Reconstruction, Jim Crow
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
freedmen
men and women who had been slaves

Reconstruction
The process of remitting of the former confederate states to the Union
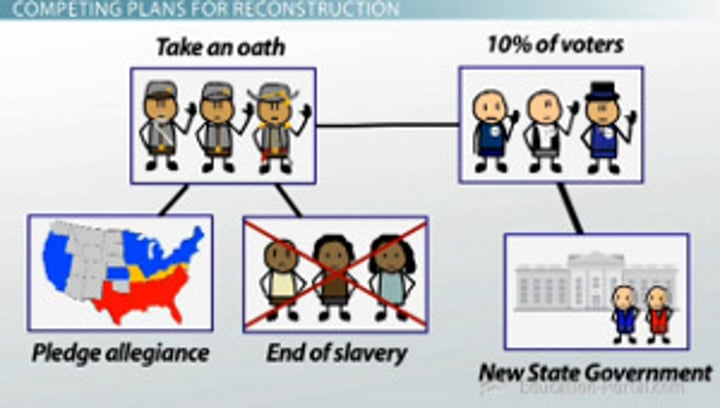
Ten Percent Plan
Lincoln's plan that allowed a southern state to form a new government after 10 percent of its voters swore an oath of loyalty to the United States
amnesty
government pardon

Wade-Davis Bill
an 1864 plan for Reconstruction that denied the right to vote or hold office to anyone who had volunteered to fight for the Confederacy

Freedmen's Bureau
government agency founded during Reconstruction to help former slaves

Thirteenth Amendment
an 1865 amendment to the United States Constitution that bans slavery throughout the nation

black codes
Southern laws that severely limited the rights of African Americans after the Civil War

Radical Republicans
members of Congress during Reconstruction who wanted to ensure that freedmen received the right to vote

Fourteenth Amendment
An amendment to the United States Constitution that guarantees equal protection of the law and rights of citizenship to all people born or naturalized in the USA, including former slaves.

Radical Reconstruction
period beginning in 1867, when the Republicans who had control in both houses of Congress, took charge of Reconstruction

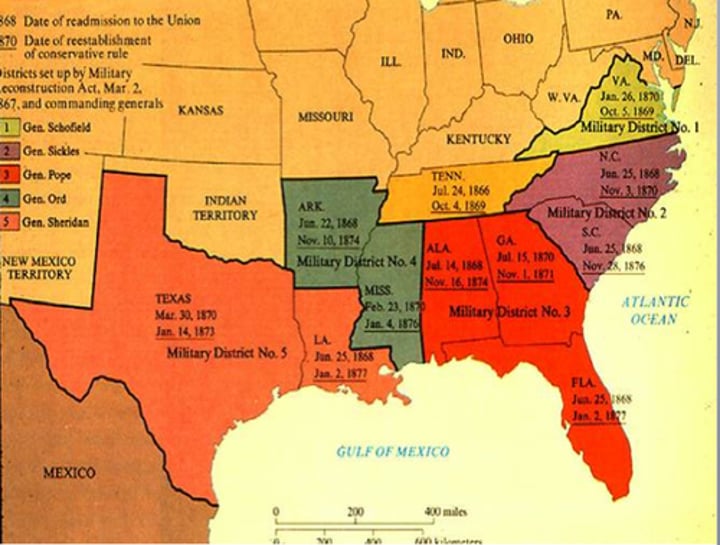
Reconstruction Act
an 1867 law that threw out the southern state governments that had refused to ratify the Fourteenth Amendment
impeach
to bring charges of serious wrongdoing against a public official

Fifteenth Amendment
Amendment to the United States Constitution that forbids any state to deny African Americans the right to vote because of race. All males 21+ can vote.

scalawag
white Southerner who supported the Republicans during Reconstruction

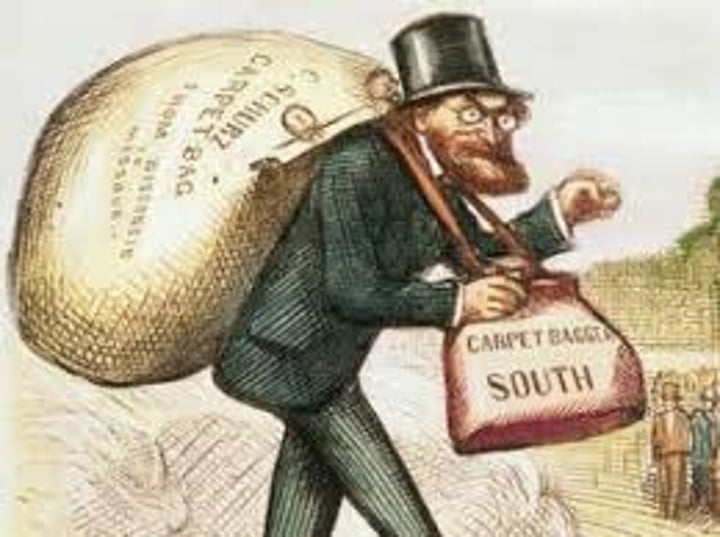
carpetbagger
uncomplimentary nick-name for a northerner who went to the South after the Civil War

