Org Behavior - Leadership: Styles and Behaviors
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Leader effectiveness
The degree to which a leader’s actions result in the achievement of goals, commitment of employees, and development of quality relationships with employees.
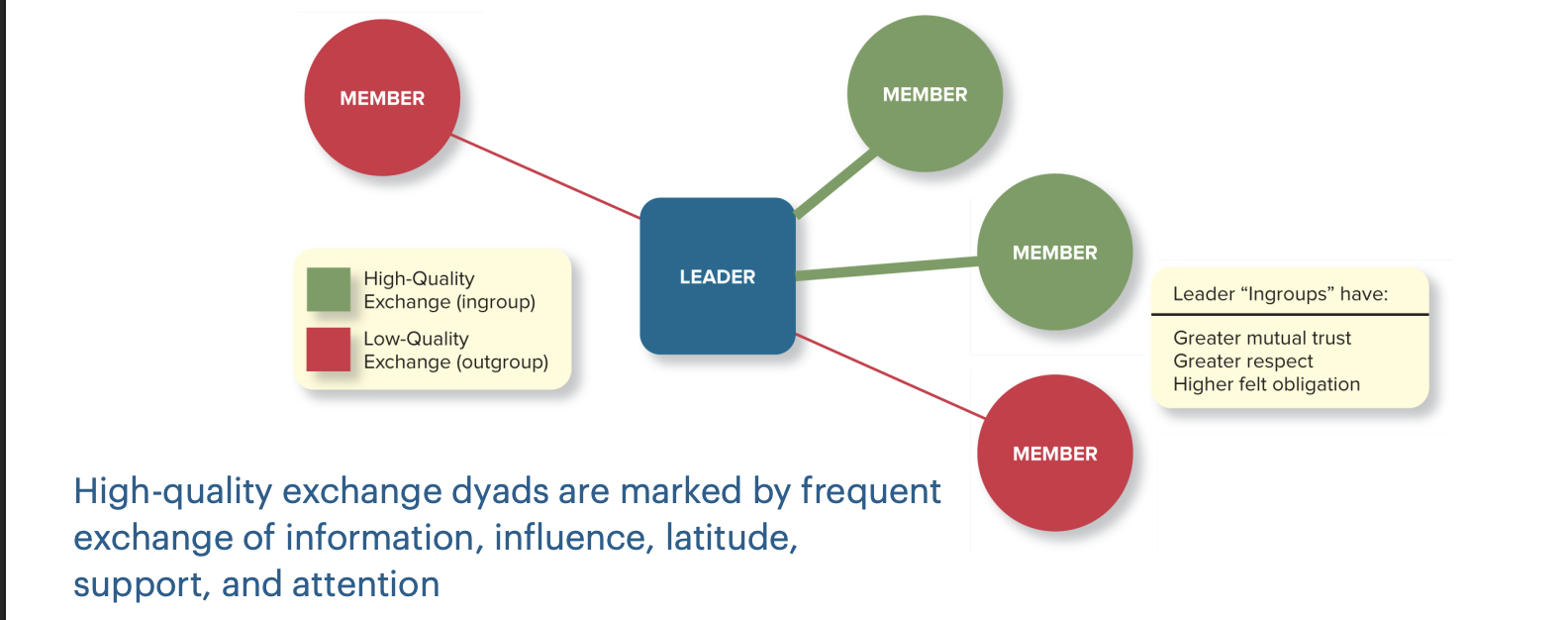
Leader member exchange
• Assessment of the strength of a leader’s relationships with employees
• Leaders have limits on time, energy, & resources, so they can’t have high quality exchanges with every employee
