Bleeding in Pregnancy
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
bleeding at _____________ would be considered early in pregnancy
< 14 weeks
what things are considered "normal" causes of bleeding in early (< 14 wks) pregnancy?
- implantation
- cervical
- subchorionic hemorrhage
implantation bleeding =
- brief
- light
- around missed menses
cervical bleeding =
- brief
- light
- post coital
what are the most common causes of cervical bleeding?
- polyps (post coital)
- ectropion (sporadic)
what is a subchorionic hemorrhage?
bleeding between uterine wall and chorion
- may be asymptomatic or w/ light bleeding
- associated w/ increased miscarriage risk
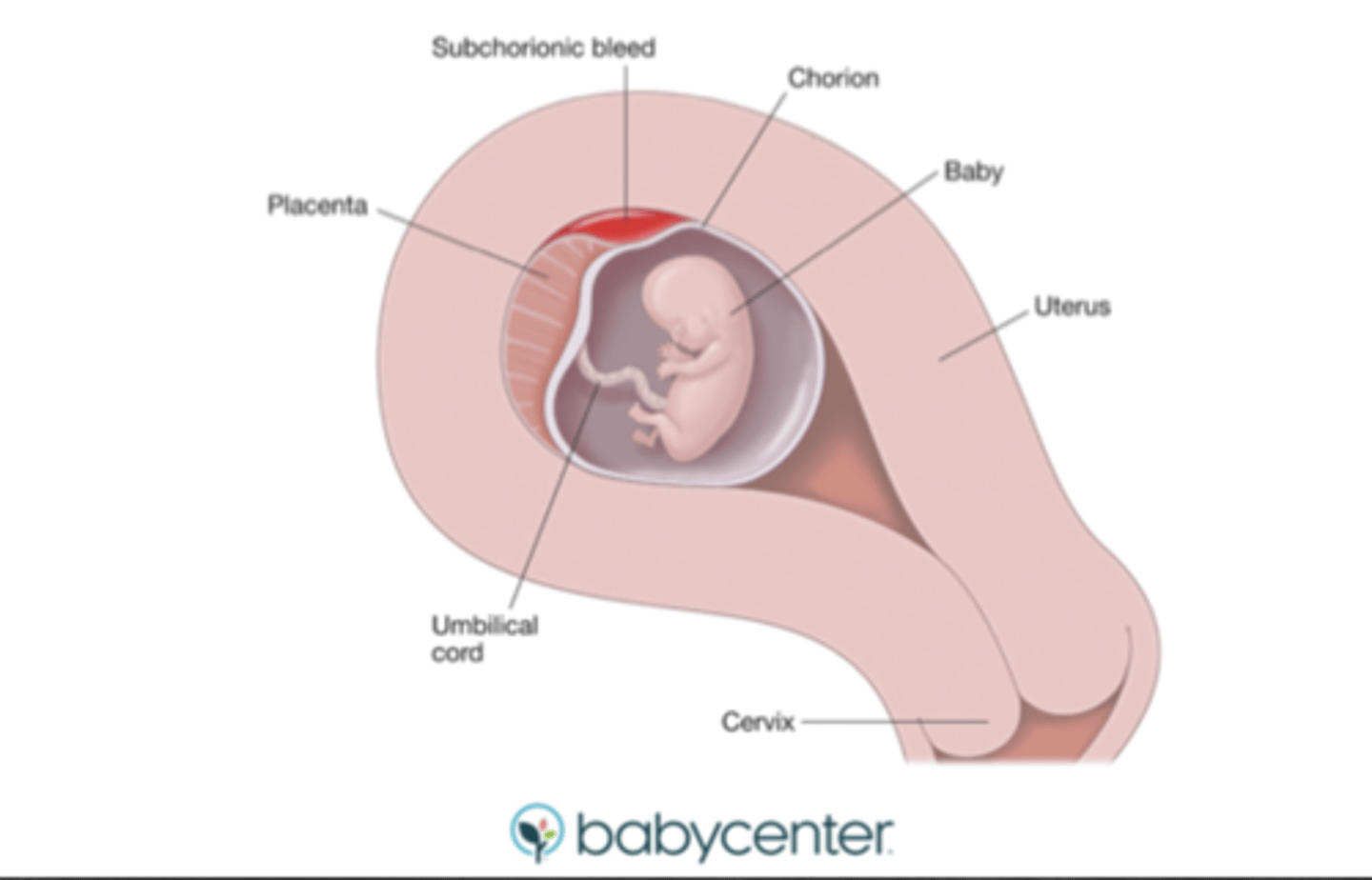
how are subchorionic hemorrhages managed?