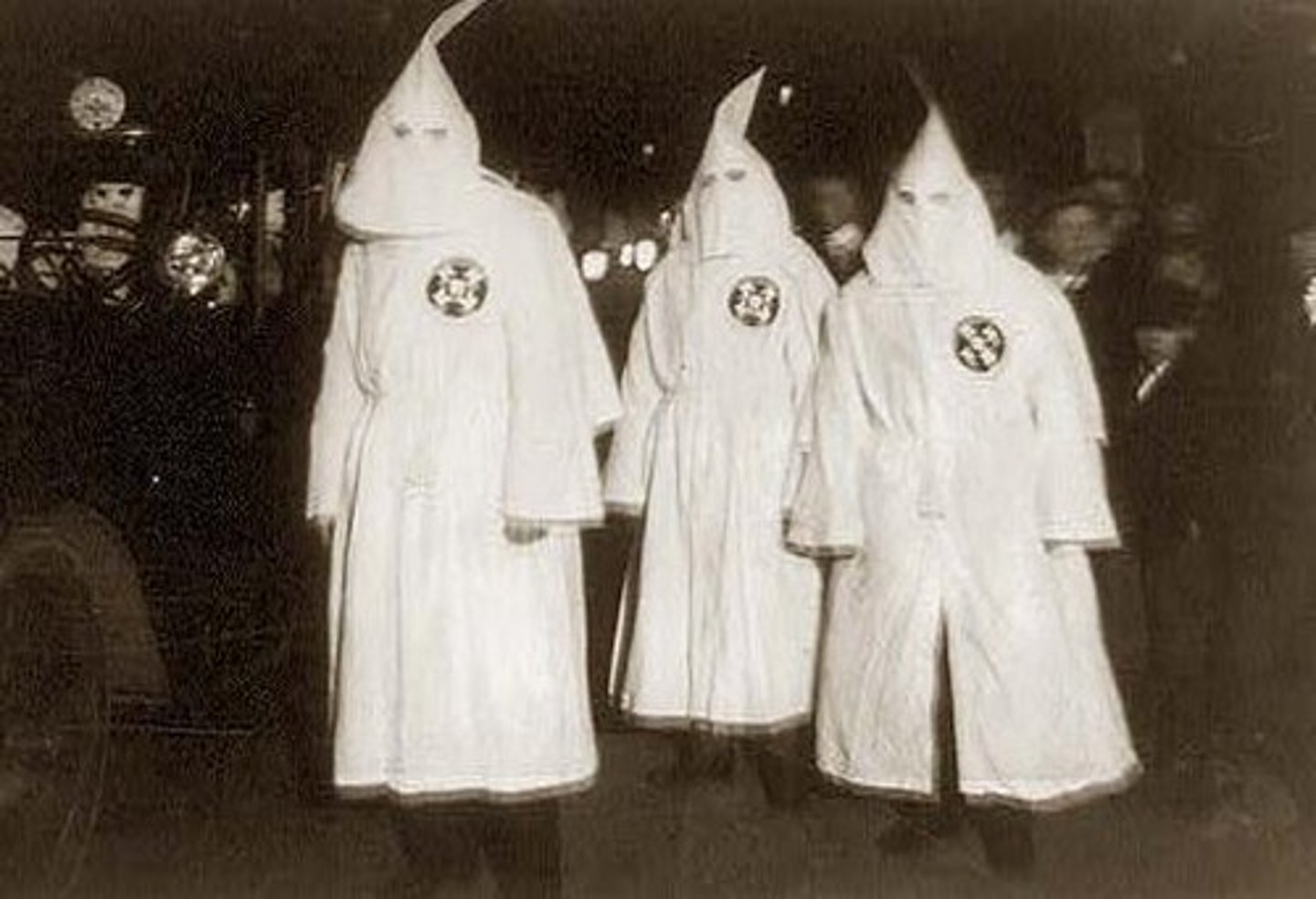
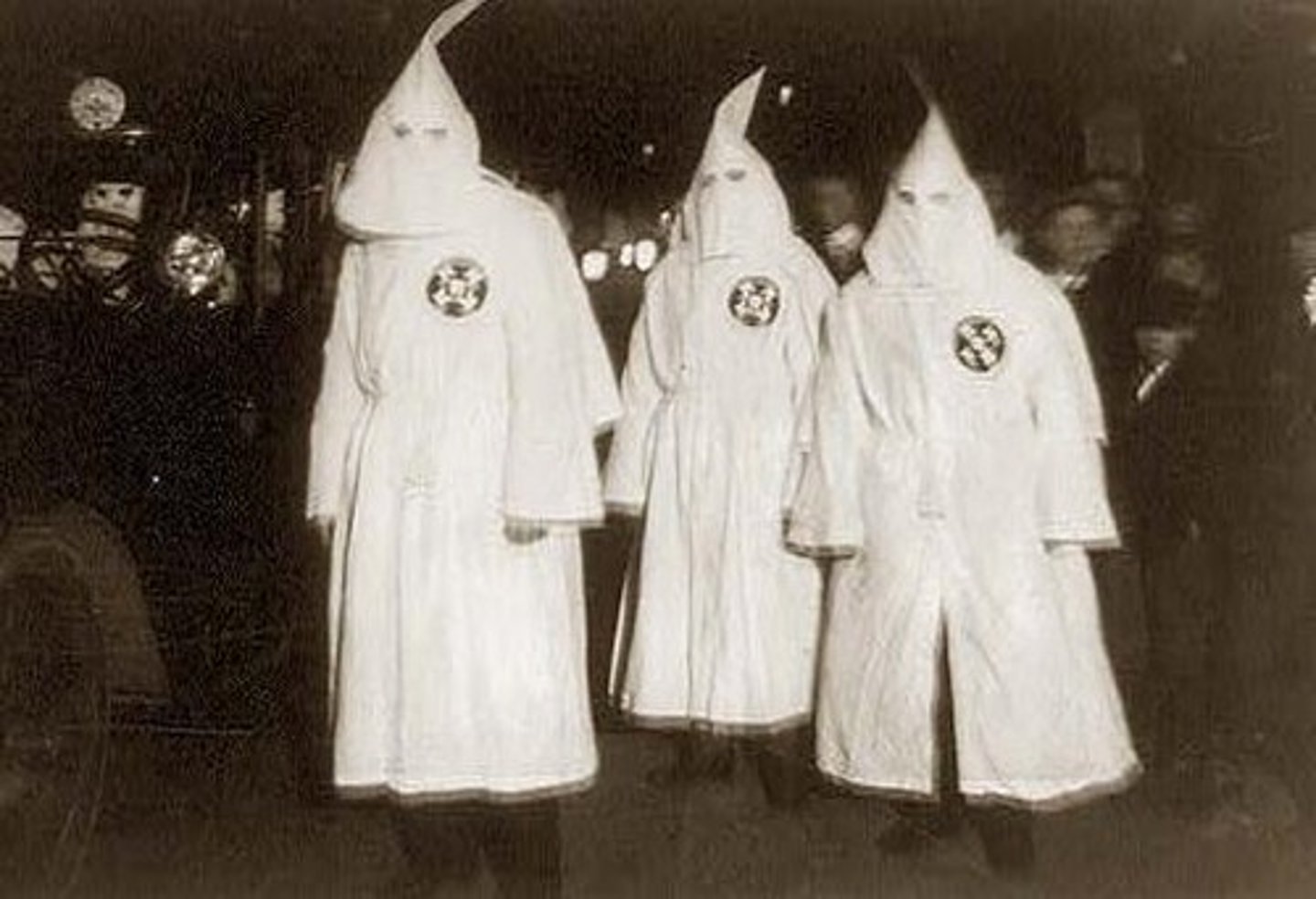
Ku Klux Klan
secret society organized after the Civil War to reassert white supremacy by means of violence

