Bone physiology I: cartilage and bone tissue and gross and microscopic anatomy of bones
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Cartilage
connective tissue in between bones
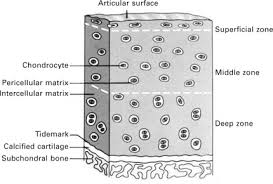
structure of cartilage
cartilage plate surrounded by a well vascularized dense CT membrane-perichondrium. Nutrients diffuse to chondrocytes from blood vessels in perichondrium
Skeletal Cartilage
type of connective tissue that forms the framework of the skeleton.
fetal skeleton
made of cartilage and fibrous membranes which are eventually replaced by bones.
what are the three skeletal cartilages
hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage
hyaline cartilage
-provides support with flexibility and resilience.
-it is the most abundant type of skeletal cartilage.
locations:
-ends of movable joints - articular cartilage.
-connecting the ribs to the sternum - costal cartilage.
-forming the skeleton of the larynx - laryngeal cartilage.
-reinforcing passageways to the respiratory system - tracheal and bronchial cartilages.
-supporting the external nose - nasal cartilages
Elastic cartilage
able to withstand repeated bending.
-found in two skeletal locations: external ear and the epiglottis.
Fibrocartilage
-highly compressible and provides for tensile strength.
-found in skeletal locations that are subjected to heavy pressure and stretch.
-pad-like cartilages of the knee - menisci.
-intervertebral disks.
Appositional cartilage growth
growth from the outside.
-chondrocytes below surrounding perichondrium secrete a new matrix against the existing cartilage.
Interstitial cartilage growth
growth from within.
-lacunae bound chondrocyte divide and secrete new matrix
Organic components of bone
responsible for bone’s flexibility and high tensile strength, has GAG, glycoproteins, collagen
what are the cell types
Osteoblast, osteocytes, osteoclasts
Osteoblasts
found in inner and outer surfaces of a bone
osteocytes
trapped by osteoid, mature bone cells, enclosed by mineralized osteoid maintain matrix-resorptive, synthetic
Osteoclasts
found in inner and outer surfaces of a bone. destroy bone, secrete proteases and acids
Proteases
destroy osteoid
Acids
dissolve bony matrix, release stored calcium and phosphates
Osteoid
organic part of matrix, secreted by osteoblast: GAG, glycoproteins, and collagen fibers
collagen fibers
responsible for bone's flexibility and high tensile strength
Hydroxyapatites
mineral salts, mostly calcium phosphates
calcium hydroxide
Responsible for hardness of bones
How are bones classified?
by shape as long, short, flat, or irregular
two types of osseous tissue
compact bone and spongy bone
compact bone
smooth and homogenous. dense and solid
spongy bone
composed of trabeculae and has much open space; space between the trabeculae is filled with marrow.
Large bones
-longer than wide
-include most bones of limbs.-
primarily compact bone but can contain spongy bone in the interior
Short bones
-include bones of the wrist and ankle.
-roughly cube-like.
-mostly spongy bone with a thin compact bone surface layer.
Flat bones
-include the sternum, ribs, and most skull bones.
-thin, flattened, and slightly curved.
-two, roughly parallel, compact bone surfaces with enclosing a layer of spongy bone.
Irregular bones
-include the vertebrae and hip bones.
-don't fit in any of the previous classes.
-mostly spongy bone enclosed by a thin layer of compact bone.
