M1 | Histopathology of Dental Caries Pt. 2
1/130
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Enamel Caries | Dentin Caries | Root Caries
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
ENAMEL
usual site of initial lesion
gingival recession
unless dentin or cementum becomes exposed by [BLANK], then the attack will proceed there
initial lesion
earliest evidence of enamel caries lesion
white spots
partially or totally disappear visually when the enamel is wet; “suddenly” appeared
hypocalcified enamel
affected less by drying and wetting; developed slowly or long term
facial and lingual surfaces of teeth
initial caries is usually observed in:
5 seconds
chalky white, opaque areas can be seen after drying the tooth for:
desiccated
initial lesion is seen only when the tooth surface is:
demineralization
areas of enamel lose their translucency because of the extensive subsurface porosity caused by
subsurface of enamel
the most external part of enamel comes in contact with calcium, phosphate and brushing action; hence it is not much affected by demineralization unlike:
ICDAS CODE 1 or ADA INITIAL CARIES
classification of initial lesion in ICDAS and ADA CSS
advanced lesion
irregular surface that is rougher than the unaffected normal enamel
ball ended instrument
advance lesion has softened chalky enamel that can be chipped away but should be kept for it to be remineralized again, so this instrument is used
active caries
what type of caries is advanced lesion a sign of?
surface enamel
affected by advance lesion
porosities and small cavitation
advanced lesion is different from the beginning, it has:
topical fluoride
treatment for advanced lesion
ICDAS CODE 2 and 3
classification of advanced lesion in ICDAS
pits and fissures caries
what kind of enamel caries is this?
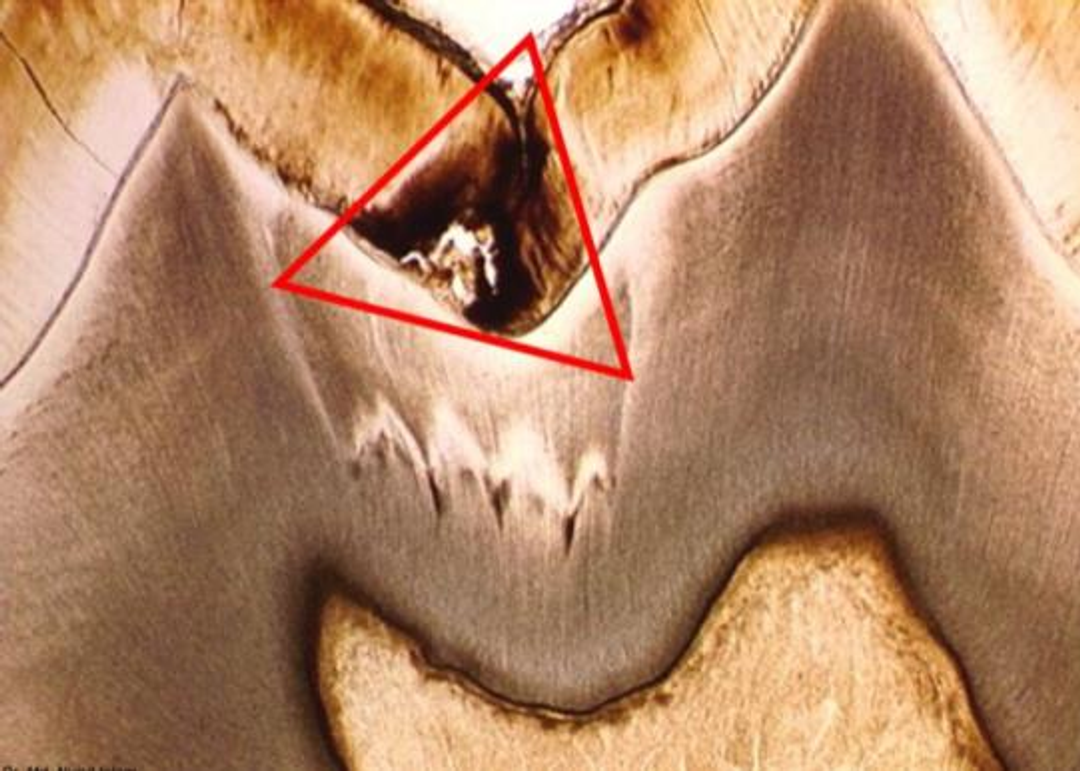
pyramidal, triangular or conical
shape of pits and fissures caries
going towards the pits and fissures
apex of pits and fissures caries
going to the DEJ
base of pits and fissures caries
smooth surface caries
what kind of enamel caries is this?