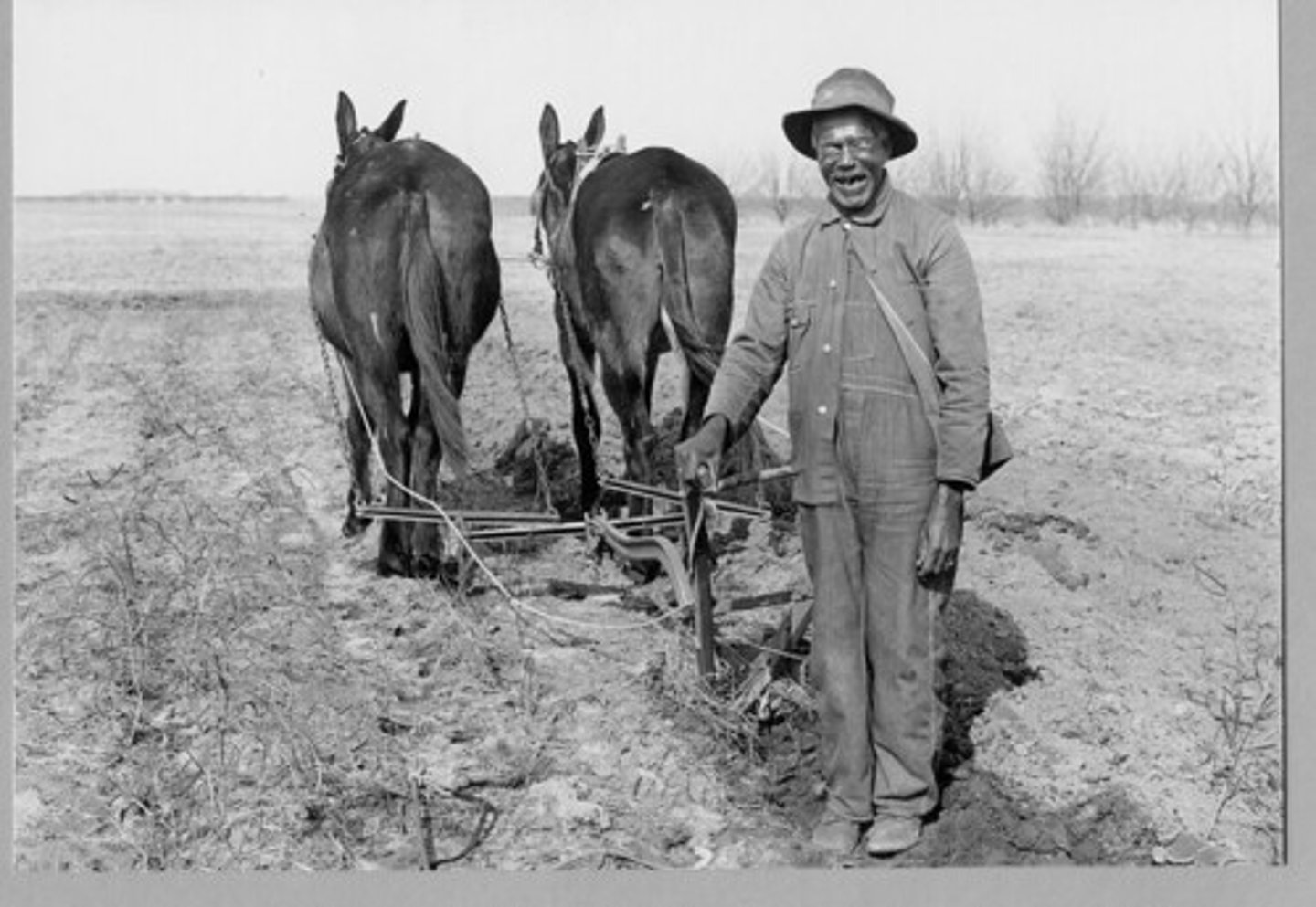
sharecropper
person who rents a plot of land from another person and farms it in exchange for a share of the crop

