Biology 1 Honors Unit 1
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Quantitative Data
numbers that are obtained by counting or measuring
Qualitative Data
descriptions that involve characteristics that can’t be counted
Experiment
the procedure used to test the hypothesis
Scientific Method
the series of steps that a scientist used to answer a question or solve problem
Controlled Experiment
an experiment in which only 1 variable changes and all others stay constant
Control Group
the portion of the experiment in which the variable being tested is removed
Independent Variable
the variable that is changed or manipulated by the scientist
Dependent Variable
The measurable result at the end of the lab - occurs b/c of of the independent variable - the factor that changes in response to the manipulating of other factors
Experimental Group
portion of an experiment that shows the effect of the variable being tested
Inference
logical interpretation based on prior knowledge or experience
Theory
explanation that’s supported by considerable evidence
Data
information gathered from making observations
Observation
process of gathering information about events of processes in a careful, orderly way
Hypothesis
a proposed explanation for a particular question or problem
Variables
factors in an experiment that can be changed
Observation
-Description of something you can see, smell, touch, taste or hear (these are FACTS, you use your 5 senses)
-Not an opinion
-Example: The ground is wet.
Inference
-A guess about an object or outcome based on your observations (Putting the facts together. Draw a conclusion based on evidence)
-There may be many conclusions from a single set of observations
-Ex: It rained. OR Someone watered the plants.
Example of Observations vs. Inferences
Observations: It was raining at some point. He’s on the ground. The bike is upside down.
Inferences: He’s hurt. He crashed his bike.
Control Setup
-Normal, everyday situation
-No variable so NOTHING is changed
-Not testing anything here
Experimental Setup
-ALL of the samples that have something changed
-Has an independent variable
-Gives date that we compare to control
Independent Variables - Hypothesis: The amount of sunlight a plant gets during each day affects how much it grows.
IV: Amount of sunlight (You can move the plant from the sun & manipulate the amount of light it gets.)
Dependent Variables - Hypothesis: The amount of sunlight a plant gets during each day affects how much it grows
DV: (what are we measuring) How much the plant grows
Constant - Hypothesis: The amount of sunlight a plant gets during each day affects how much it grows.
Constants: soil, type of plant, same amount of water for each plant
Constant
something that is the same throughout the experiment
Control
something that has nothing done to it so it can be used for comparison. Sometimes control groups are used in experiments
Control - Hypothesis: The amount of sunlight a plant gets during each day affects how much it grows
a plant that is not exposed to sunlight and NOT moved into the sun
Graphing in Science
-Dependent responding Y-axis
-Manipulated Independent (what we control) X-axis
Variable Practice
IV: the amount of light each day
DV: # of eggs the chicken lays
IV: mass of pig
DV: size of litter
All cells contain DNA.
DNA is genetic info required to make PROTEINS
In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is housed within a…
NUCLEUS
In prokaryotic cells, the DNA contains free…
CHROMOSOMES within a NUCLEOID
All cells contain ribosomes.
Ribosomes are important b/c they provide a site to make PROTEINS that the DNA codes for.
All cells contain cytoplasm.
The cytoplasm is the INTERIOR of the cell. The fluid portion of the cytoplasm is called CYTOSOL.
All cells have a cell membrane.
The cell membrane regulates WHAT CAN ENTER AND LEAVE THE CELL
All cells have a cytoskeleton.
