Histology
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Simple Columnar Epithelium
single layer of tall cells
secretion and absorption
found in the small intestine
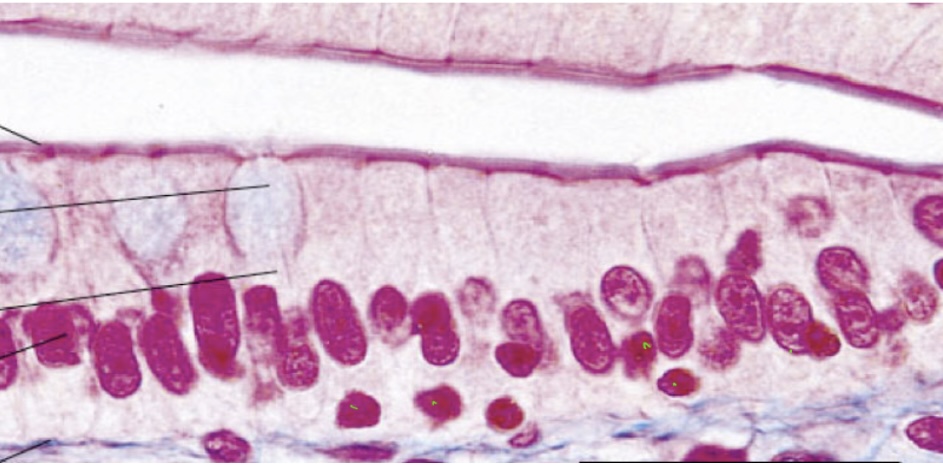
Transitional Epithelium Tissue
Resembles both stratified squamous and stratified cuboidal
Stretches readily permits stored urine to distend urinary organ
Found in the bladder
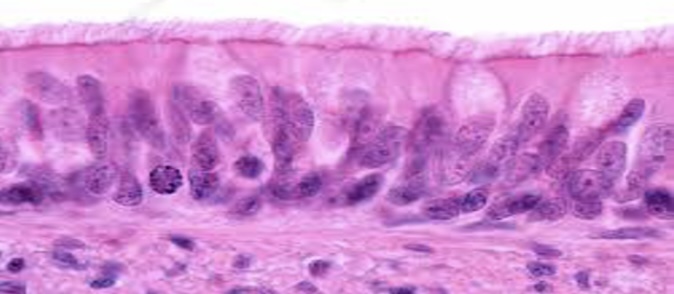
Psuedostratified Ciliated Colummar
Epithelium
Single layer of cells of differing heights with cilia
Secrete substances
Located in the trachea
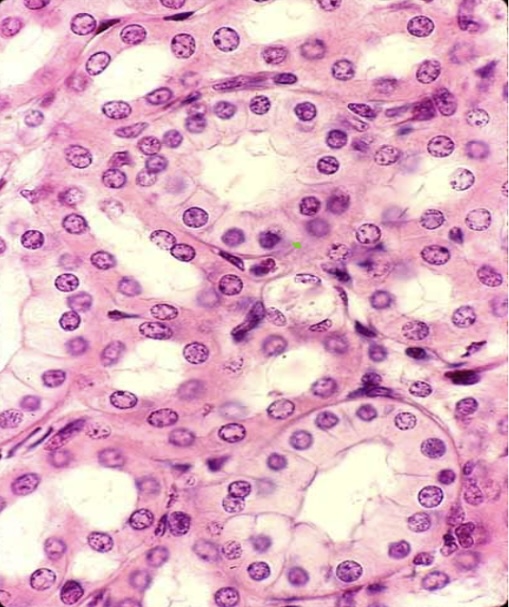
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Single layer of cube like cells with large nuclei
Secretion and absorption
Found in the kidneys and glands
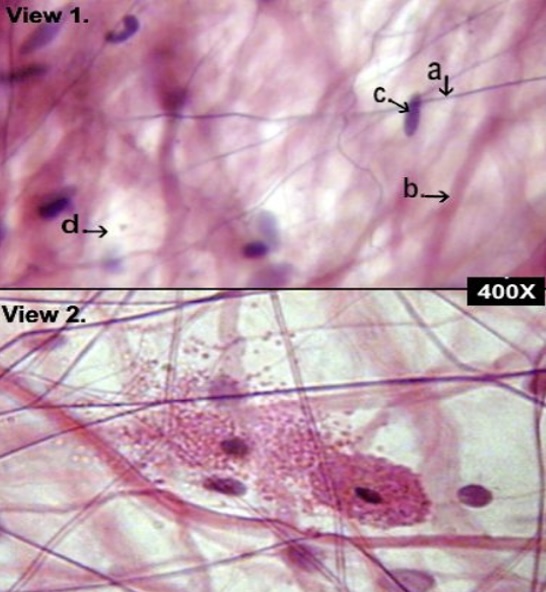
Loose (areolar) Connective tissue
Provides support and elasticity
Composed of a gel-like matrix with collagen and elastin fibers.