poll tax
tax required before a person can vote

literacy test
examination to see if a person can read and write; used in the past to restrict voting rights

grandfather clause
law that excused a voter from a literacy test if his father or grandfather had been eligible to vote on January 1, 1867; kept freedmen from voting.

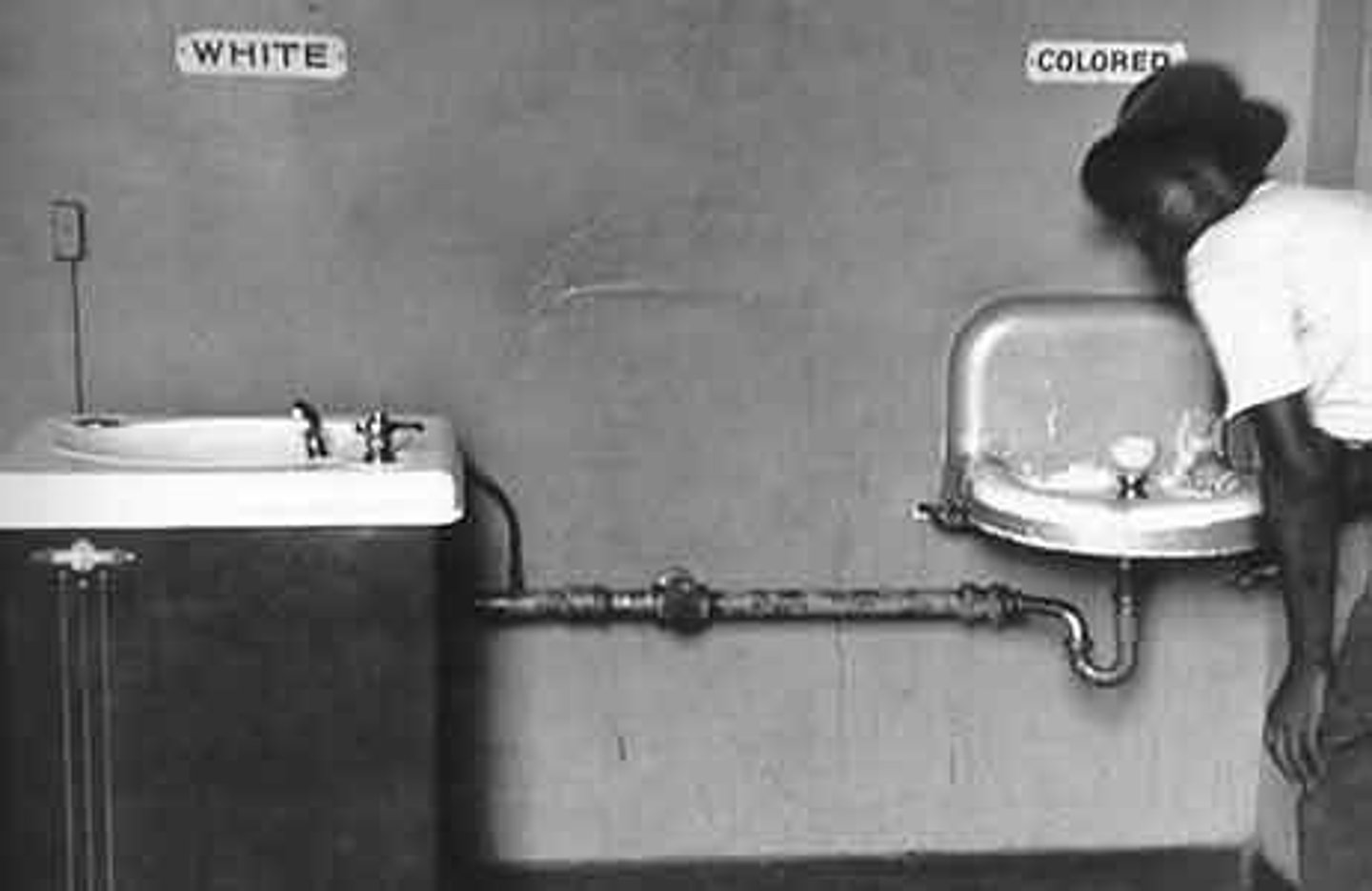
segregation
legal separation of people based on racial, ethnic, or other differences

