C9 - Crude Oil and Fuels
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
A Hydrocarbon
compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
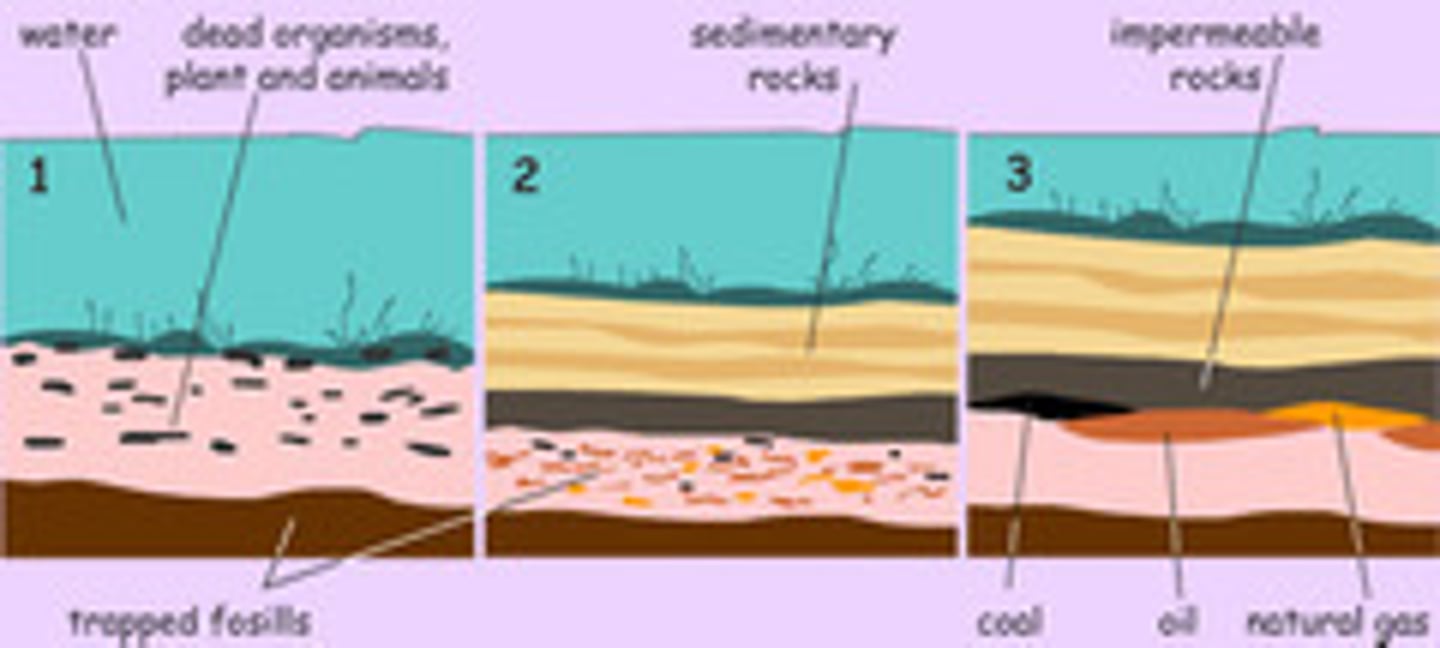
How Crude Oil is Formed
- plankton from thousands of years ago absorbs energy from the sun
- the plankton dies but doesn't decay as it's in the sea
- it is deposited to the sea floor
- over the years, sedimentary rock builds up and buries it
- over millions of years, heat and pressure builds up on the rock
- a "soup" of vegetation is made as water is squeezed up
- the plankton is eventually turned into crude oil
Crude Oil
a mixture of different hydrocarbons that are wrapped up as a liquid