Serves as a binding tissue and wraps around organs, blood vessels, and nerves.
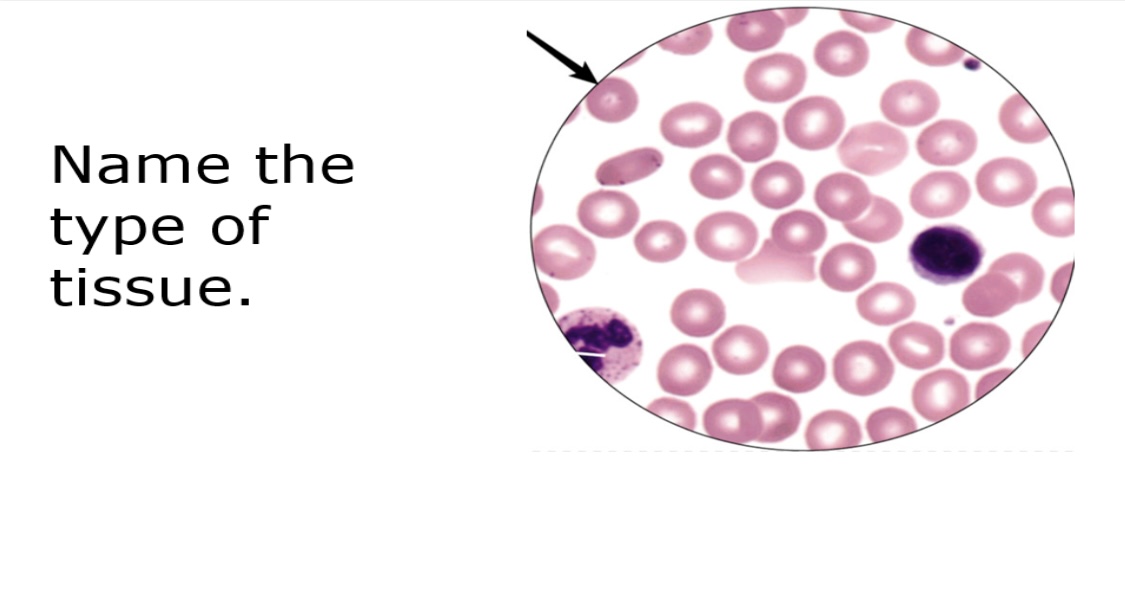
blood connective tissue
Composed of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma.
Fluid ECM
It plays a crucial role in transportation, immunity, and homeostasis.
Located in blood vessels
Fibrocartilage connective tissue
Cells sitting in holes
Wavy background “blue”
Strength
A tough, flexible type of cartilage that provides support and absorbs shock. It is found in intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, and menisci in the knee.
Reticular connective tissue
A type of connective tissue that forms a supportive framework for organs, composed of a network of reticular fibers and cells. It is commonly found in lymphoid tissues, bone marrow, and the spleen.
