PSYC 4008 FINAL EXAM
1/322
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
323 Terms
Methodological behaviorism
focus on observing behavior rather than the mental processes and subjective experiences
Psychological behaviorism
psychology is the science of behavior (behavior determinants are external)
Logical Behaviorism
philosophy about semantics of mental concepts
Radical behaviorism
methodogical, logical & psychological behaviorism combined
Environmentalism
behavior derives from environmental experience
this is how behaviorists applied British empiricism into their view of behavior
Auguste Comte
founder of:
sociology
philosophy of science
positivism
Positivism
view that the only source of absolute knowledge is publicly observable data
a few concepts of positivism:
unity & utility of science
rejection of introspection & metaphysics
Law of 3 Stages
stages in how humans understand nature, which include
theological
methodological
positive: mind stops looking for causes of events, but rather describes the laws governing them
1 & 2 is where we seek answers, but 3 is where we accept we cannot know truth fully
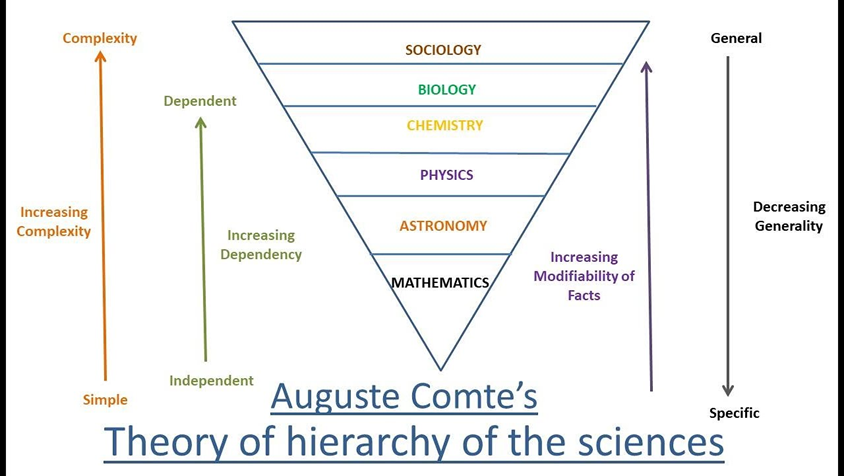
Hierarchy of Science
sciences develop on a hierarchy, building on previous layers
Logical positivism
gives science a firm foundation by establishing an agreed truth
uses verifiability
legacy: failed since verification is not verifiable
Logical positivism: Verifiability
statements must be “truth analyzed“ under these rules:
rejects metaphysical reasoning
empirical & logical language
empirically/logically verifiable
Behaviorists on Reflexology
views all behavior as reflexive to stimuli
elaborates on responses that are conditioned & emitted
Pavlov
classical conditioning
S-S association or stimulus substitution
Thorndike
introduces idea that consequence of behavior is important (S-R associationism)
Behaviorist Manifesto (how they view psych)
psych is an objective experimental branch of science
goal: predict & control behavior
introspection is useless
Watson on instinct
instinct is natural and used early in life
quickly replaced by learned behaviors
Watson on learning
emphasized phylogenetic continuity
demonstrated classically conditioned emotional responses
criticized Law of effect
classical conditioning is important to learning
Conditioning
Little Albert Experiment
discovered that deconditioning is possible
began work on methods (counter conditioning & systematic desensitization)
Neobehaviorism
not all behavior is learned through classical conditioning
uses operational definitions to study internal states
Operational definition
how you define/measure a construct
Guthrie’s Contiguity Theory
applies Pavlovian model to S-R learning
contiguity between S & R required for S-R association
other features
molecular behavior
learning occurs fully the first time w/o reinforcement
punishment deters unwanted behavior
associations can’t be unlearned
Molecular behavior
complex acts of many components and small S-R associations
(i.e., the many learned microinteractions within moving your arm)
Tolman’s Cognitive/Gestalt Behaviorism
combined behavioral & gestalt principles
emphasized animal learning research
Purposive behaviorism
behavior has a goal
molar behavior: holism
cognition: behavior has cognitive determinants
intervening variables
Intervening Variables
hypothetical variables mediating relationship b/w S & R
Latent learning
Tolman believed learning happens randomly w/o reinforcement
learning is defined in terms of behavior/performance
thus, latent learning is learning that is not reflected in performance
Cognitive Map
spatial mental map of an area
Clark Hull
physician
believed organisms were complex machines, thus explained behavior using physics
drive reduction theory of learning
Drive reduction theory of learning
formula: E = D * H
E = excitatory potential: probability of a response occuring