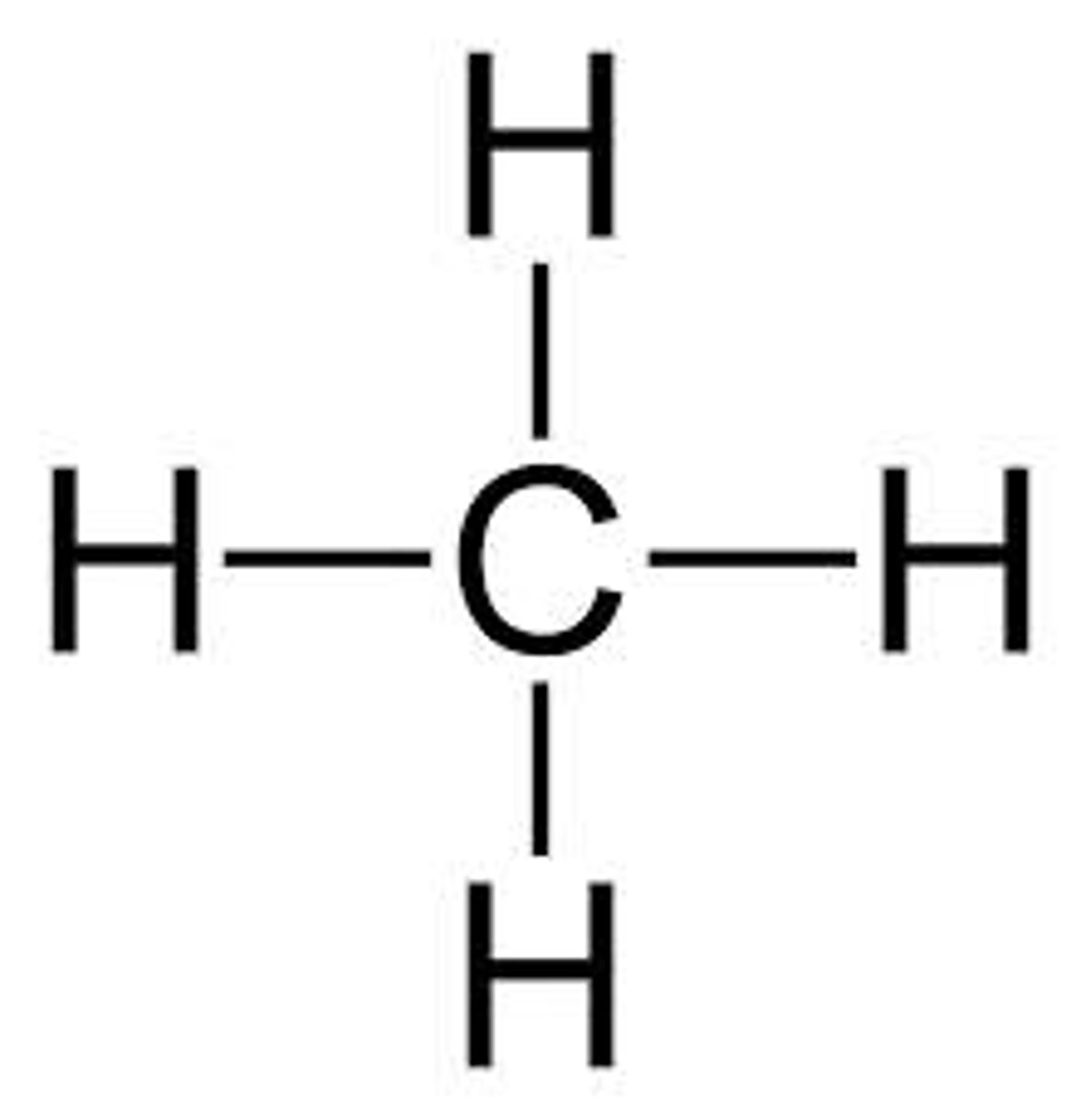
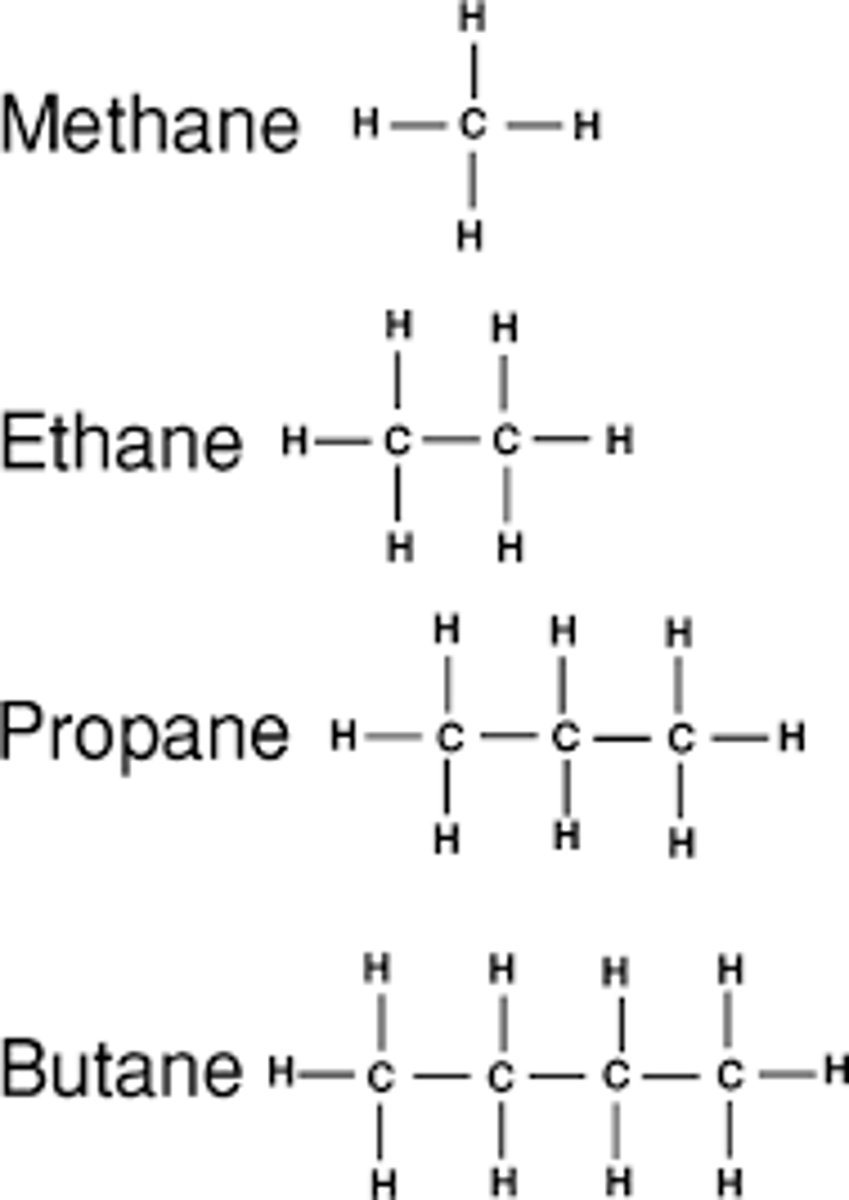
1 Carbon
meth
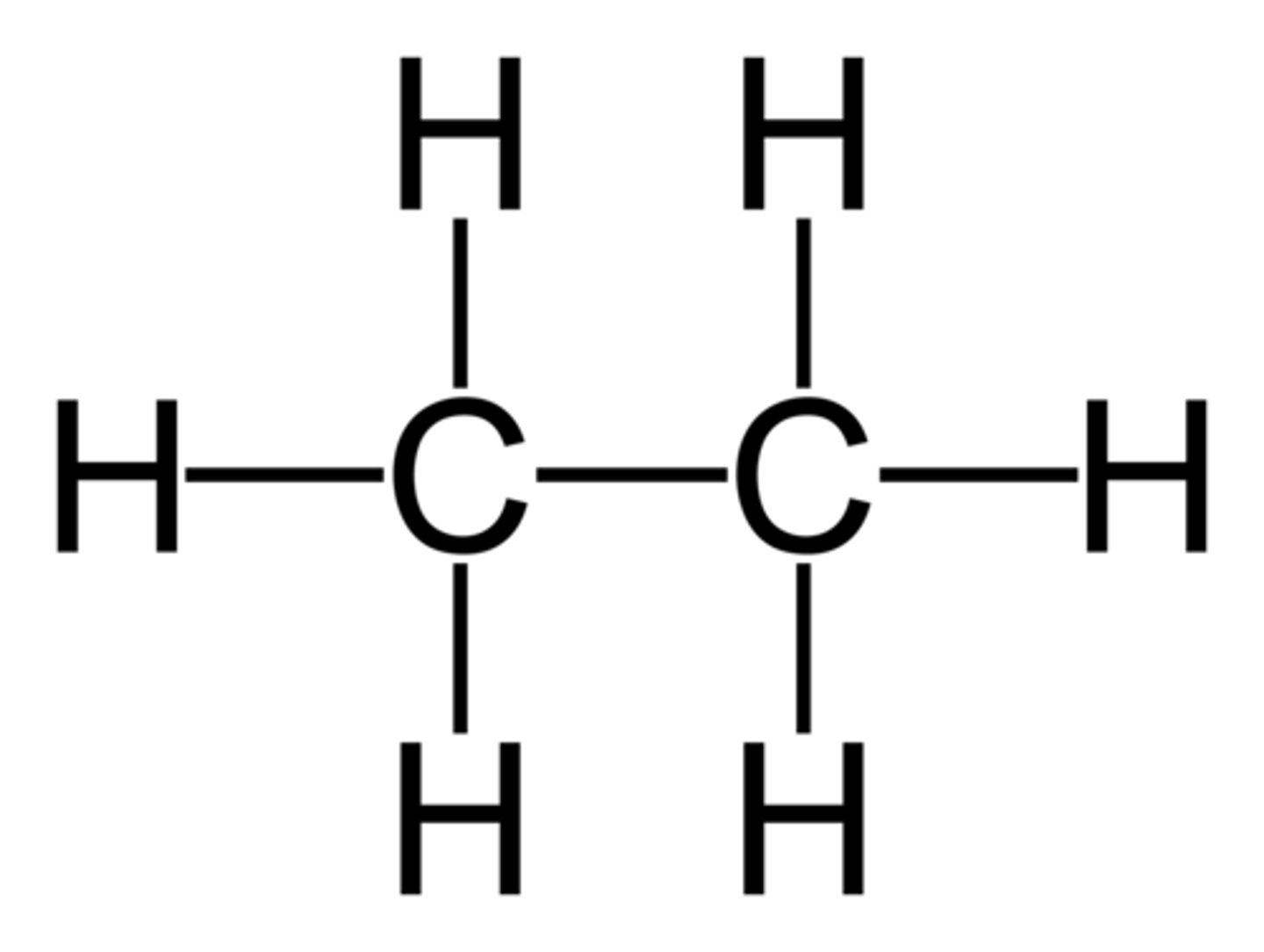
2 Carbons
eth
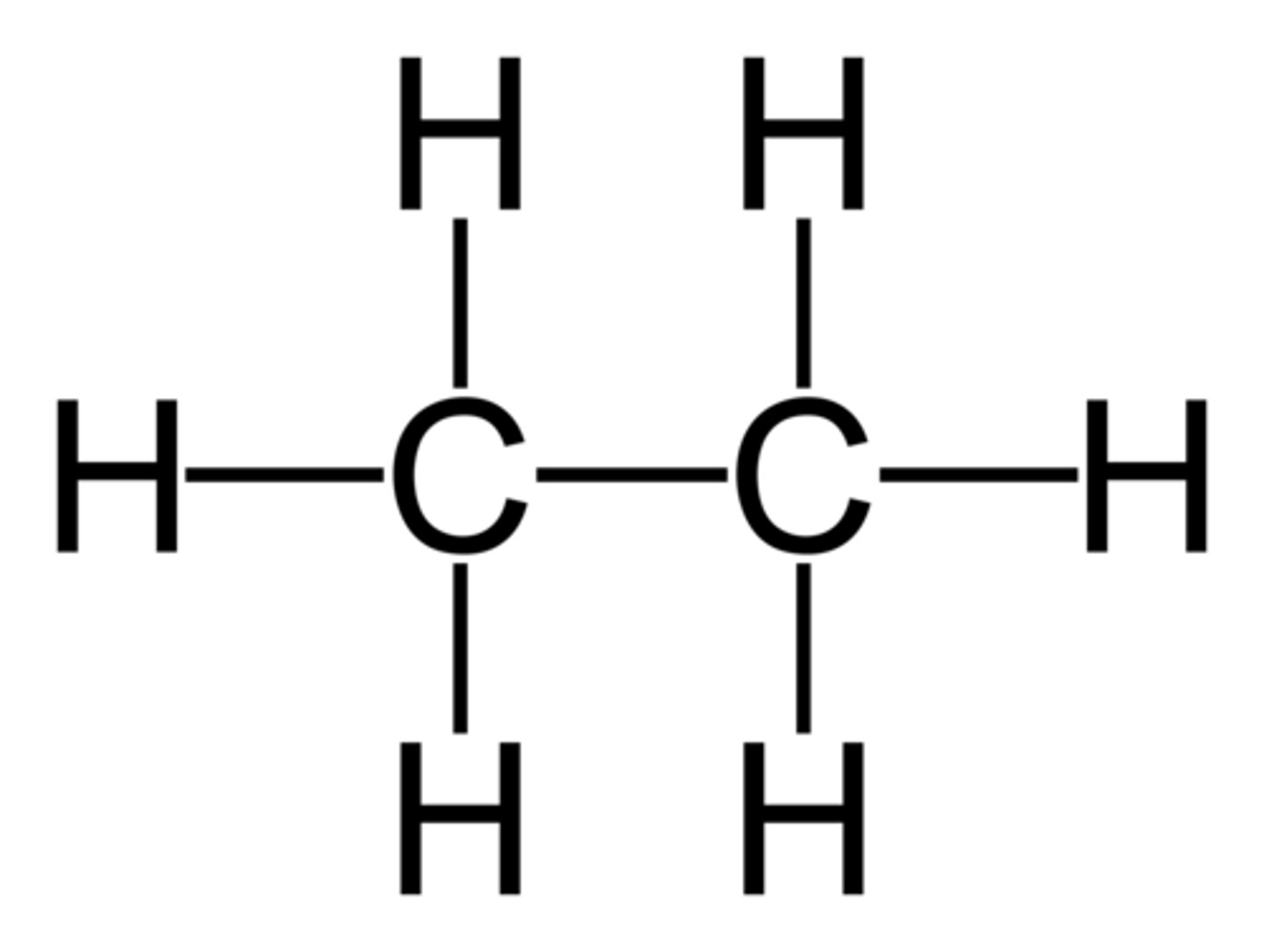
3 Carbons
prop
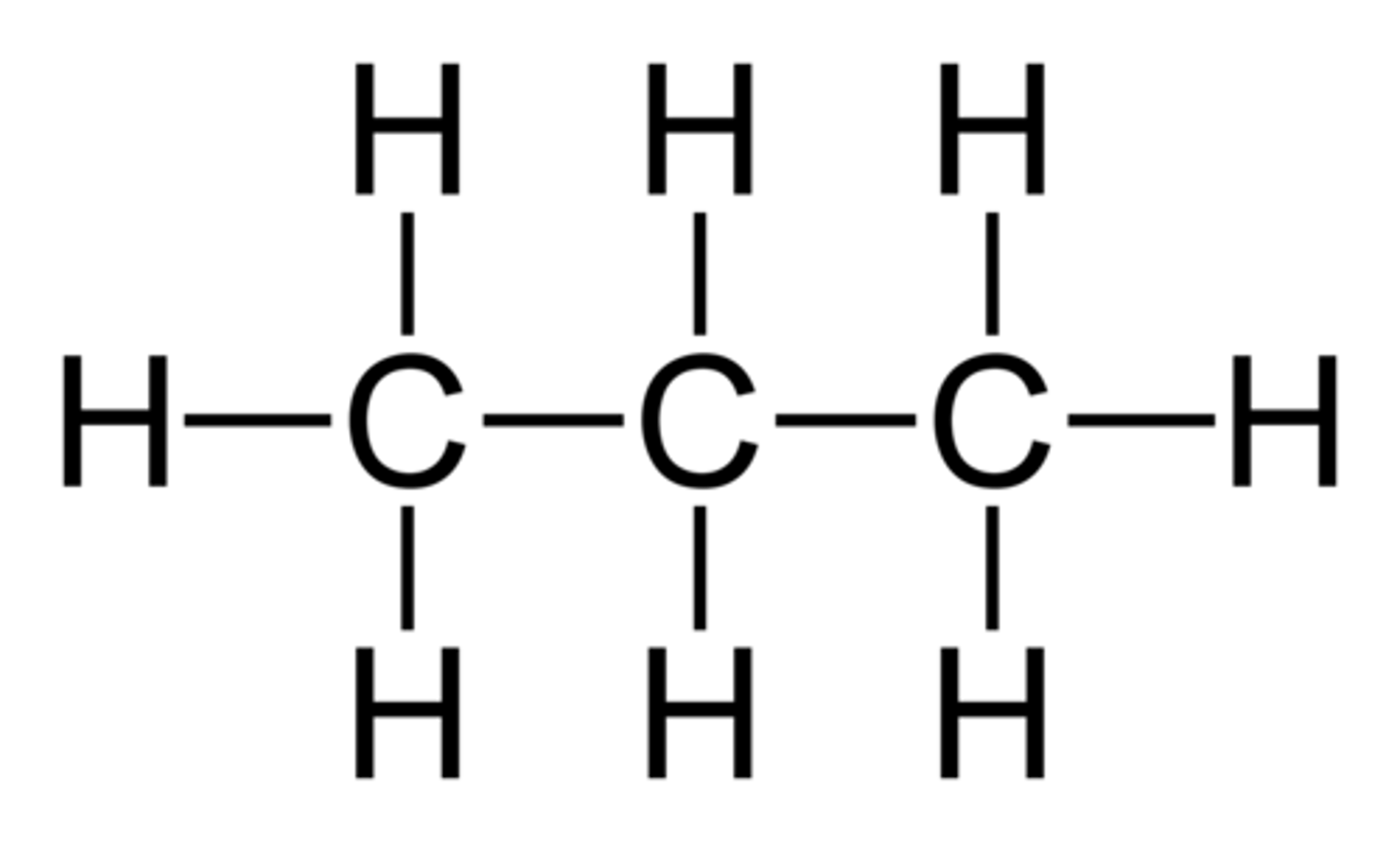
4 Carbon
but
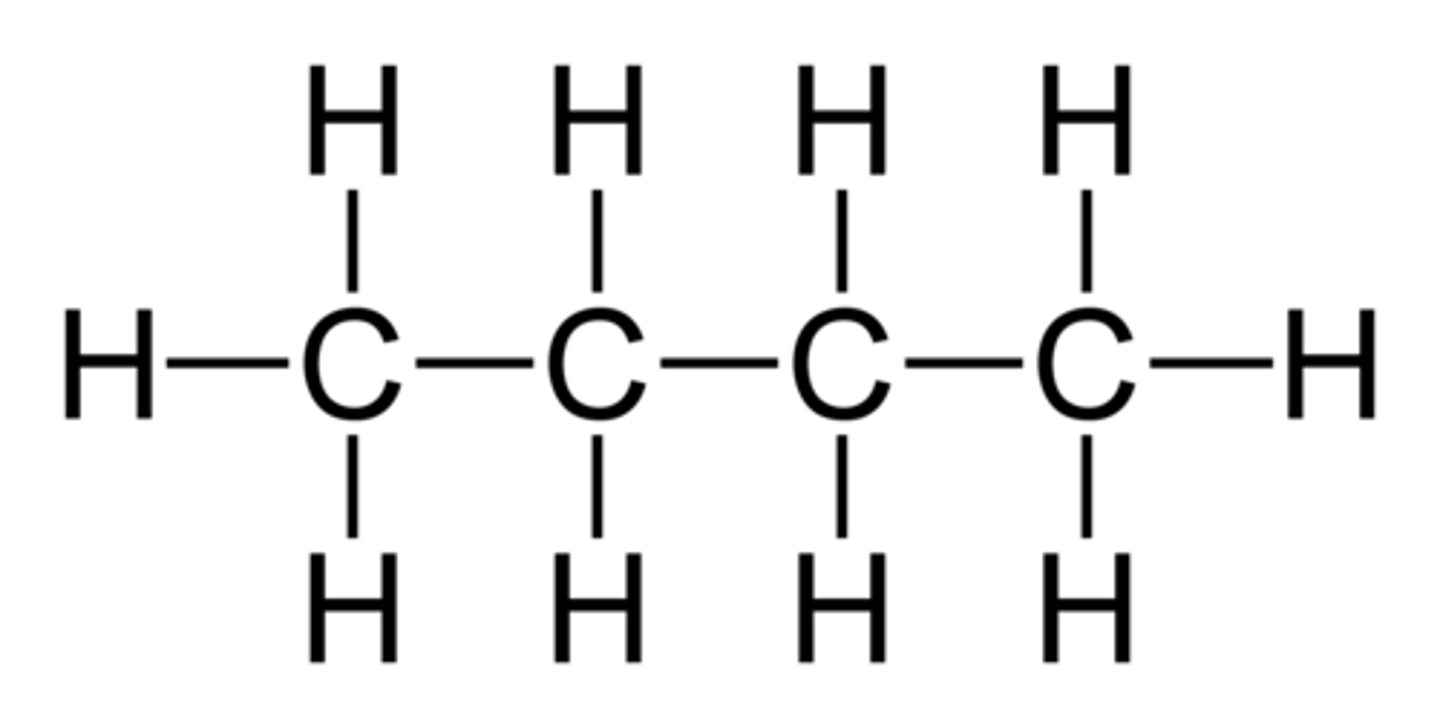
5 Carbons
pent
Distillation
- heat
- evaporate
- cool
- condense
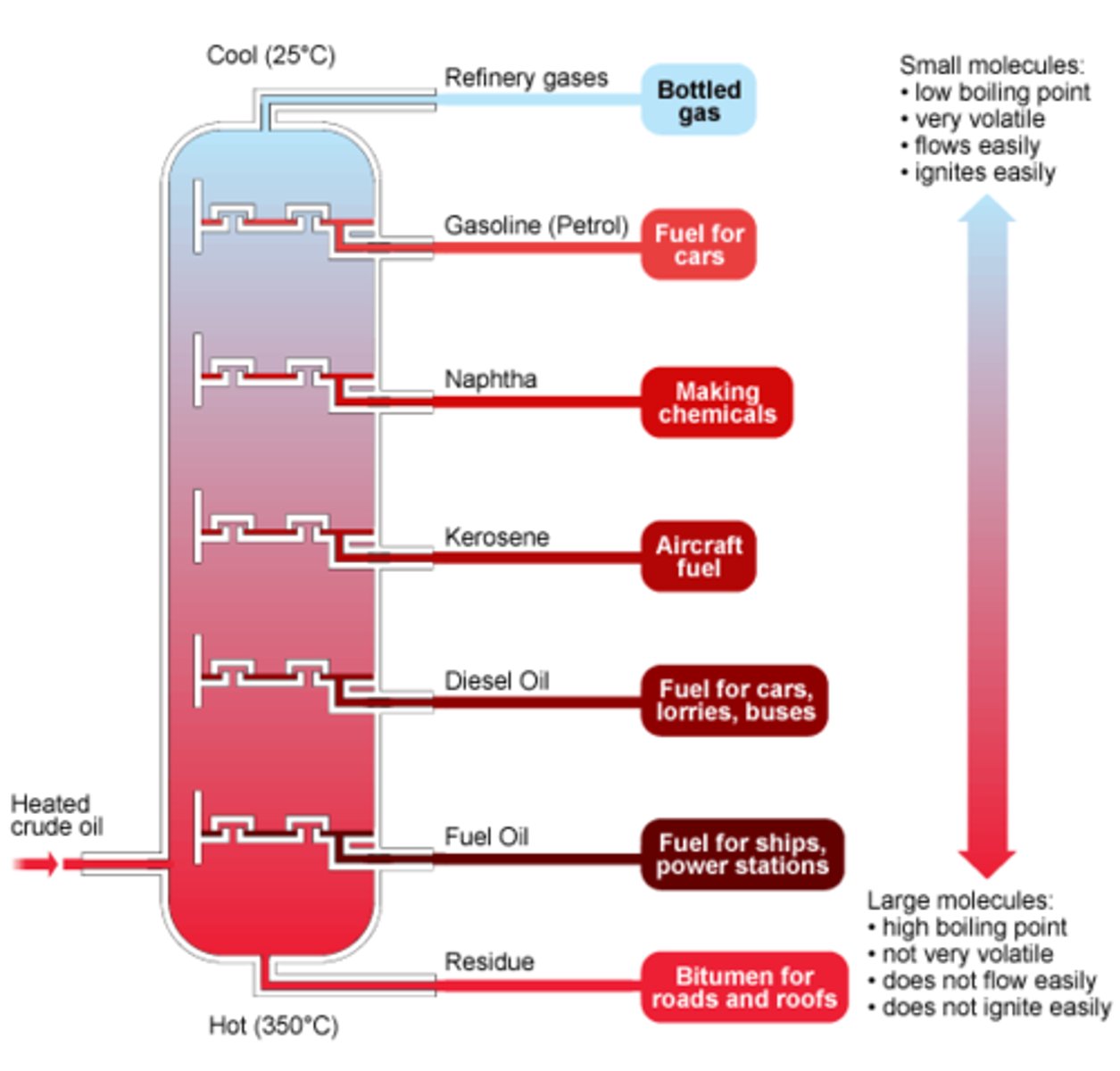
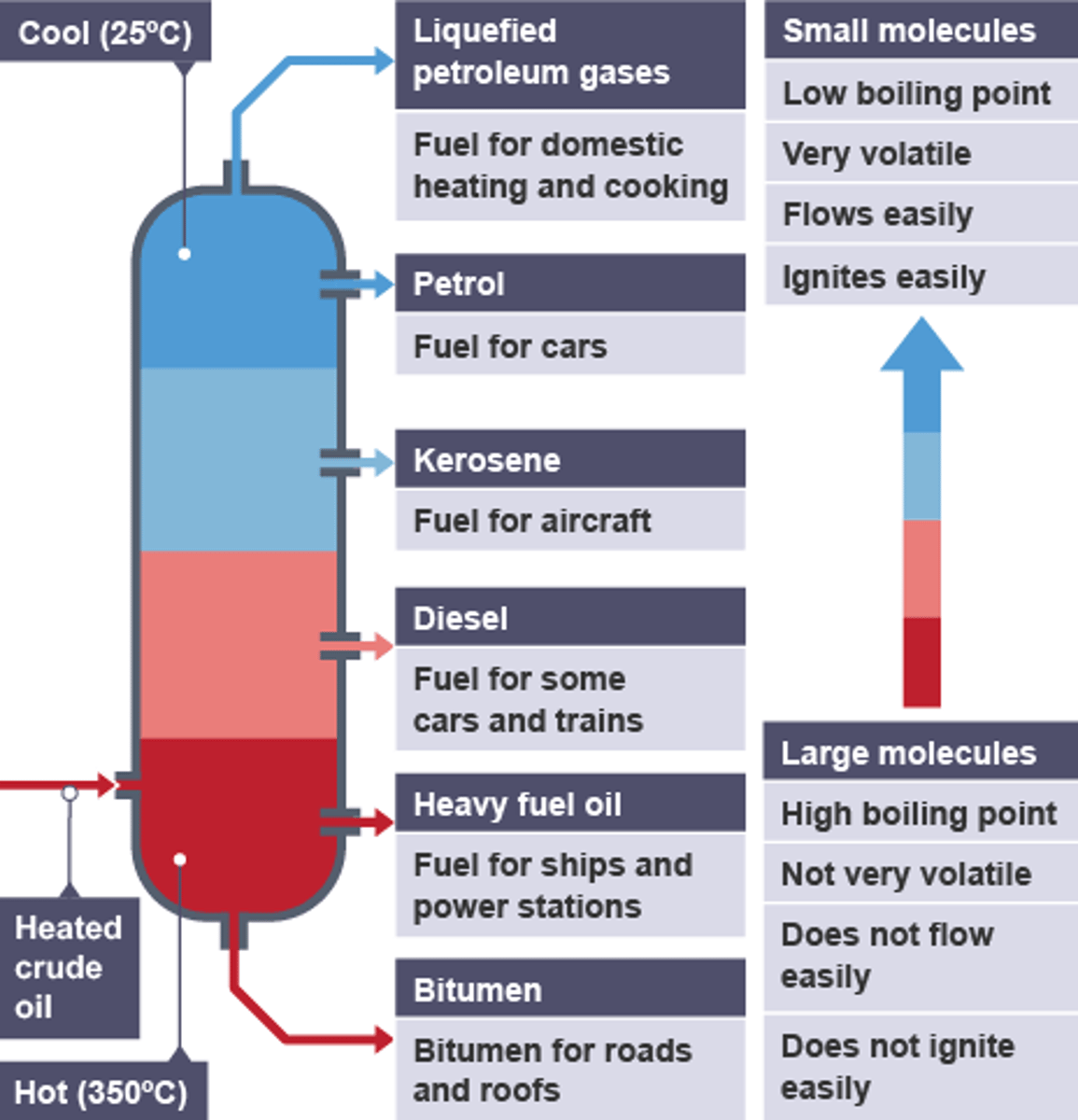
Fractional Distillation of Crude Oil
- there's different length hydrocarbon chains in crude oil
- all have different boiling points
- this means that they can be separated
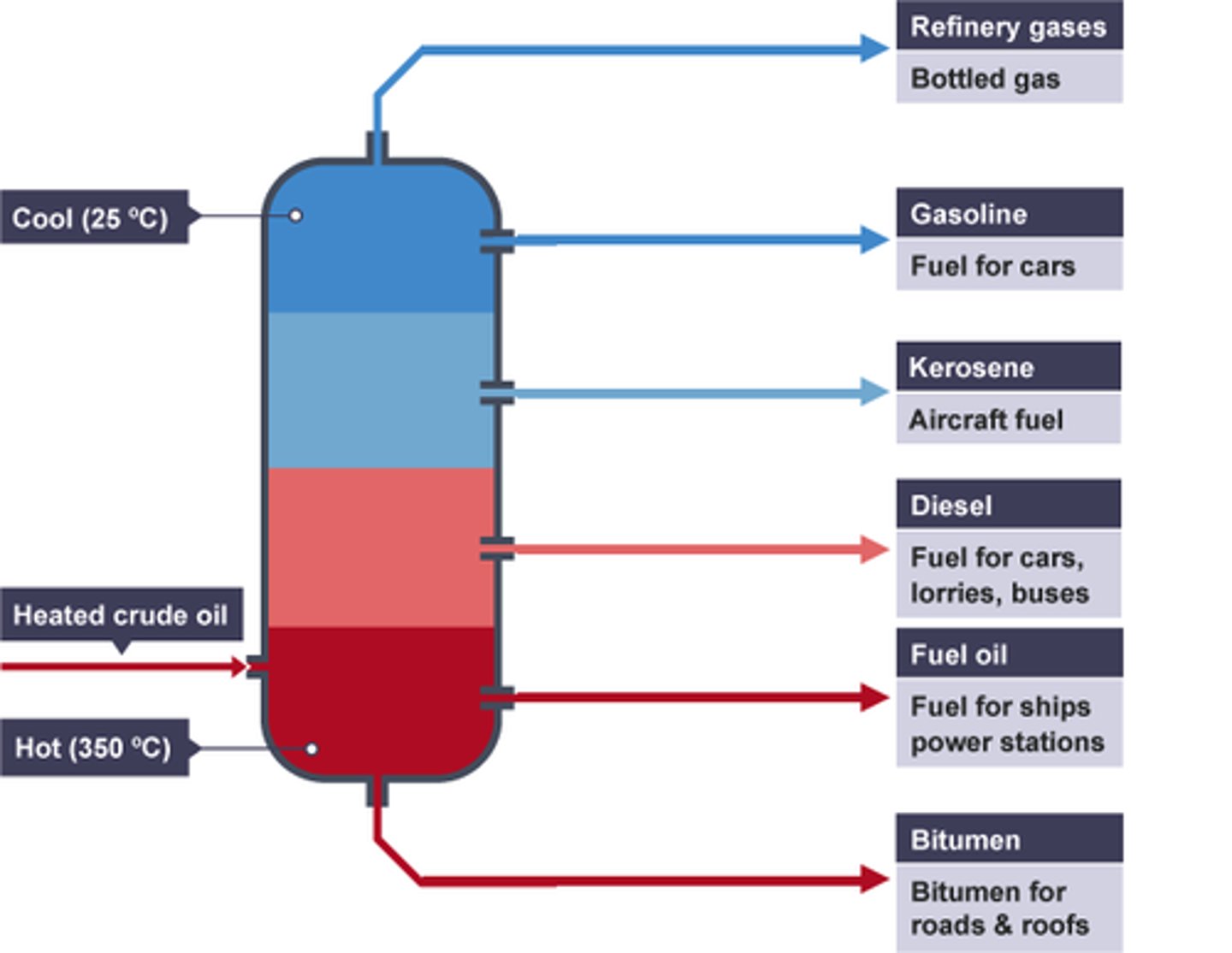
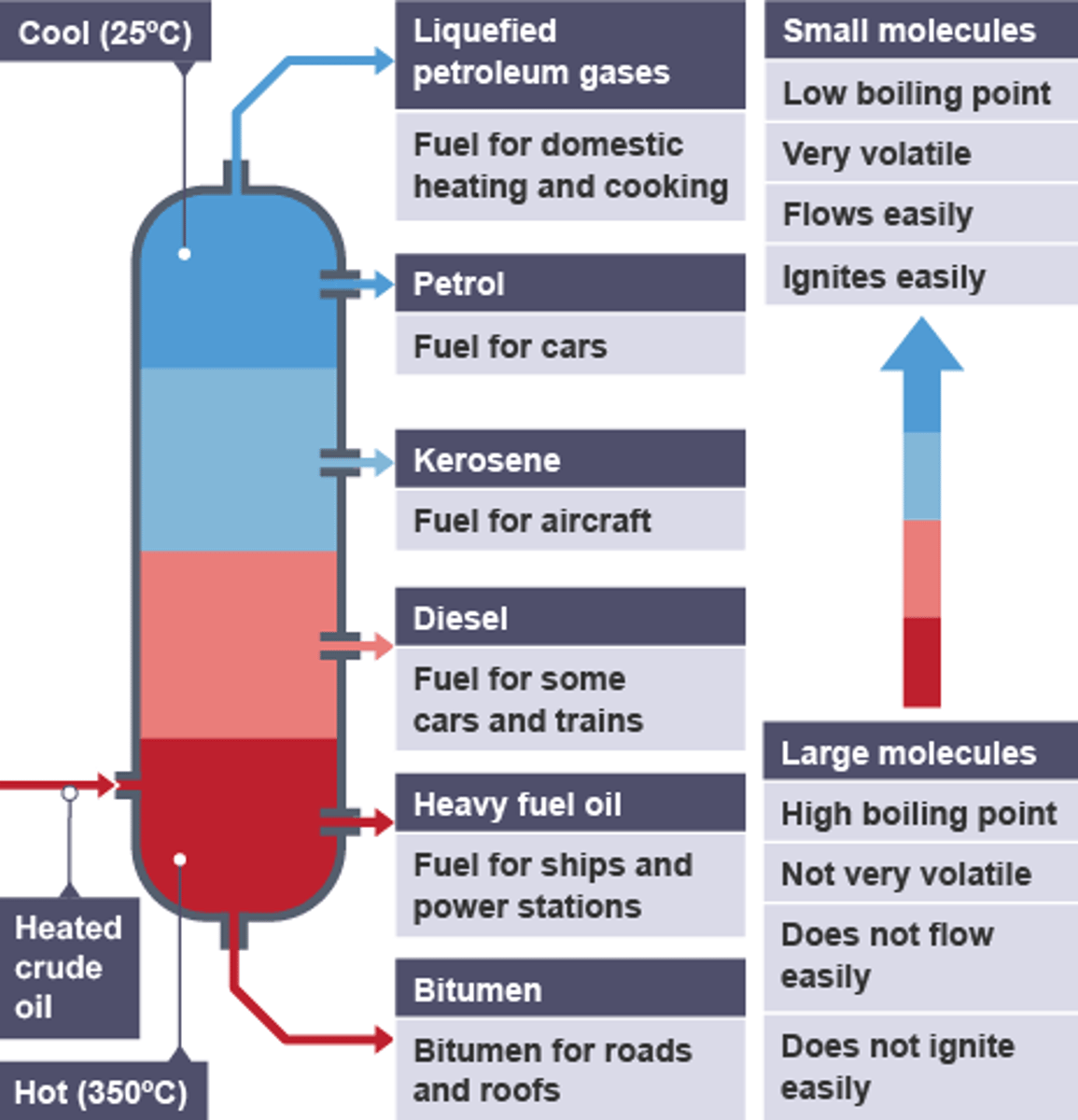
How Crude Oil is Distilled