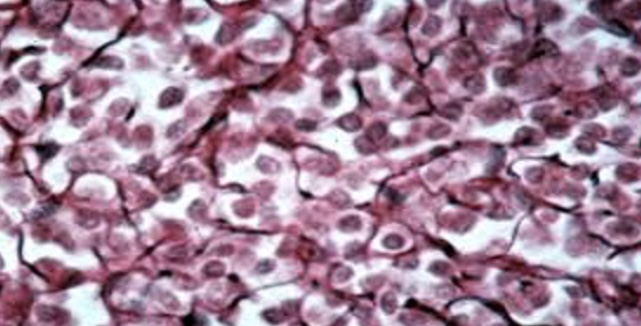
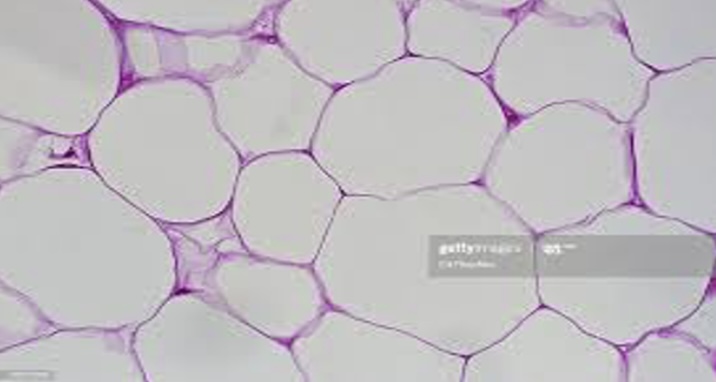
Adipose Tissue
A type of connective tissue that stores fat, providing insulation and energy storage. It is located beneath the skin in breasts
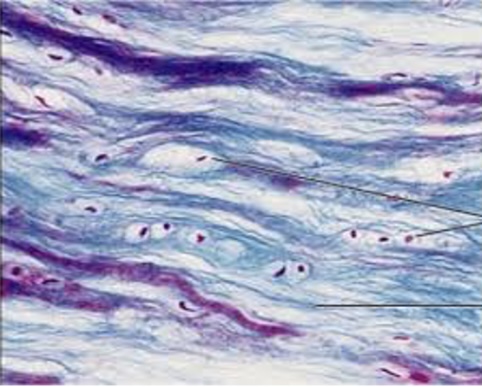
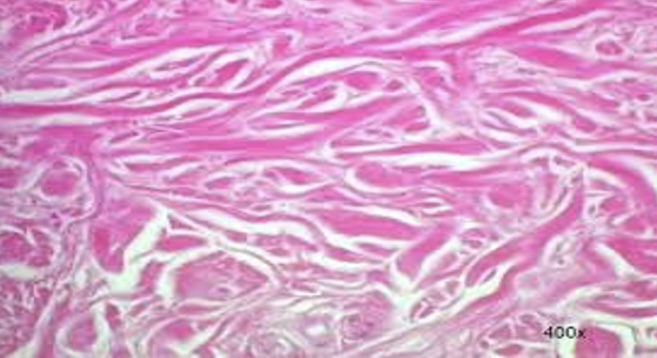
Dense regular collagenous connective tissue
a type of connective tissue characterized by closely packed parallel collagen fibers, providing tensile strength in one direction. It is commonly found in tendons and ligaments.
Avascular (takes a long time to heal)

Dense irregular connective tissue
a type of connective tissue characterized by collagen fibers arranged irregularly, providing strength in multiple directions.
It is found in the dermis
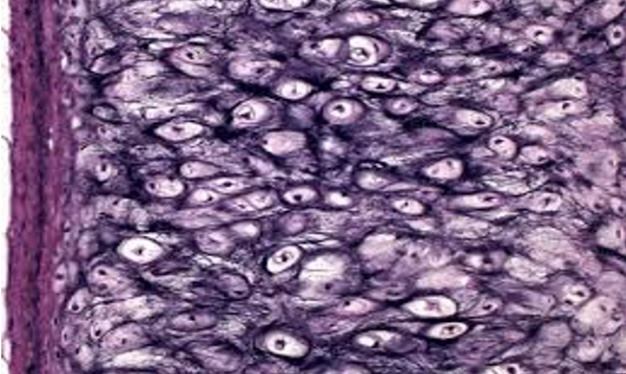
Elastic cartillage connective tissue
Cells sitting in holes
Short black fibers in ECM
Flexibility
a type of connective tissue containing a high concentration of elastic fibers
found in structures such as the ear and epiglottis.
bone connective tissue
a type of connective tissue that provides structural support and protection for organs
Solid ECM
It plays a key role in the skeletal system and houses bone marrow.