Plessy v. Ferguson
an 1896 court case in which the United States Supreme Court ruled that segregation in public facilities was legal as long as the facilities were equal

Homestead Act of 1862
any citizen could occupy 160 acres of government land, if improvements were made to the land citizens would own the land after 5 years

Jim Crow Laws
State laws in the South that legalized segregation.

13th Amendment (FREE)
Abolished Slavery

14th Amendment (CITIZENS)
Declares that all persons born in the U.S. are citizens and are guaranteed equal protection of the laws

15th Amendment (VOTE)
Citizens cannot be denied the right to vote because of race, color, or precious condition of servitude

Literacy Test
examination to see if a person can read and write; used in the past to restrict voting rights

Grandfather Clause
Southern laws that excluded African Americans from voting by restricting the right to vote only to those whose grandfathers had voted before 1865

Poll tax
Southern method of excluding African Americans from voting by requiring payment of a tax prior to voting

Plessy v. Ferguson
Supreme court ruled that segregation of public places and facilities were legal as long as the facilities were equal - "separate but equal"

Ku Klux Klan
A secret society created by white southerners in 1866 that used terror and violence to keep African Americans from obtaining their civil rights.

Factors that contributed to growth of institutionalized Racism in the South
1. Withdrawal of federal troops from Southern states
2. Passage of Plessy v. Ferguson
3. Southern Democrats regaining control of government
Black Codes
Southern laws designed to restrict the rights of the newly freed black slaves

disenfranchise
to lose the right to vote

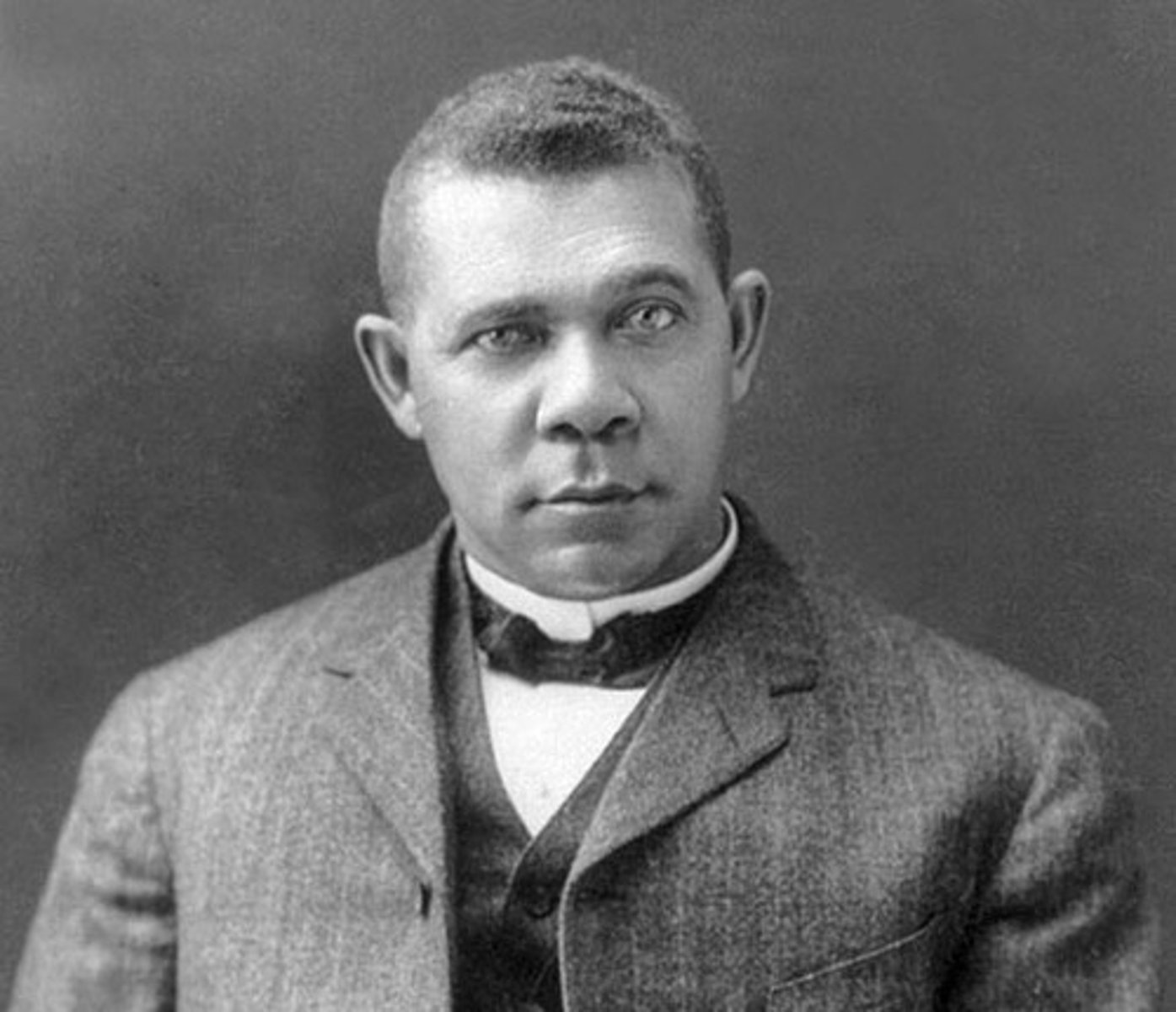
Booker T. Washington
I argued that African Americans could only demand civil and equality when they achieved economic success; founded Tuskegee Institute