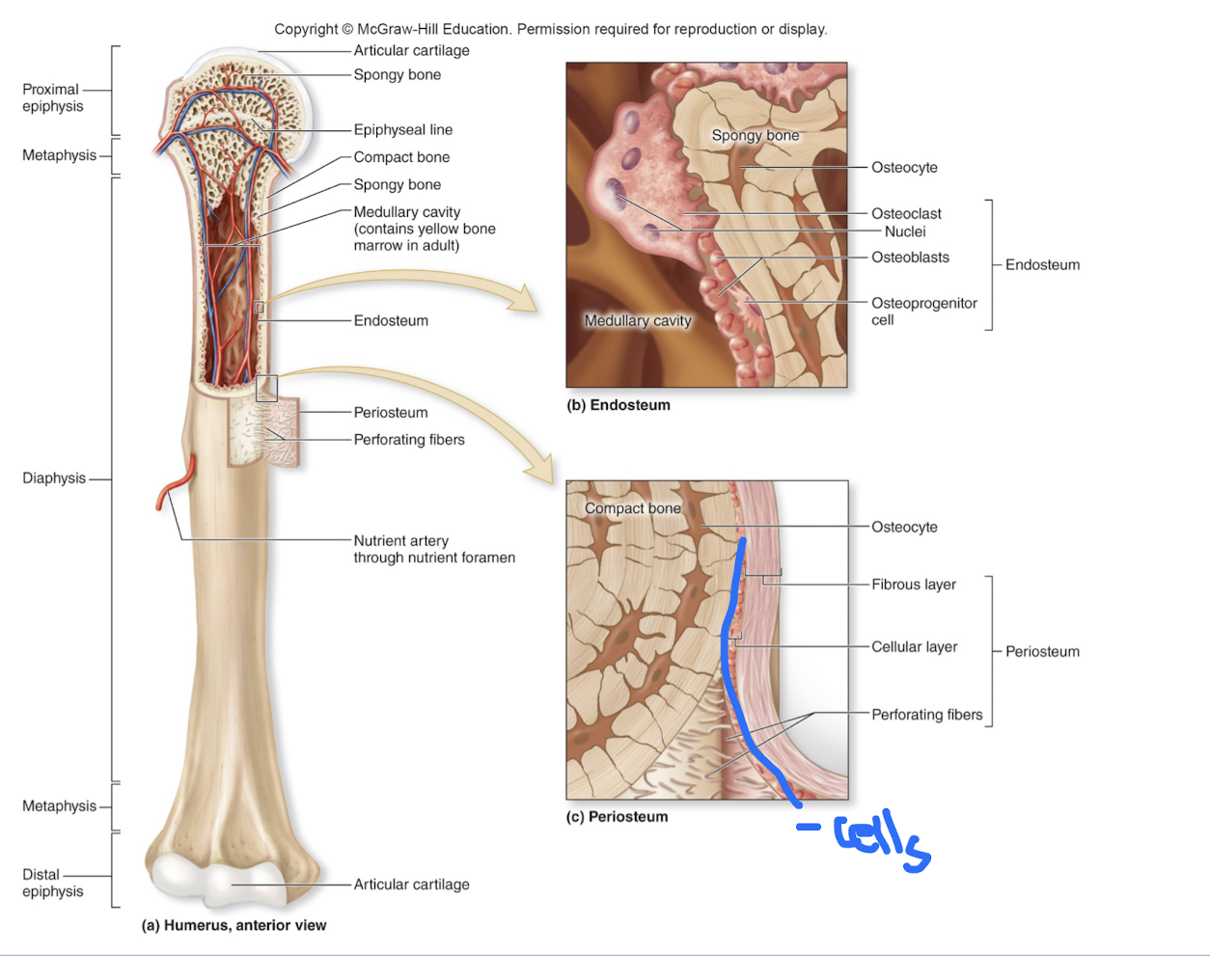
Periosteum
doubled layered membrane that lines the external bone surface.
periosteum is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels, secured to the underlying bone by collagen fibers extending from the outer fibrous layer (Sharpey's Fibers)
· outer fibrous layer - dense irregular connective tissue.