D = drive: motivation of behavior
H = habit strength: strength of S-R relationship, requires S-R contiguity
believed that reinforcement (drinking) was to get rid of a drive (thirst)
BF Skinner
highly important & controversial figure in psychology
rigidly believed in behaviorism (radical behaviorism)
BF Skinner’s Experimental Analysis of Behavior
finding variables that affect probability of response
DV: response rate
disliked nomothetic approach, preferred individual intense study over time instead
Nomothetic Approach
comparing means of two groups (ignores variability)
Stimulus control
change in probability of a response when stimulus is present
Evaluation of Radical behaviorism
once ruled US psych, but is replaced with cognitive psych
is too exaggerated and incomplete
giving psychologists behavioral control is ethically questionable
Psychosis
severely distorted perception of reality
important to history of mental hospitals & psychiatry
2 Psychosis Types
organic (neurology & toxins)
functional (disfunction such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder)
Moral therapy
an attempt to “fix psychosis“
had many humanitarian treatments
led to start of mental asylums
Dorothea Dix
hears of mental illness while teaching at women’s prison
advocate for mental asylums
Asylum Era
idea of a therapeutic mental hospital
introduction of moral therapy and psychiatry
Problem of Asylums
not enough beds for # of patients
fear that mental illness was rising
new “dementia praecox“ (schizophrenia)
led to aggressive therapies
Asylum Reform
a set of events that led to the reform of asylums
Clifford Beers
founded National Committee for Mental Hygiene
mental hygiene - preventing mental illness
Statistical Manual
standardized stat reporting in mental hospitals
evolves into DSM
John Maurice Grimes
conducts study on asylum problem
independently publishes that mental hospitals can’t be reformed
Asylum Reform: WWII
12% draftees rejected for mental illness
asylums resembling nazi concentration camps
Thorazine/Chlorpromazine
first true antipsychotic
effectiveness helped depopulate asylums
Neurosis
derives from neuritis (nerve inflammation)
thought to be of neurological cause, but later shifts to psychological cause
Jean-Martin Charcot
founded modern neurology
linked neuropathology to symptoms in multiple sclerosis
studied hysteria & hypnosis
believed hypnosis susceptibility indicates hysteria
George Beard
surgeon/neurologist
discovers neurasthenia (mental&physical fatigue)
thought that discorder was caused by exhaustion of nervous energy
pioneered “electrical treatment”
Weir Mitchell
neurologist
invents rest cure for nervous disorders (forced inactivity for two months)
becomes a symbol of 19th c. patriarchal oppression of women
neurosis shifts from physical to psychological
Sigmund Freud
neurologist
studied hysteria & hypnosis
began psychoanalysis
had a psychoanalysis “cult“
Alfred Adler
early member (now defector) of Freud
questions sexual determinism
proposes social & environmental determinants
proposes inferiority complex
created school of individual psychology
Carl Jung
early member (now defector) of Freud
questions sexual determinism
develops analytical psychology & collective unconscious
archetypes, extraversion/introversion
Collective unconscious
inherited ancestral experiences
Psychoanalysis successes
better relationship b/w doctor & patient
psychiatry expands to neurosis
psychiatry becomes popular
Psychoanalysis failures
skeptic of medicine
no empirical validation
long and expensive treatment
What aspect(s) of psychology was America more focused on compared to Europe?
application of psychology & mental testing
American Zeitgeist
Democracy
Diversity
Private Property
Individual Freedom
Self-reliance
Competition
Meritocracy
Why was Darwinism hated in America?
it had negative theological implications
Why was Darwinism loved in America?
