Chapter 1: The Modern State of Health and Fitness
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Obesity
A complex disease involving an excessive amount of body fat; classified by a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater
Kinesiology
Study of movement as it relates to anatomy and physiology
Evidence Based Practice
A practice that relies on evidence for guidance and decision-making and includes developing individual expertise, staying current on the best sources of external evidence (e.g., peer-reviewed research), and prioritizing client values and expectations.
3 Fundamental Components of Evidence-Based Practice
Developing individual professional expertise
Staying current on the best sources of external evidence
Prioritizing client values and expectations
Practices that are not evidence-based may rely more on…
Tradition, intuition, or other unproven methods that cannot be effectively quantified or qualified through the scientific process
Client Values and Expectations
Unique preferences, concerns, goals, and expectations brought by each client to a personal training session
The integration of _____, _____, and _____, define a personal trainer’s practice as evidence based
Evidence based practice, individual personal expertise, and client values and expectations
Peer Reviewed Research
A process of subjecting an author’s scholarly work, research, or ideas to the scrutiny of others who are experts in the same field
An essential component of the evidence-based practice model
The Optimum Performance Training (OPT) Model
Developed with evidence-based practice as a core guiding philosophy
Backed by scientific research and has been successful for many types of clients, including those seeking weight loss or improvements in health, strength, muscle mass, or athletic performance
The 5 Phases of the Optimum Performance Training (OPT) Model
Phase 1: Stabilization Endurance
Phase 2: Strength Endurance
Phase 3: Muscular Development
Phase 4: Maximal Strength
Phase 5: Power
Musculoskeletal System
The combined interworking system of all muscles and bones in the body
The condition of a person’s _____ is directly related to the potential risk of injury
Muscoloskeletal System
Deconditioned
A state of lost physical fitness, which may include muscle imbalances, decreased flexibility, and a lack of core and joint stability
Overweight
A body greater than what is considered within normal standards; a BMI of 25.0 to 29.9
Muscle Imbalance
When muscles on each side of a joint have altered length-tension relationships
Joint Stability
The support provided by tissues surrounding a joint to maintain and provide control during movement
Integrated Approach to Exercise
To address the many physical and physiological needs of a client, an optimally designed fitness program should follow an _____.
An _____ represents the inclusion of the following forms of training:
Flexibility and mobility
Core strength and stability
Cardiorespiratory (cardio)
Balance
Plyometrics
Speed, agility, and quickness
Resistance
Socioeconomic Status
The social standing of a person or group that includes education, income and occupation
_____ and _____ are two simple steps within any person’s grasp that have immediate benefits toward improving overall health
Physical activity and eating healthy foods
Morbidity
The state of having a disease
Mortality
A state or a risk of death or dying
The World Health Organization (WHO)
Functions as the international public health agency of the United Nations and is focused on the development and promotion of international public health and well-being efforts
The WHO’s Definition of “Health”
A state of complete physical, mental and social-well being, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity
Health is not a static condition, but rather an ever-changing condition due to the human body’s continual need to adjust internal and external situations, changes in physiology, or changing environments
Homeostasis
The process by which the human body strives to maintain a relatively stable equilibrium in relation to the surrounding environment and the regular tasks it is required to perform
Disease
Includes any abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of a part of the body
The Two Types of Diseases
Chronic or Noncommunible (NCDs)
Acute
Chronic or Noncommunible Diseases (NCD’s)
Not contagious
Tend to be of long duration and are the result of a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental and behavioral factors
Acute Diseases
Contagious diseases, for example, the flu
The leading cause of death in the world today are classified as _____
Chronic disease and conditions
A _____ is one of the biggest causes of developing a chronic health condition
Sedentary lifestyle
How many people do not meet the recommended physical activity guidelines?
3 in 4 adults and more than 80% of adolescents
Primary Prevention (Treating Before the Conditions Develop) of Chronic Health Conditions
Regular physical activity and exercise
The strongest overall predictor of death, disability and disease
Regular physical activity
Risk Factor
Any attribute, characteristic or exposure of an individual that increases the likelihood of developing a disease or injury
Cholesterol
A waxy, fatlike substance found in bodily cells
Body Mass Index (BMI)
A comparison of a person’s height to their weight in kg by the square of the person’s height in meters or dividing body weight in pounds by the square of the height in inches and multiplying by 703.