-inner osteogenic layer - abuts bone surfaces; osteoblasts, osteoclasts
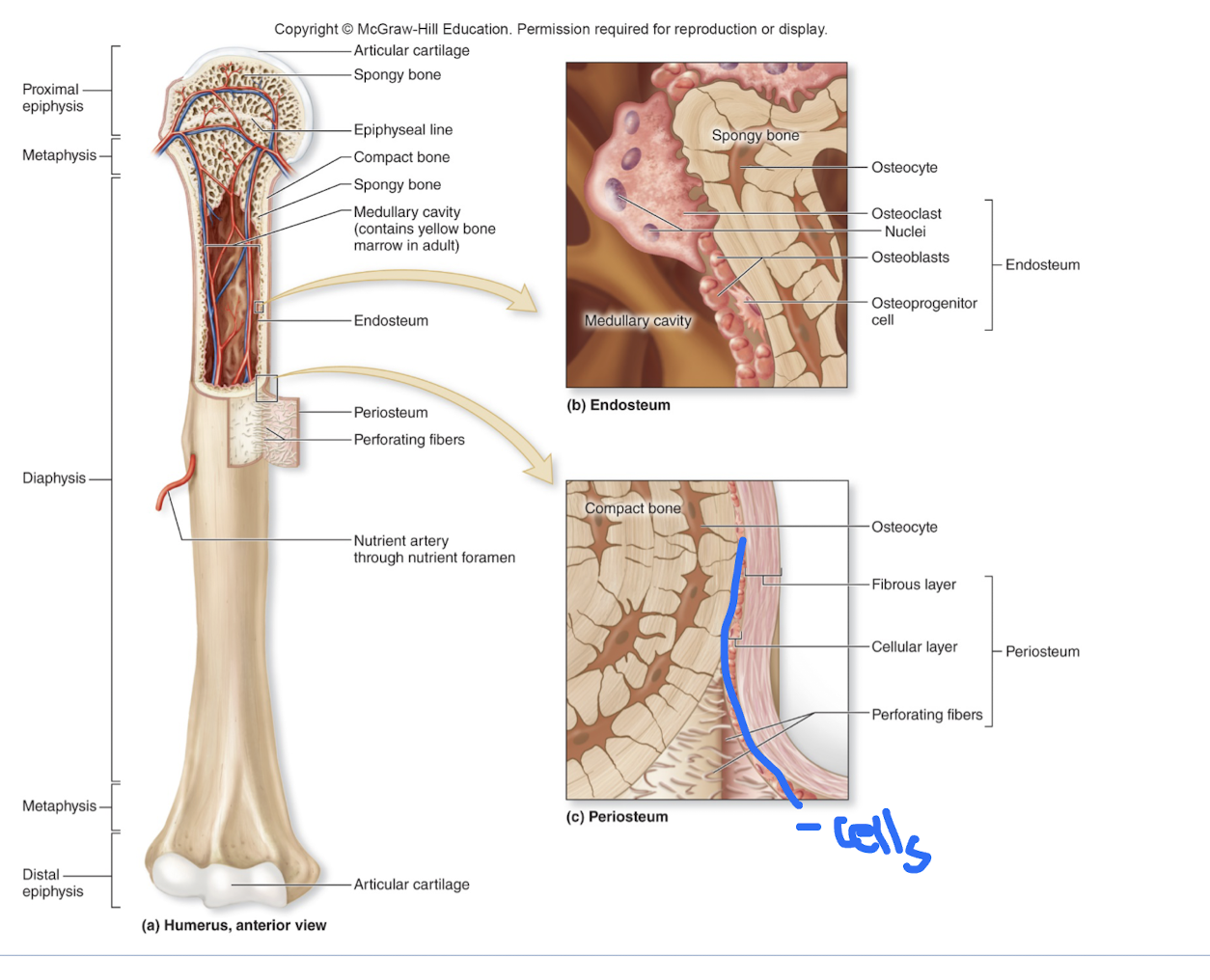
Endosteum
a delicate connective tissue membrane lining all internal bone surfaces: trabeculae of spongy bones in marrow cavities, medullary cavities in compact bone, canals of compact bone; contains osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
Structure of short, irregular and flat bones
thin pates of periosteum covered compact bone enclosing endosteum covered spongy bone -no diaphysis or epiphyses.
-bone marrow is found between the trabeculae.
-in flat bone the inner layer is spongy bone = diploë.
Location of hematopoietic tissue in bones
found within some cavities of spongy bone in long bones and in diploë of flat bones.
Microscopic structure of compact bones
very dense, contains thorough system of canals and passageways.
-osteon (Haversian System) - structural unit of compact bone.