it justified America’s economic & social system, since capitalism reflects “natures way“
Pre-Jamesian Psychology
influenced by Scottish Realism (common sense view of reality)
Reid’s Faculties
active powers (powers of will)
intellectual powers (powers of understanding)
Thomas Upham
wrote a book integrating philosophy & science of mind, primarily as sensory physiology
trilogy of mind
Trilogy of Mind
intellect (cognition)
sensibilities (emotions)
will (action)
Early Higher Education
free public ed starts (early 1800s)
higher ed starts at Harvard (1636)
mostly religious higher ed schools
secular universities more common after Morill Grand Act 1862
Inequalities in Early Higher Education
solely white male students
schools for minorities and women only created after Civil War
Variability Hypotheses
women are thought to be less mentally capable
men thought to be more varying in intelligence
Francis Summer
1st black man to get PhD in psych
established & chaired psych dept at Howard University
Kenneth & Mamie Phipps Clark
Kenneth becomes first black president of APA
Conducted doll study for Brown v Board, which helped abolish segregation
Mary Whiton Calkins
teacher at a woman’s college
requested to do grad study at Harvard as a “guest“ to offer teaching material for her college
research and original findings at Harvard’s lab, regarding “paired-associates“ learning
Harvard refused her a PhD despite met requirements
first woman president of APA
Margaret Floy Washburn
grad study in psych @ Cornell
1st woman to earn doctorate in psych
2nd woman president in APA
original research in color perception, imagery & social consciousness (empathy & altruism)
William James
1st American psychologist
2nd most important psychologist
functionalist
James’ 3 Psychology Methods
introspection
experimentation
comparative
James’ Truth
property of an idea, statement, belief, etc.
correspondence theory - ideas true when corresponding to reality
pragmatism - defining truth in terms of utility
Problems of Pragmatism
utility isn’t enough for truth, as useful false beliefs exist
utility isn’t needed for truth, as useless true beliefs exist
reversal of cause & effect. beliefs can only be useful if true, not the other way around
James’ Self
2 Selfs
I - the conscious self
Me - self as an object of thought
James’ Free Will
was disturbed by determinism
although freedom may be illusive, it is a useful concept (pragmatism)
According to James, why do habits have significance?
allows consciousness to focus on important problems
preserves social order
important to education, especially early on
James’ Emotions
consequence of perceiving bodily reactions, rather than the cause of the reaction
James’ Categories of Religious Experiences
mystical - sense of unity w/ divine & transcendence
conversion - profound change in belief & personal identity
G. Stanley Hall
doctorate student of James
1st US doctorate in psych
studied w/ Wundt after doctorate
founded 1st lab for exp psych in US @ Hopkins
founded APA
founded American Journal of Psychology
Hall’s Psychology
contributed in 2 areas
developmental psych of child study
genetic (evolutionary) psych
these areas were linked by recapitulation theory
established adolescence as a stage of development
Recapitulation theory
biological development of organism mimics evolutionary progression of its species
Hall’s Education
advocate for educational tracking
against co-ed
education for boys and girls were focused on their gender roles
What sparked the psychoanalytic movement in America?
Hall invited Freud to give lectures at Clark University
George Ladd
introduced Wundt’s experimental psychology to America
James Baldwin
introduced concepts of accommodation & assimilation
Baldwin effect - learning by imitation was an evolutionary adaptation
What were the similarities and differences b/w structuralism & functionalism?
they both valued introspection and conscious experience
they valued structure or function of mind
Edward Titchener
lead structuralism in US
completed PhD under Wundt
Why did Titchener dislike the APA, and what did he do about it?
he had issues with APA not promoting lab psychology, scientific rigor, & structuralism
formed a group called “experimentalists“ (it excluded women)
Titchener & the 2 schools
named both schools
structuralism = anatomy
functionalism = physiology
saw functionalism as old
Mental Elements
sensation vs feeling
had 4 qualities (quality, intensity, duration, clearness)
both elements have all qualities, but feelings lack clearness
Titchener’s solutions to internal perception
post-mortem examination
break the experience into parts
introspective habit
Post-mortem examination
internal perception relying on memory, rather than immediately recalling
Introspective habit
“calibrating“ (training) participants to do internal perception
Social Darwinism
a view on society based on a combination of Darwin’s ideas
compares societies as “better“ or “worse”
Laissez-faire capitalism
market forces determine people’s fate
no limit to wealth or poverty
a form of evolutionary “natural eugenics“
based around intelligence, which pushed mental testing in US
John Dewey
believed psych & philosophy are inseparable
founded school of pragmatism w/ James
founded functional psych
Dewey’s education
against laissez-faire
emphasized provision of equal opportunity
experiential learning
Dewey’s reflexes
believed that reflexes were a coordination of sense and action