Ectoparasites and fungi
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms

Fleas (Ctenocephalides felis / canis)
Intermediate for tapeworm (Dipylidium coninum)
Transmit plague
Medium level zoonosis risk
Flea bite dermatitis
16 days - 2years life cycle
“2D”
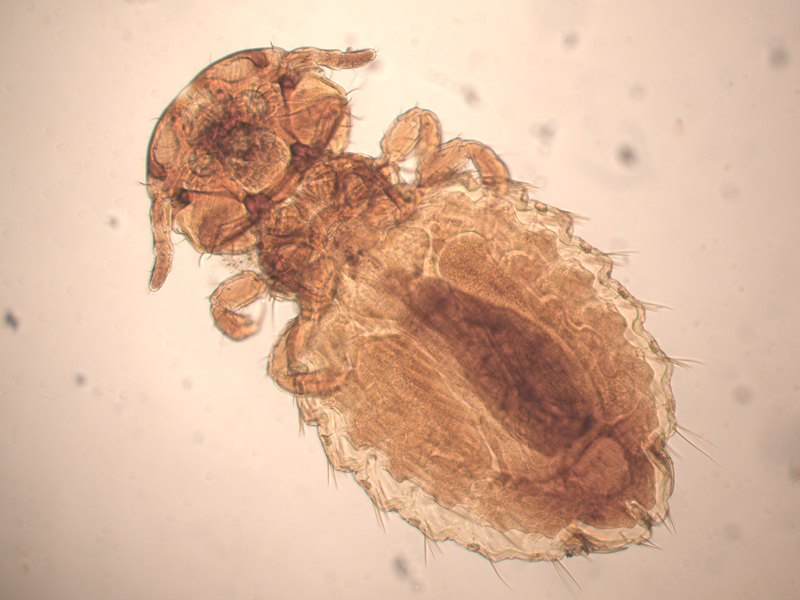
Lice (Mallophaga)
“Chewing” lice
Eggs called ‘nits’