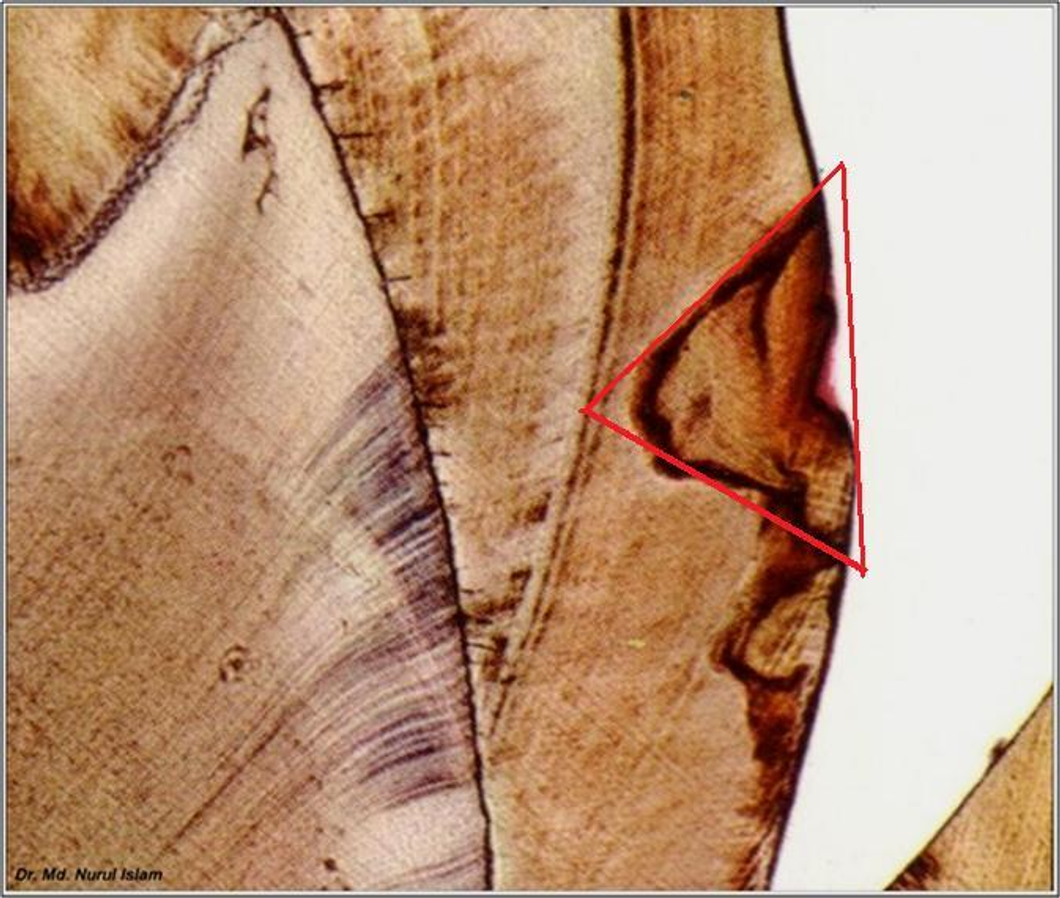
pyramidal, triangular or conical
shape of smooth surface caries
going to the DEJ
apex of smooth surface caries
going to the surface enamel
base of smooth surface caries
proximal caries
most common caries that form on the smooth surfaces because it is between adjacent teeth; thus it is protected from: mastication, tongue movement or salivary flow
plain transmitted light
polarized light-clearer picture
smooth surface caries can be viewed microscopically in:
pits and fissures caries
smooth surface caries
enamel caries that follow the direction of the enamel rods
early submicroscopic lesion
phase of non-bacterial enamel crystal destruction
cavity formation
bacterial invasion of enamel
undermining of enamel
five stages of enamel caries
subsurface enamel
once affected by the acid does not remineralized as much as the exposed enamel, hence they are affected greatly
carbohydrates
acid producing microorganism will act upon:
demineralization
metabolized carbohydrates result in acid that will cause:
laterally
demineralization will cause microcavitation for caries with MGs to enter the tooth, subsequently DEJ and spread:
smooth surface enamel (proximal)
zones in enamel caries are found and more appreciated in:
ZONE 4 | Surface Zone
ZONE 3 | Body of the Lesion
ZONE 2 | Dark Zone
ZONE 1 | Translucent Zone
four zones in enamel caries
ZONE 4 | Surface Zone
ZONE OF ENAMEL CARIES
less demineralized
outermost zone; most superficial zone
calcium and phosphorus
zone 4 of enamel caries has the highest amount of mineral content with saliva and biofilm rich in:
plaque and saliva
zone 4 of enamel caries is the area of active re-precipitation of minerals derived from both:
9.9%
mineral reduction in ZONE 4 | Surface Zone
less than 5%
pore volume in ZONE 4 | Surface Zone
ZONE 3 | Body of the Lesion
ZONE OF ENAMEL CARIES
area with greatest demineralization due to marked band of Retzius
24%
mineral reduction in ZONE 3 | Body of the Lesion
10-25% in central part; 5% at the periphery
pore volume in ZONE 3 | Body of the Lesion
relatively unaffected surface layer and the dark zone
ZONE 3 | Body of the Lesion lies between the:
negative birefringence
ZONE 3 | Body of the Lesion is the zone of:
penetrated some way into the dentin
the surface zone remains intact and also well mineralized because it is a site were calcium and phosphate ion released by subsurface dissolution, become reprecipitated, eventually the surface zone is demineralized usually at the stage when the lesion has:
ZONE 2 | Dark Zone
ZONE OF ENAMEL CARIES