- if light bleeding: conservative
- Rhogam if indicated
- clinic f/u w/i 1-2 wks
what is the most common cause of miscarriage?
chromosomal abnormalities (aneuploidy)
- may be:
*pre-embryonic (< 6 wks)
*embryonic (6-9 wks)
*fetal (10-19 wks)
causes of miscarriage:
- embryo chromosomes
- infection
- maternal uterine abnormalities
- antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
- low progesterone
- chronic stress
- trauma/IPV (intimate partner violence)
during which phase is miscarriage due to chromosomal abnormalities most common?
a. pre-embryonic (< 6 wks)
b. embryonic (6-9 wks)
c. fetal (10-19 wks)
b. embryonic (6-9 wks)
is it more common for a bacterial or viral infection to cause miscarriage?
viral
1 multiple choice option
infection causes ____ of late (>10-14 wks) miscarriages
66%
infection causes ____ of early (<10-14 wks) miscarriages
15%
maternal uterine anomalies that may cause miscarriage:
*uncommon (up to 15%)
- adhesions
*rare (0-10%)
- fibroids
- polyps
- septum
what is antiphospholipid antibody syndrome?
an acquired thrombophilia; body makes antibodies that attack fat molecules found naturally in blood cells and lining of blood vessels
- should test for this in a patient w/ recurrent miscarriage
what are the types of miscarriage?
on a spectrum of completion:
- missed
- threatened
- inevitable
- incomplete
- complete
spontaneous abortion =
miscarriage
missed abortion
- sx: variable bleeding (none to very light)
- cervical os: closed
- ultrasound (US): specific criteria used based on measurement or timeline
- viability: no
what are the measurement based US diagnostic criteria for missed abortion?
- crown rump length (CRL) >/= 7 mm w/ no cardiac activity
- gestational sac >/= 25 mm w/o embryo ("blighted ovum")
what's the difference between the gestational sac & yolk sac?
yolk sac is inside of the gestational sac
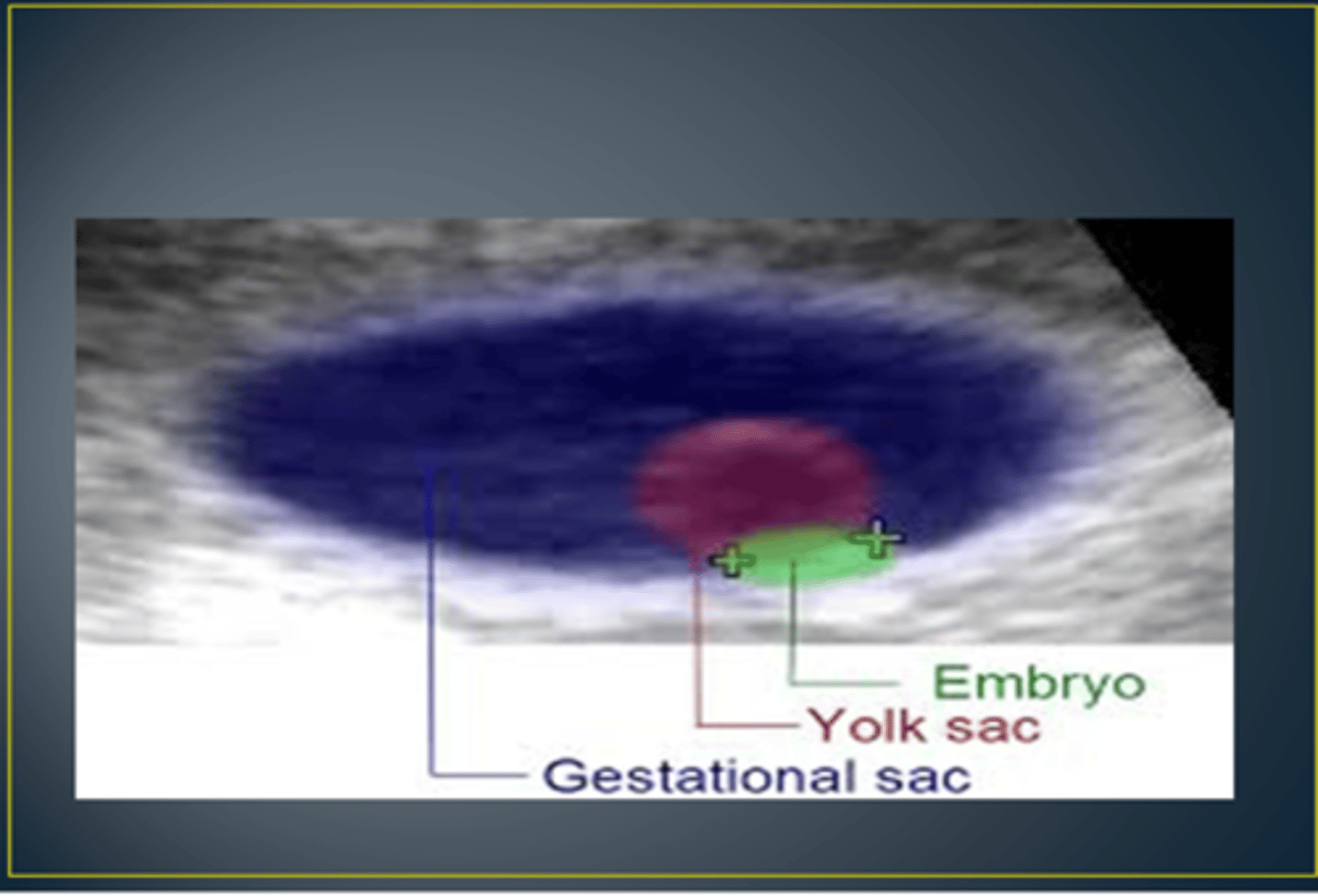
what are the timeline based US diagnostic criteria for missed abortion?
no cardiac activity:
14+ days from seeing gestational sac
or
11+ days from seeing yolk sac
threatened abortion
- sx: bleeding (light to moderate)
- cervical os: closed
- ultrasound (US): normal for GA
- viability: yes
- prevalence: 15-20%
inevitable abortion
- sx: bleeding (light to heavy) & cramping
- cervical os: open
- ultrasound (US): normal for GA
- viability: yes
incomplete abortion
- sx: bleeding (moderate to heavy), cramping, & tissue passage
