Energy and Enzyme exam 3
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
One characteristic of
life is
all life takes
in and uses energy
Energy
the ability to
do work/move
matter/supply heat
Potential energy
stored energy
available to do work
Kinetic energy
energy
being used to do work
potential energy
Top of hill
Kinetic energy
Coasting downhill
Non polar have higher or lower potential energy
Higher
Does polar molecule have high potential energy?
No
Chrmical bonds, chemical and electrical gradients
Potential energy
Thermal and heal, solar
Kinetic energy
law - energy cannot be
created or destroyed, can be
converted to other forms
1st law
law – all spontaneous
reactions increase entropy of
the system and/or its environment
2nd law
Study of energy tranformation
Themodynamics
true or false
Energy transformation are completely efficient
False
Describes natural phenomenon
Law
Theory
Well supported explanation of natural phenomenon
what is entropy
Disorder physical distribution and interactions of molecules
Spontaneous reactions can happen without ____ _____ of energy
Net input
Spontaneous reaction can also happen slowly, if so give me example
Diamonds to graphite
How do you know if it is sponstaneous or not
Likely spontaneous if products< potential energy than reactants (lower energy after rxn)
Products < ordered than reactants (products have increased entropy)
How happen to the difference in potentia energy?
Released often as heat
How do wwe no with more certainty whther the reaction is spontanrous?
G- gibbs free energy amount of energy in the reaction available to do work.
G= H-TdeltaS
If G is negative….
Exergonic-Reaction has energy available to do work, will be sponntaneous
Delta G is positive..
Endergonic-Energy has to be added for the reaction to happen. Wil not be spontaneous
What does each mean
T
S
H
Thermal energy, entropy, enthalpy
Enthalpy: total energy in a molecule includes potential energy and kinetic energy
How does life require macromolecules mostly produced through endergonic reactions?
Through energetic coupling between exergonic and endergonic
How does energetic coupling happen
Allowing capture of some energy from exergonic that would otherwise be released as heat.
In cells usually tranfer phosphate or electron
How does ATP store energy
Stores energy in phosphate-phosphate bonds
Phosphorylation
What does it produce
Transfering a phosphate group
It produces an activated intermediate to raise potential energy of that reactant.
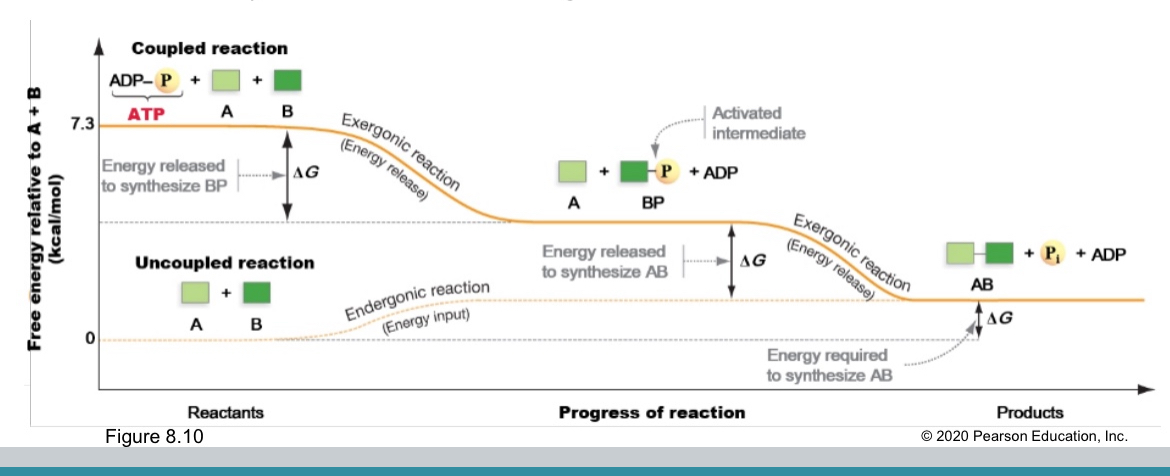
Exergonic or endergonic
Exergonic
Whats redox reactions
Reduction-oxidation
Transfer of e-
Electron donor loses energy and electron recipient gains energy
Higher energy forming is Longer and waker bonds
T or F
T-Longer / weaker
To bonds to be proken and formed, it must collide.
Likelihood of collision if:
Higher temperature and more reactants required
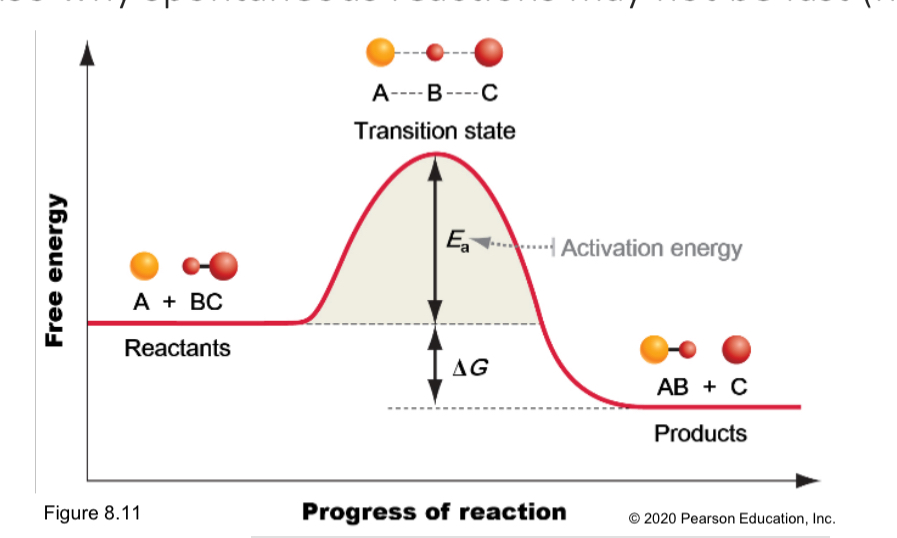
All reaction require ____ amount of kinetic energy to _____ bonds and form a ____ state is called ____
Minimum, strain, activation energy
According to Activation energy,
Higher tempetature means_____
It is also why spontaneous reaction _____
Higher reaction rates
May not be fast
What are two hurdles for the even spontaneous reactions?
