Business Statistics: Key Concepts, Data Types, and Analytics Techniques
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CH 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
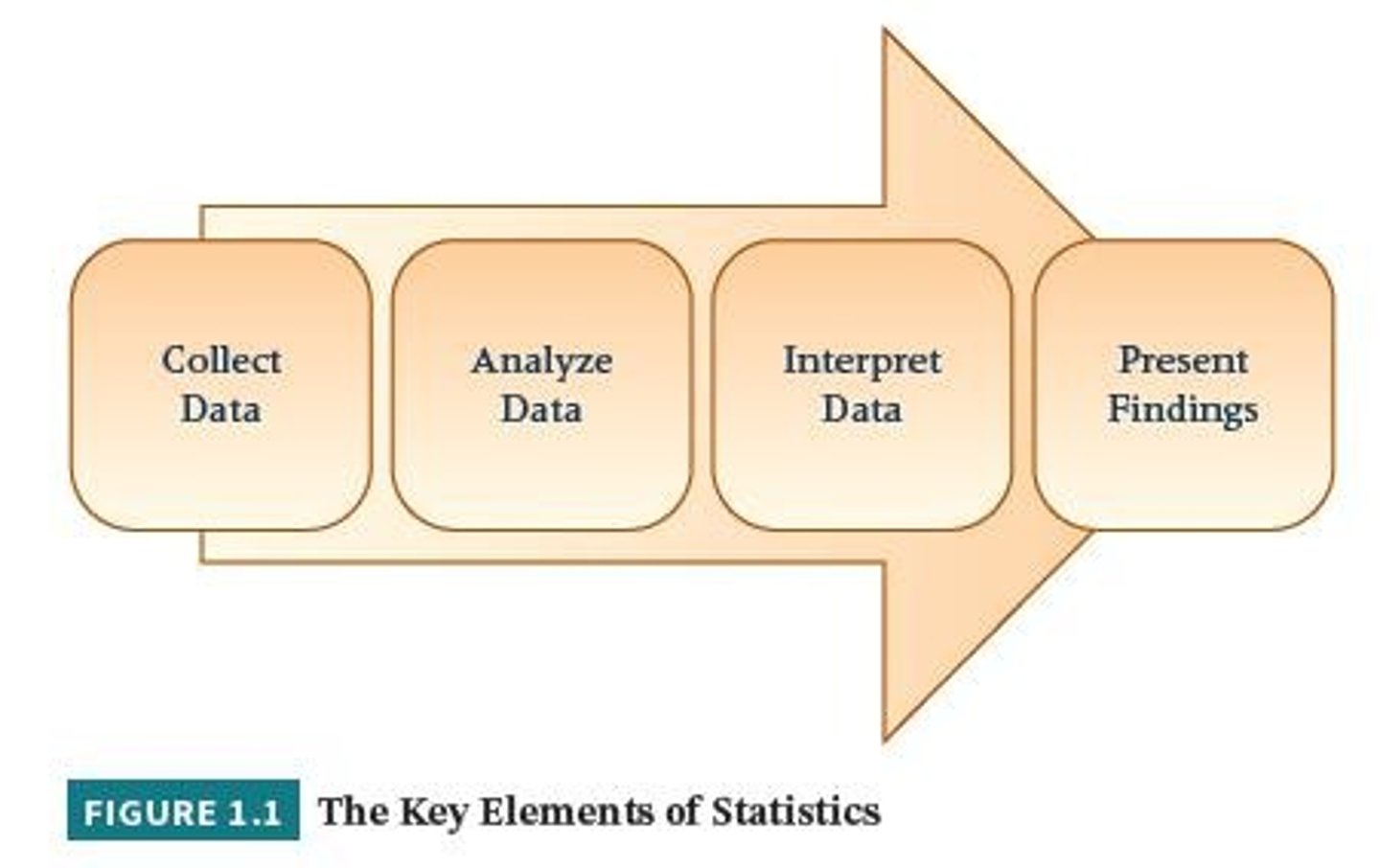
Statistics
A science dealing with the collection, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of numerical data.
Population
A collection of all persons, objects, or items under study.
Census
Gathering data from the whole population.
Sample
Gathering data on a subset of the population that should be representative of the whole population.
Descriptive Statistics
Uses data gathered on a group to describe or reach conclusions about that same group, producing graphical or numerical summaries of data.
Inferential Statistics
Gathers data from a sample and uses the statistics generated to reach conclusions about the population from which the sample was taken.