- cervical os: open
- ultrasound (US): retained products
- viability: no
complete abortion
- sx: bleeding (moderate to heavy), cramping, & tissue passage
- cervical os: closed
- ultrasound (US): empty uterus
- viability: no
ectopic pregnancy =
pregnancy of unknown location
- implantation of the fertilized egg in any site other than the normal uterine location
what is a septic miscarriage?
any of the above (missed, threatened, inevitable, incomplete or complete) in presence of sepsis
RhoGAM should be given for ____ patients
Rh-
w/ Rh+ babies
a _________ dose of RhoGAM is sufficient for < 14 wks
50 mcg
- 300 mcg doses are sometimes available in pharmacy for other indications
RhoGAM should cover for ____________
12 weeks
- may be repeated around procedures or completion of miscarriage
miscarriage return precautions:
- soaking through a pad in 1 hr (front to back & side to side)
- 2 consecutive hours
- per patient's judgement/intuition
workup for missed abortion =
blood type & screen
workup for threatened abortion =
blood type & screen
+ US for viability
workup for inevitable abortion =
blood type & screen
+ US for viability
+/- CBC
workup for incomplete abortion =
blood type & screen
+ US to assess for tissue
+/- CBC
workup for complete abortion =
blood type & screen
+/- US
+/- CBC
workup for abortion of pregnancy of unknown location (ectopic) =
hCG & US
workup for septic abortion =
- hCG
- US
- CBC
- blood cultures
GYN clinic setting abortion management =
for all: RhoGAM if Rh-
- missed: counsel on options (expectant, medical, surgical)
- threatened: return precautions
- inevitable: return precautions vs send to hospital
- incomplete: counsel on options (medical or surgical)
- complete: return precautions
- unknown location (ectopic): hCG & return precautions
- septic: send to hospital
ER setting abortion management =
- missed: follow up in clinic
- threatened: return precautions
- inevitable: consult GYN (may need observation)
- incomplete: consult GYN (needs treatment)
- complete: return precautions
- unknown location (ectopic): consult GYN
- septic: consult GYN (needs treatment)
when someone presents w/ bleeding in early pregnancy, you should be sure to visualize the ______________!!
cervical os
- use suction &/or ring forceps w/ gauze to determine if patient is still actively bleeding &/or where it is coming from
what findings confirm an intrauterine pregnancy?
