decreases
In the absence of friction or other opposing forces, a horizontally moving object would continue moving indefinitely
How does Newton's first law of motion relate to Galileo's concept of inertia?
Galileo stated that it was the tendency of things to resist changes in motion. Newton refined it by adding: "Every object continues in a state of rest or uniform speed in a straight line unless acted on by a nonzero net force"
What is the net force on a cart that is pulled to the right with 100 lbs. of force and to the left with 30 lbs. of force?
70 pounds to the right
According to the parallelogram rule, what quantity is represented by the diagonal of a constructed parallelogram?
The diagonal shows the resultant-the sum of two or more vectors
Figure 2.11 (page 29). If the ropes were vertical, with no angle involved, what would be the tension in each rope?
The tension on each rope would be half her weight
What is the net force on an object that is pulled with forces of 80 newtons to the right and 80 newtons to the left?
The net force is zero newtons
What does it mean to say that something is in mechanical equilibrium?
When the net force on something is zero
Consider a book weighs 15 N at rest on a flat table. How many newtons of support force does the table provide? What is the net force on the book in this case?
The number of newtons of support force must equal the weight of the book=15 N.
The net force on the book is zero
A bowling ball at rest is in equilibrium. Is the ball in equilibrium when it moves at constant speed in a straight-line path?
yes
If you push on a crate with a force of 100 newtons and it slides at constant velocity, how great is the friction acting on the crate?
The friction is 100 N
A bird sitting in a tree is traveling at 30 km/s relative to the faraway Sun. When the bird drops to the ground below, does it still move at 30 km/s, or does this speed become zero?
It moves at 30 km/s relative to the sun
Is acceleration proportional to net force, or does acceleration equal net force?
acceleration and net force are proportional to each other. Notated as acceleration ~ net F
Which is more fundamental: mass or weight? Which varies with location?
Mass is more fundamental than weight. Weight varies with location, mass does not vary.
Fill in the blanks: Shake something to and fro and you’re measuring its _______. Lift it against gravity and you’re measuring its _______.
mass, weight
Fill in the blanks: The Standard International unit for mass is the _____. The Standard International unit for force is the ______.
kilogram (kg), pounds (lb)
What is the approximate weight of a quarter-pound hamburger after it is cooked?
about 1 newton (1N)
What is the weight of a 1-kilogram brick resting on a table?
about 10 N
In the string-pull illustration in Figure 4.8, a gradual pull of the lower string results in the top string breaking. Does this occur because of the ball’s weight or its mass?
The string breaks because of the weight of the ball
In the string-pull illustration in Figure 4.8, a sharp jerk on the bottom string results in the bottom string breaking. Does this occur because of the ball’s weight or its mass?
It occurs because of the mass of the ball. The ball's inertia resists change
Is acceleration directly proportional to mass, or is it inversely proportional to mass? Give an example.
Acceleration is inversely proportional to mass
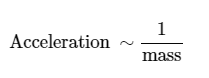
State Newton’s second law of motion.
the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, is in the direction of the net force and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
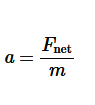
If we say that one quantity is directly proportional to another quantity, does this mean they are equal to each other? Explain briefly, using mass and weight as an example.
No. Weight is proportional to mass, but not equal to mass
If the net force acting on a sliding block is somehow tripled, what happens to the acceleration?
The acceleration decreases to ¹/₃
If the mass of a sliding block is somehow tripled at the same time the net force on it is tripled, how does the resulting acceleration compare with the original acceleration?
the acceleration remains the same
How does the direction of acceleration compare with the direction of the net force that produces it?
Acceleration is in the direction the net force.
When you push horizontally on a crate on a level floor that doesn’t slide, how great is the force of friction on the crate?
it takes more force to get it going to keep it sliding
the force of friction is opposite and equal to your push
As you increase your push, will friction on the crate increase also?
yes. As you increase your push, friction also increases just as much
(Ex: if you push with 70 N, the friction builds up to become 70 N)
Once the crate is sliding, how hard do you push to keep it moving at constant velocity?