Metric formula: BMI = weight (kg) ÷ [height (m)]2
Imperial formula: BMI = 703 × weight (lb) ÷ [height (in.)]2
BMI provides the most practical measurement of overweight and obesity because it’s the same for both sexes, and for all ages of adults
BMI is not a substitute for more precise, objective measurements of body fat composition when examining people on an individual basis. For example, elite athletes with very high levels of lean muscle mass can be mistakenly classified as obese by BMI alone, even though they may have very little body fat. For that reason, calculating BMI is just a starting point, and other body composition assessments should be considered with clients who are on a weight loss journey.
![<p>A comparison of a person’s height to their weight in kg by the square of the person’s height in meters or dividing body weight in pounds by the square of the height in inches and multiplying by 703.<br></p><ol><li><p><strong>Metric formula: </strong>BMI = weight (kg) ÷ [height (m)]2</p></li><li><p><strong>Imperial formula:</strong> BMI = 703 × weight (lb) ÷ [height (in.)]2<br></p></li></ol><p>BMI provides the most practical measurement of overweight and obesity because it’s the same for both sexes, and for all ages of adults<br><br>BMI is not a substitute for more precise, objective measurements of body fat composition when examining people on an individual basis. <span>For example, elite athletes with very high levels of lean muscle mass can be mistakenly classified as obese by BMI alone, even though they may have very little body fat. For that reason, calculating BMI is just a starting point, and other body composition assessments should be considered with clients who are on a weight loss journey.</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ff3f5140-f5e8-4477-b9c6-d48181cf021a.png)
Cardiovascular Disease
A broad term describing numerous problems of the heart and blood vessels and includes conditions such as strokes, heart attacks, heart failure, heart valve problems, and arrhythmias.
Stroke
A sudden lack of blood supply to the brain, caused by either a blockage in an artery or ruptured blood vessel
Heart Attack
The action that occurs when an artery supplying the heart with blood and oxygen becomes blocked; medically known as a myocardial infarction
Heart Failure
A condition in which the heart can’t pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs
Heart Valve Problem
A condition that occurs when one or more heart valves do not function properly, causing shortness of breath and reduced oxygen supply to the body
Arrhythmia
A problem with the rate or rhythm of a person’s heartbeat. The heart beats too quickly, too slowly, or with an irregular pattern
The most common root cause of cardiovascular disease is _____
Ischemic Heart Disease
Ischemic Heart Disease
A category of heart-related problems caused by the narrowing of coronary arteries, which supply blood and oxygen to the heart muscle
Atherosclerosis
The process by which plaque is formed in arteries leading to reduced blood flow
The most common type of heart disease which can directly result in heart attacks and strokes
Usually caused by the presence of a combination of risk factors such as tobacco use, obesity, physical inactivity, harmful use of alcohol or drugs, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, chronic stress, and poor diet
What is the most common type of heart disease?
Atherosclerosis
_____ is the number one cause of death, accounting for more loss of life than any other chronic disease
Heart Disease
Note: Studies have consistently demonstrated that individuals who maintain their aerobic fitness through regular and sustained exercise over the course of their lifetimes reduce their risk for developing heart disease
Exercise
A structured and planned form of human movement to elicit a physical adaptation, such as weight loss or improved endurance or strength. (Ex: Weight lifting, cycling, running, etc)
Physical Activity
Movement that expends energy, such as walking, yard work, recreational sports, or playtime.
_____ can be categorized as continuous or intermittent and can be performed across a wide range of intensity levels, from walking a dog to vigorously shoveling snow after a storm.
_____ is not typically structured or planned, rather, it represents natural movement throughout a person’s day.
Hypertension
Consistently elevated blood pressure
One of the primary risk factors for heart disease and stroke
Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP)
The pressure in arteries and other blood vessels when the heart is beating or contracting. It is the first (top) number recorded.
Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP)
The pressure in arteries and other blood vessels when the heart is at rest or between beats; it is the second (bottom) number recorded
Blood Pressure is Classified As….
Normal (healthy): Less than 120/80 mm Hg
Elevated: Systolic between 120 and 129 and diastolic less than 80 mm Hg
Stage 1 hypertension: Systolic between 130 and 139 or diastolic between 80 and 89 mm Hg
Stage 2 hypertension: Systolic 140 or higher or diastolic 90 mm Hg or higher
Hypertensive crisis: Systolic greater than 180 and/or diastolic greater than 120 mm Hg
Becoming more physically active can lower systolic blood pressure by an average of…
4–9 mm Hg
For individuals diagnosed with hypertension, the typical approach to treatment is…
A combination of overall lifestyle modification (e.g., smoking cessation, diet improvement, and increased physical activity) and medication.
_____ increases the risks of heart disease and stroke
Chronically elevated cholesterol levels
Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL)
Bad cholesterol
Tends to increase risk of cardiovascular disease; the form of cholesterol that makes up plaque that clogs arteries.