Skeletal muscle
a type of muscle tissue that is striated (banding) and under voluntary control. It is responsible for the movement of the skeleton and is composed of long, multinucleated fibers.

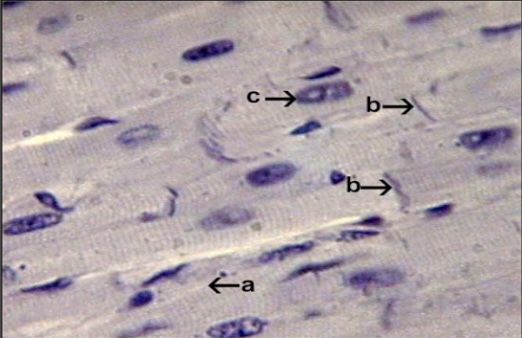
cardiac muscle
Branching striated with intercalated discs
pumps blood through the body
located in the walls of the heart
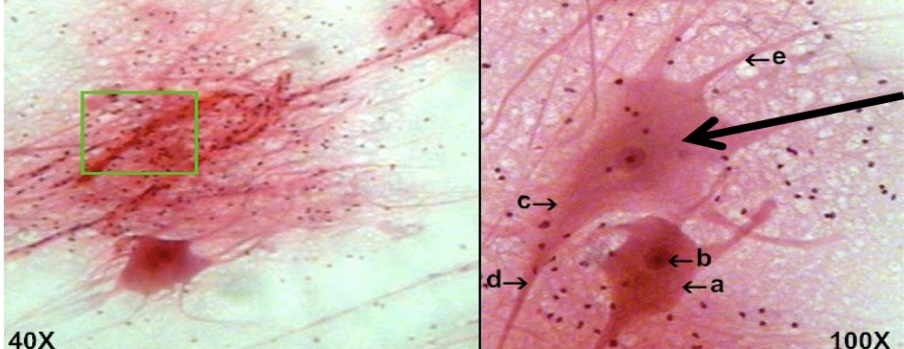
Neuron Nervous tissue
neurons transmit electrical signals
located in brain spinal cord and nerves
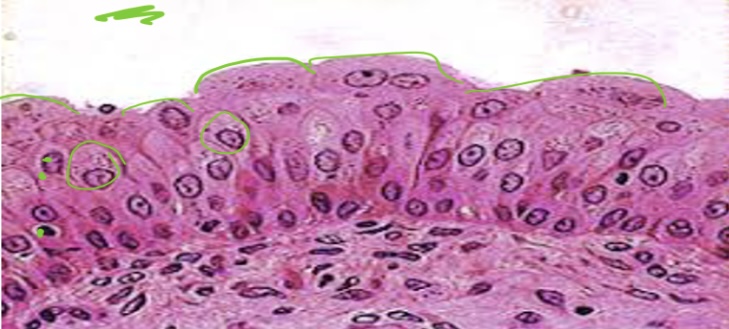
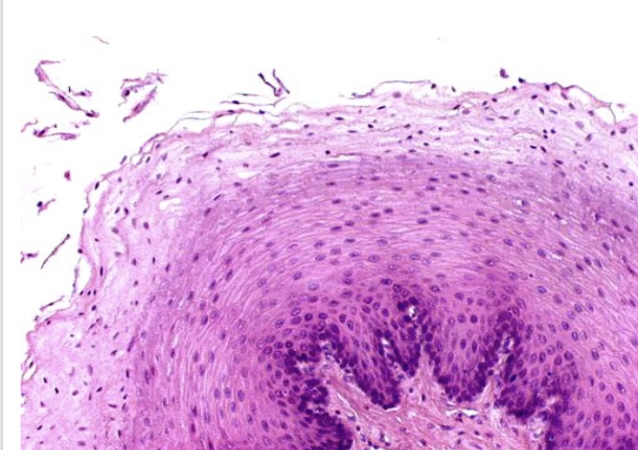
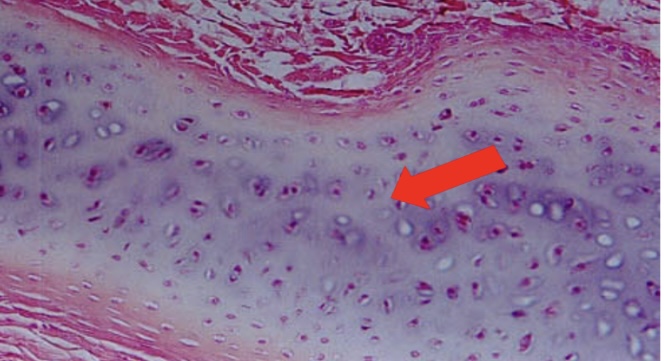
