2.6.4 conflicts and trade offs between objectives
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Which two objectives go hand in hand
Economic growth and unemployment
Economic growth vs __________
Economic growth vs. protection of the environment: As the economy grows, we expect more resources to be used. As we use resources and produce goods, we produce pollution and noise and destroy habitats. Economic growth in China has been rapid but it hasled to serious levels of pollution. Economic growth can be achieved without damaging the environment, but the growth is likely to be slower and have higher costs.
Economic growth vs ______
Economic growth vs. Balance of Payments: Some countries (such as India) have seen rapid economic growth leading to balance of payments problems. The country is so large that its industry is largely producing goods for its own people and the wealth of the people has led to increased demand for imported goods. In comparison, China has seen massive growth but that has been largely been by producing goods for exports and therefore their balance of payments is in a surplus.
Trade offs
Economic growth vs protection of the environment
Economic growth vs balance of payments
Unemployment vs inflation
Unemployment vs ________
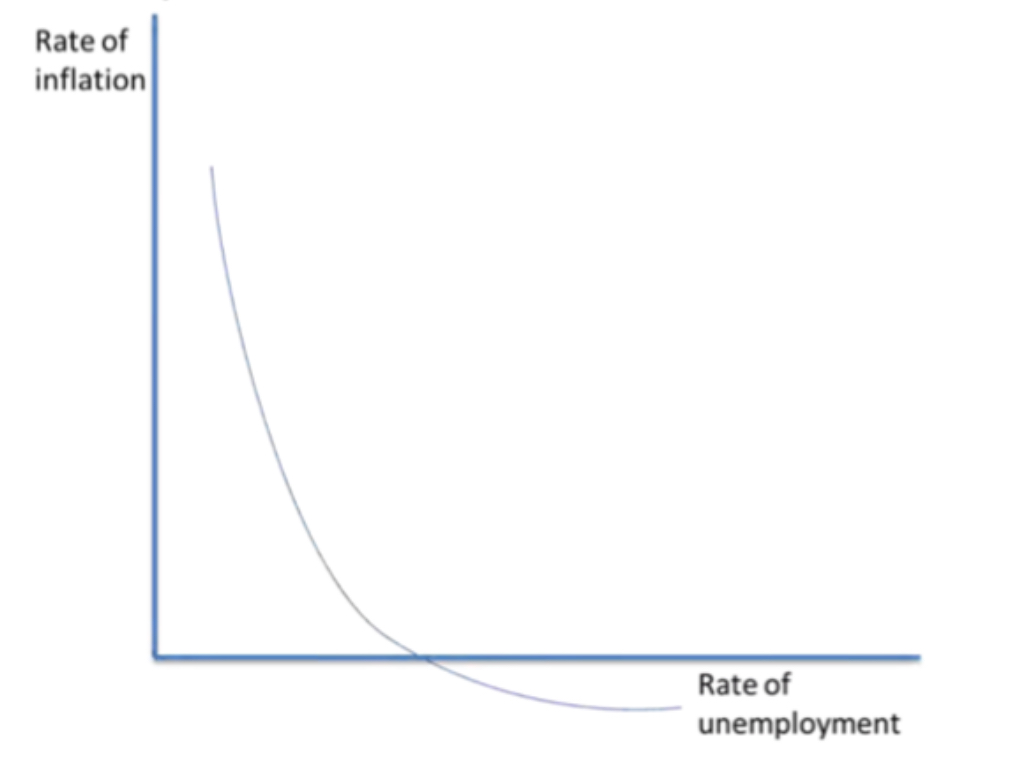
Unemployment vs Inflation- Short run Phillips curve generalised into a relationship between unemployment and inflation, by arguing that firms pass on increases in wages to the customer in increased prices. The reason for this connection is that businesses know that if there is a high level of unemployment, they can attract the workers they want with low wages. If there is high employment, firms are competing for the best workers and the way to obtain the best is by offering higher wages. Initially, the Phillips curve seemed to accurately show the relationship well. However, during the 1970s, we saw high levels of unemployment and low inflation, called stagflation.
Phillips curve
A. W. Phillips found a trade-off between inflation and unemployment, called the Phillips curve. He found the existence of an empirical regularity, which said that the rate of change in money wages increased as the rate of unemployment fell. This was then generalised into a relationship between unemployment and inflation. Initially, the Phillips curve seemed to accurately show the relationship well. However, during the 1970s, we saw high levels of unemployment and low inflation (stagflation)
Conflict and trade offs between policies
Expansionary and deflationary fiscal and monetary policies
Changes in interest rates
Supply-side policies
Fiscal deficits
Expansionary and deflationary fiscal and monetary policies
Expansionary policies will increase AD, to increase output, employment and economic growth but will lead to increased inflation and may worsen the balance of payments as some of the increased demand for goods and services will be met by imports. On the other hand, deflationary policies will decrease AD to improve inflation but will decrease employment and economic growth
Changes in interest rates
An increase in interest rates will be used to decrease inflation. However, continuously high rates will damage long-term investment as less businesses will want to invest, and this will decrease long-term growth. Moreover, they will raise the value of the pound which will decrease exports and increase imports, worsening the balance of payments. Also, the interest rate will affect distribution of wealth: high interest rates benefit savers and lenders, tending to be older people as they are more likely to have savings. Low interest rates tend to increase income inequality, as the richest people hold a larger proportion of their wealth in non-money assets, such as stocks, shares and belongings and so aren't affected much by interest rates, whilst middle and working-class people are more likely to have savings in the bank
Supply side policies
Supply side policies intend to increase aggregate supply, and therefore improve long term economic growth. They are also able to decrease long term inflation but may increase it in the short term if they encourage investment as this will increase AD. Moreover, policies which decrease trade union power, reduce wages, lower benefits, change taxation etc. may increase income equality as these will negatively affect the poorest in the country. Some supply-side policies have adverse effects on the budget or on the environment
Fiscal deficits
In order to reduce fiscal deficits, the government may decide to reduce government spending and increase taxes. Firstly, this will reduce AD and decrease short term economic growth and higher unemployment. Also, the higher the fall in output as a result of these measures, the higher the fall in tax revenues will be and so therefore the more ineffective the policy. Moreover, it is likely to affect income equality as the poor are the ones who use the government services most and so will be worst affected