a result of demineralization that appears dark brown with presence of small pores in ground section surrounding the body of the lesion and lies adjacent to the translucent zone
dark brown
color of ZONE 2 | Dark Zone
body of the lesion
ZONE 2 | Dark Zone surrounds the:
translucent zone
ZONE 2 | Dark Zone lies adjacent to:
85-90%
ZONE 2 | Dark Zone has positive birefringence in [BLANK] of the lesions which may be due to the arrest of microorganism
2-4% of spaces
pore volume in ZONE 2 | Dark Zone
6% per unit volume
mineral reduction in ZONE 2 | Dark Zone
“positive zone”
ZONE 2 | Dark Zone is usually present thus referred to as:
ZONE 1 | Translucent Zone
ZONE OF ENAMEL CARIES
not always present
zone of reaction found in enamel
white area adjacent to the dark zone
lies at the advancing front of the lesion
slightly more porous than sound enamel
advancing front of the lesion
translucent zone lies at the:
prism boundaries and other junctional sites
spaces or pores created in the tissue at zone 1 of enamel caries are located at:
white opaque
earliest visible changes of early lesion in proximal
lateral walls of the fissure
initial lesions of pits and fissures caries develop on the
remineralization of enamel surface
initial cavitation of the opposing walls of the fissure is not seen on the occlusal surface due to:
pits and fissures caries
more tubules will be involved because its base going to the DEJ is wider and will spread laterally
what produce greater cavitations as compared to smooth surface caries?
why?
A | progression of pits and fissures caries
The initial lesions develop on the lateral walls of the fissure.
Demineralization follows the direction of the enamel rods, spreading laterally as it approaches the dentinoenamel junction (DEJ).
B | progression of pits and fissures caries
Soon after the initial enamel lesion occurs, a reaction can be seen in the dentin and pulp.
Forceful probing of the lesion at this stage can result in damage to the weakened porous enamel and accelerate the progression of the lesion.
Clinical detection at this stage should be based on observation of discoloration and opacification of the enamel adjacent to the fissure.
These changes can be observed by careful cleaning and drying of the fissure.
C | progression of pits and fissures caries
Initial cavitation of the opposing walls of the fissure cannot be seen on the occlusal surface.
Opacification can be seen that is similar to the previous stage.
Remineralization of the enamel because of trace amounts of fluoride in the saliva may make progression of pit-and-fissure lesions more difficult to detect.