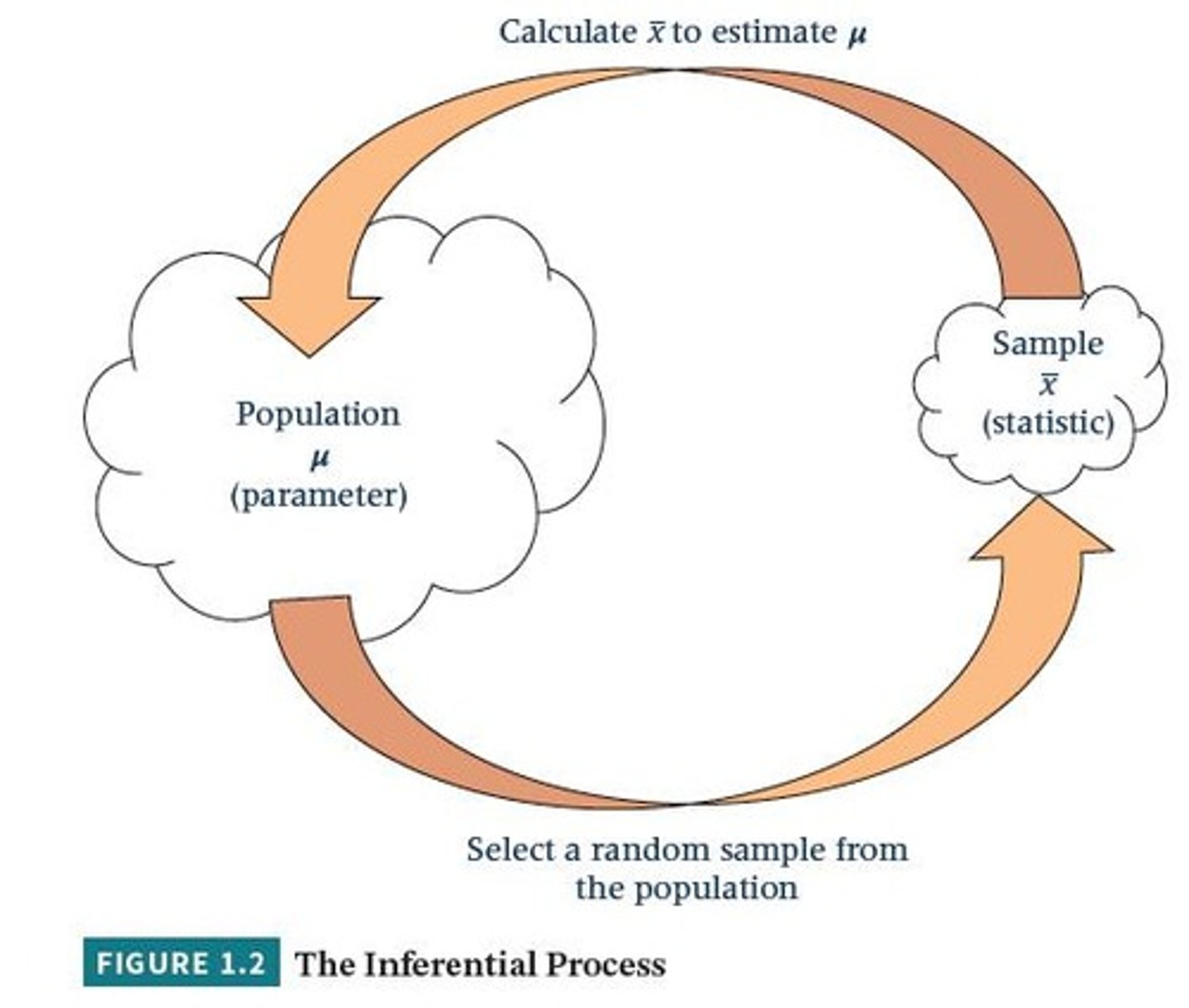
Parameter
Descriptive measure of the population, usually represented by Greek letters.
Statistic
Descriptive measure of a sample, usually represented by Roman letters.
Population Mean (µ)
Parameter, Denotes the average of the population.
Population Variance (σ²)
Parameter, Denotes the variance of the population.

Population Standard Deviation (σ)
Parameter, Denotes the standard deviation of the population.