Push with force equal to and opposite the friction force. Dynamic friction is less than static friction and will take less force to keep the object sliding)
Which is normally greater: static friction or sliding friction on the same object?
static friction is greater
How does the force of friction for a sliding object vary with speed?
The friction force remains approximately the same whether it is high speed or low speed. Not dependent on speed
Does fluid friction vary with speed?
yes
When you push against a wall with your fingers, they bend because they experience a force. Identify this force.
the force of the wall pushing back on your fingers
A boxer can hit a heavy bag with great force. Why can't he hit a piece of tissue paper in midair with the same amount of force?
because there is not enough mass in the tissue paper to react to the force of the punch by the boxer
How many forces are required for an interaction?
two forces
State Newton's third law of motion
Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first or, to put it simply: to every action there is always an opposed equal reaction
Consider hitting a baseball with a bat. If we call the force on the bat against the ball the action force, identify the reaction force
the reaction force is the force of the ball against the bat
If the system of only the orange (in a cart), is there a net force on the system when the apple pulls?
yes, there is the action of the apple on the orange
If the system is considered to be the apple and the orange together, is there a net force on the system when the apple pulls (ignoring friction on the floor)?
no, the pair of forces is internal to the apple-orange system
To produce a net force on a system, must there be an externally applied net force?
yes, there must be an externally applied force
Consider the system of a single football. If you kick it, is there a net force to accelerate the system? If a friend kicks it at the same time with an equal and opposite force, is there a net force to accelerate the system?
yes, the net force is provided by contact with your foot. If two opposite and equal forces act on the ball, the net force on it is zero and it will not accelerate
Earth pulls down on you with a gravitational force that you call your weight. Do you pull up on the Earth with the same amount of force?
yes
If the forces that act on a cannonball and the recoiling cannon from which it is fired are equal in magnitude, why do the cannonball and cannon have very different acceleration?
the cannon has more mass than that of the cannonball making its acceleration less
Identify the force that propels a rocket.
the rocket is propelled by the reaction force exerted by the material it fires
How does a helicopter get its lifting force?
the helicopter gets its lifting force by pushing air downward, in which case the reaction is the air pushing the helicopter upward
Can you physically touch a person without that person touching you with the same amount of force?
no
Fill in the blanks: Newton's first law is often called the law of _________; Newton's second law is the law of ________; and Newton's third law is the law of ___________ and ___________.
inertia, acceleration, action-reaction
Which of Newton's three laws focuses on interactions?
Newtons third law
How great is the force of friction acting on a shoe at rest on an incline compared with the resultant of the vectors mg and N?
The friction's magnitude is equal to the resultant of N and mg when the shoe remain at rest. The sum of all forces equals zero.
How does the magnitude of the vertical component of velocity for a ball tossed at an upward angle change as the ball travels upward? How about the horizontal component of velocity when air resistance is negligible?
How does the magnitude of the vertical component of velocity for a ball tossed at an upward angle change as the ball travels upward? How about the horizontal component of velocity when air resistance is negligible?
What is meant by the term vector resolution?
A vector can be broken into two components at right angles that add together to make the original vector.
What happens to the magnitude of the normal vector on a block resting on an incline when the angle of the incline increases?
The magnitude of the normal vector decreases.
What did Newton discover about gravity?
Newton discovered the gravity extends beyond earth- that gravity is universal.
What is the Newtonian synthesis?
The union of terrestrial laws and cosmic laws
In what sense does the Moon “fall”?
The moon falls in the sense that it falls away from the straight line it would follow if there were no forces acting on it
State Newton’s law of universal gravitation in words. Then do the same with one equation.
Everybody attracts every other body with a force that, for any two bodies, is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance separating them. F= mass1 x mass2/distance²
What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between two 1-kg bodies that are 1 m apart?