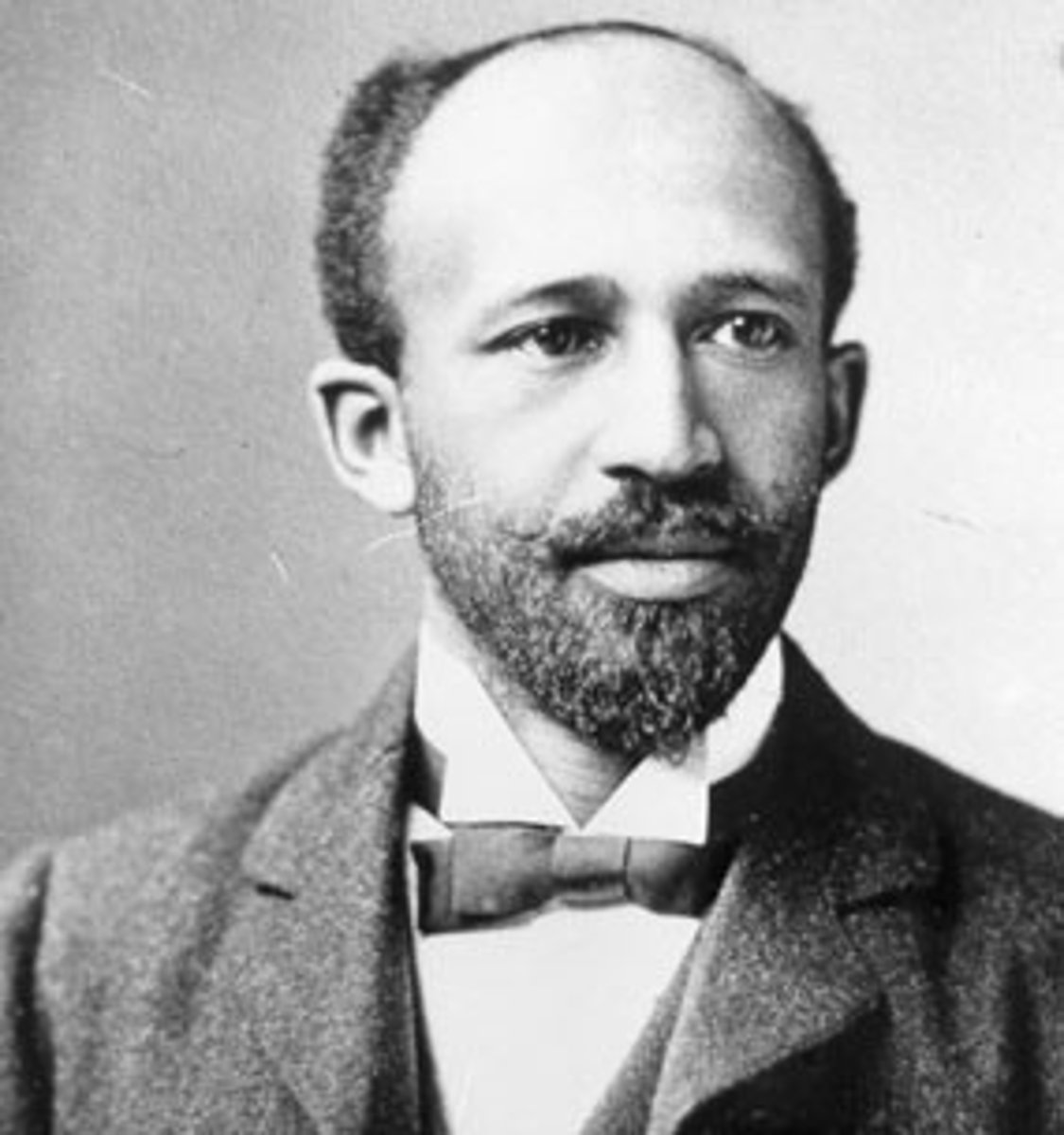
W.E.B. DuBois
Founding member of the NAACP; demanded immediate social and political equality for African Americans