- the mixture of crude oil is heated to 37C
- all the substances in the mixture evaporate and turn into gas
- the gases are injected into a column and begins to rise
- the column is hot at the bottom and cold at the top
- the gases with the shortest chains/ lowest boiling point condense at the top and are extracted
- the gases with the longest chains/ highest boiling points condense near the bottom
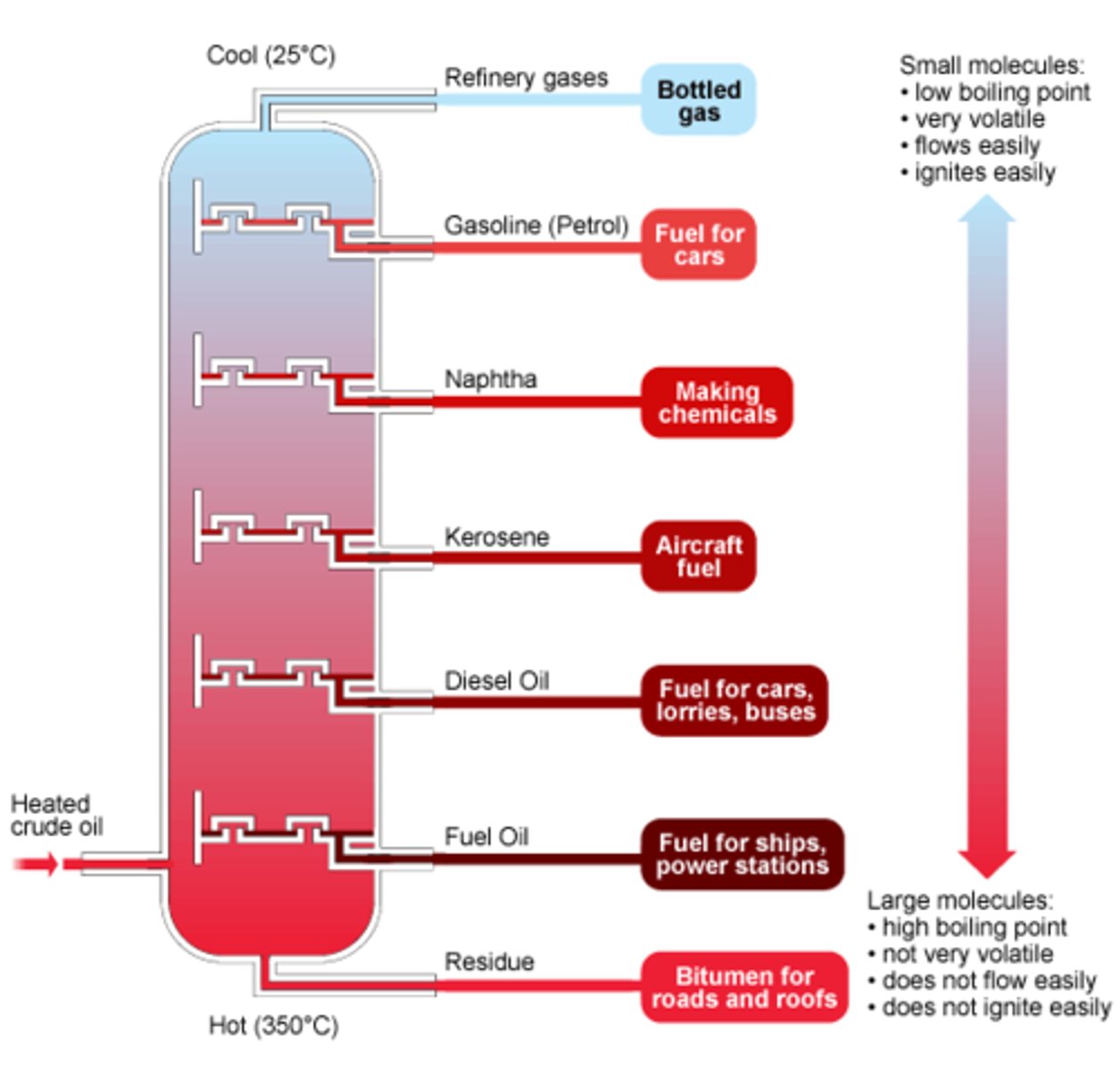
Order of Crude Oil Fractions - Top to Bottom
- methane/natural gas
- octane/gasoline
- kerosene/aviation fuel
- diesel oil
- bitumen/residue
Order of Crude Oil Mnemonic
my
obese
kid
died
brutally
Order of Crude Oil Fractions Characteristics - As Length Increase