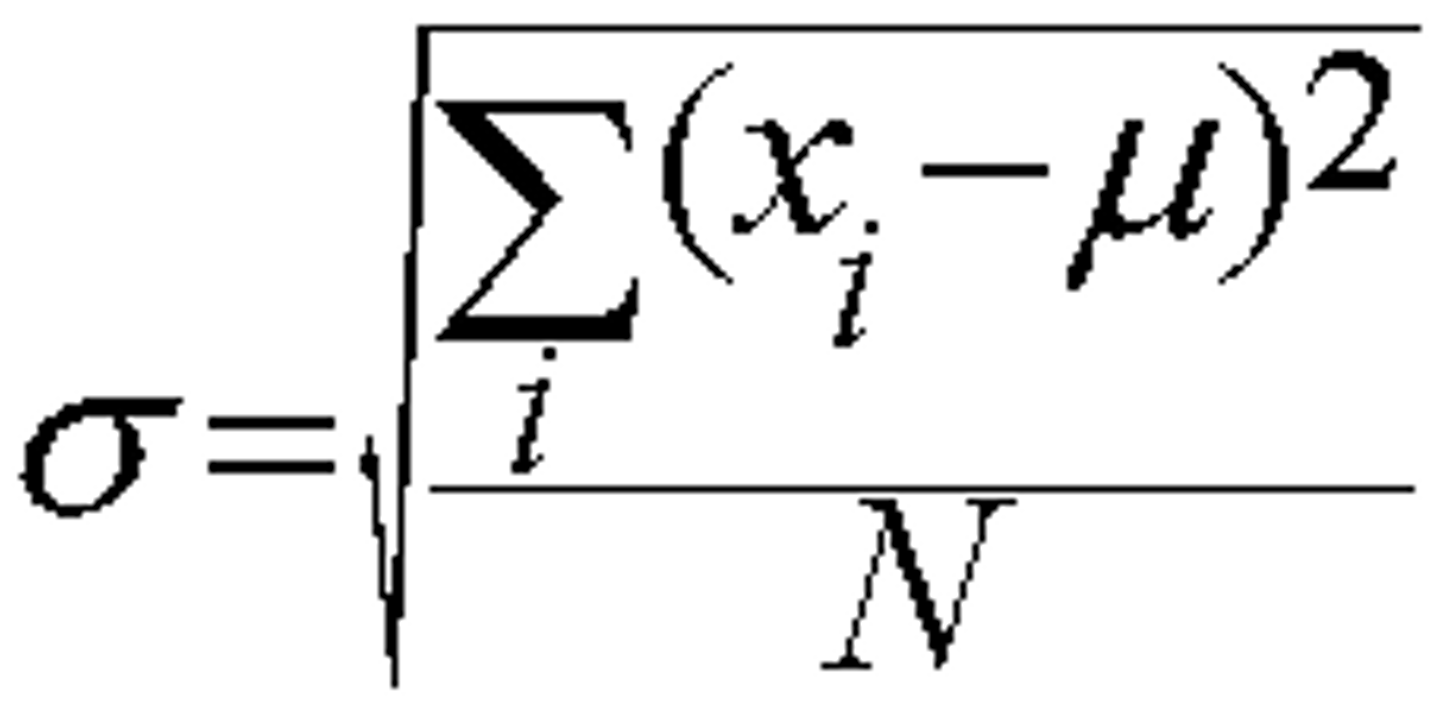
Sample Mean (x̄)
Statistic, Denotes the average of the sample.
Sample Variance (s²)
Statistic, Denotes the variance of the sample.
Sample Standard Deviation (s)
Statistic, Denotes the standard deviation of the sample.
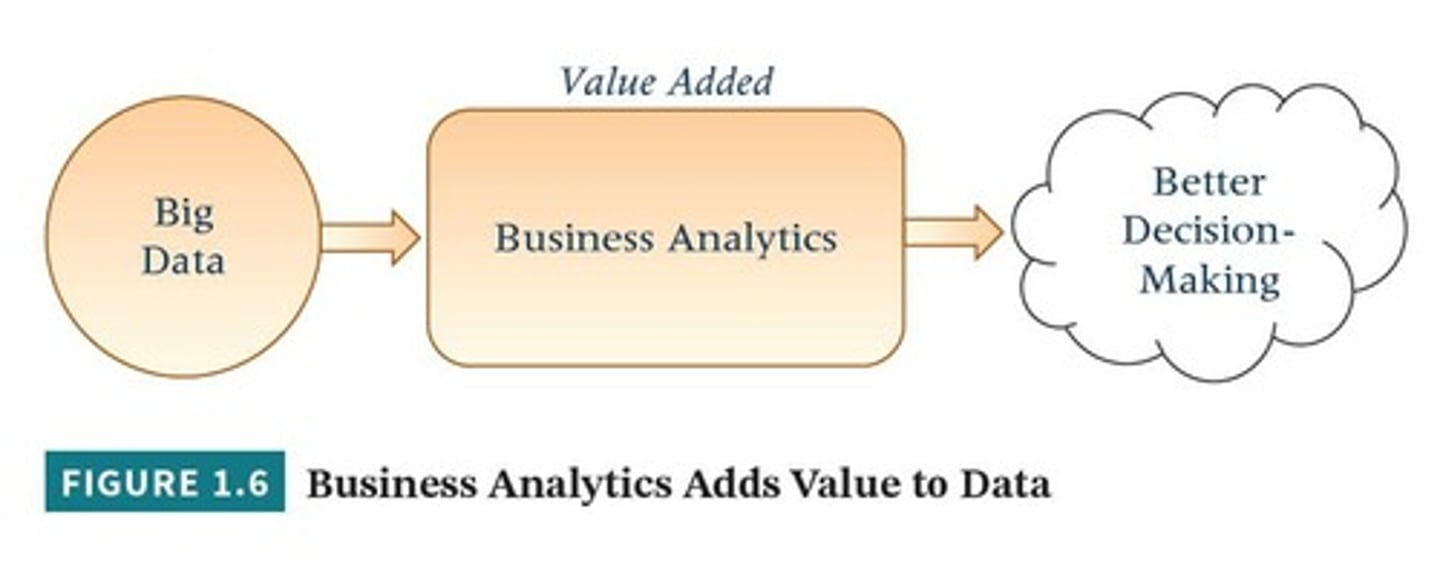
Big Data
A term used to describe large and complex data sets that traditional data processing software cannot deal with.