Round head
No zoonotic potential
Itching and hair loss
3-5 week life cycle
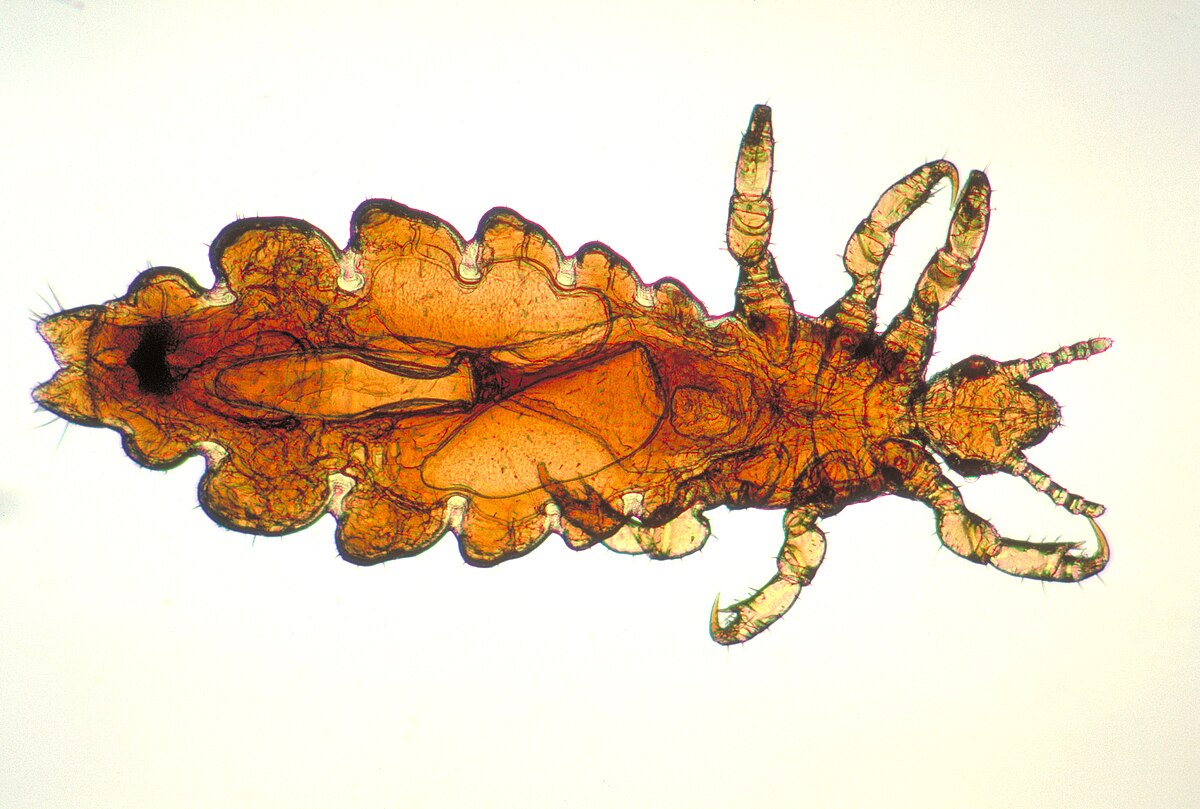

Lice (Anoplura)
“Sucking” lice
Narrow head
Burrow into skin
No zoonotic potential
Dorsoventrally compressed
Itching and hair loss
Pediculosis = infestation
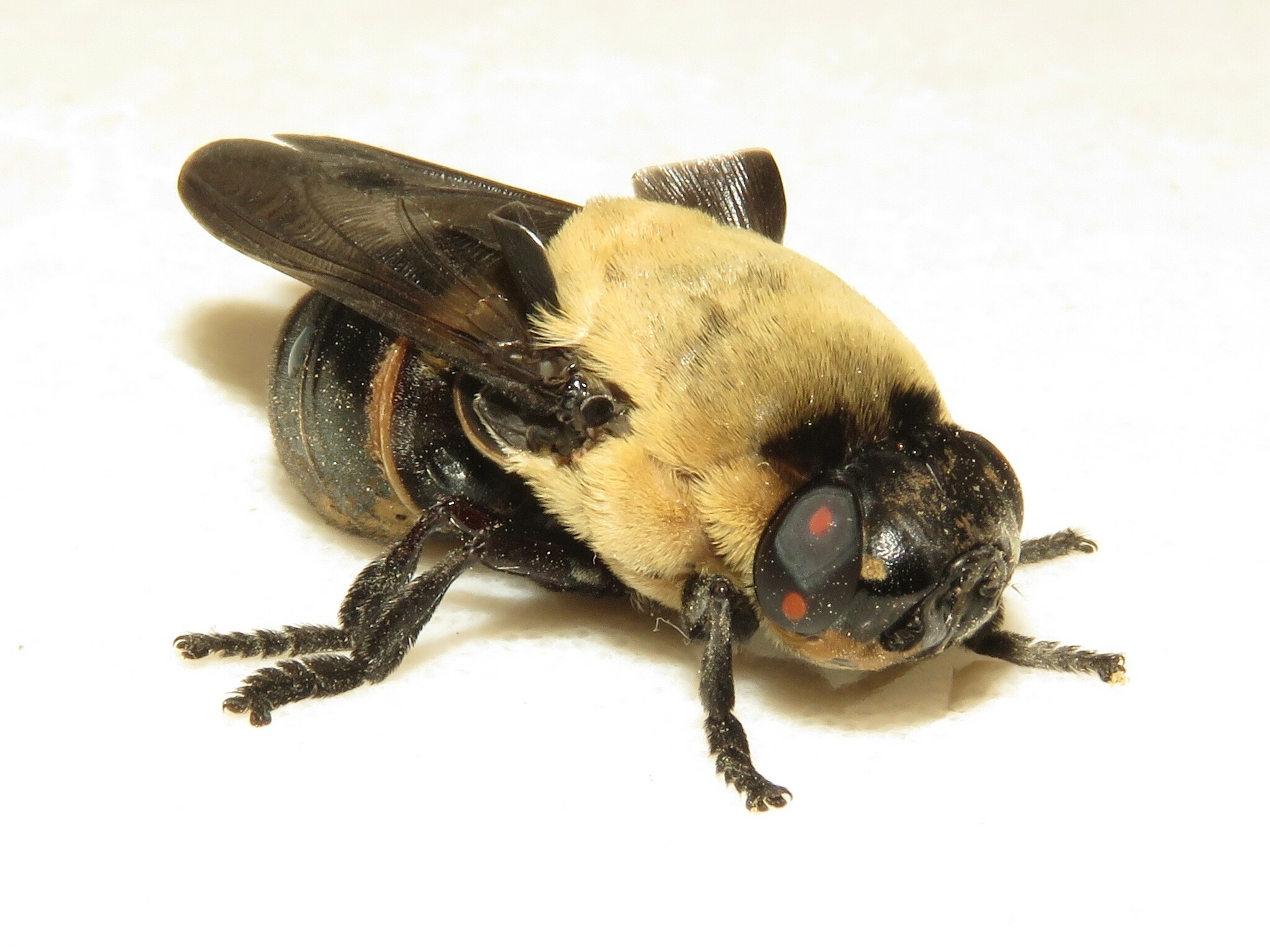

Bot fly: Small Animal (Cuterebra)
Burrow and leave opening
Develop for 30 days and then emerge
Common in rodents and small mammals
Medium zoonosis potential (Myiasis in larva)
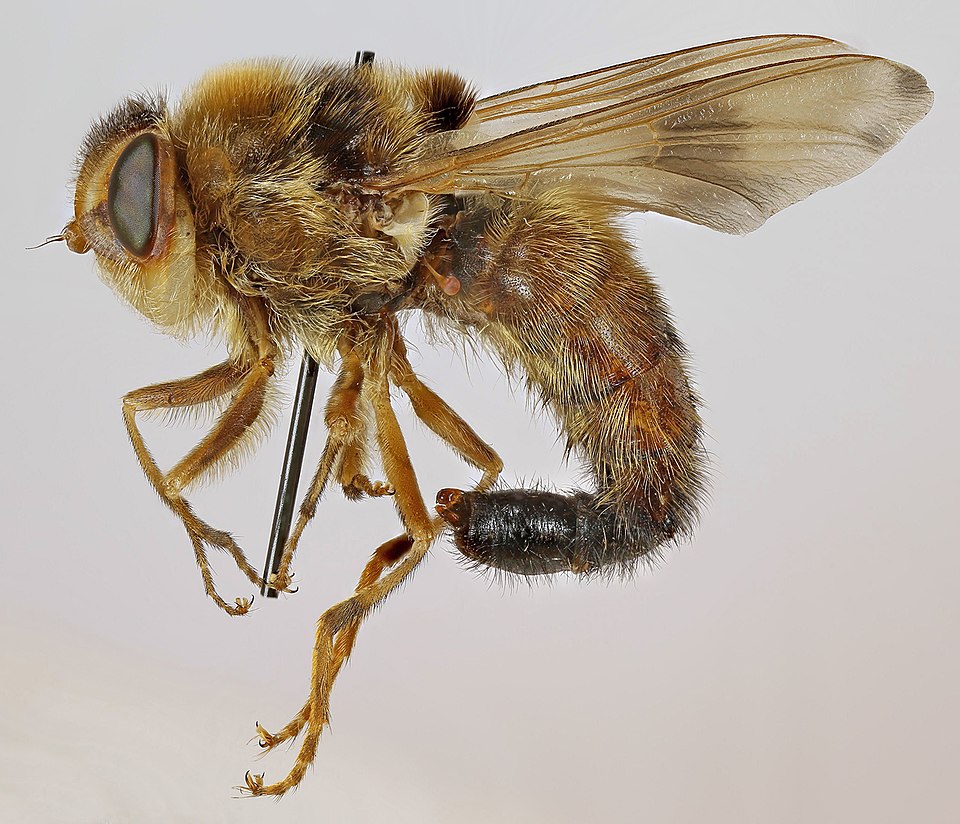

Bot fly: Equine (Gastrophilus intestinalis)
Common in equine
Develop in the stomach Warble flies
Ectto/endoparasite
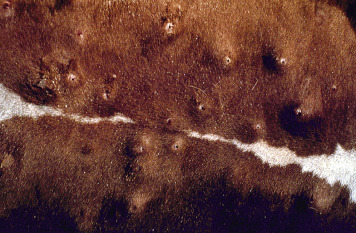
Bot fly: Cattle (Hypo-derma spp.)
Common in cattle
Grubs develop under the skin
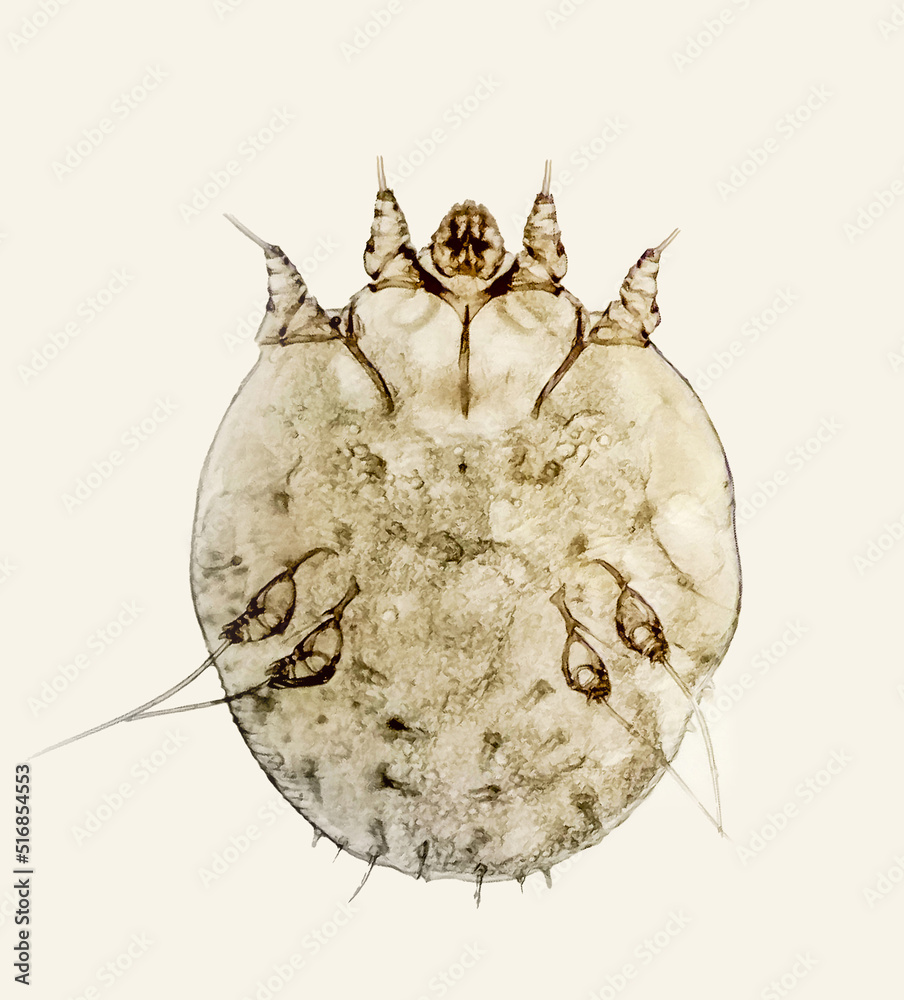

Burrowing Mite (Sarcoptes scabei)
Canine mange
Walnut shaped
Lives in superficial layers of epidermis
Feeds on tissue fluid
High zoonotic potential
Hair loss and intense pruritus
Ear flaps, groin, arm pits
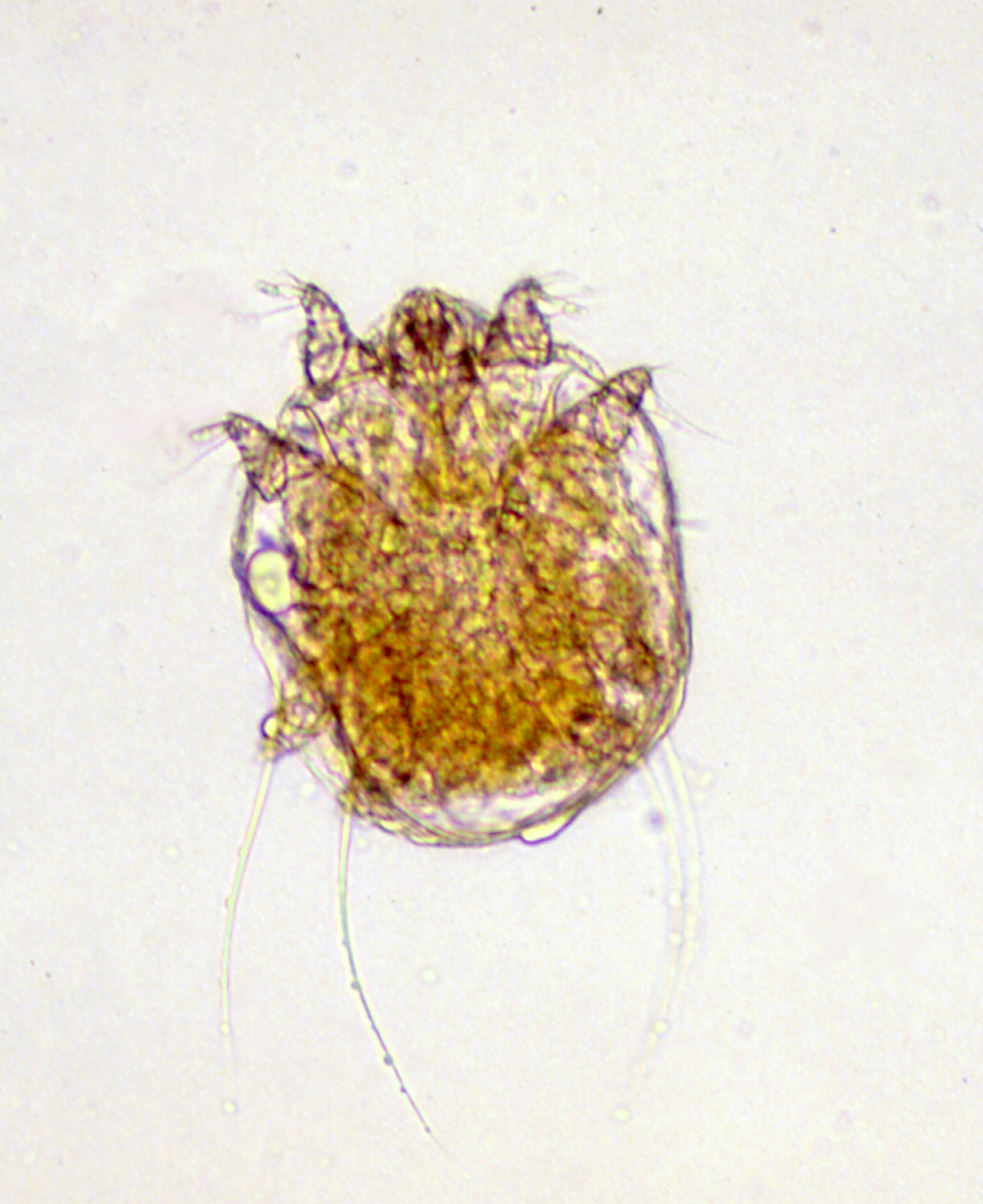
Burrowing Mite (Notodres Cati)
Feline mange
Round in shape (no scallops)
Usually confined to head and neck
High zoonotic potential
Mite infestation=acariasis

Burrowing Mite (Demodex spp.)
Cigar shaped
Live in hair follicles and sebaceous glands
Natural skin fauna
Low zoonotic potential
Generalized infection can be a sign of immunodeficiency

Non- burrowing: Ear Mite (Otodectes cynotis)
Otitis externa (cats, dogs, ferrets)
Live in outer ear canal
Feed on epidermal debris
Typically bilateral infection
Low zoonotic potential

Non-burrowing: Walking Dandruff Mite (Cheyletiella spp.)
Live on keratin layer
Feed on keratin debris and tissue fluids
Visible to the naked eye
Huge hook-like mouth parts
Low zoonosis potential
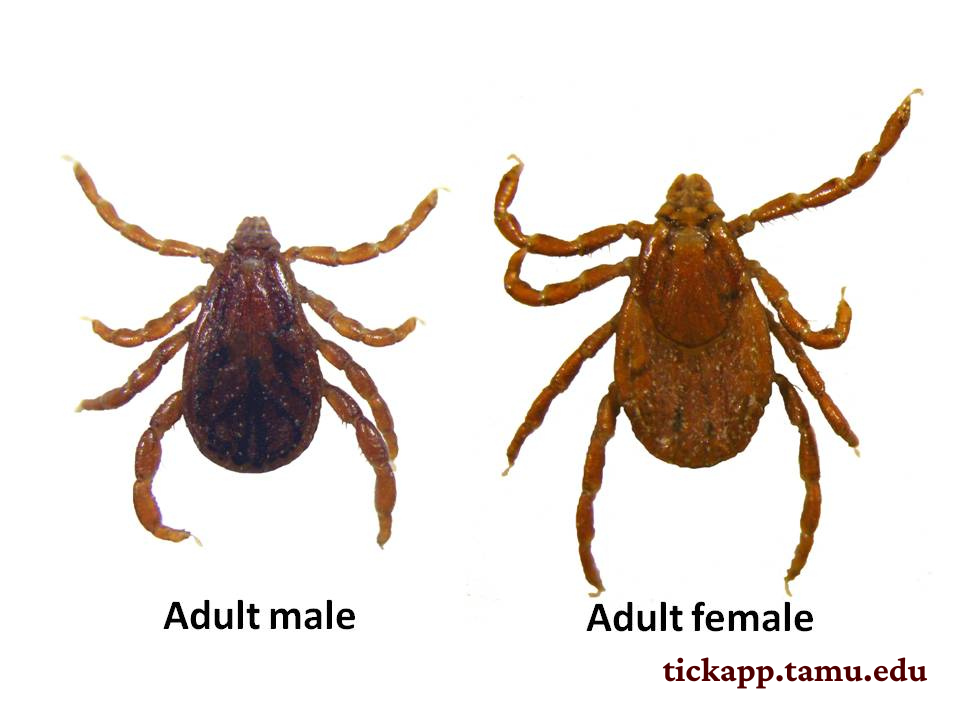

Brown Dog Tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus)
Hard ticks (Ixodidae)
Raisin appearance
Intermediate for Babesia canis
Can cause hemolytic anemia
Vector for Ehrlichia canis
High zoonotic potential

Blacklegged/ Deer Tick (Ixodes scapularis)
Mainly in north eastern U.S
Hard tick (Ixodidae)
Carry Lyme disease (Borrelia burgdorferi)
Look like deer tail
Must be attached for 48 hrs for infection to occur
Skin, joint, heart and brain abnormalities
High zoonotic potential