- number of carbon & hydrogen atoms/length of chain: low to high/ increase in LengI
- boiling point: low to high/increase in BPI
- viscosity/thickness : low to high/ increase in VisI
- flammability: high to low/ decrease in FlaD
- volatility: high to low/ decrease - in VoD
Uses for Crude Oil
- fuel or petrol for transport: usually short chain as they're flammable
- the petrochemical industry: as feedstock
- new compounds for polymers, solvents, lubricants and detergents
- making plastics
Alkane Formula
CnH2n+2
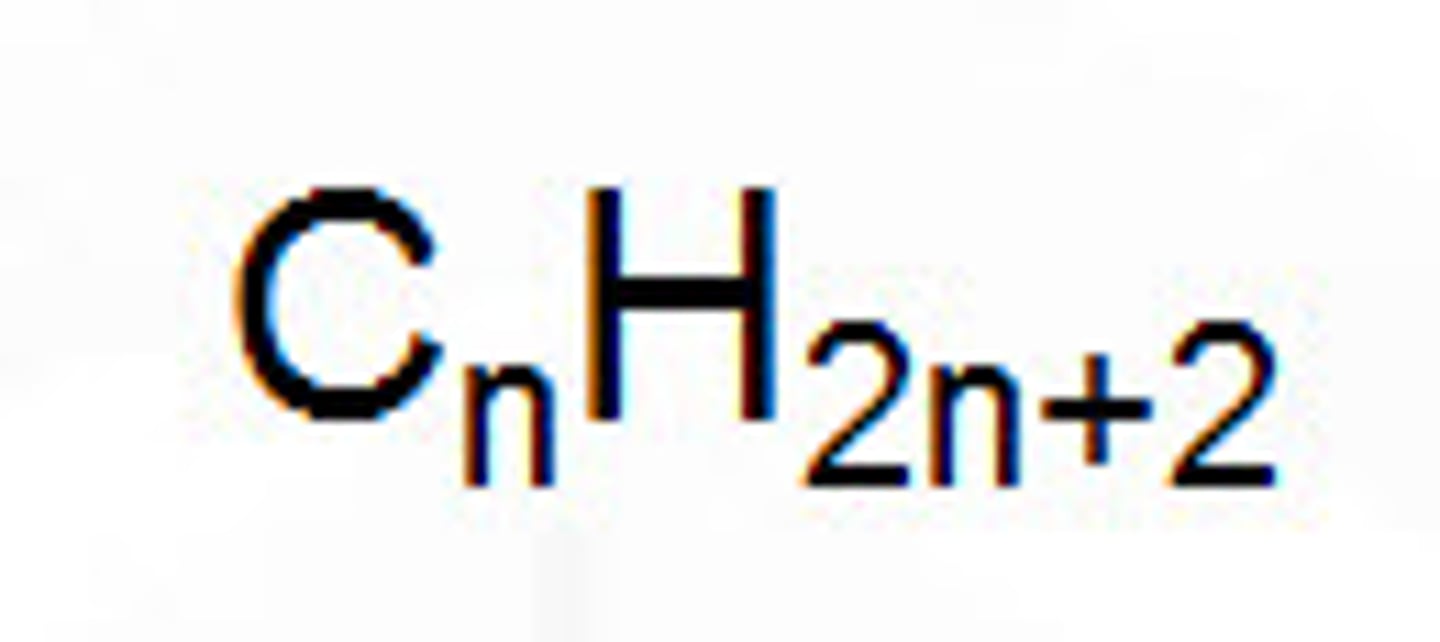
Fire Combustion Triangle
- fuel
- heat
- oxygen

Fire Blanket
removes oxygen

CO2 Fire Extinguisher
removes oxygen

Water Fire Extinguisher