- yolk sac
- embryo
is an empty gestational sac enough to confirm an intrauterine pregnancy (IUP)?
no, you need to see the yolk sac inside of the gestational sac to confirm IUP
1 multiple choice option
what is a heterotopic pregnancy?
intrauterine pregnancy + ectopic pregnancy
- very rare, but technically possible even when IUP is confirmed
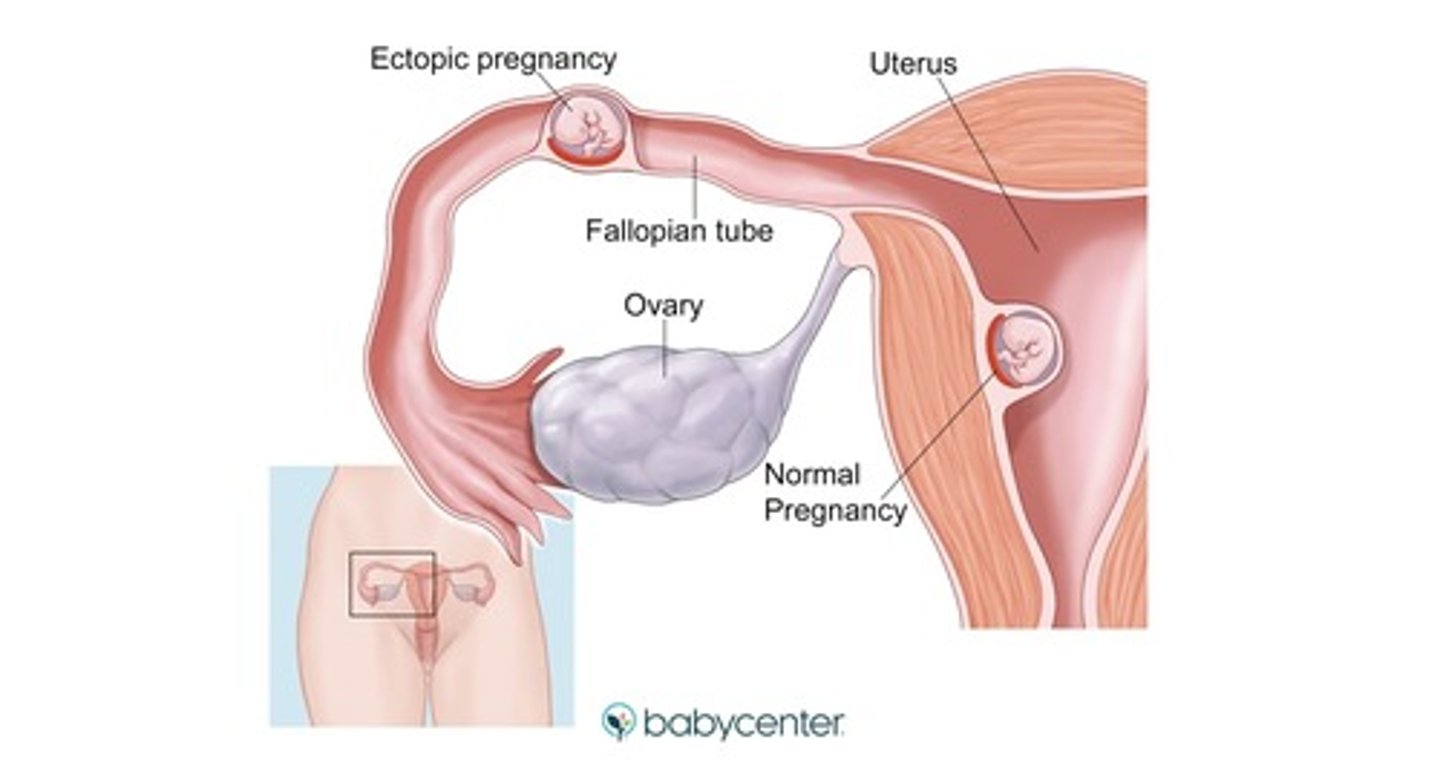
what things can confirm an ectopic pregnancy?
