Ecosystem Dynamics
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
original source of energy
Sun
1st Law of Thermodynamics
“Energy cannot be created or destroyed”
Energy input must be continuous
Energy is converted to chemical energy stored in food
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
“Every exchange of energy increases entropy”
Energy conversion is inefficient: some is lost as heat as it transfers through ecosystems
Law of Conservation of Mass
“Matter cannot be created or destroyed”
Nutrient inputs must equal outputs
Chemicals/atoms are continuously recycled through the ecosystem
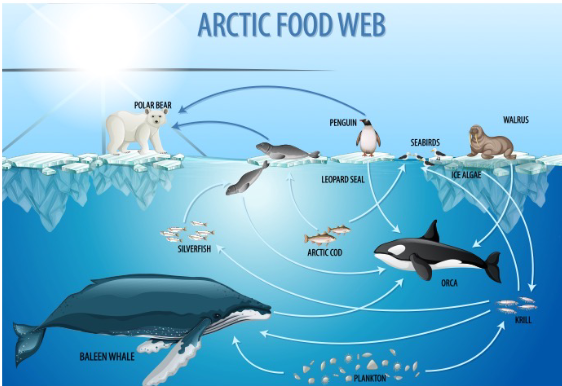
trophic levels
any step in a nutritive series, or food chain, of an ecosystem, organised on the basis of feeding behavior
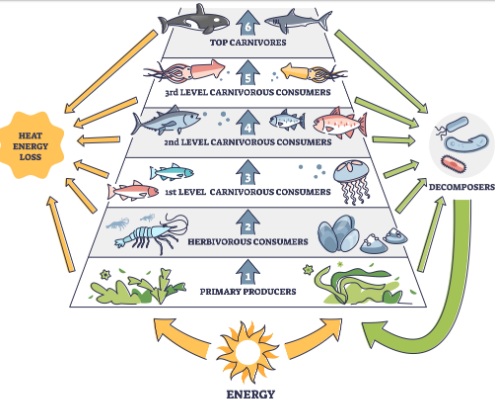
primary producers
photosynthesis; autotrophs
ie. plants, bacteria
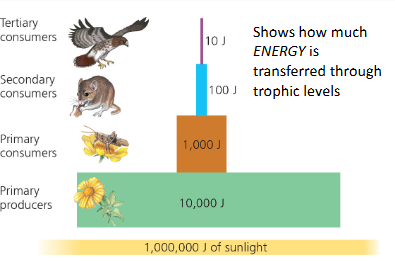
Trophic efficiency
percent of energy transferred from one level to the next
10% passes on to next level; 90% released as heat
primary consumers
eat primary producers; heterotrophs
e.g. herbivores
secondary consumers
eat primary consumers; heterotrophs
e.g. carnivores, insectivores, piscivores
tertiary consumers
eat secondary consumers; heterotrophs
e.g. carnivores, insectivores, piscivores
apex consumer/predator
highest link in energy cycle; is not eaten/preyed on by any other consumer
decomposers
take leftover energy and matter from dead producers/consumers and return to environment
conservation of matter
no matter is lost; may be changed in form but atoms in = atoms out
biogeochemical cycles
cycles that involve molecules that are essential for life and how they circulate through an ecosystem/biosphere
ex. carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, water
water cycle
recycling of all water in the biosphere since it is essential to all life
ie. precipitation and evaporation
carbon cycle
recycling of all carbon in the biosphere for organic molecules & energy (storage)
ex. photosynthesis and cellular respiration, sediments & rock
nitrogen cycle
recycling of all nitrogen in the biosphere - essential component of amino acids, proteins, & DNA
Plants can use ammonium (NH4+) & nitrate (NO3-)
Animals can only use organic forms of nitrogen (amino acids)
ex. air (80% atmosphere); fixation in soil
phosphorous cycle
recycling of all phosphorus in the biosphere - main component of nucleic acids, phospholipids, and ATP - local
ex. Marine sedimentary rocks, organisms, ocean, and soi
evaporation
water molecules go from liquid to gaseous state
water vapour
gaseous water
condensation
water vapour returns to liquid droplets/solid cyrstals in the sky to form clouds
precipitation
water falling from cloud onto land or body of waterr
river
stream of flowing water; forms from runoff from precipitation
sublimation
ice/snow to vapourtr
transpiration
evaporation of water from the surface of plants
freshwater
water with minimal ionic solutes; 2.5% of total water on planet, 68.9% of which is in glaciers, 30.8% in groundwater, and 0.3% in lakes and rivers
Average residence time for water molecules

gross primary production (GPP)
total amount of energy acquired by primary producers (via photosynthesis or chemosynthesis) in an ecosystem; total amount of energy converted to organic molecules over time
net primary productivity (NPP)
remaining usable amount of energy transmitted out of a producer after metabolic processes, heat, etc.; amount of stored energy available to consumers
NPP = GPP - Ra
Primary Productivity in Aquatic Systems
light penetration, nutrient availability, micronutreients (minerals)
Primary Productivity in Terrestrial Systems
driven by climate and vascular plants; temperature, moisture, nutrients
Respiration by autotrophs (RA)
amount of energy used by photosynthesizing organisms (~1/2 of GPP)
high productivity/NPP ecosystems
warm temperatures, high humidity and an influx of nutrients
ex. tropical wet rainforests and estuaries
low productivity/NPP ecosystems
dry and either too hot or too cold for high rates of plant growth
ex. deserts and the Arctic
Net Ecosystem Production (NEP)
amount of biomass accumulated by producers & consumers; tells us if the ecosystem is gaining or losing carbon over time
NEP = GPP - Rt
Respiration by producers and consumers (Rt)
amount of energy used by ALL organisms in the ecosystem
Carbon sinks
NEP > 0 ; net storage of carbon
Carbon sources
NEP < 0; losing more carbon than is being stored in plants and animals
Secondary production
amount of energy from food converted into new biomass
Production Efficiency
percentage of energy from food used for growth and reproduction but not respiration; inversely related to energy demands
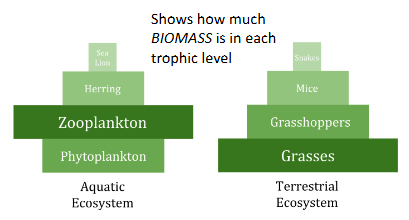
Biomass pyramids
Shows how much BIOMASS is in each trophic level; can be inverted if there is exceptionally high turnover (consumption)
Upwelling
brings nutrients from deeper water to the surface
eutrophication
excessive influx of nutrients from agricultural runoff can cause exponential growth in algal and phytoplankton populations, depleting the water of oxygen, and negatively affecting the aquatic flora and fauna
Food chain
Linear sequence of consumers, producers, and detritovores (who eats whom); Primary productivity and Loss of energy between trophic levels limits food chain length (<5 links)
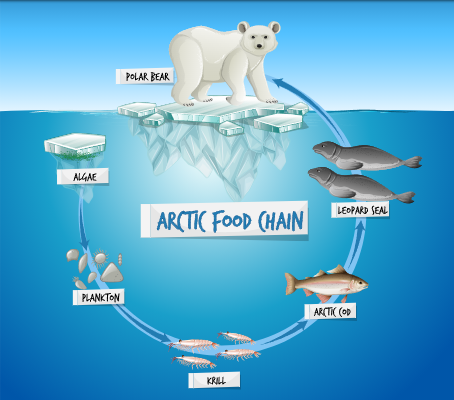
Food web
A network of interconnected food chains