D | progression of pits and fissures caries
Extensive cavitation of the dentin and undermining of the covering enamel darken the occlusal surface
DENTIN CARIES LESION
V-shaped in cross section with a wide base at the DEJ and the apex directed to the pulpal cavity
presence and orientation of dentinal tubules
less minerals, more organic content as compared to enamel
area of dentin would have cavitation later on
dentin caries lesion advance more rapidly than enamel caries lesion because:
dentinal tubules
provide a pathway for the ingress of bacteria and egress of minerals
DEJ’s lower mineral content as compared to primary dentin
“when enamel demineralization advances to the DEJ, rapid lateral spread or expansion of the caries lesion along the DEJ may occur if there is bacterial contamination” this was attributed to:
DEJ’s high concentration of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs)
“when enamel demineralization advances to the DEJ, rapid lateral spread or expansion of the caries lesion along the DEJ may occur if there is bacterial contamination” this is attributed to:
area of the DEJ
high concentration of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) can be found in the:
Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs)
enzymes related to tissue healing/re-modelling and now implied in dentin caries lesion progression
beaded dentin
oblong cleft
transverse cleft
seen in advance dentin caries:
beaded dentin
string of pearls
length of dentinal tubules
beaded dentin is found within the:
small beads on string
microscopic view of beaded dentin:
1 dentinal tubule along its length
affected in beaded dentin
distension on the walls of dentinal tubules
seen in beaded dentin
oblong cleft
2 or more dentinal tubules will be affected, coalesce or fuse because of MGs that will result in one big cavity or area with MGs
adjacent dentinal tubules will have the same condition as the beaded dentin
parallel to the direction of dentinal tubule
the center will be the most affected - necrotic area
2 or more dentinal tubules
affected in oblong cleft
direction of dentinal tubule
oblong cleft is parallel to the:
center
which area will be the most affected (most necrotic) in oblong cleft?
transverse cleft
area perpendicular to dentinal tubules
lateral branching of the dentinal tubules
microorganism inside the dentinal tubules will occupy that area
globular dentin
in transverse cleft [BLANK] is present, meaning there is not enough calcification near area of dentinal tubules
ZONE 0 | Zone of Retreating Odontoblastic Process
ZONE 1 | Zone of Fatty Degeneration of Odontoblast Process
ZONE 2 | Zone of Dentinal Sclerosis
ZONE 3 | Zone of Decalcification of Dentin
ZONE 4 | Zone of Bacterial Invasion of Decalcified but Intact Dentin
ZONE 5 | Zone of Decomposed Dentin
six zones of dentinal caries
ZONE 0 | Zone of Retreating Odontoblastic Process
ZONE OF DENTIN CARIES
not the first zone, but happens in the innermost zone before the cycle starts again
ZONE 1 | Zone of Fatty Degeneration of Odontoblast Process
ZONE OF DENTIN CARIES
preparation for sclerosis
fat globules
ZONE 1 | Zone of Fatty Degeneration of Odontoblast Process
disposition of [BLANK]
receded early sclerotic changes
fat contributes to impermeability
predisposing factor for dental sclerosis
odontoblast process
inside dentinal tubules
no sclerosis
no fatty deg. =
ZONE 2 | Zone of Dentinal Sclerosis
ZONE OF DENTIN CARIES
characterized by deposition of calcium salts in the dentinal tubules
ZONE 3 | Zone of Decalcification of Dentin
ZONE OF DENTIN CARIES
a narrow zone, receding bacterial invasion
there’s no microorganisms yet, only their byproducts
ZONE 4 | Zone of Bacterial Invasion of Decalcified but Intact Dentin
ZONE OF DENTIN CARIES
happens after they’ve been given a portal of entry via decalcification or demineralization
ZONE 5 | Zone of Decomposed Dentin
ZONE OF DENTIN CARIES
the bacteria that invaded will destroy organic substances leading to decomposition of dentin
continuous cycle of this will lead to a more visible necrotic area of dentin
proximal root surface
facial/lingual/buccal/ surface
2 possible location of root caries lesion
proximal root surface
most common area of root caries lesion
gingival recession → exposed root
concaved surface contour
occasional roughness in CEJ
proximal root surface near the cementoenamel junction is often unaffected by the action of hygiene procedures such as flossing and favor the formation of mature, cariogenic biofilm and proximal root surface caries lesions due to:
negligence in hygiene procedures (like brushing)
protection from friction during mastication
presence of cariogenic biofilm
caries form in facial/lingual/buccal root surfaces due to:
gingival recession → exposed root
concaved surface contour
occasional roughness in CEJ
root caries are caused by: