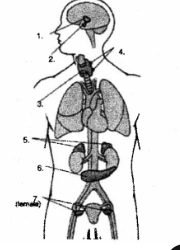
Endocrine system
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
a)Identify the hormone the hormone that targets all body cells to increase cell metabolism and body heat
b) Identify the gland that secretes this hormone
c)Identify the nutrient required to manufacture this hormone
d) identify the condition that results if there is hypsecretion
a)thyroxine
b) thyroid gland
c) iodine
d) Goiter
a)List 3 hormones that increase blood glucose levels
b)Identify each gland that secretes these hormones
c) Identify the effect of these hormones upon the target
a)Glucagon, epinephrine/non-epinephrine, cortisol
b) islet alpha cells of the pancreas secretes glucagon,the adrenal medulla epinephrine/nor-epinephrine and the adrenal cortex secrets cortisol
c)
glucagon promotes the conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver
cortisol promotes the conversion of amino acids to glucose
epinephrine/norepinepherine promotes the conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver
a)Identify two hormones which lower blood sugar
b)Identify each gland that secretes these hormones
c)Identify the effect of each of these hormones upon the target
a)insulin and thyroxine
b) beta cells of the pancreas secretes insulin and the thyroid gland secretes thyroxine
c)
insulin increases permeability of cells to glucose; increases glucose uptake
thyroxine increases cellular metabolism and the cells demand for glucose
a)Identify the hormone that raises blood calcium levels
b)Identify the gland that secretes this hormone.
c)Identify the target(s) of this hormone and effects upon the target.
a) PTH (parathryoid hormone)
b) parathyroid gland secretes PTH
c) 3 targets:
kidney is stimulated to reabsorb more calcium ion
bones are stimulated to release calcium ion
intestines are stimulated to absorb more calcium ion
Identify the 6 hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary gland and the target of each of the 6 hormones.
Six hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary gland and the target of each of the six hormones:
TSH: thyroid gland
ACTH: adrenal cortex
hGH: most cells,especially bones and muscle
FSH: ovaries,testes
LH: ovaries,testes
PRL: mammary glands
Identify the 2 hormones secreted by the posterior pituitary gland the target of each of the 2 hormones
The 2 hormones secreted by the posterior pituitary gland and the target of each of the 2 hormones:
oxytocin: uterus and mammary glands
ADH: kidneys
a)Identify the gland that controls the secretions of the anterior pituitary gland.
b)Identify the hormone that stops anterior pituitary secretions.
c)Identify the hormone that stimulate the anterior pituitary to secrete a hormone.
a) hypothalamus
b) inhibiting hormone(IH)
c) releasing hormone(RH)
a) Define homeostasis
b) Define an endocrine gland
c) Differentiate between positive and negative feedback.
a) Homeostasis is the body’s attempt to keep all its systems operating within normal limits in a fluctuating environment
b) An endocrine gland produces chemicals(hormones) that are secreted directly into the blood.
c) Negative feedback mechanisms trigger a response that reverses the changed condition; positive feedback mechanisms move the controlled variable even farther away from a steady state.
Define diabetes mellitus
Type 1 diabetes results from beta cells that are unable to produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes develops when the insulin receptors on the cells do not respond properly to insulin.
a)Identify the gland that secretes growth hormone.
b)Describe the effect of growth hormone.
a) Anterior pituitary
b)
promotes protein synthesis by increasing the uptake of amino acids by cells.
causes a switch in cellular fuels from glucose to fatty acids.
a)Identify the hormone that lowers blood calcium levels
b)Identify the gland that secretes this hormone.
c) Identify the target(s) of this hormone and the effects upon the target
a) calcitonin
b) thyroid gland secretes calcitonin
c) three targets:
kidney is stimulated to reabsorb less calcium ion
bones are stimulated to deposit calcium ion
intestines are stimulated to absorb less calcium ion
a)Explain what is meant by hypo-secretion of a hormone.
b)Explain what is meant by hyper-secretion of a hormone
a) A condition where a gland is hypo-secreting a hormone.
b) A condition where a gland is hyper secreting a hormone.
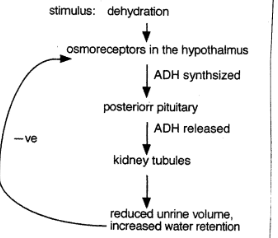
a)Identify the main function of ADH
b)Identify the gland that releases ADH to the blood.
c) What are osmoreceptors
a) ADH conserves body water by reducing urine output
b) The posterior pituitary gland releases ADH to the blood.
c) Osmoreceptors are sensory receptors in the hypothalamus that detect changes in the osmotic pressure of the blood and surrounding extracellular fluid(ECF)
a) Identify the hormone that controls sodium ion homeostasis.
b) Identify the gland which secretes this hormone.
c) Where is this gland located?
a) The hormone that controls sodium ion homeostasis is aldosterone
b)The gland which secretes this hormone is the adrenal cortex
c) The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Each adrenal gland is made up of two glands encased in one shell. The outer casing is the adrenal cortex.
a)Identify the 3 hormones secreted by the adrenal cortex.
b) Identify the effect of each hormone.
a) The three hormones secreted by the adrenal cortex are : cortisol,aldosterone and androgen.
b)
cortisol stimulates the conversion of amino acids to glucose by the liver, increasing blood sugar
aldosterone stimulates the kidney tubules to increase the absorption of sodium ions into the blood, water follows, increasing blood volume and then blood pressure
androgens supplement the sex hormones produced by the ovaries and testes and promote secondary sexual characteristics.
Illustrate the feedback mechanisms that controls the secretion of ADH from the hypothalamus
a)Identify the two closely related hormones produced by the adrenal medulla.
b)What do these hormones regulate?
c)List 6 effects of these hormones upon the body.
a) Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
b) The short- term stress response that is commonly referred to as the fight-or-flight response
c)
increase in breathing rate
increase in heart rate and blood pressure
conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver
dilates pupils
decreases blood flow to the extremities
a) Identify the two hormones that make up the long-term stress response.
b) Identify the gland that produces these hormones
c)Describe the long-term stress response for each hormone.
a) Cortisol and Aldosterone
b) Adrenal cortex
c)
aldosterone stimulates the kidney to absorb ions and water,and blood volume and blood pressure increases
cortisol stimulates protein and fat metabolism,which releases glucose,increasing blood sugar.
coritisol reduces inflammation
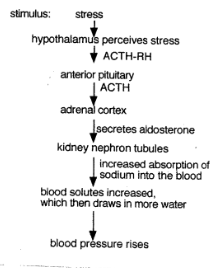
a)Identify the gland which controls the adrenal cortex.
b)Explain how this gland signals the adrenal medulla.
c) Explain how this gland signals the adrenal cortex
a) Hypothalamus
b) The hypothalamus sends a nerve signal via the sympathetic nervous system to the adrenal medulla
c)
The hypothalamus secretes ACTH-releasing hormone which stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete ACTH.
ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to release cortisol and aldosterone.
Illustrate the mechanisms for aldosterone release in the long-term stress response
Insulin causes blood glucose levels to increase or decrease?
Decrease
The pancreas secretes more insulin when blood glucose increases or decreases
Increases
Insulin causes glycogen formation by the liver to increase or decrease?
Increases
Between meals, glucose levels tend to increase or decrease?
Decrease
Glucagon stimulates liver cells to increase or decrease the conversion of glycogen to glucose?
Increases
Glucagon cause blood glucose to increase or decrease?
Increase
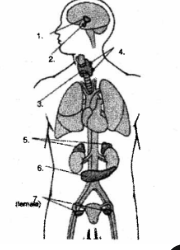
Parts of the endocrine system
Hypothalamus
pituitary gland
thyroid gland
parathyroid glands
adrenal glands
pancreas
ovaries
testes