Final Exam IT 341 Chapter 4
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Inter-VLAN Routing
process of forwarding network traffic from one VLAN to another VLAN
Which solution is the most scalable solution for medium to large organizations?
layer 3 router and switch
Why is a SVI created?
its created for a VLAN that exists on a switch, it performs the same functions for a VLAN as a router interface would
Put the following steps in order for a layer 3 switch config
Enable IP Routing
Configure access ports
Create VLANs
Create SVI VLAN Interfaces
Step 1: create VLANs
Step 2: create the SVI VLAN Interfaces
Step 3: configure access ports
Step 4: enable ip routing
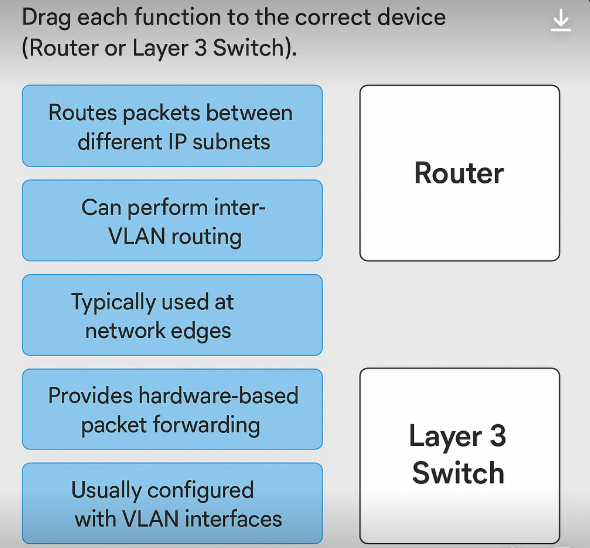
Drag each function to correct device?
router:
-routes packets between diff ip subnets
-typically used at network edges
layer 3 switch:
-can perform inter-vlan routing
-provides hardware-based packet forwarding
-usually configured with VLAN interfaces
Label the correct decision point that each device uses to forward traffic
Options:
-MAC Address Table
-Routing Table
-IP Address
-VLAN ID
-ARP cache
Drop Zones:
-Layer 2 Switch
-Layer 3 switch
-Router
-MAC Address Table: Layer 2 Switch
-VLAN ID: Layer 2 Switch
-Routing Table: Layer 3 Switch
-IP Address: Layer 3 Switch
-Routing Table: router
-IP Address: router
Match each inter-VLAN routing method to the device that can perform it
Options:
-Router on a Stick
-SVIs
-Routed Ports
-Sub-Interfaces
Drop Zones:
-router
- layer 3 switch
-Router on a Stick: router
-sub interfaces: router
-SVIs: layer 3 switch
-routed ports: layer 3 switch
Match each interface type under the correct device
Options:
-VLAN 10
-FastEthernet 0/0
-GigabitEthernet 1/1
-VLAN 1
-Serial 0/1/0
Drop Zones:
-router
-layer 3 switch
-VLAN 10: layer 3 switch
-FastEthernet 0/0: router
-GigabitEthernet 1/1: layer 3 switch
-VLAN 1: layer 3 switch
-Serial 0/1/0: router
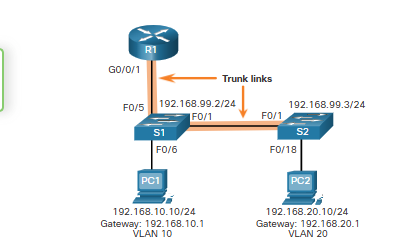
Why are the trunk links necessary?
its required for forward traffic within and between the VLANs
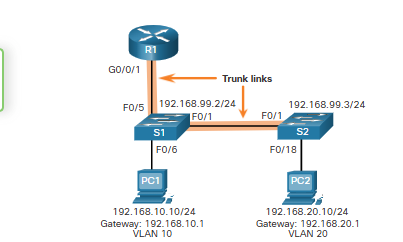
R1, S1, and S2 have initial basic config. Why can’t PC1 and PC2 ping each other?
They cannot ping each other because they are on separate networks
How can you enable devices to ping each other?
switches must be configured with VLANs and trunking
router must be configured for inter-VLAN routing
What are the 3 inter-vlan routing options
-legacy inter-vlan routing
-router on a stick
-layer 3 switch using SVIs