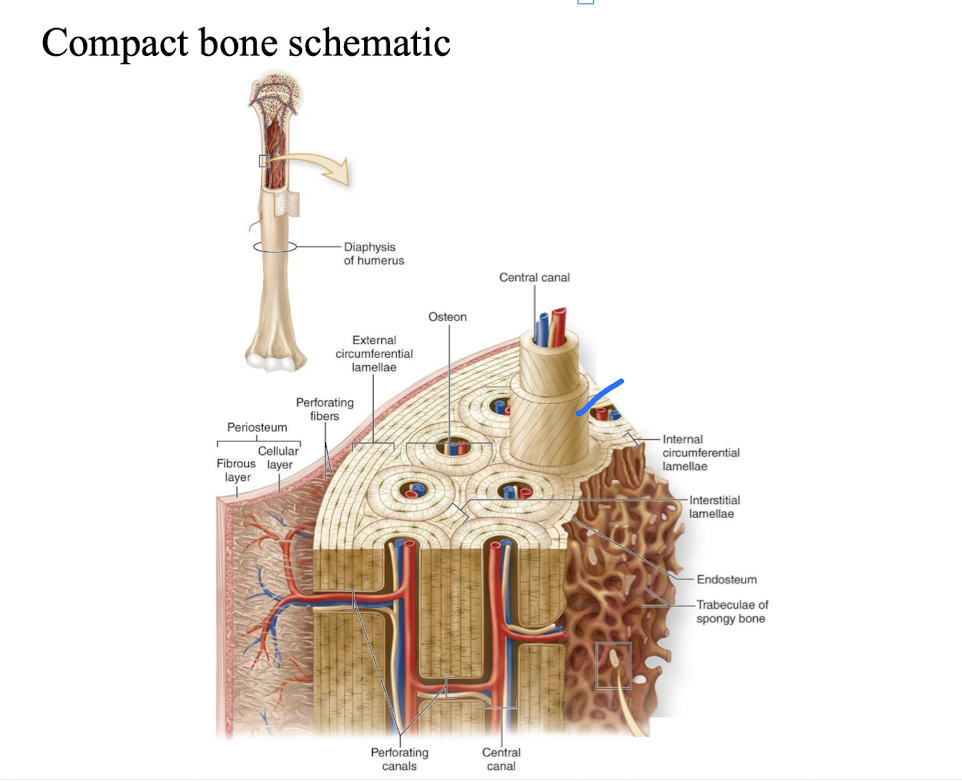
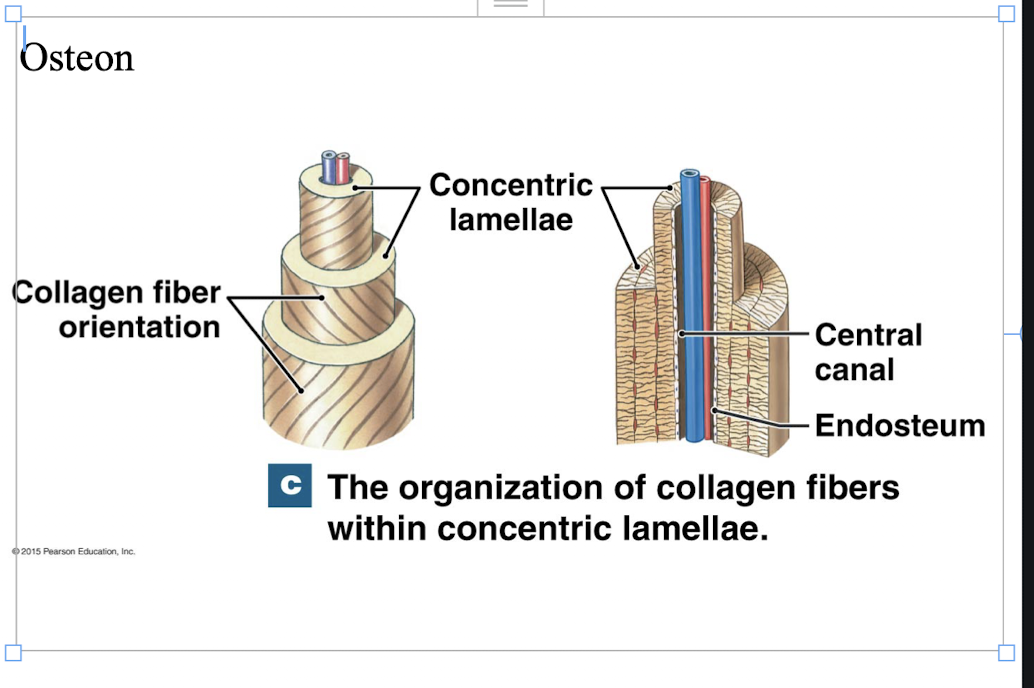
osteon (Haversian System)
-elongated cylinders running parallel to the long axis of the bone.