- endometrial aspiration w/o chorionic tissue
- laparoscopy
what findings are highly suspicious for an ectopic pregnancy?
- unspecified mass separate from ovary
- moderate or greater free fluid on US
- hCG > 5000 w/o confirmation of IUP
what findings are non-specific for an ectopic pregnancy?
- hCG < 3500
- unspecified adnexal masses (usually corpus luteum cyst)
- empty gestational sac
what is the goal when evaluating pregnancy of unknown location?
get to one of the aforementioned categories
are hCG trends helpful in establishing pregnancy location?
no
1 multiple choice option
are abnormal rises in hCG much more likely miscarriage or ectopic?
miscarriage
1 multiple choice option
do normal rises in hCG r/o ectopic?
no
1 multiple choice option
"doubling" hCG levels q 48hrs..
too high a standard for many pregnancies
if your initial hCG is higher, then..
you won't see as much of a rise
you should always assess patient's reliability to follow-up, what does this include?
- live with at least 1 adult?
- live w/i an hour or so of hospital?
- have means of transportation?
what should you do if you are highly suspicious for ectopic?
consider consulting GYN for obs admit
- place an IV, blood type/screen, & NPO
ED mgmt if pregnancy location is nonspecific/unknown
- if exam is reassuring: provide return precautions
- if exam is concerning: consult GYN
clinic mgmt if highly suspect ectopic
call/consult GYN
- if rupture suspected: laparoscopy
- if rupture unlikely: counsel on options (laparoscopy or methotrexate)
clinic mgmt if pregnancy location is nonspecific/unknown
- trend hCGs
- arrange f/u US
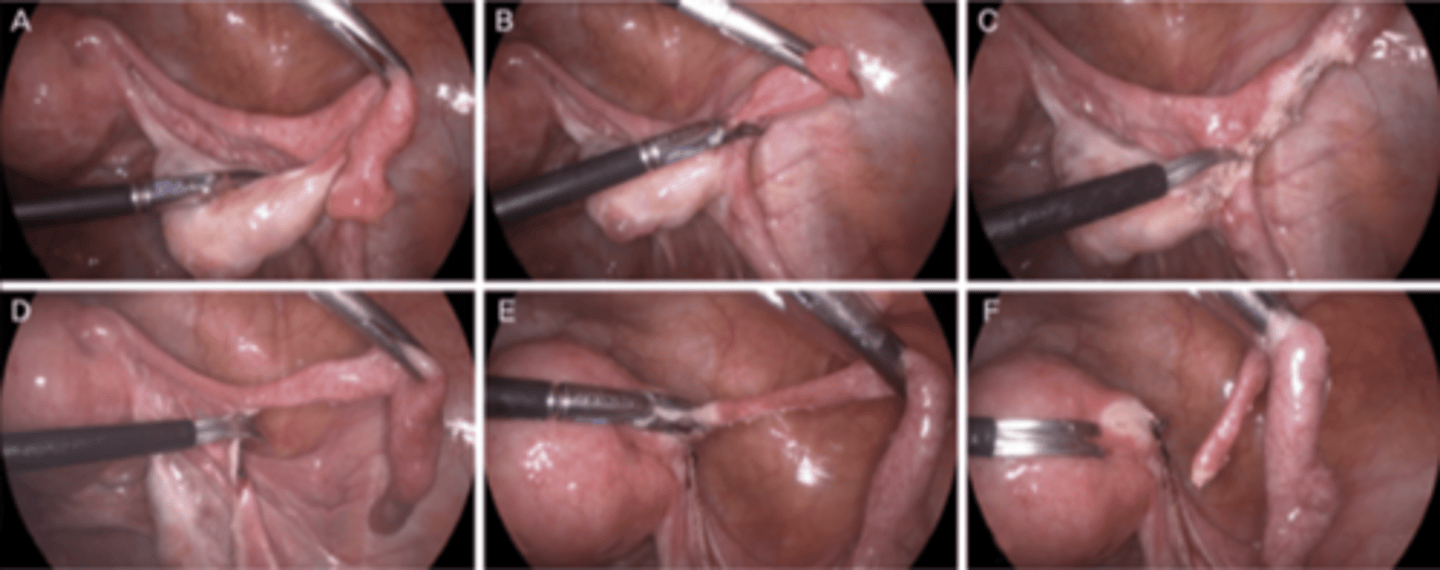
what is done for treatment of ruptured ectopic pregnancy?