Business Analytics
The practice of iterative, methodical exploration of an organization's data with an emphasis on statistical analysis.
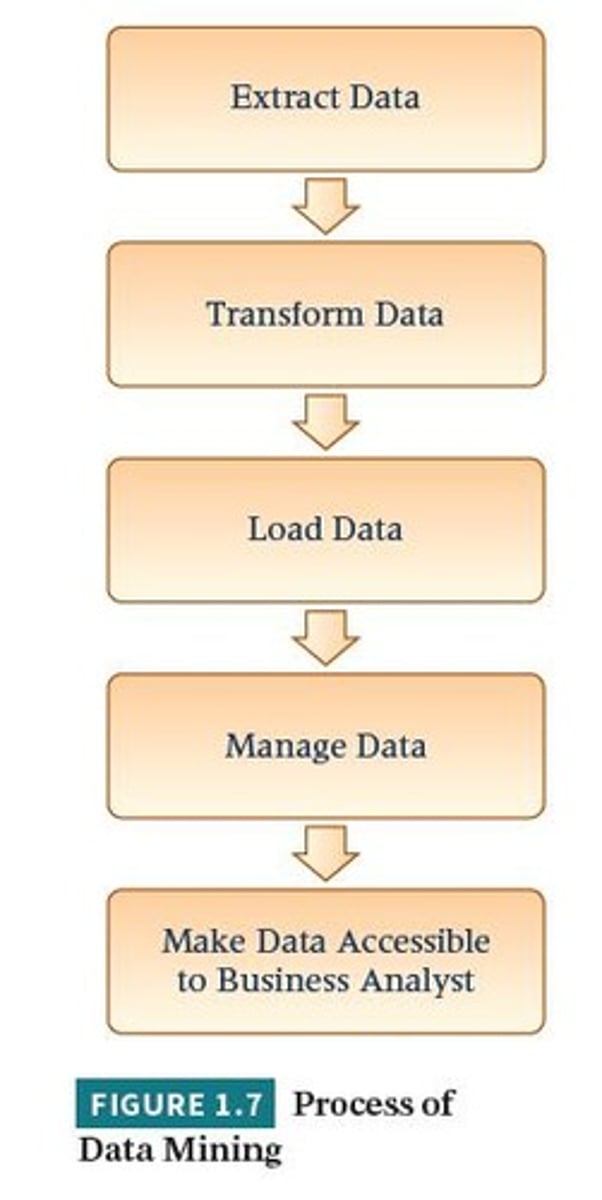
Data Mining
The process of discovering patterns and knowledge from large amounts of data.
Data Visualization
The graphical representation of information and data.
Nominal Data
Data that can only be used to classify or categorize
Ordinal Data
Data that can be categorized and ranked
Interval Data
Data that can be categorized, ranked, and has meaningful intervals between values, but no true zero.
Ratio Data
Data that can be categorized, ranked, has meaningful intervals, and has a true zero point.
Variable
A characteristic of any entity being studied that is capable of taking on different values.
Measurement
The standard process used to assign numbers to particular attributes of a variable.
Parametric Statistics
Require interval or ratio data.
Nonparametric Statistics
Can be used with any data, but nominal and ordinal data require nonparametric methods.
Variety in Big Data
Different forms based on sources of data.
Velocity in Big Data
The speed with which the data are available and can be processed.
Veracity in Big Data
Data quality, correctness, and accuracy.
Volume in Big Data
Ever-increasing size of data and databases.
Descriptive Analytics
takes traditional data and describes what has or is happening in a business
Reporting Analytics
Another term for descriptive analytics
Predictive Analytics
finds relationships in the data that are not readily apparent with descriptive analytics
Prescriptive Analytics
examines current trends and likely forecasts to make better decisions
Data
Recorded Measurements