The cytoskeleton contributes to cell SHAPE & HELPS MOVEMENT WITHIN THE CELL
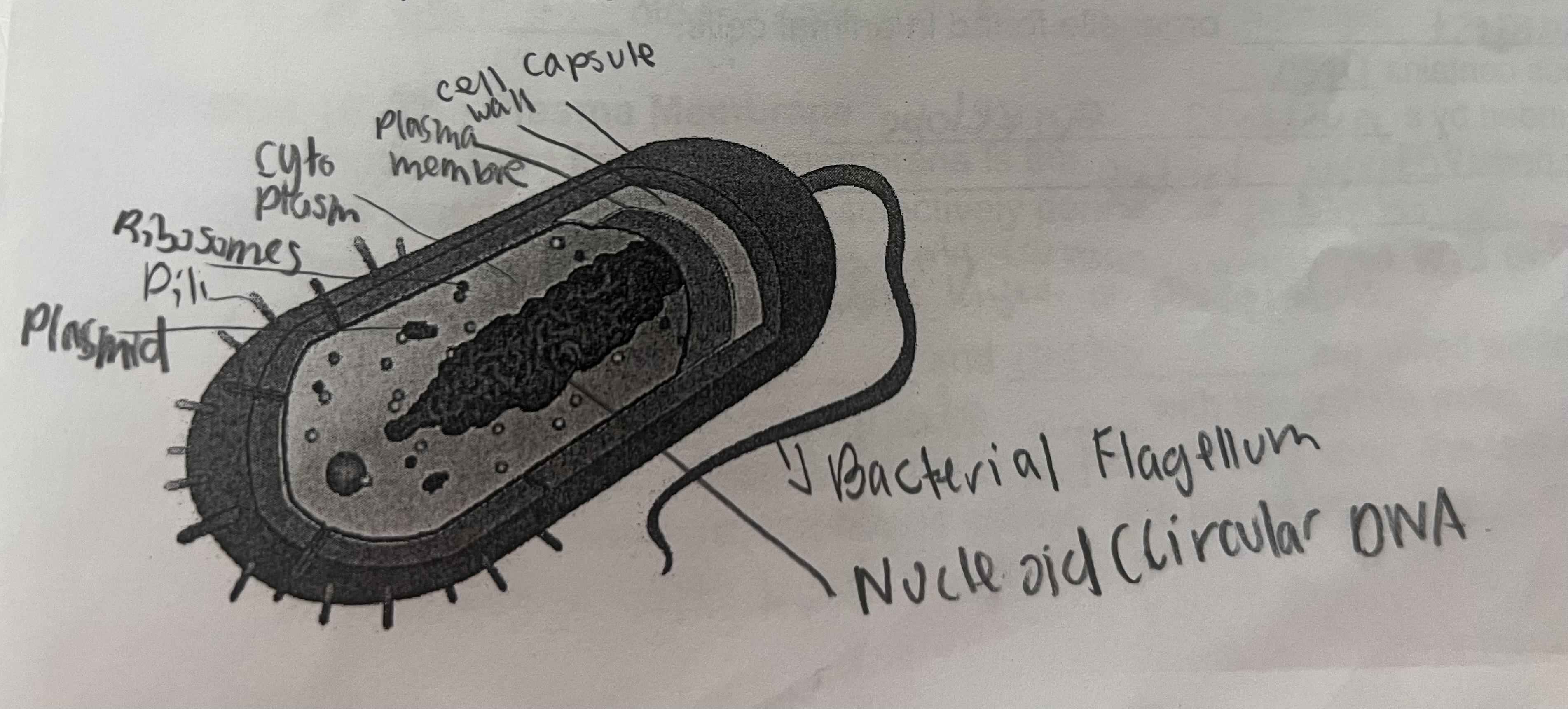
Prokaryotes
-DON’T have a nucleus
-Nucleoid - a clump of circular DNA
-Evolved approx 5.5 billion yrs ago
-Smaller than eukaryotes (about 5 microns)
-Always unicellular
Diagram of Prokaryotic Cell
Eukaryotes
-Contain a nucleus
-Ex’s: animal and plant cells, fungi & some protists
-Organelles - little organs
-Larger than prokaryotes (about 10 microns)
-Can by unicellular OR multicellular
Multicellular
-Multicellular organisms are made up of more than one cell
-Ex’s: plants, fungi, animals & algae
-In complex organisms, CELLS are the building blocks of TISSUES & ORGANS
-Have levels of organization
Unicellular
-Unicellular organisms are made up of 1 single cell
-Larges living - bubble algae or sailors eyeballs
-Colony - many unicellular organisms that act & live as one
Levels of organizations (from smallest to largest)
Atoms
Molecules
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ Systems
Organisms
The nucleolus is found inside the…
nucleus
The nucleus’ primary function is to make…
ribosomes
The nucleus is a central, MEMBRANE-enclosed organelle found in all EUKARYOTIC cells.