laparoscopic salpingectomy
what is placenta previa?
placental tissue over the internal cervical os
- complications: contraindicates labor, intrapartum or postpartum hemorrhage
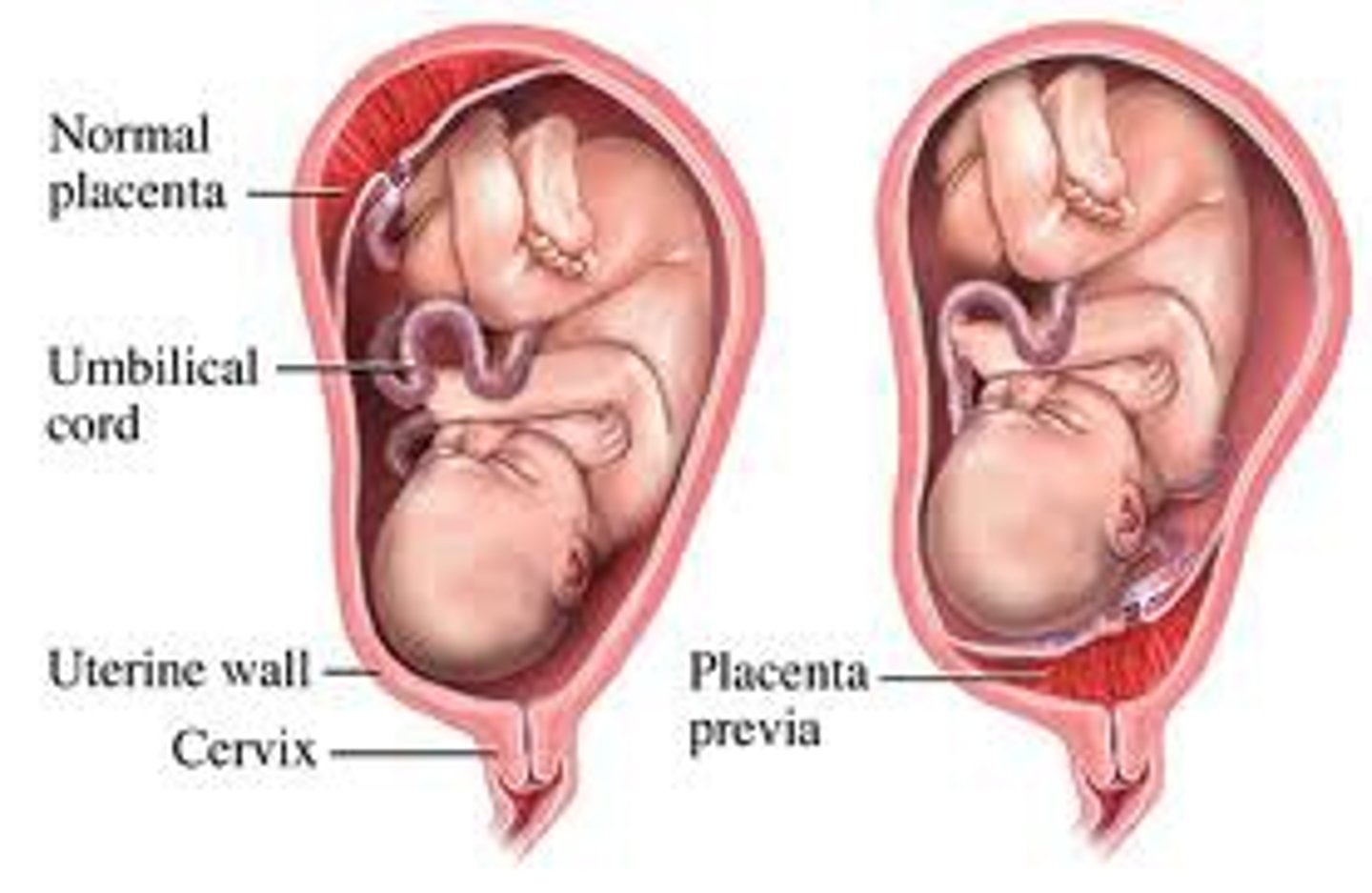
bleeding w/ placenta previa usually occurs _____ 20 wks
after
1 multiple choice option
is the bleeding w/ placenta previa painful?
no, painless
you should always anticipate the possibility of previa; therefore, w/o confirming placental location..