Stratified squamous epithelium
several layers of
protects tissues
located in esophagus
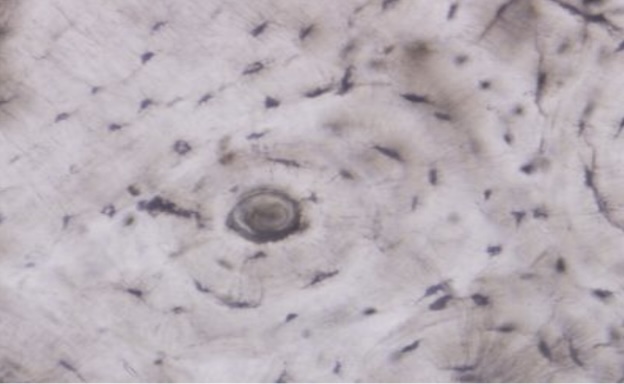
Hyaline cartilage connective tissue
Cells sitting in holes
Glossy/hazy ECM
Strength and flexibility
located in the cartilage of the ribs
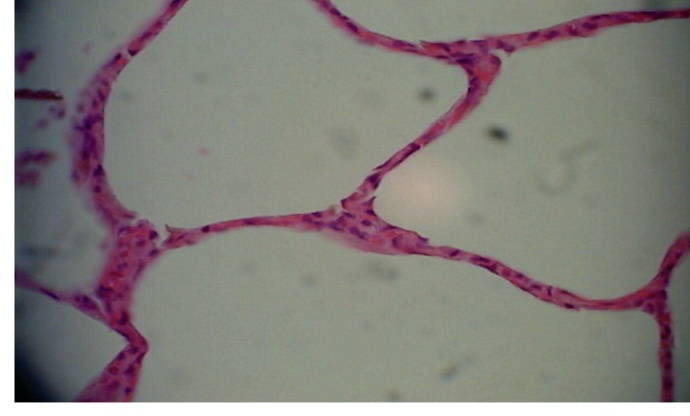
Simple squamous epithelium
single layer of flattened cells Allows
allows materials to pass through diffusion
located in lungs
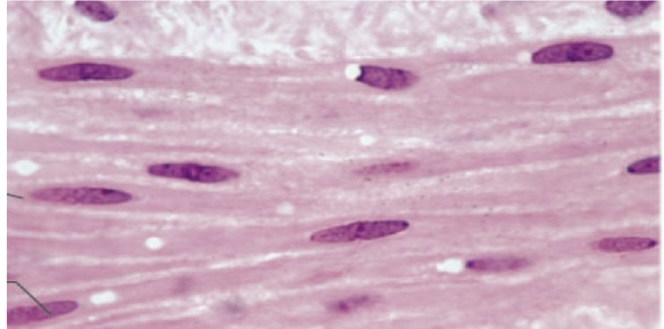
Smooth muscle
spindle shaped with central nuclei
Non striated
propels substances
in the walls of hollow organs (digestive)