Lone Star Tick (Ambyomma americanum)
Signature white spot
Hard tick (Ixodidae)
Very painful bite
Carries tularemia and Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
High zoonotic potential
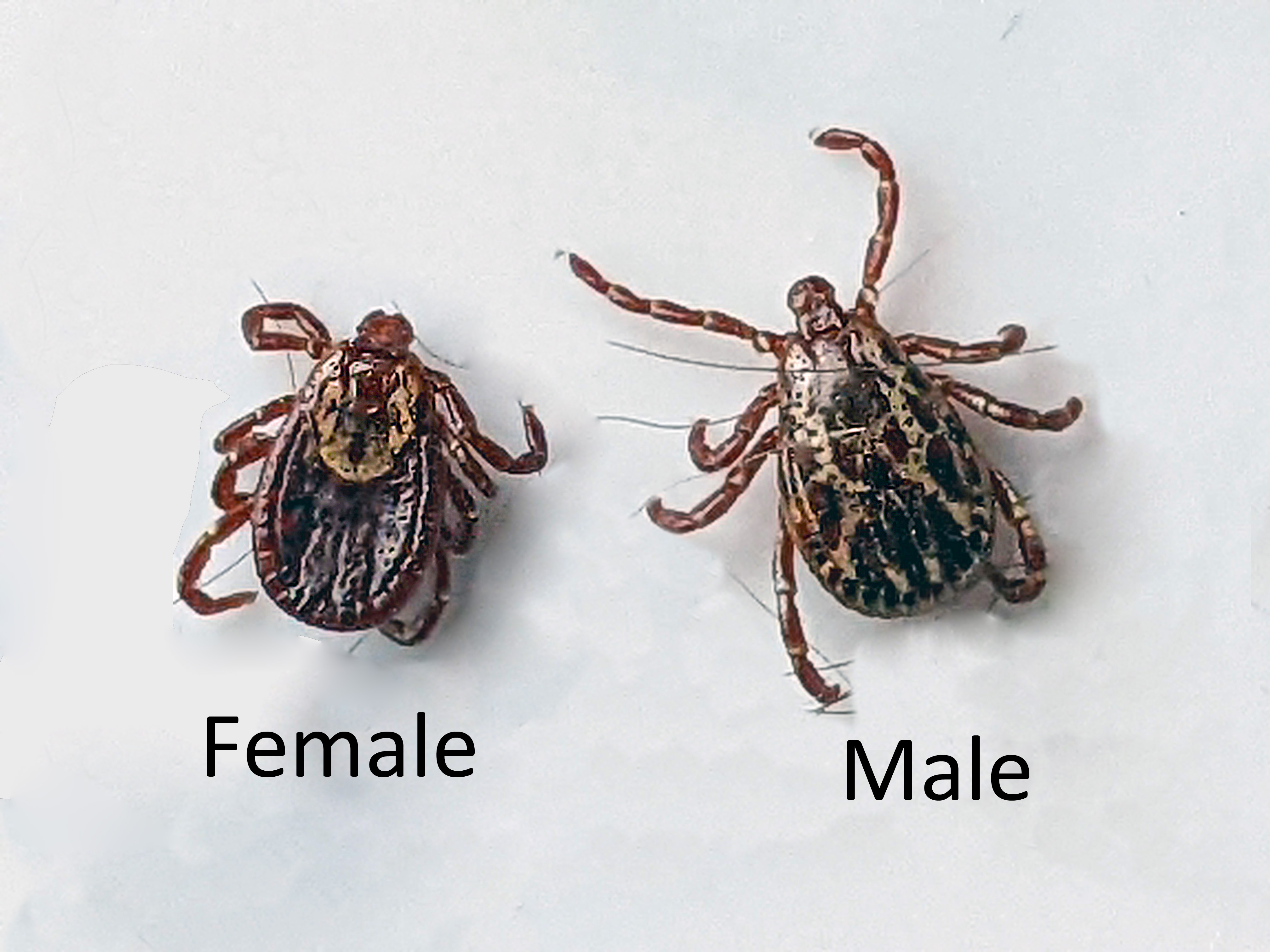

American Dog Tick (Dermacentar variabilis)
Brown body/ yellow stripe marks (bon bon)
Hard tick (Ixodidae)
Vector for Rocky Mountain Spotted fever (bacterium Rickettsia rickettsii)
Flu like symptoms
High zoonotic potential
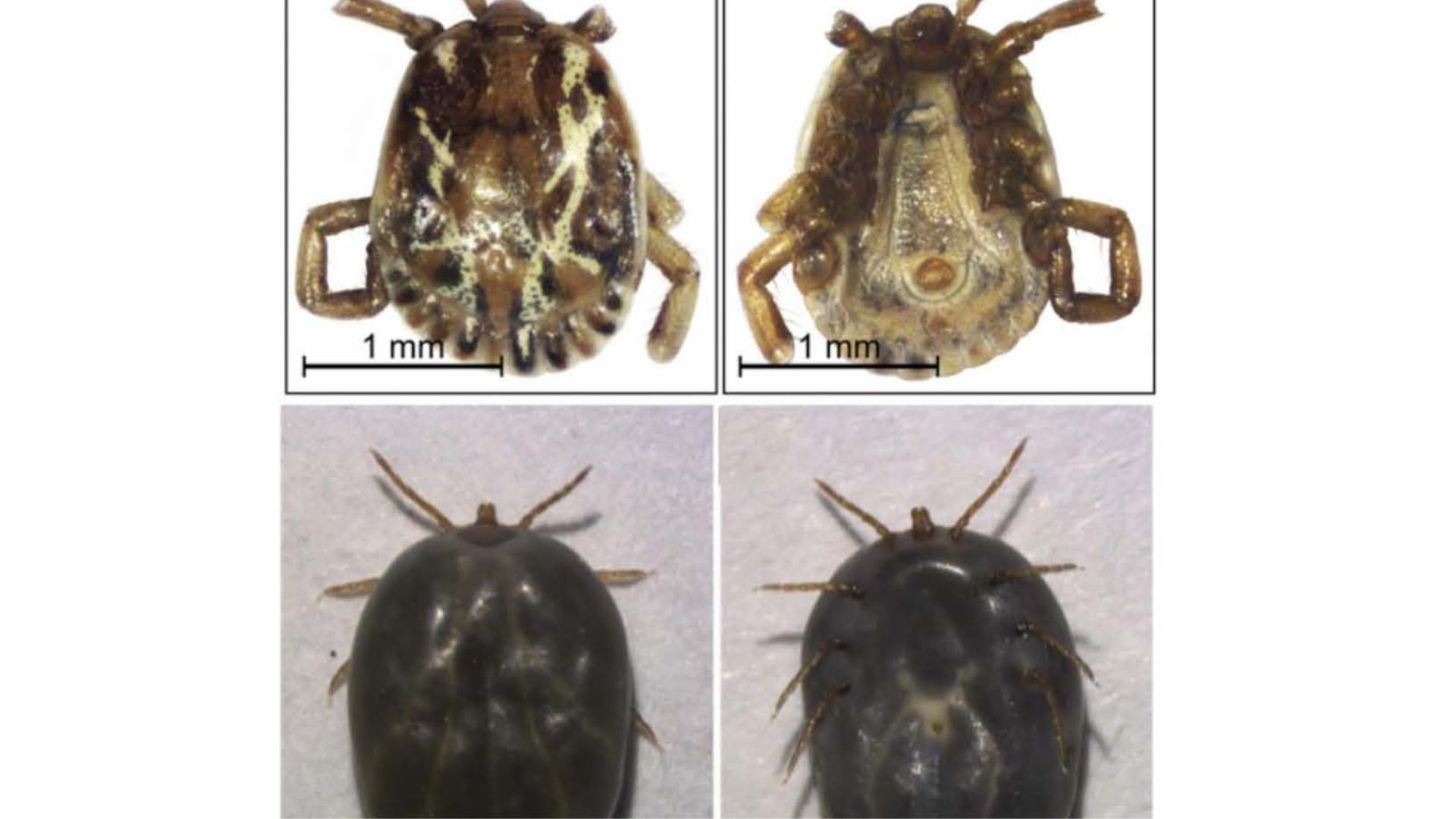

Spinose Ear Tick (Otobius megninni)