NO digital vaginal exams after 20 wks
should you worry when placenta previa is noted around 20 weeks?
no
1 multiple choice option
those w/ placenta previa should avoid:
- strenuous exercise
- heavy lifting
- activites likely to cause orgasm
*due to association w/ bleeding, NOT inducing labor
after placenta previa is found, monitor placental location every _____________
4-7 wks
if found in 2nd trimester, ______ of the time placenta previa will resolve by delivery
90%
if bleeding after 20 wks..
send to hospital
if bleeding persists, plan scheduled c-section at _____________
36-37 wks
ER approach to placental previa:
- prior to 20 wks: disregard
- after 20 wks: send to L&D if bleeding
no _______________ after 20 wks until placental location confirmed
vaginal exams
placental abruption takes place at _________________ 20 wks GA
greater than (>)
subchorionic hemorrhage takes place at _________________ 20 wks GA
less than (<)
what is placental abruption?
partial or complete detachment of placenta before delivery of fetus
- rupture of maternal vessels in decidua basalis
clinical findings w/ placental abruption:
- vaginal bleeding (highly variable)
- abdominal pain
- uterine tenderness
- uterine tachysystole (frequent contractions)
risk factors for placental abruption:
- history of abruption
- abdominal trauma
- hypertension/preeclampsia/eclampsia
- drugs (especially cocaine)
- smoking
- premature rupture of membranes (PROM)
what should you do if placental abruption is at all suspected?
send to hospital
ER mgmt of placental abruption
- continuous fetal monitoring
- stabilize patient (1-2 large bore IVs, fluid bolus, frequent vitals)
- labs (CBC, blood type & screen, coags)
- transfer to OB service (notify anesthesia if applicable)
when should you give a baby magnesium?
if born at < 32 wks
- for fetal neurodevelopment (protective against cerebral palsy)
when should you give a baby steroids?
if born < 36 wks 6 days
when should you give a baby group B strep (GBS) antibiotics?
if preterm & unknown GBS status
when should RhoGAM be given (if mom Rh- & baby Rh+)?
- 28 wks (clinic)
- with bleeding
- postpartum
what is your ddx for 1st trimester bleeding?
- spontaneous abortion (complete or incomplete)
- threatened abortion
- inevitable abortion
- anembryonic pregnancy/blighted ovum
- ectopic pregnancy
- GTD (complete or partial moles)
what is a blighted ovum?
a fertilized ovum that fails to develop
what is the most common type of gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD)?
complete mole
3 multiple choice options
what is the clinical presentation of a complete mole?
vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy, with either “prune-juice” discharge or expulsion of grape-like clusters
- anemia
- LGA
- hyperemesis gravidarum
- pre-eclampsia before 20 weeks gestation
- hyperthyroidism with tachycardia
- absence of fetal heart sounds
- ovarian cysts
- extremely high β-hCG levels (>100,000)
what is the clinical presentation of a partial mole?
symptoms are much less severe, present similarly to a spontaneous abortion (vaginal bleeding after a + pregnancy test)
- fetal cardiac activity may be present as a XXY fetus initially develop
- β-hCG levels are only slightly elevated, which is why the symptoms are less
what is the clinical presentation of a persistent mole?
varies widely
- most common symptom is abnormal uterine bleeding after the evacuation of a complete or partial mole
what is the clinical presentation of choriocarcinoma?
often present with late postpartum bleeding
- may have symptoms from metastatic lesions
what is the treatment/follow-up for a complete or partial mole?
both require immediate removal of uterine contents and close monitoring of β-hCG levels for 6 mo to ensure resolution of the disease.
- no pregnancy during this time (contraception!)
what is the treatment/follow-up for a persistent mole?
- D&C
- single-agent chemo (methotrexate or actinomycin-D) if pt is high risk
- OCPs
what is the treatment/follow-up for coriocarcinoma?
- single-agent or multi-agent chemotherapy
- OCPs