activation energy and orientation of collision
In enzyme, substrate formed? With
Glucose and ATP
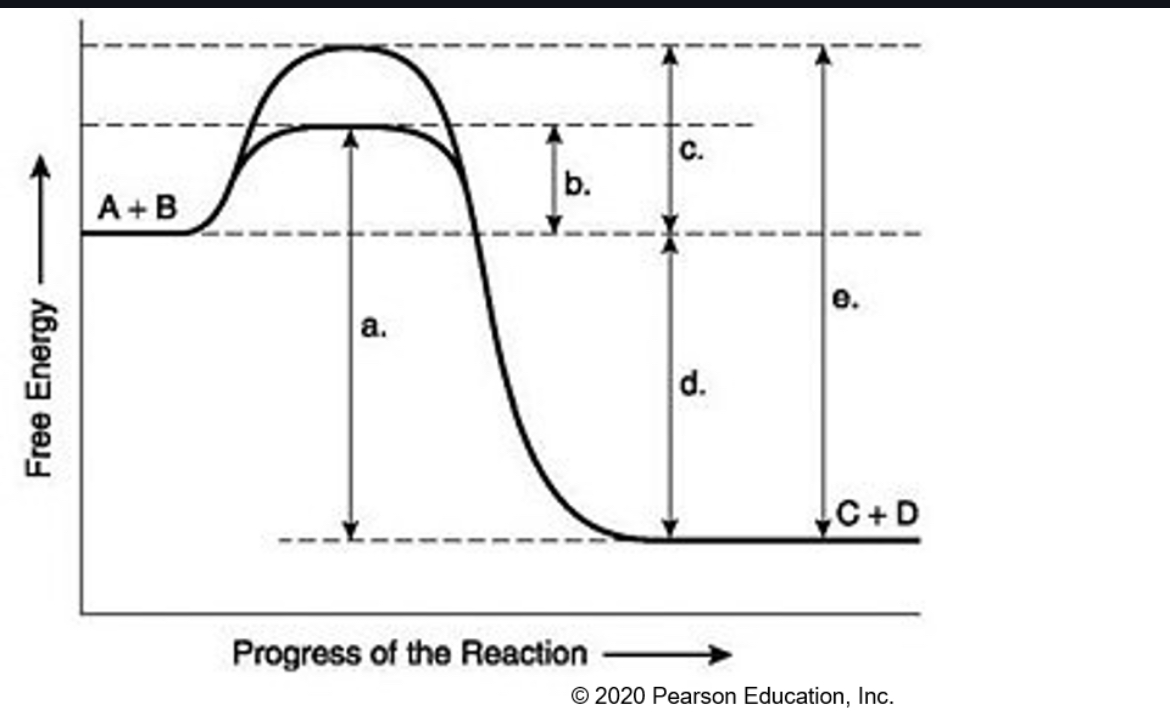
activation energy needed for
the enzyme-catalyzed reaction,
• activation energy needed for
the noncatalyzed reaction,
What does each letter mean
A+B=C+D
a | Activation energy (uncatalyzed) | Energy barrier without catalyst |
b | Activation energy (catalyzed) | Energy barrier with catalyst |
c | Difference between a and b | Reduction in barrier due to catalyst |
d | ΔG (overall free energy change) | Product energy − Reactant energy |
e | Activation energy for reverse reaction |
In Enzymes and activation energy, it ___ activation energy. How does it facilitates transition state?
Lowers,
shape change and
interactions between R
groups at active site and
reactants/substrates)
T or F
Many proteins need more than amino acids to function
T- ions and organic molecules often important part of enzyme active site.
Cofactors- and their example
Coenzyme-
Prosthetic groups- and their example
Cofactors are ions that reversibly interact with enzymes, minerals
Coenzymes are organic molecules that reversitbly interact
Prosthetic groups permanently attached to proteins. Many coenzyme and prosthetic groups are vitamins in your diet.
What factors that affect enzyme activity and ffunction?
Substrate concentration
Temperature
And so on( add later)
Why does the reaction rate go up with increased
temperature (at first)? Why does it start going down at
even higher temperatures?
In high temperature at first i
All active sites used means _____ at ____ substrate
Satureated, high
how does the Most enzymes have ideal temperature and p H ranges
usually correspond well to the environment they are most
often found
natural selection.
Enzymes are highly regulated, in what way does the enzyme change shape and function? it is also calledd controlling enzyme so enzymes are not always active, so it doesn’t waste energy.
by adding phosphate groups: phosphorylation
In regulatory molecules, what are
Competitive inhibition -
Allosteric regulation -
Competitive inhibition -Inhibiting molecule may bind to
active site to block substrates
Allosteric regulation - Regulatory molecule may bind
in a different spot (not active
site) to change shape to make it active or inactive
Most enzymes don’t act alone — they work as steps in a chain of reactions, what is it called
Metabolic pathway
why does early enzyme inhibited by late(last) product in matabolic pathway? and what is it called?
It prevents the cell from overproducing molecules and saves energy and materials.
Negative feedback(feedback inhibition).
Some metabolic pathways build molecules whereas others _____
break them down.
Anabolic- build
Catabolic - break