MKTG 300 - Chapter #13 Material
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Product as a service?
Letting customers to use the product instead of to own the product.
You should consider ”something” as a service if?
Your product is one time purchased good (e.g., software).
Your product is expensive to purchase for many customers.
Your product requires maintenance and after-services frequently.
Services are intangible?
We cannot see or touch services
No physical presence
Service providers therefore offer what to help their customers experience and perceived their services more positively, such as a waiting room stocked with a large TV, beverages, and comfortable chairs?
Cues
Word-of-mouth becomes more important for services than for?
Hard goods
In the absence of a physical product and associated cues
such as packaging and logo, what becomes a crucially important factor?
Word-of-mouth
With what, the rate at which information moves has increased exponentially. Consumers are consistently asked to provide ratings of everything from hotels, to restaurants, to contractors and landscapers
The rise of social media.
Marketers of services must be vigilant about what?, emphasizing positive experiences and dealing quickly and effectively with negative reports.
Managing their digital reputation
Even before this new wave of social media, the general rule of thumb was that?
Every customer who has an extreme service encounter, positive or negative, tells ten other people
Services are perishible?
Services cannot be inventorized,
Operational excellence?
Is a necessary core competence for many service business.
Planning for demand fluctuations?
Offload demand during peak periods
Boost what sufficiently to support the fixed and labor costs necessary to meet peak demand?
Low-period demand
Offloading demand?
Comfortable bar
Lounge area
Boosting low-period demand?
5pm happy hour to generate increased revenues during a commonly slow period.
Other characteristics of service?
Services are generally produced and consumed at the same time.
Some services are co-produced by the service provider and the consumer
Humans typically perform services
Customers have certain expectations about how a service
should be delivered. When the delivery of that service fails to meet those expectations, what happens?
A service gap results.
To provide great service?
Close the knowledge gap
Close the standards gap
Close the delivery gap
Close the communication gap
The knowledge gap?
An important early step in providing good service is knowing the customer wants.
The knowledge gap exists when management misunderstand customer expectations for service quality.
Zone of tolerance?
Define service quality dimensions
Ask questions about each service quality dimension
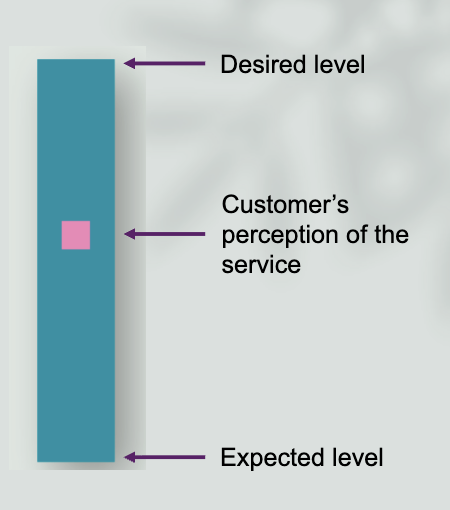
Check image
Desired level
Customers perception of the service
Expected level
The standards gap?
The standards gap exists when the service standards differ from customer expectations for service quality.
By doing what firms can close the standards gap?
Setting appropriate service standards
Training employees
Measuring service performance
The delivery gap?
The delivery gap is where the rubber meets the road, where the customer directly interacts with the service provider.
Delivery gaps can be reduced when?
Employees are empowered to spontaneously act in the customers’ and the firm’s best interests when problems or crises arises.
The communication gap?
If a firm promises more than it can deliver, customers’ expectations won’t be met.
Service recovery?
Despite a firm’s best efforts, sometimes service providers fail to meet customer expectations.
When this happens, the best course of action is to attempt to make amends with the customer and learn from the experience.
Effective service recovery efforts can?
Increase customer satisfaction and positive word of mouth
Distributive fairness?
Pertains to a customer’s perception of the benefits he or she received compared with the costs (inconvenience or loss).
Procedural fairness?
Refers to the perceived fairness of the process used to resolve them.