3 ways African Americans were disenfranchised
1. literacy tests
2. poll tax
3. grandfather clause
Negative impact of segregation of public accommodations
-Led to institutionalized racism, discrimination, and inferior treatment of African Americans
Negative impact of segregation on education
- denied African Americans an equal education because the conditions of schools and materials were of poor quality, therefore receiving a lower quality education
Negative impact of Jim Crow in regards to voting restrictions
- Restrictions such as the literacy tax, grandfather clause, and poll tax denied African Americans their constitutional right to vote
- took away their voice and representation on issues in government
- limited their role/power in government to serve in public positions or on juries
Negative impact of segregation on marriage and family
- Interracial marriage laws prohibited people from marrying the person they loved, denying equal rights
- could not adopt a child of another race, denying equal rights
Examples of Jim Crow Laws
- segregated busing, railroads, restaurants, and other public facilities
- banned interracial marriage and adoption
- segregated schools
- voting restrictions (literacy tests, grandfather clause, poll tax)
Racial Discrimination
any discrimination against any individual because of their skin color, race or ethnic origin.

Colorism
Giving special treatment to people of the same ethnicity solely based on their skin color, with a belief in a hierarchy that places white people at the top and Africans at the bottom.
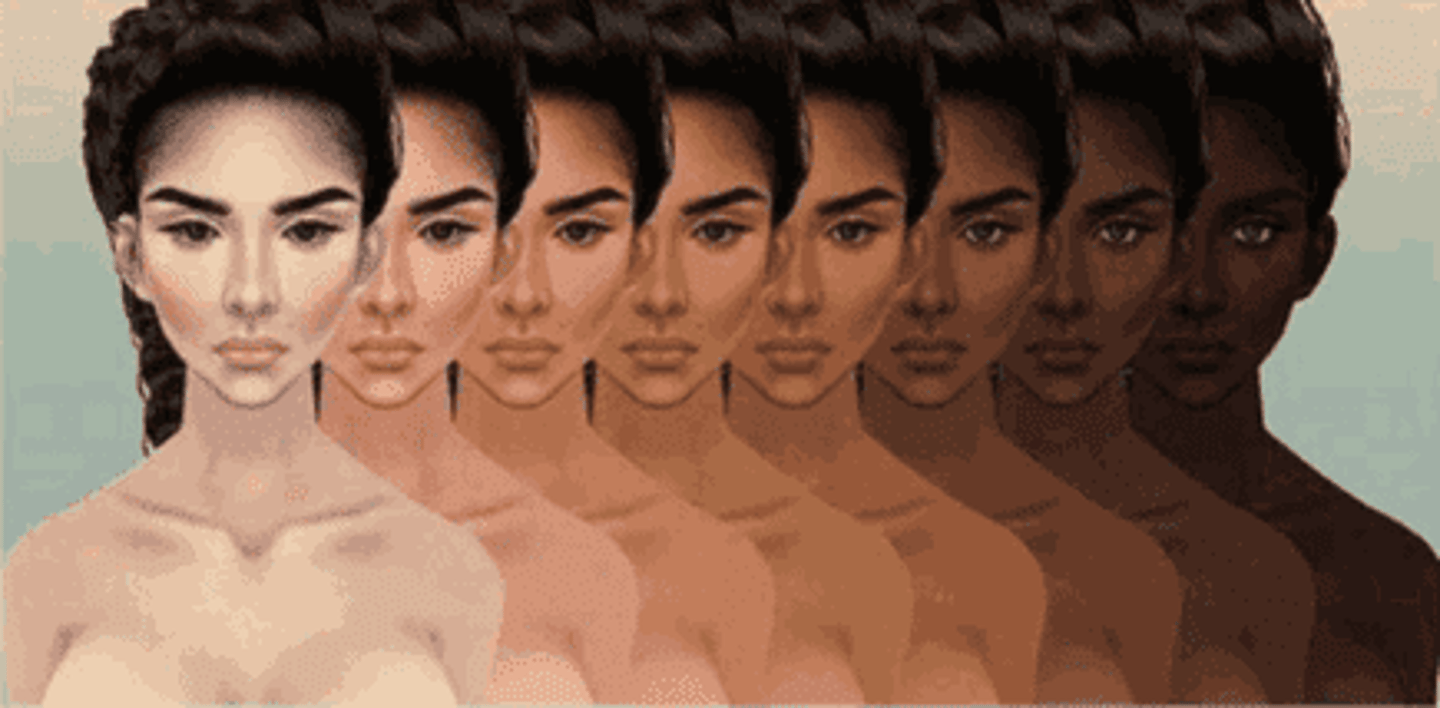