removes heat

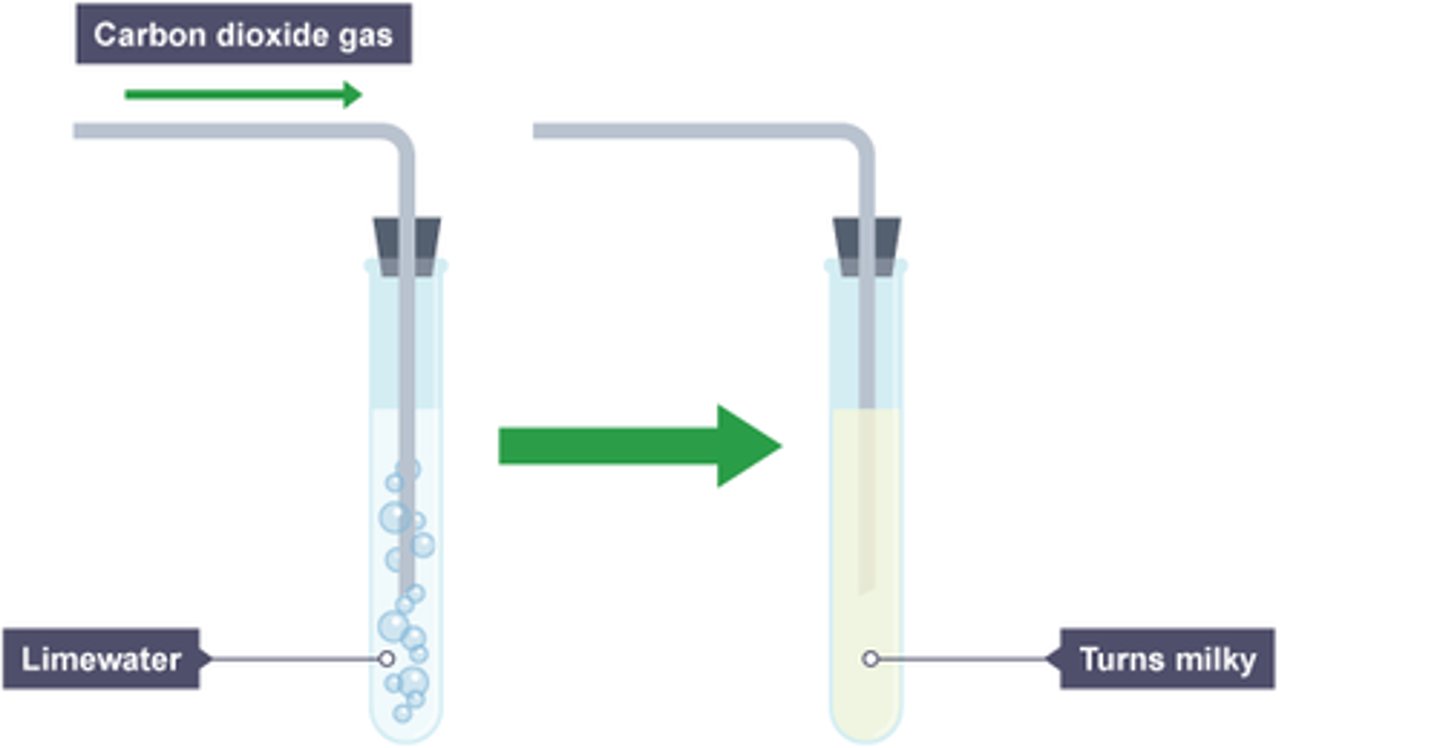
Test for Carbon Dioxide
turns limewater cloudy when bubbled through it
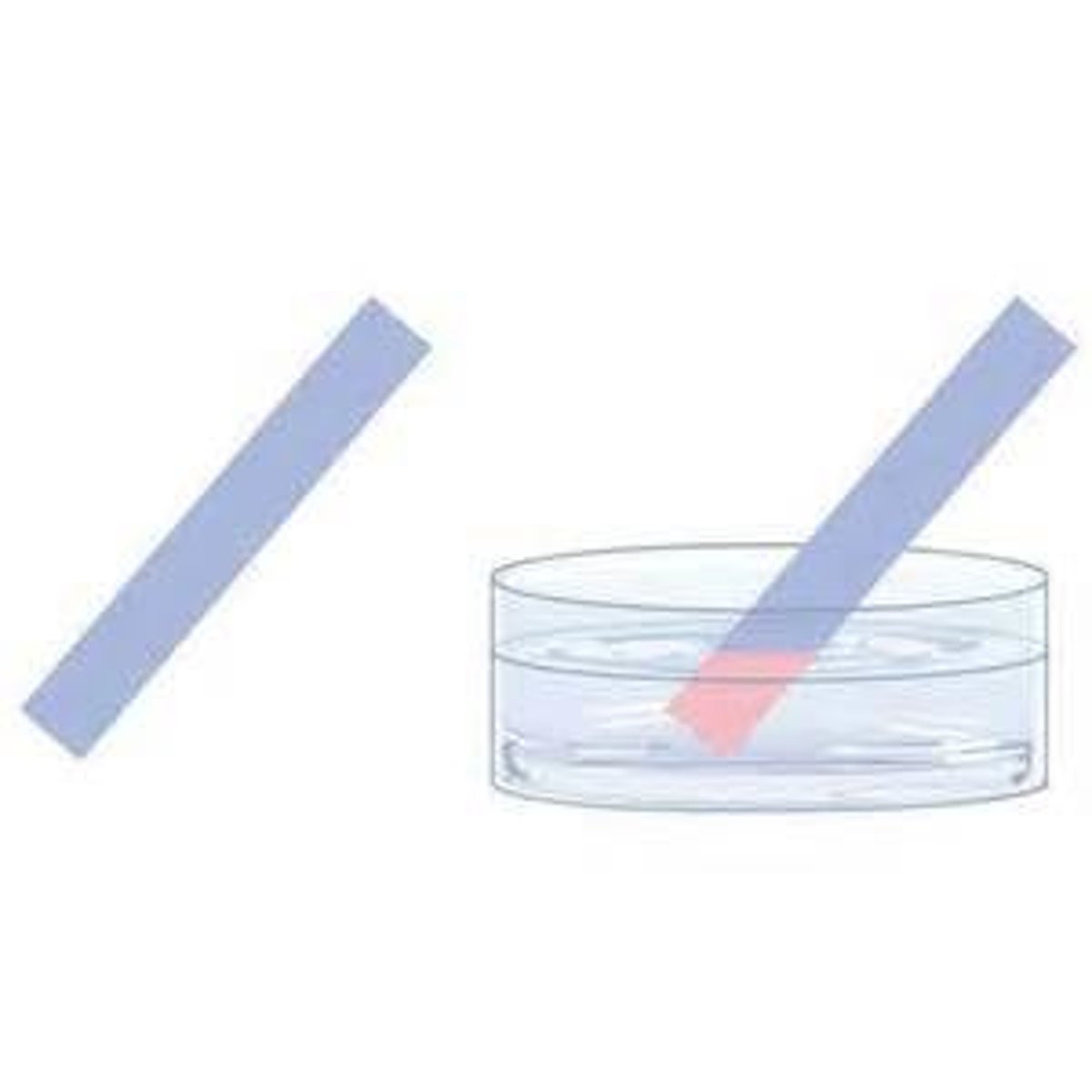
Test for Water
cobalt chloride paper turns from blue to pink
Complete Combustion
- occurs when there is plenty/ sufficient amount of oxygen
- propane + oxygen
- produces carbon dioxide and water vapour
- equation: C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
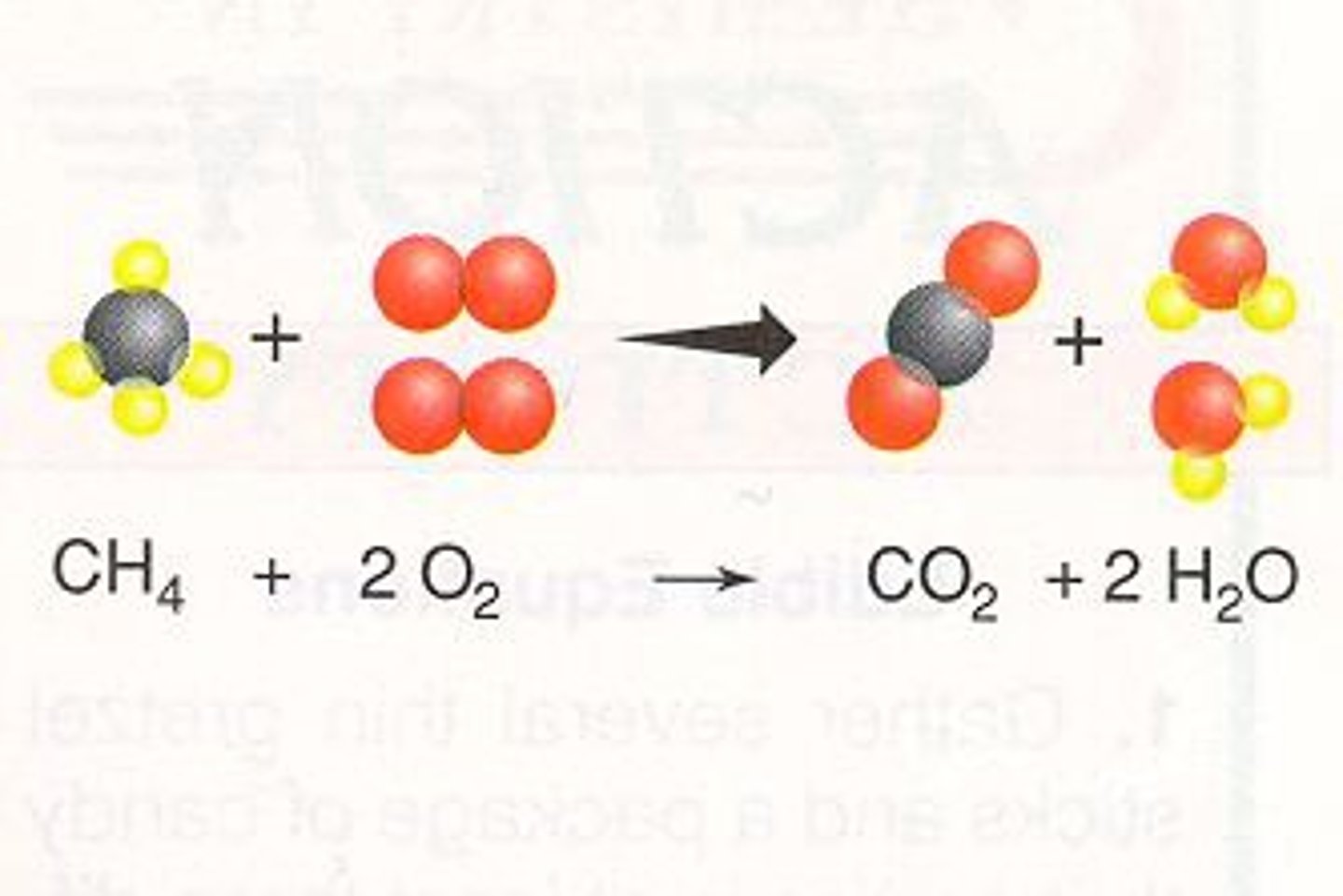
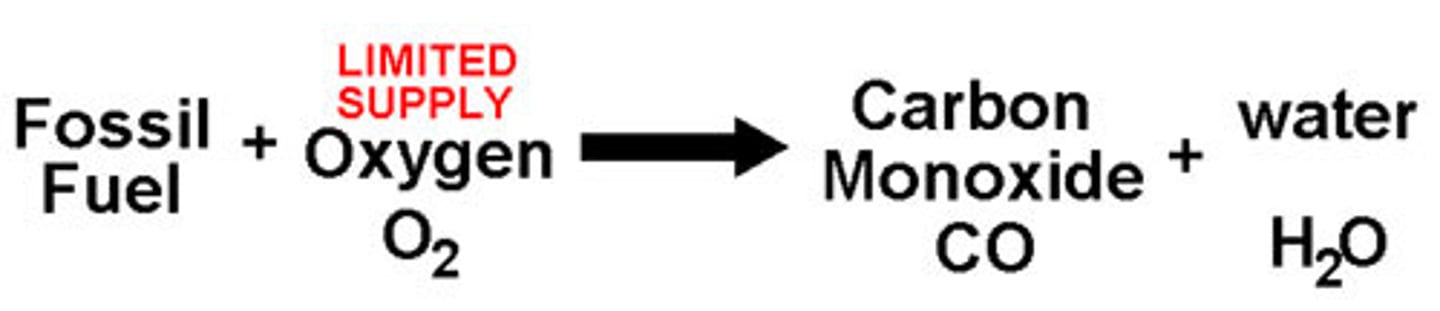
Incomplete Combustion
- occurs when there is not enough/insufficient amount of oxygen
- propane + oxygen
- produces carbon monoxide + water + carbon (as soot)
- C3H8 + 3O2 → 2CO + 4H2O + 1C