-formed groups of hollow tubes of bone matrix arranged concentrically.
-each matrix tube is called a lamella.
-collagen fibers within lamella run in a single direction, in adjacent lamella fibers run in opposite directions - withstand tensions.
-core of the osteon - Haversian canal (central canal) - contains blood vessels and nerve fibers serving cells in osteon.
-Perforating canals (Volkmann's): lie perpendicular to the long axis of bone.
-connect nerve and vascular supply of periosteum to those in the central canals and medullary cavity .
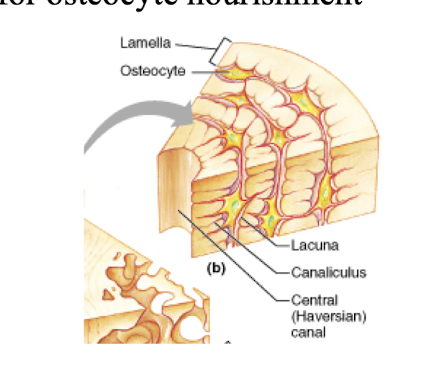
Compact bone – osteon structure
Osteocyte, canaliculi, interstitial lamellae, circumferential lamellae
Osteocyte
spider shaped mature bone cells occupy lacunae between lamellae.
canaliculi
hair-like canals between lacunae, continuous with central canal
circumferential lamellae
lamellae beneath periosteum, extend around circumference of the shaft.
interstitial lamellae
incomplete lamellae.
Spongy bone
consists of trabeculae a few cell layers thick; contain irregular lamellae and osteocytes interconnected with canaliculi; no osteons.
-trabeculae are arranged along the lines of stress.
osteogenesis
the process of bone formation
in embryos - leads to the formation of bony skeleton.
-in childhood through early adulthood - results in bone growth and increased size.
-in adulthood - remodeling and repair of bones.
Osteogenesis
formation of bony skeleton
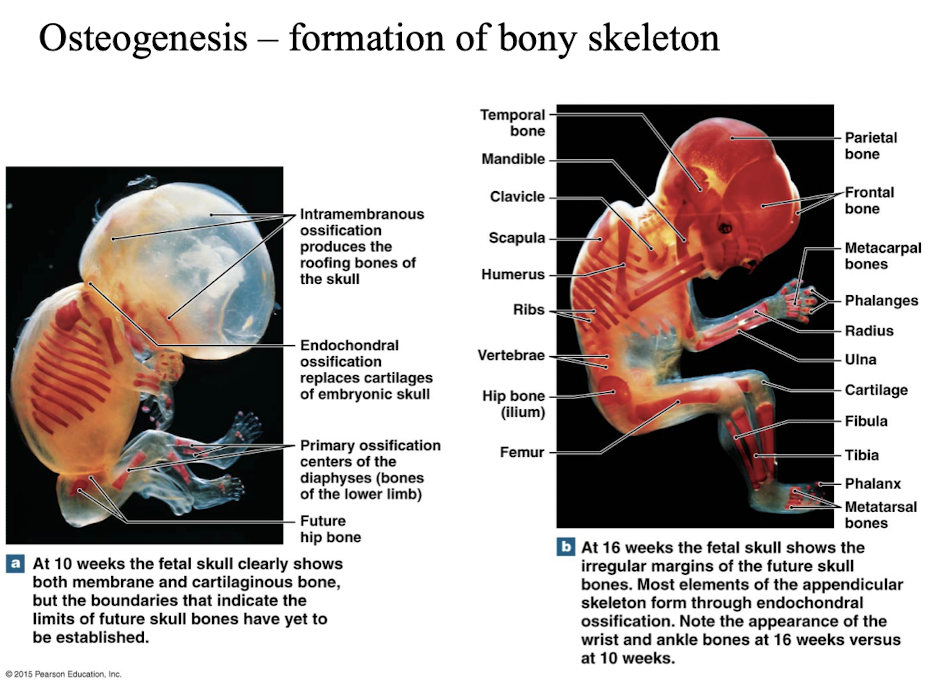
Formation of bony skeleton: (ossification in embryo)
at 6 weeks, the skeleton of an embryo - fibrous membranes/hyaline cartilage.