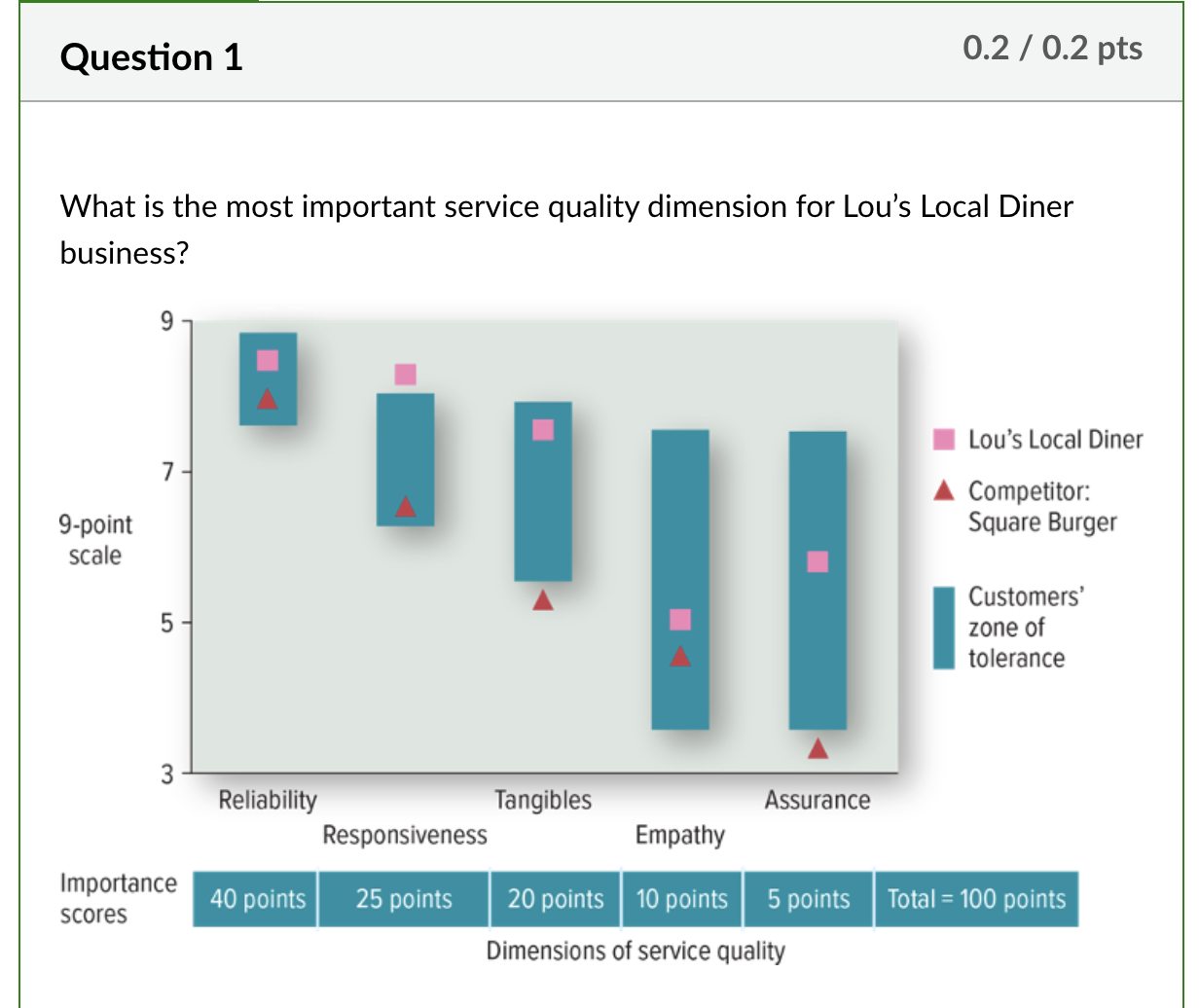
What is the most important service quality dimension for Lou’s Local Diner business?
Realiability
Because services cannot be inventoried, _________ ____is necessary?
Operational excellence
What becomes a critical factor when the absence of a physical product and associated cues diminish?
Word of mouth
The restaurant manager asked the new chef, “can you prepare a gluten-free meal that is consistently prepared and predicable?” Which of the service dimensions was the restaurant manager expressing concern about?
Reliability
Last month, the cable service was out at Ellis’s house for four days. When Ellis called the cable company, the representative agreed to credit his next bill for a full week of service and gave him free access to a popular movie channel for the next six months. Ellis felt this was adequate compensation for the inconvenience. What is this an example of?
Distributive fairness