pregnancy
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
when does the highest rate of pregnancy loss occur?
often occur in early stages due to early embryonic death
what are some causes of early embryonic death?
embryo: polyspermy, aneuploidy, abnormal development
maternal factors: infections, hormonal diseases (imbalances), uterine diseases/defects
non-invasive placenta
implant later
large surface area
relatively loose attachment to uterus
invasive placenta
implant early
small surface area
invade deep into uterus
chorionic villi
functional unit for nutrient exchange in chorion surface
diffuse placenta
uniform distribution of chorionic villi
horse, pig
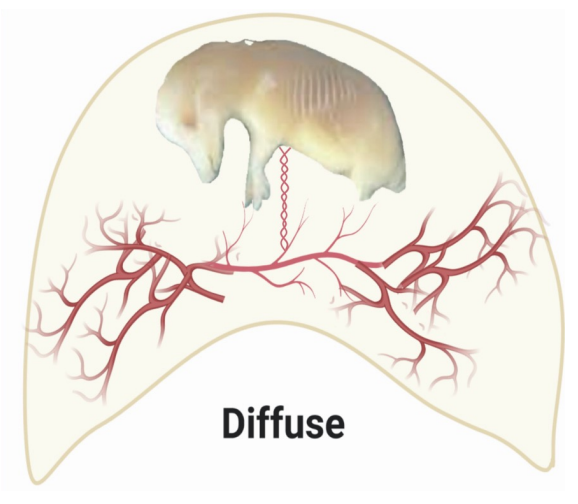
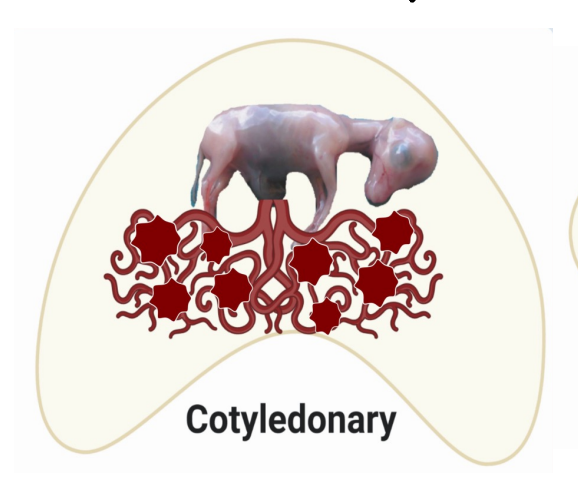
cotyledonary placenta
numerous discrete “buttons” (cotyledons) of chorionic villi
ruminants (sheep, cows, goats)
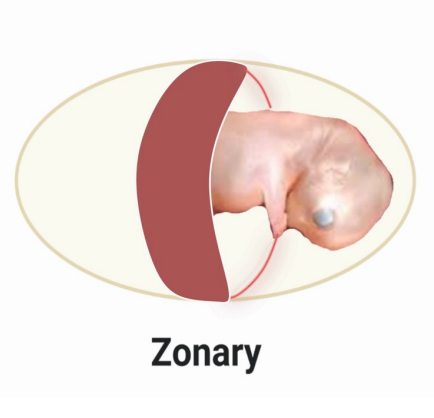
zonary placenta
band-like zone of chorionic villi
canids, felids
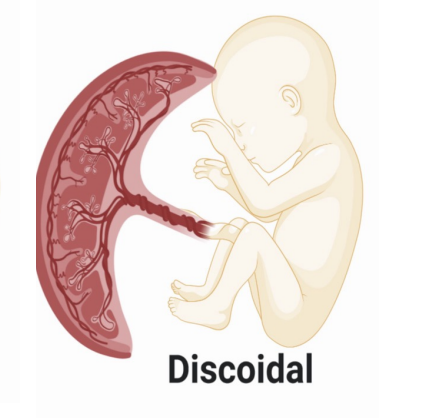
discoidal placenta
regional disc of chorionic villi
primates, rodents
epitheliochorial placenta
uterine epithelial + endothelial cells separate fetal/maternal blood
horses, pigs, ruminants (cows, sheep, goats)
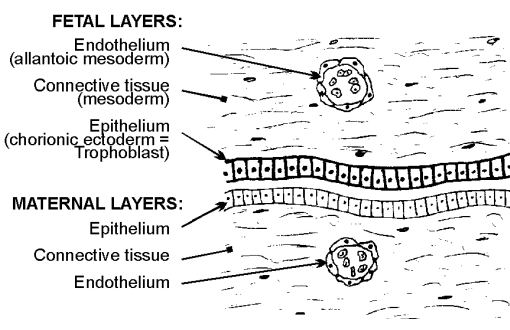
endotheliochorial placenta
uterine endothelial cells separate fetal/maternal blood
canids, felids
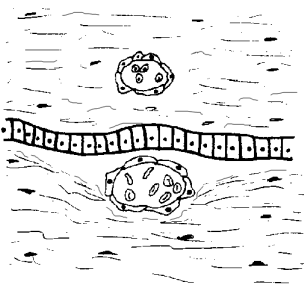
hemochorial placenta
neither uterine epithelial nor endothelial cells separate fetal/maternal blood
more efficient nutrient exchange
primates, rodents

functions of the trophoblast
maternal recognition of pregnancy signaling
hormone production
implantation
fetal part of placenta
allantois functions
collect liquid waste from the embryo
gas exchange
present early on before fetus is functional
how does the placenta create an immunological barrier?