-It is the LARGEST organelle found in animal cells
-The nucleus contains DNA
-It is surrounded by a NUCLEUR ENVELOPE
Nuclear Pores
tiny holes
Endoplasmic Reticulum
-HOLLOW network of tiny HOLES
-Smooth ER makes ENZYMES for tasks such as: CALCIUM regulation DETOXICATION; makes STEROIDS FOR CELL MEMBRANE - doesn’t have ribosomes on its surface
-Rough ER makes RIBOSOMES, & serves as a ROADWAY for the proteins to travel - have ribosomes on its surface
Golgi
-body is a STACK of flattened MEMBRANES that RECEIVES PROTEINS from the ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
-send proteins to other parts of the cell by CREATING VESICLES
Vesicles
MEMBRANE-bound ORGANELLE that are used to SEND various items around the cell
Mitochondria
-organelles surrounded by a DOUBLE MEMBRANE
-use glucose to store energy as ATP during a process known as CELLULAR RESPIRATION
-contain their OWN DNA
-inherited from your MOTHERS
-surrounded by an INNER & OUTER MEMBRANE
-DNA in the mitochondrial DNA known as Eve’s DNA b/c you inherit your mother’s mitochondria
Ribosomes
-Made up of PROTEINS & RNA
-Protein synthesis occurs
-Found in prokaryotic cells, plant cells & animal cells
Cytoplasm
-Everything between cell membrane & nucleus/nucleoid
Cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm
Vacuoles
-Small MEMBRANE-BOUND organelles that STORE WASTE & assist with TRANSPORTING substances
Lysosomes
-Specialized VESICLES that contain powerful ENZYMES to help DIGEST old cell parts & FOREIGN particles
Plasma Membrane
-Also called Cell Membrane
-Selectively permeable PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER
(Selectively Permeable - lets only certain things in & out)
(Phospholipid bilayer - double layer of phospholipid)
Various _____ and ______ are mixed within the phospholipid bilayer to help the cell _______ with the outside world.
PROTEINS - CARBS - COMMUNICATE
The heads of phospholipids __________ water; the tails of phospholipids ________ water. Therefore, the heads always face the __________ and extracellular matrix, which contains __________.
LOVE - FEAR - CYTOPLASM - WATER BASED FLUIDS
Cytoskeleton
-Network of PROTEIN FIBERS
-Maintains CELL SHAPE
-Plays a role in CELL DIVISION & cellular TRANSPORT
-Is composed of ACTION FIBER & MICROTUBULES, which are types of PROTEINS
Prokaryotic cytoskeletons are NOT made of the same type of proteins as eukaryotic cytoskeletons.
TURE
Chloroplast
-Membrane-bound organelles that contain LIGHT-ABSORBING pigments, such as CHLOROPHYL
-Perform PHOTOSYNTHESIS; they are able to harvest ENERGY from the SUN & use it to create SUGAR
-Leaves are green b/c chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, a pigment that absorbs red & blue light from sunlight.
Central Vacuole
-Stores ORGANELLE in PLANT cells
-It contributes to a plant’s TURGOR pressure, which keeps it AGAINST THE CELL
Cell Wall
-Made out of CELLULOSE & PROTEINS
-Surrounds the CELL MEMBRANE
-Gives the plant cell its SHAPE
Mercator (Developed by Gerardus Mercator in 1569)
Advantages: developed as a navigational tool for sailors, it uses longitude & latitude to help navigators accurately navigate direction & travel routes
Disadvantages: distorts the area & shapes of countries & continents, especially close to the N & S Pole - Greenland & Africa look the same size, but Africa is 14 times larger than Greenland
Robinson (developed by Arthur Robinson in 1963)
Advantages: a map was designed to for general use & to be visually appealing to users
Disadvantages: the map doesn’t accurately represent area, shapes,, distance, or direction
5 Themes of Geography
MR. HELP
Movement - Region - Huma-Environment Reaction - Location - Place
Location
Where is it?
-ABSOLUTE LOCATION - exact on the globe, COORDINATES
-RELATIVE LOCATION - in relation to other things (Ex. next to the Dollar General, across from the cow pasture)
GPS (Modern Tool for Mapping)
Global Positioning System
-Accurately determines the PRECISE location of something on Earth
-Originally designed for SHIP & AIRCRAFT navigation - most commonly used when we drive our CARS
GIS (Modern Tool for Mapping)
Geographic Information Systems
-Info on location is stored in LAYERS
-Layers can be viewed individually or combined
Place
What is it like?
-Physical - CLIMATE, MOUNTAINS, RIVERS
-Human Characteristics - types of FOOD people EAT, RELIGIONS practiced, etc.
Region
How are places similar or different?
-When places have common CHARACTERISTICS (physical or human) across an AREA
-May differ based on PERCEPTION
Human-Environment Interaction
How do people RELATE to the world?
-How people USE & CHANGE their environment & the IMPACT of those changes
-INTENTIONAL or ACCIDENTAL/GOOD or BAD
-How NATURE defines our behavior choices
Movement
How do PEOPLE, GOODS, & IDEAS move from one place to another?
-Places CHANGE as people, goods, & ideas move from 1 place to another
-MIGRATION of people
TRADING goods