Levels should be less than 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL)
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
Good cholesterol
Helps remove some LDL cholesterol from the body
To help reduce the risk of heart disease, in conjunction with lowering LDL levels below 100 mg/dl, HDL levels should typically be kept around 60mg/DL
Diabetes
Chronic metabolic disorder, caused by insulin deficiency, which impairs carbohydrate usage and enhances usage of fat and protein.
Glucose
The simplest form of carbohydrate used by the body for energy
Type 1 Diabetes
The pancreas does not make enough insulin (or none at all), which is a hormone that helps transport glucose into cells to be used for energy.
Without insulin, glucose in the blood (i.e., blood sugar) can rise to dangerous levels, causing numerous health complications.
Typically genetic and is not something a person can actively prevent.
Regular exercise can help people with this disease considerably improve their blood glucose management and quality of life
Type 2 Diabetes
The body still produces insulin; however, it is not used properly by the cells.
When excess carbohydrates (specifically sugar) are chronically consumed in the diet, high levels of insulin need to be produced to help regulate blood sugar.
When excess insulin continually tries to deliver glucose to cells when they already have more than they can use, cells stop responding to it. This state is called insulin resistance.
Insulin Resistance
The inability of the cells to respond to insulin; occurs in type 2 diabetes
_____ is one of the primary indicators for a person to develop Type 2 Diabetes
Obesity
Cancer
A group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body.
Can occur in virtually every part of the body, such as muscle tissue, internal organs, bones, the blood, and the brain.
_____% of Cancers can be prevented by avoiding risk factors and implementing existing evidence-based prevention strategies
30-50%
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
A general term used to describe progressive lung diseases, including emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and refractory (nonreversible) asthma.
These symptoms are not fully reversible and significantly limit activities of daily living for those who are diagnosed
Endorphins
A group of hormones secreted by the brain that provides a variety of physiological functions, such as reducing the perception of pain
Skeletal Muscle
The type of muscle tissue that connects bones and generates the forces that create movement
_____ and _____ can also cause dysfunction in our body’s muscular and skeletal systems, which can lead to an increased risk of injury and instances of low-back, shoulder and neck pain
Sitting and inactivity
Two of the most common issues at the foot and ankle complex:
Sprains
Plantar Fasciitis
Sprains
Stretching or tearing of ligaments
Plantar Fasciitis
An inflammation of the fibrous tissue (plantar fascia) along the bottom of the foot, which often results in intense heel pain
The Three Most Common Types of Knee Injuries
Patellar Tendonitis
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tear
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Tear
Patellar Tendonitis
An injury or inflammation of the tendon that connects to the patella (kneecap) to the tibia (shin bone).
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tear
A stretch, partial tear, or complete tear of the ACL of the knee
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Tear
A stretch, partial tear, or complete tear of the MCL of the knee
Lumbo-Pelvic-Hip Complex (LPHC)
Made up of the lumbar spine (low-back area), pelvis, abdomen, and hip musculoskeletal structures and is commonly referred to as “the core.”
Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
Shoulder pain caused by rotator cuff tissues rubbing against the acromion bone of the shoulder
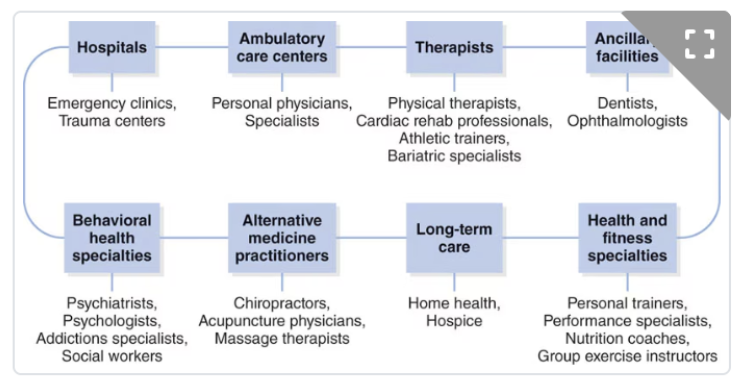
The Healthcare Continuum
Represents a systematic way to view the healthcare industry through various entry points (i.e., why healthcare is needed), types of care provided (i.e., which professional to choose), and the intended outcomes (i.e., what the individual wants to accomplish)
Describes the spectrum of preventive, acute (immediate) and long-term healthcare needs
For example, admittance to the emergency room for an injury would be acute care, whereas training with a fitness professional would be classified as preventive.