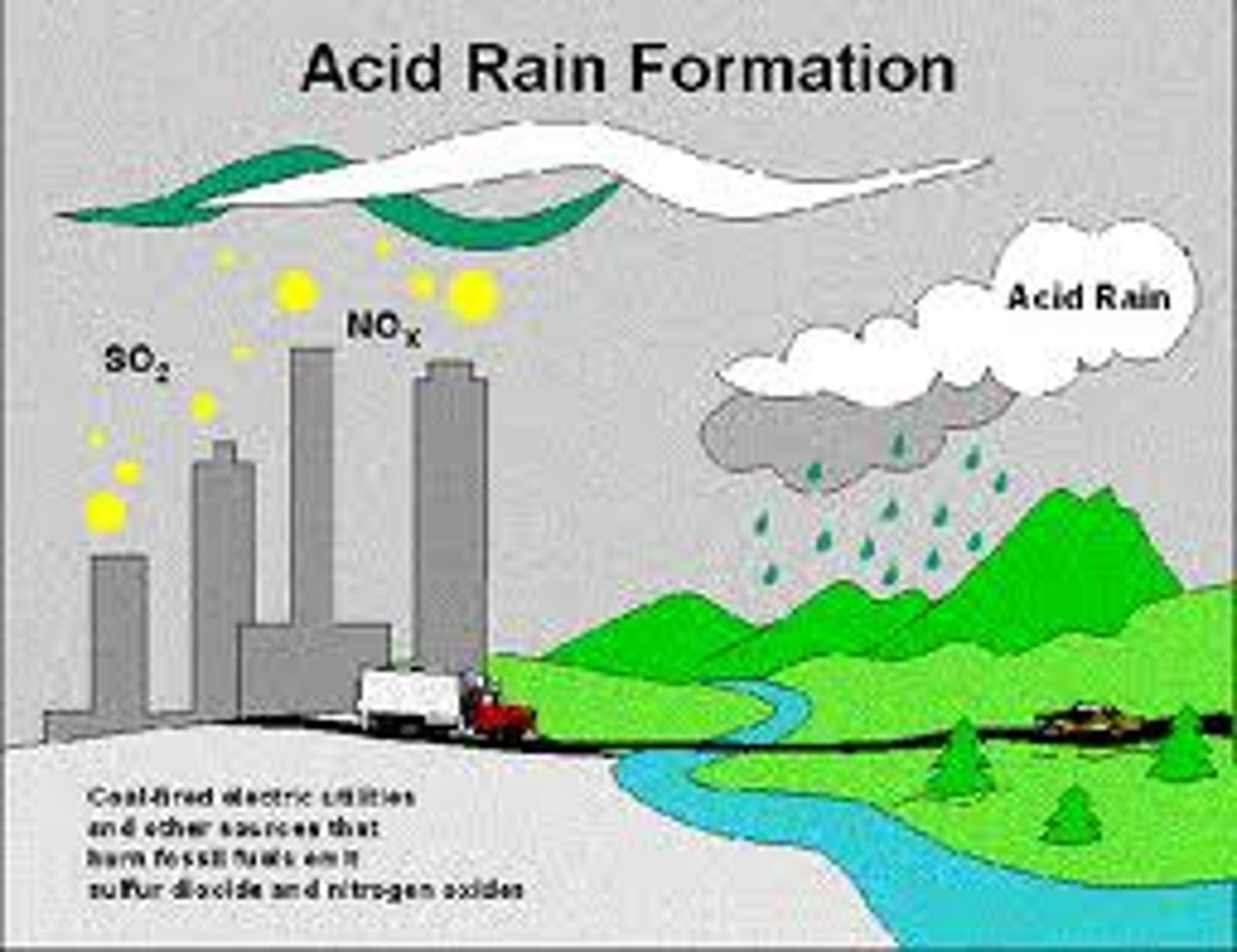
Fossil Fuels
- coal, oil, natural gas
- burn in oxygen to make carbon dioxide and water
- produce sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides

Carbon Monoxide
- from incomplete combustion
- toxic
- attaches to haemoglobin in red blood cells instead of oxygen
- not enough oxygen for cells to respire

Carbon Dioxide
- from combustion of fuel
- contributes to global warming

Carbon Paticulates
- from incomplete combustion
- global dimming
- lung & brain damage

Sulphur Dioxide
- from fossil fuel combustion
- acid rain
- asthma
Nitrous Oxide
- from combustion in car engine
- acid rain
- asthma
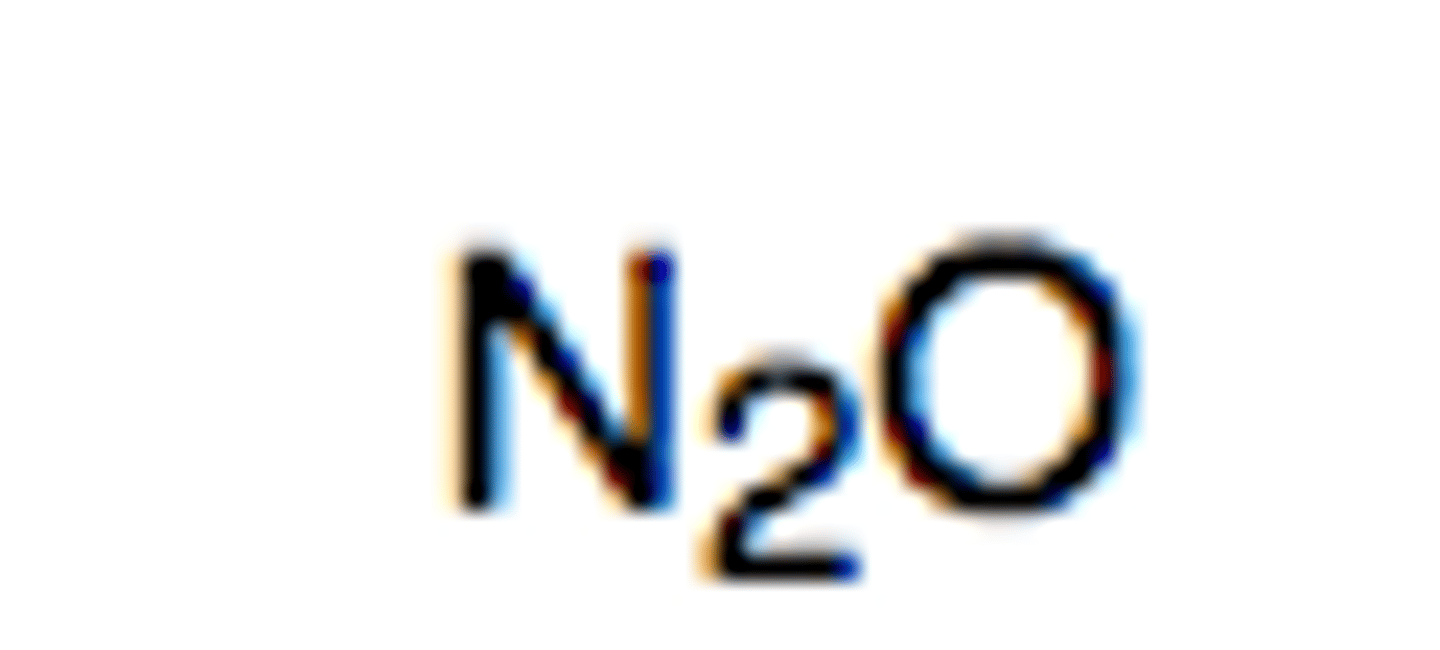
Cracking