Soft tick (Argosidae)
Cause pain and muscle spasms
Common in livestock
Destroy ear canal and tympanic membrane
Only nymph and larvae are parasitic
High zoonotic potential
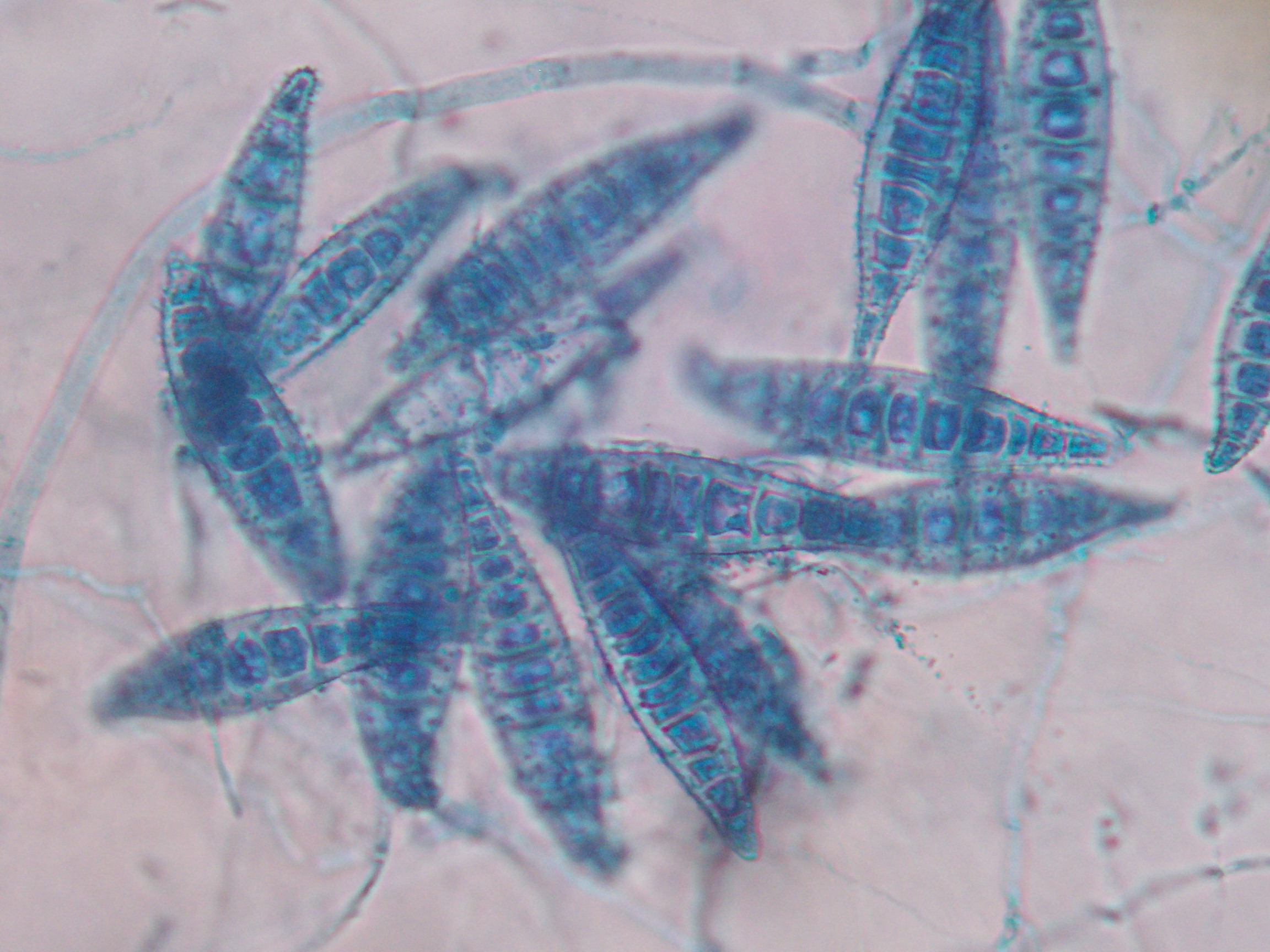
Ringworm (microsporum canis)
Caused by dermatophytes
Transmitted via contact or airborne spores
High zoonotic potential
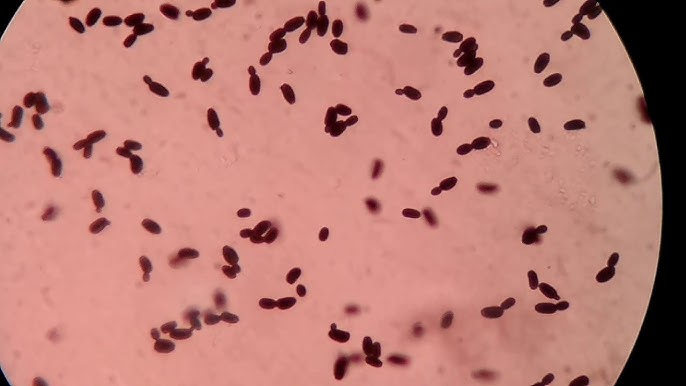
Yeast infection (Unicellular fungi)
aerobic or anaerobic
sexual or asexual
400x for best viewing
Smelly and greasy
Look like snowmen or footprints