-bone formation involves replacing this skeleton with bone tissue.
intramembranous ossification
a type of bone formation that occurs directly from mesenchymal tissue, without a cartilage intermediate, resulting in the flat bones of the skull, clavicles, and mandible
bone develops from a fibrous membrane.
formation of all flat bones.
-mesenchymal cells of fibrous membrane differentiate into osteoblasts, secrete osteoid.
endochondral ossification
bone develops from hyaline cartilage.
a process by which cartilage is converted into bone tissue, forming most of the bones in the human skeleton
forms other bones of the skeleton (non-flat bones).
-template is hyaline cartilage.
-begins at the primary ossification center at the center of the hyaline cartilage shaft.
All bones grow in thickness by
appositional growth
Why do carrier proteins have to be phosphorylated in active transport?
Increases the affinity for the substrate.
What happens to a carrier when a substrate binds?
Carrier undergoes conformational change.
What happens to the carrier after the change?
De-Phosphorylation of carrier follows conformational change.
How much sodium and potassium are moved in and out of a NaK pump?
3 Na
2 K
Does Sodium potassium pump actively use atp?
yes
NaK pump creates?
electrical gradient
What does NaK pump establish?
ion gradient
Synport?
2 molecules are moved in the same direction
Secondary Active
One molecule moved low to high, other molecule moves high to low
SGLT
Antiport?
Two substances move in opposite directions
Sodium Potassium Pump
Uniport
Facilitated diffusion into body cells; one substance transported
What does secondary active transport need to do
Create sodium gradient- has no direct use of ATP
Which messenger has cholesterol
Steroids
Are steroids polar or nonpolar
nonpolar
Are amines polar or nonpolar
nonpolar
Are peptides polar or nonpolar
polar
Where do prostaglandins act?
Smooth muscles, platelets, kidney and bone
What is mode of action
how chemical messengers exert effects on other cells varies- depends on chemical structure of messenger
Hormone binding receptors can...
alter membrane permeability by acting on a channel protein directs, directly activate enzyme, alter cytoskeletal shape, result in production of second messenger
What differs in epinephrine and heart cells and ADH and Kidneys if the membrane pathway is the same?
Protein that phosphorylates is different.
What initiates transcription in lipid soluble messengers?
Hormone/receptor complex binding to DNA promoter
Where is cartilage most prominent?
Areas where tensile strength and resiliency is needed
What are the two properties of cartilage
H2O (resiliency) and Collagen (strength)
Can cartilage regenerate?
Has limited opportunities
More collagen=
more exposure to stressors
What are the functions of bones?
Support, protection, movement, storage, blood cell formation
Organic components of bone tissue
Cells (osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes)
Matrix
Collagen
What are the inorganic components of bone tissue
Calcium salts
What are osteocytes
mature bone cells, enclosed by mineralized osteoid
What are osteoblasts
Builds bones (osteoids)
Diaphysis
shaft of lone bone
epiphyses
ends of long bone
epiphyseal line
remnant of epiphyseal plate
2 parts of periosteum (outer bone)
outer fibrous layer, inner osteogenic layer (with cells)
Endosteum (inner bone)
lining in the hollow part of a bone (cells)
What is the periosteum
double layered membrane that lines external bone surface
double layered membrane that lines external bone surface
red marrow
What type of marrow do adults have
yellow marrow
Osteons
concentric bone layers that run longitudinally alone bone
What is the function of perforating canals and central canals
help nutrients into the bone via vessels
What does the concentric lamellae do?
Make longitudinal stress easier
What do canaliculi help do?
diffuse nutrients
Where are trabeculae located
along lines of stress
are lamellae concentric
no
Properties of carrier mediated transport
specificity, competition, saturation
What is specificity
Can move ions- made to only bind to certain ions
What is saturation
limited amount of substance can be transported across a membrane by a given carrier
What is competition
Rate of "X" transport will go down when "Y" is introduced
What is neuroendocrine
Neuron messages into blood
endocrine
messenger into cell into body
Paracrine
local
Autocrine
Message into cell