- large hydrocarbon molecules can be broken down into smaller molecules
- into alkenes and alkanes
- using a catalyst: using hot powdered aluminium oxide
- or mixing heat with steam
- a thermal decomposition reaction: heating to vaporise
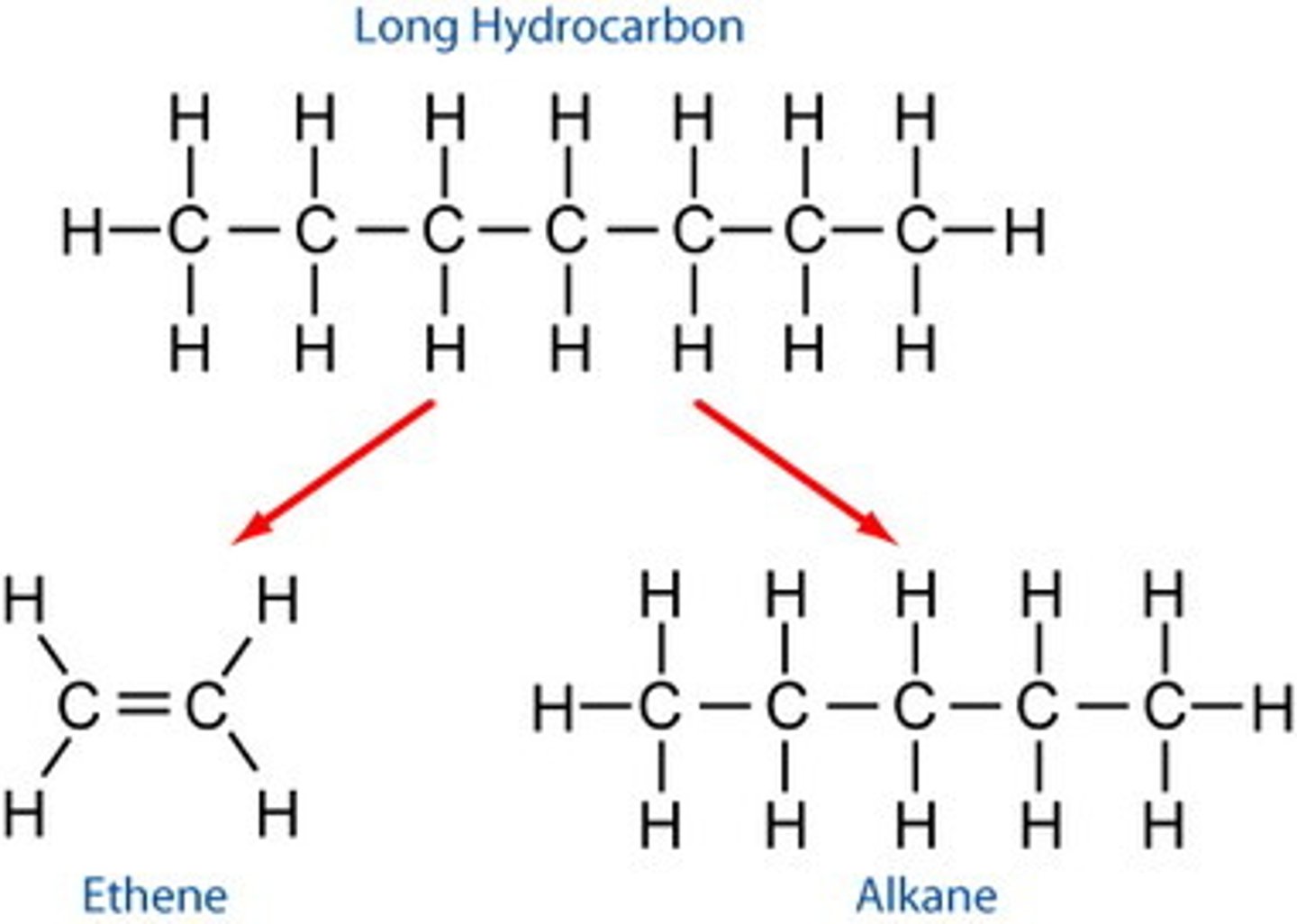
Conditions for Cracking
- high temperature
- high pressure
- a catalyst/steam

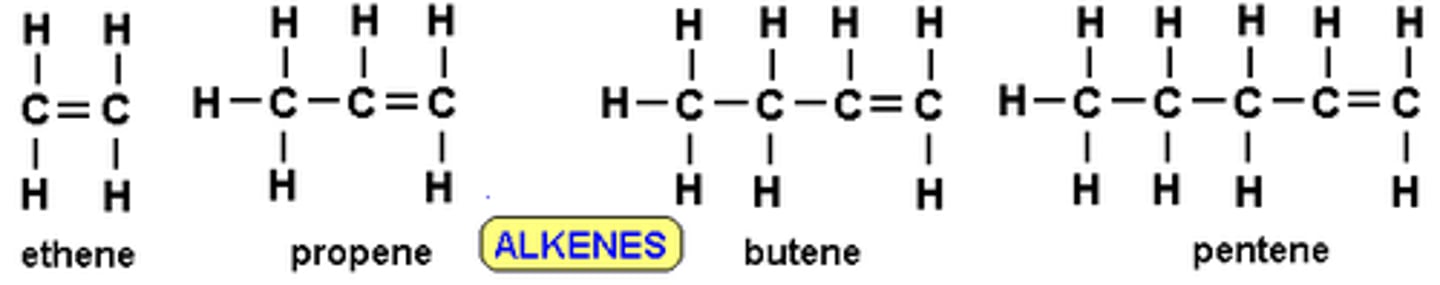
Alkenes
- a hydrocarbon
- unsaturated
- contains at least 1 C=C bond
- has a carbon carbon double bond
- is more reactive than alkanes
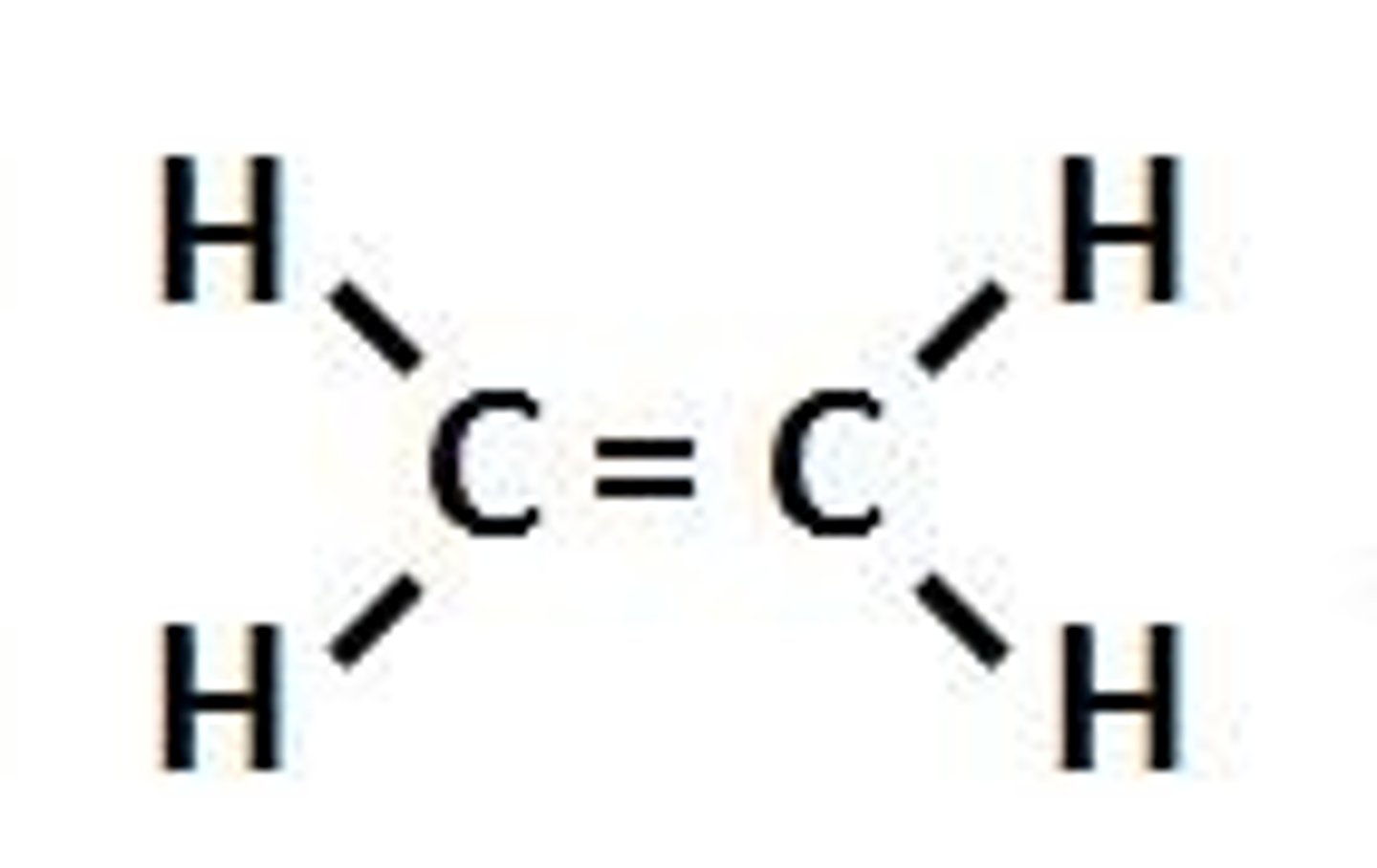
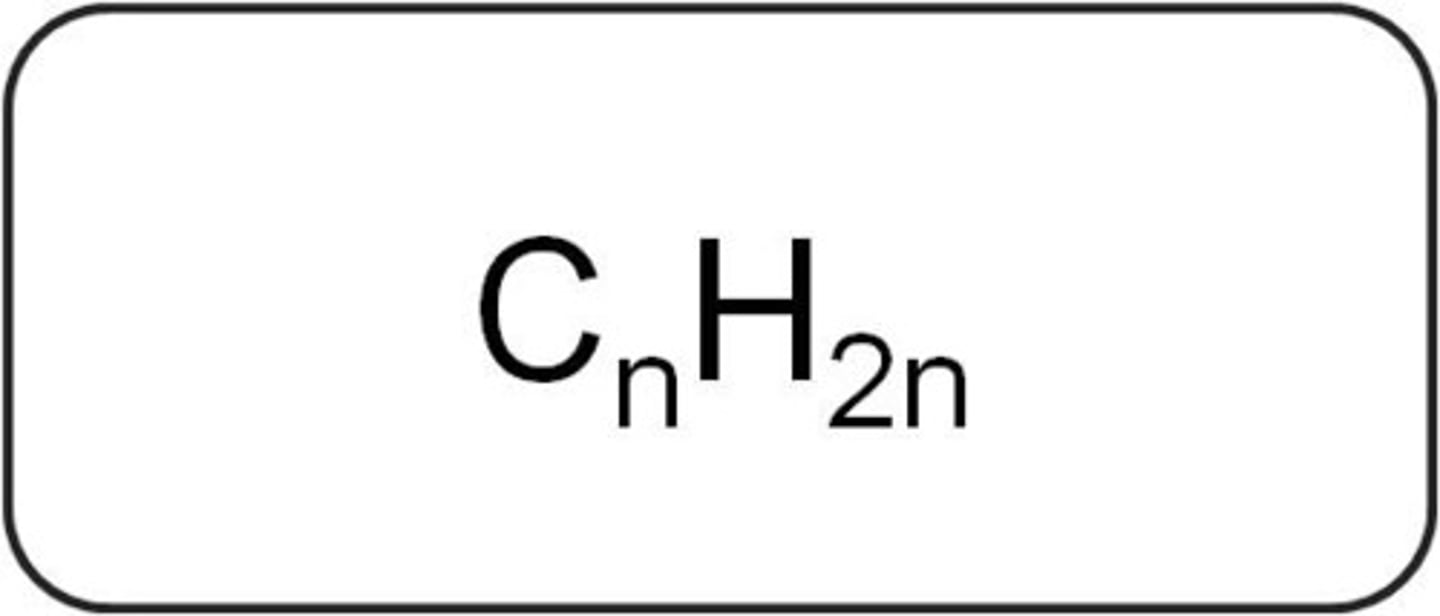
Alkenes Formula
CnH2n
Alkanes
- a hydrocarbon
- saturated
- containing at least one single carbon bond