6.67 × 10-11
What is the magnitude of Earth’s gravitational force on a 1-kg body at Earth’s surface?
10 N
When G was first measured by Henry Cavendish, newspapers of the time hailed his experiment as the “weighing Earth experiment.” Why?
Because it gives the mass of the entire planet, with all its oceans, mountains, and inner parts yet to be discovered.
How does the force of gravity between two bodies change when the distance between them is doubled?
The force decreases to ¼ of its initial value.
How does the thickness of paint sprayed on a surface change when the sprayer is held twice as far away?
The thickness of the paint sprayed decreases by ¼.
Where do you weigh more: at the bottom of Death Valley or atop one of the peaks of the Sierra Nevada? Why?
You are closer to Earth's center at the bottom of Death Valley therefore you weigh more there than at the top peaks of Sierra Nevada.
Would the springs inside a bathroom scale be more compressed or less compressed if you weighed yourself in an elevator that was accelerating upward? Downward?
The springs inside a bathroom scale would compress more if I weighed myself in an elevator that accelerates upward. If it accelerated downward then they would compress less.
Would the springs inside a bathroom scale be more compressed or less compressed if you weighed yourself in an elevator that was moving upward at constant velocity? Downward at constant velocity?
It would be the same because there is no acceleration.
When is your weight measured as mg?
For a non-accelerating mass near the surface of Earth
Give an example of when your weight is greater than mg. Give an example of when your weight is zero.
The weight is more than mg when it is accelerating upward, and it is zero when it is in free fall
Why are International Space Station occupants weightless when they are firmly in the grip of Earth’s gravity?
Occupants of the ISS experience weightlessness because they are in a state of continuous free fall towards Earth, with the ISS's horizontal velocity keeping it in orbit. Despite the sense of weightlessness, Earth's gravity firmly holds the ISS in its grip, as gravity is what maintains its stable orbit around the planet.
Do tides depend more on the strength of gravitational pull or on the difference in strengths? Explain.
Tides depend more on the strength of gravitational pull.
Why do both the Sun and the Moon exert a greater gravitational force on one side of Earth than on the other?
Because the sun is half effective as the as the moon, the sun pulls 180 times harder on earth than the moon, sun pulls almost as hard on the far side of earth as it does on the near side. The moon's force gets weaker with distance, the gravitational force between the earth & moon is stronger on the side of earth nearer to the moon than on the opposite side of the earth.
Which has the higher tides: spring tides or neap tides?
Spring tides are higher, because the tides from the Moon and Sun add together
Do tides occur in the molten interior of Earth for the same reason that tides occur in the oceans?
Yes, but earth's tides are much smaller
Why are all tides greatest at the time of a full Moon or new Moon?
Because the pull of the Sun and the Moon work together
Would a torque on the Moon occur if the Moon were spherical, with both its center of mass and center of gravity in the same location?
Because the elongated Moon's center of gravity is slightly displaced from its center of mass
What is a gravitational field, and how can its strength be measured?
It is a force field on any body with mass, its strength is the force per unit mass on a test mass.
What is the magnitude of the gravitational field at Earth’s center?
zero
For a planet of uniform density, how would the magnitude of the gravitational field halfway to the center compare with the field at the surface?
The gravitational field halfway to the center will be half of the gravitational field at the surface
What would be the magnitude of the gravitational field anywhere inside a hollow, spherical planet?
Anywhere inside a hollow planet the gravitational field of the planet would be zero
Newton viewed the curving of the path of a planet as being caused by a force acting on the planet. How did Einstein view the curved path of a planet?
its path along the curved space (due to gravity) around an object instead of gravitational attraction as Newton saw it
If Earth shrank but there was no change in its mass, what would happen to your weight at the surface?
weight would increase
What happens to the strength of the gravitational field at the surface of a star that shrinks?
The strength of the gravitational field would become stronger if the star kept shrinking.