camouflage by trophoblasts
reduced immunological activity in the uterus: immune reactions are inhibited by products of the uterus and trophoblast
antibodies cannot cross the placenta in any species until the end of pregnancy, and they never cross in species with non-invasive placentas
how are antibodies delivered to the offspring?
in species with invasive (hemochorial) placentas, antibodies are actively transported across the placenta in late gestation
in species with non-invasive placentas, antibodies are passed via colostrum (antibodies do NOT cross the placenta)
what hormones does the placenta produce to modulate maternal physiology?
steroid hormones
estrogens, progesterone
protein hormones (more species differences)
chorionic gonadotropins (CG): hCG, eCG, rodent placental lactogens
placental lactogens (prolactin and GH activity)
many others
estrogen metabolism in the placenta
trophoblast has high levels of aromatase but primary products are generally less active estrogens
fetus inactivates estrogens by fetal liver sulfation → trophoblast reactivates and sends weak estrogens to maternal circulation
“environmental” estrogens are frequently not susceptible to inactivation by these pathways
sources of progesterone during pregnancy
corpus luteum (luteal progesterone)
prolonged life after maternal recognition of pregnancy
secondary CL in equids
trophoblasts (placental progesterone)
constitutive
does not require LH
endometrial cup
unique structure in equids for eCG production
chorionic trophoblast cells invade endometrial stroma and detach from fetal membrane, forming endometrial cup → produce eCG
due to the non-invasive placenta, trophoblast cells must invade stroma to get eCG into maternal circulation
what is the function of eCG from the endometrial cup?
results in luteinization/ovulation of a secondary follicle, forming a secondary CL
eCG mainly has LH activity in the mare → maturation and ovulation of secondary follicle → secondary corpus luteum → luteal progesterone production
synthesizes eCG from ~ day 40-120
placental lactogens
group of hormones evolutionarily related to growth hormone and prolactin (pituitary hormones)
ex. rodent placental lactogen (PRL activity), human placental lactogen (mainly PRL activity and some GH activity)
what effects do placental hormones exert?
most hormones exert effects on mother for successful pregnancy and lactation
repro tract: low muscle excitability in uterus, histotroph secretion, local immune suppression, increased blood supply, closed cervix
suppress HPG axis
metabolism: store energy during early pregnancy; during late pregnancy, make nutrients available to fetus
calcium turnover: increase maternal dietary absorption and bone resorption (especially during fetal bone ossification)
increase cardiac output to uterus (20% vs 2%)
preparations for postnatal life: develop mammary gland; maternal behavior
what are the three main stages in prenatal development?
early pregnancy: organogenesis
mid-pregnancy: system development, including specializations to survive in the uterus (cardiovascular system, oxygen exchange)
late pregnancy: GROWTH, preparations for independence, final touches
late pregnancy fetal GI function
fetus swallows amniotic fluid
undigested material accumulates as meconium (first poop)
meconium retention is one of the most common causes of colic
why is fetal respiration important during late pregnancy?
the fetus “breathes” amniotic fluid, strengthening the diaphragm
fetal kidney function in late pregnancy
begins to urinate into the allantoic sac
fetal endocrine function during late pregnancy
thyroid: thyroid hormone axis critical for fetal growth and neural development
pancreatic islets: develop ability to store and mobilize glucose
adrenal gland: ACTH-regulated cortisol production critical for initiation of labor. glucocorticoids increase surfactant in the lungs
how is fetal growth controlled?
fetal growth is influenced by:
fetal insulin, thyroid hormone, local growth factors, (maybe) placental lactogens
genetics
available nutrients: number of developing fetuses, efficiency of placental exchange, size of mother
**note: fetal growth is NOT influenced by growth hormone