Systemic Segregation
the intentional separation of people based on factors like race or ethnicity throughout various aspects of society, such as neighborhoods, schools, and public facilities.
Discrimination
treating someone unfairly or differently based on their race, gender, or other characteristics, rather than on their individual qualities or actions.
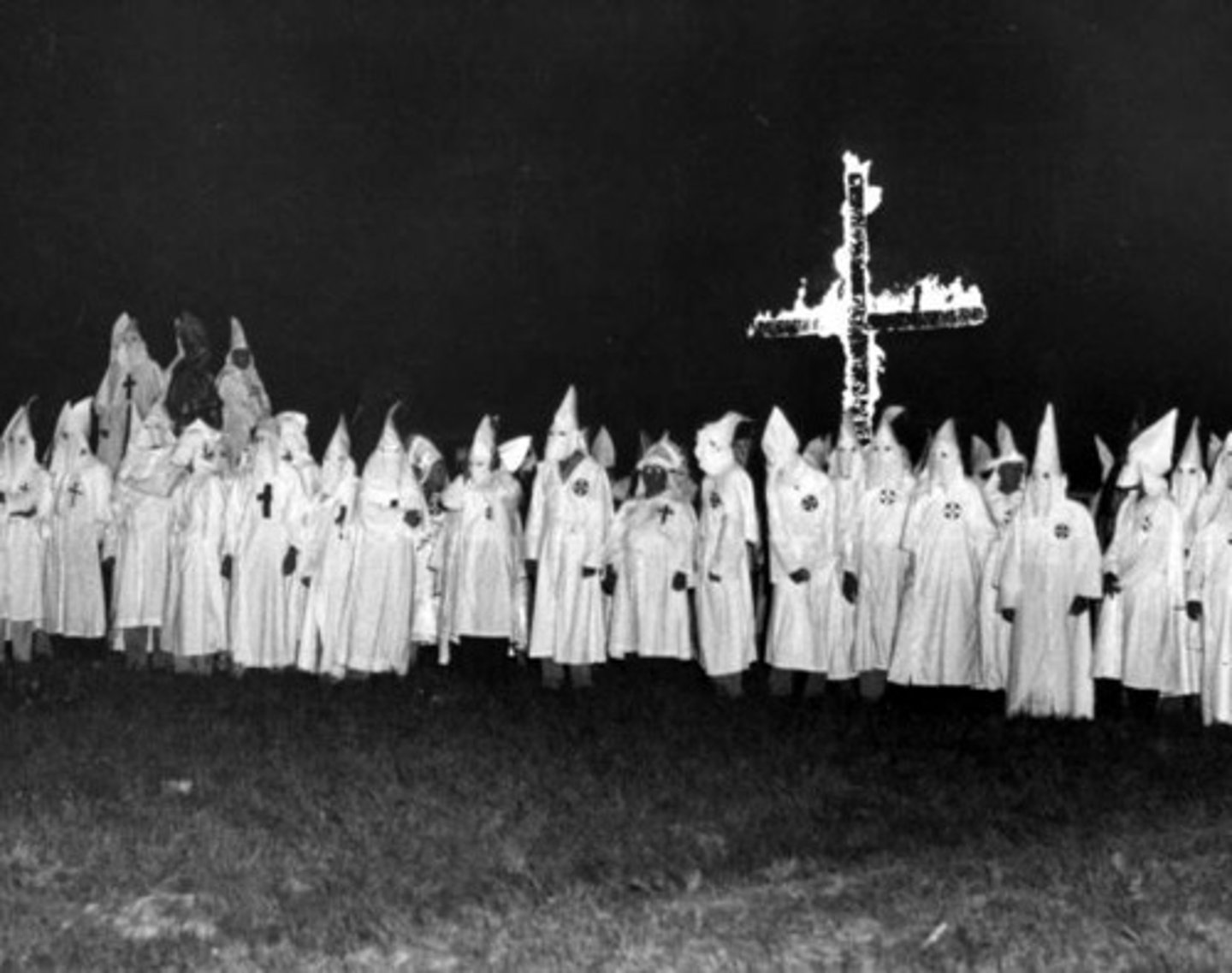
KKK
The Ku Klux Klan (KKK) is a hate group in the United States that historically promoted white supremacy, racism, and used violence against minority groups, particularly African Americans.

Minstrel shows/Minstrelsy
1840s to 1860s white performers, comical and vicious parody of slavery, musical shows