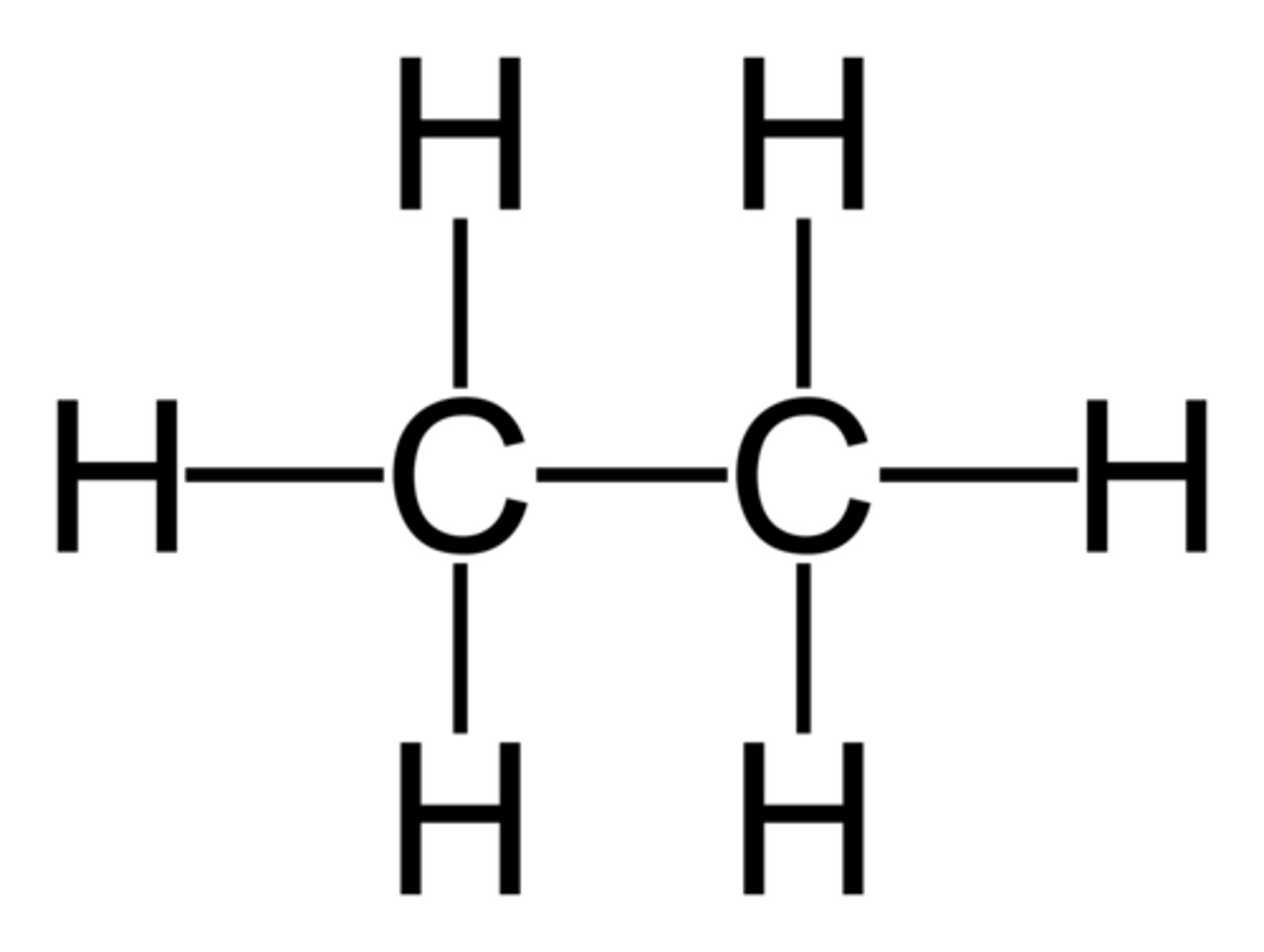
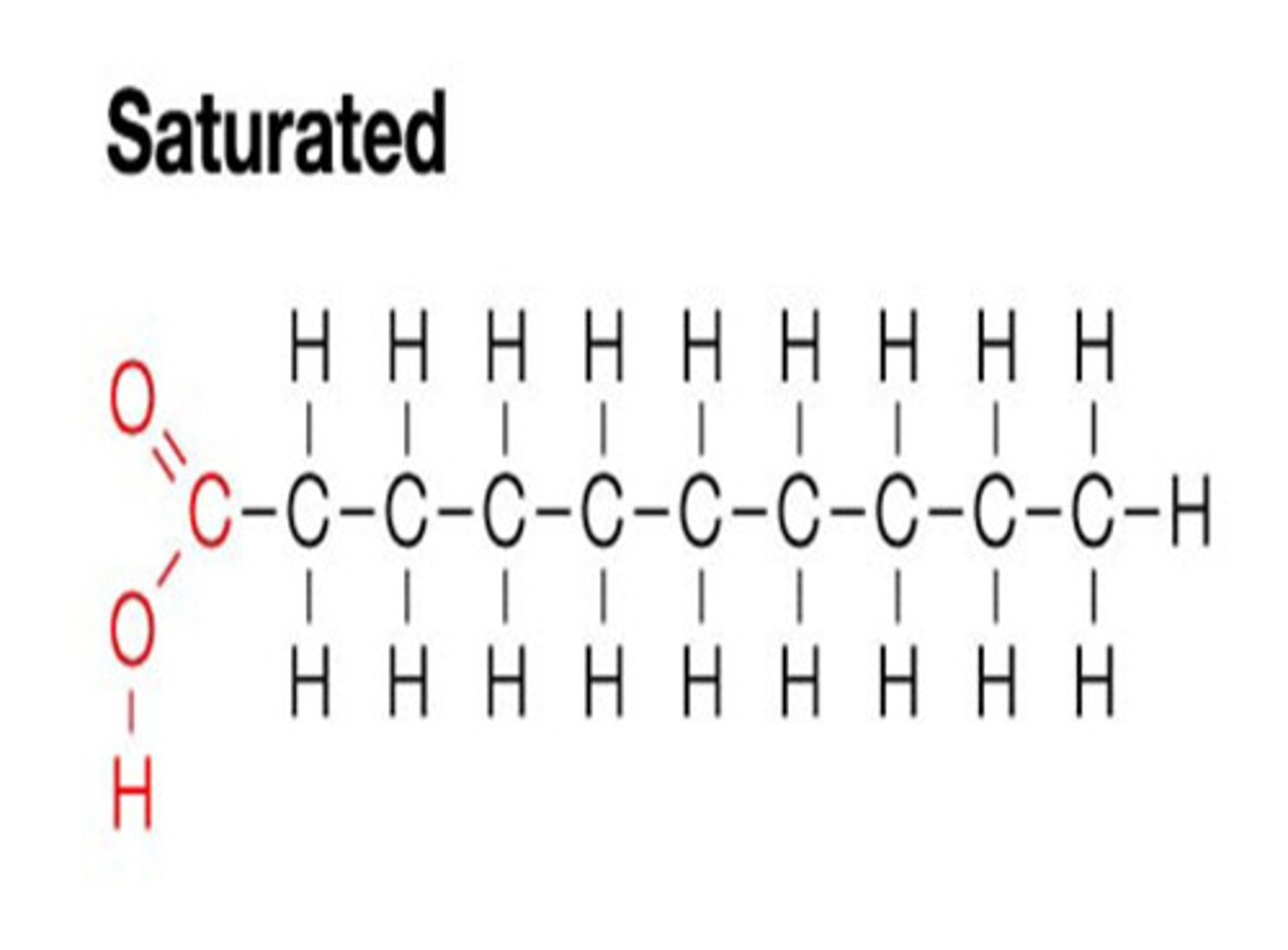
Saturated
all the bonds between carbon atoms are single bonds
- no double bonds to break
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
- one or more of the bonds between carbon atoms is double
- can break double carbon bonds
- add to chemicals in a compound
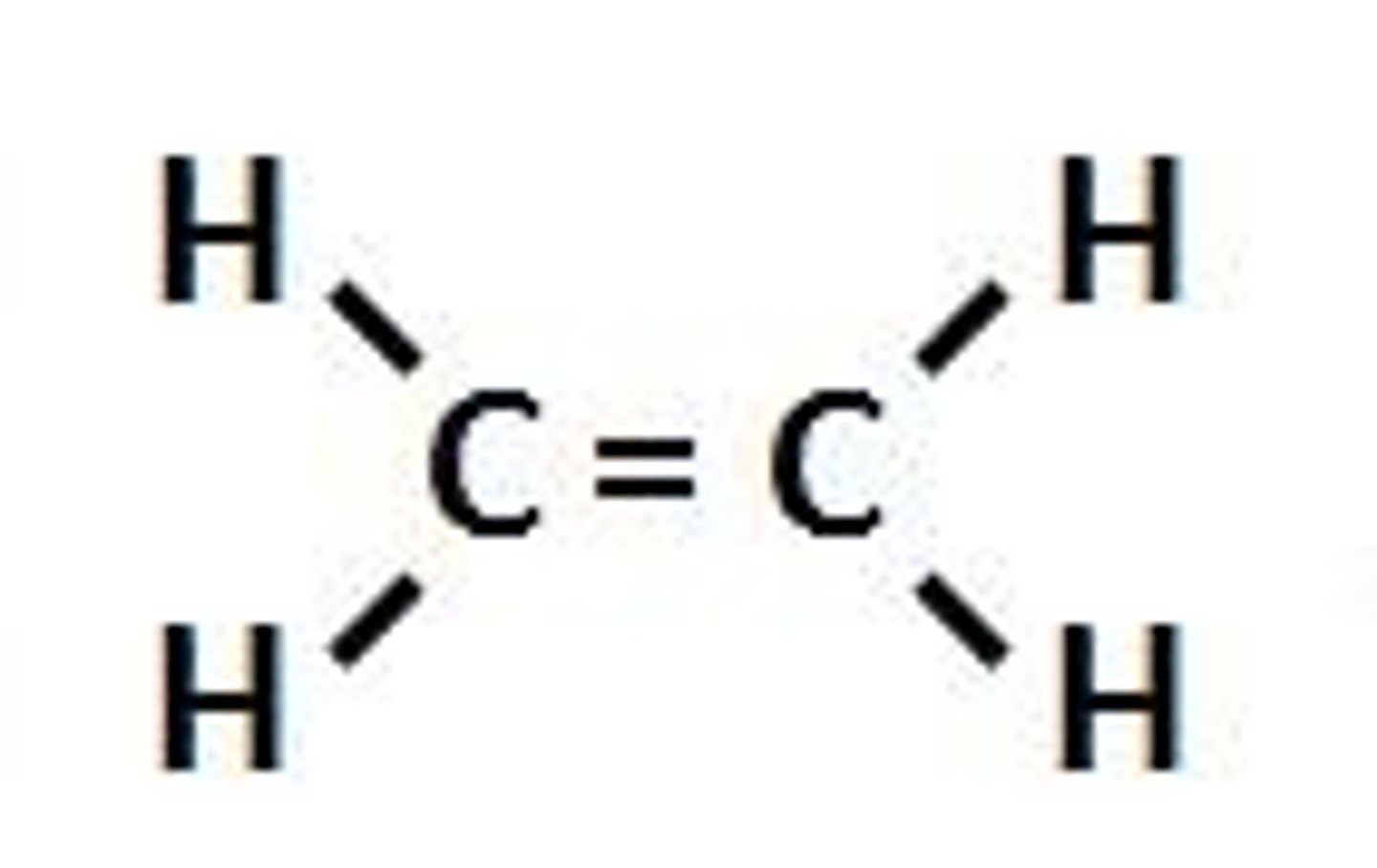
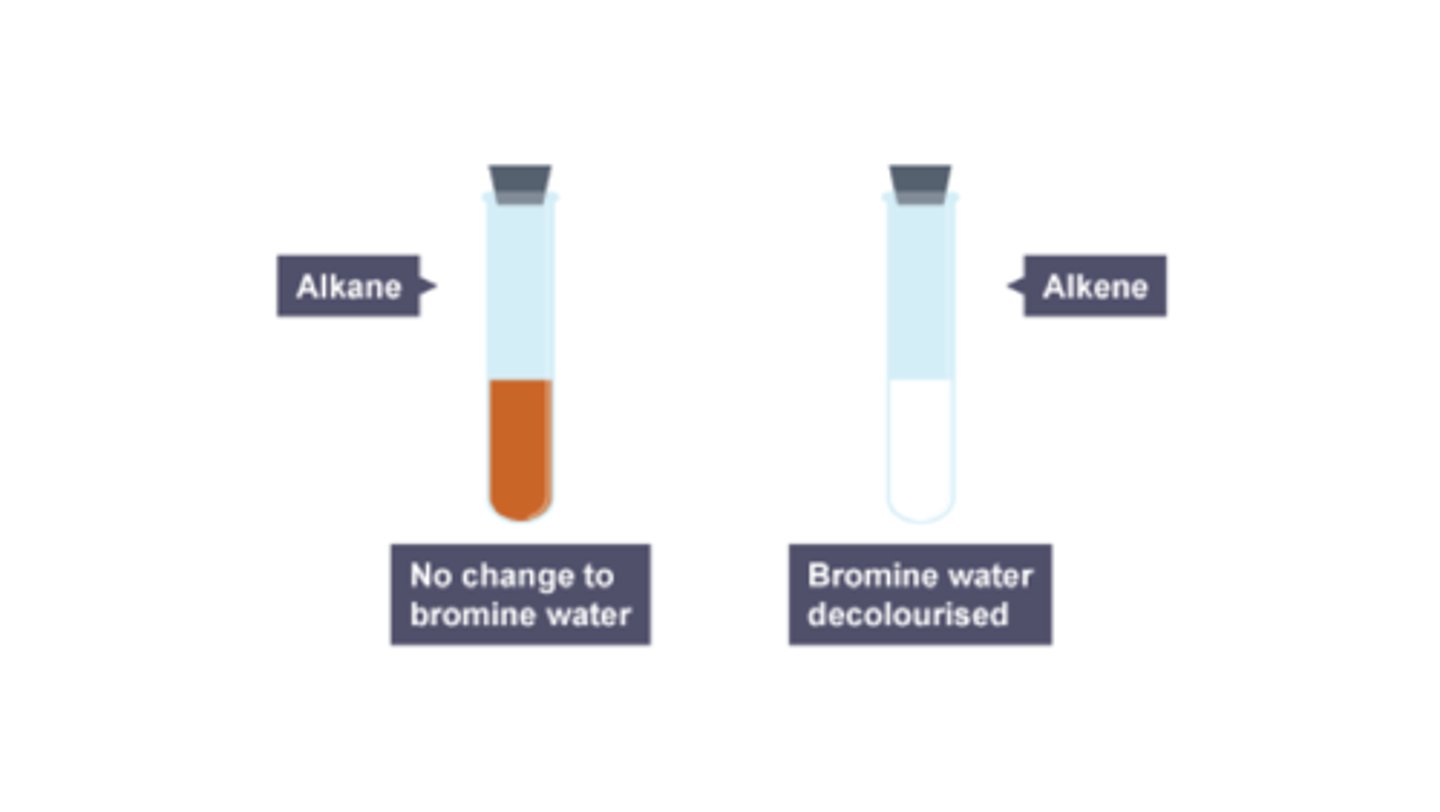
How to Test for Alkenes
- add bromine water
- the alkene should turn from orange to colourless
Thermal Decomposition
- the breaking up of a chemical substance
- into at least two chemical substances
- using heat
Display Formulas for Alkanes
Display Formulas for Alkenes