• They have some high-quality exchange dyads (“in-group”) and some low-quality exchange dyads (“out-group”)
• High-quality dyads fosters greater employee performance & satisfaction, and higher ratings of leader effectiveness
Leader member exchange diagram
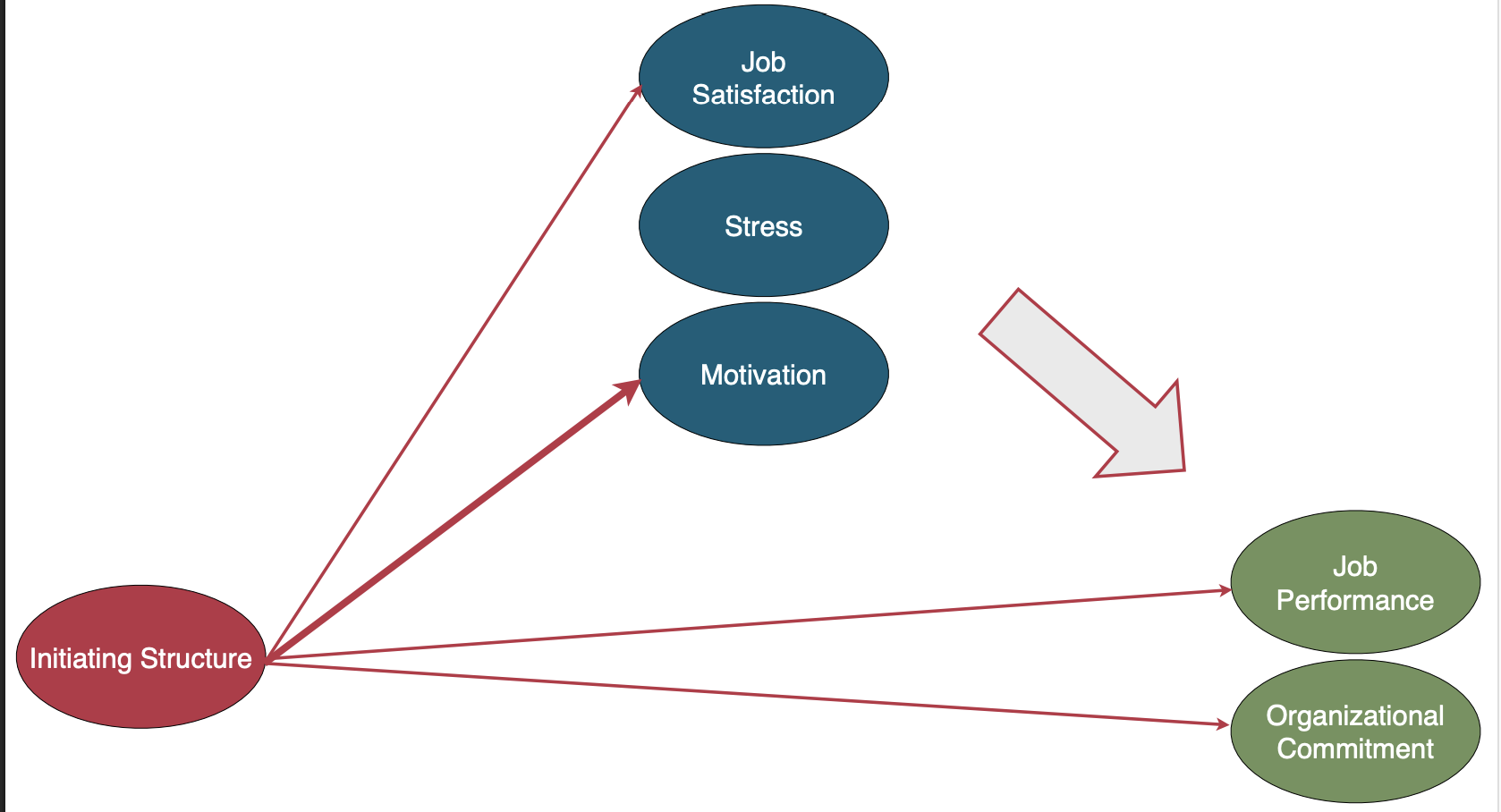
Initiating structure
Defining and structuring the roles of employees for goal attainment
Examples of Initiating structure behavior

Consideration
Creating job relationships characterized by mutual trust, respect, and consideration
Example of Consideration leader behavior

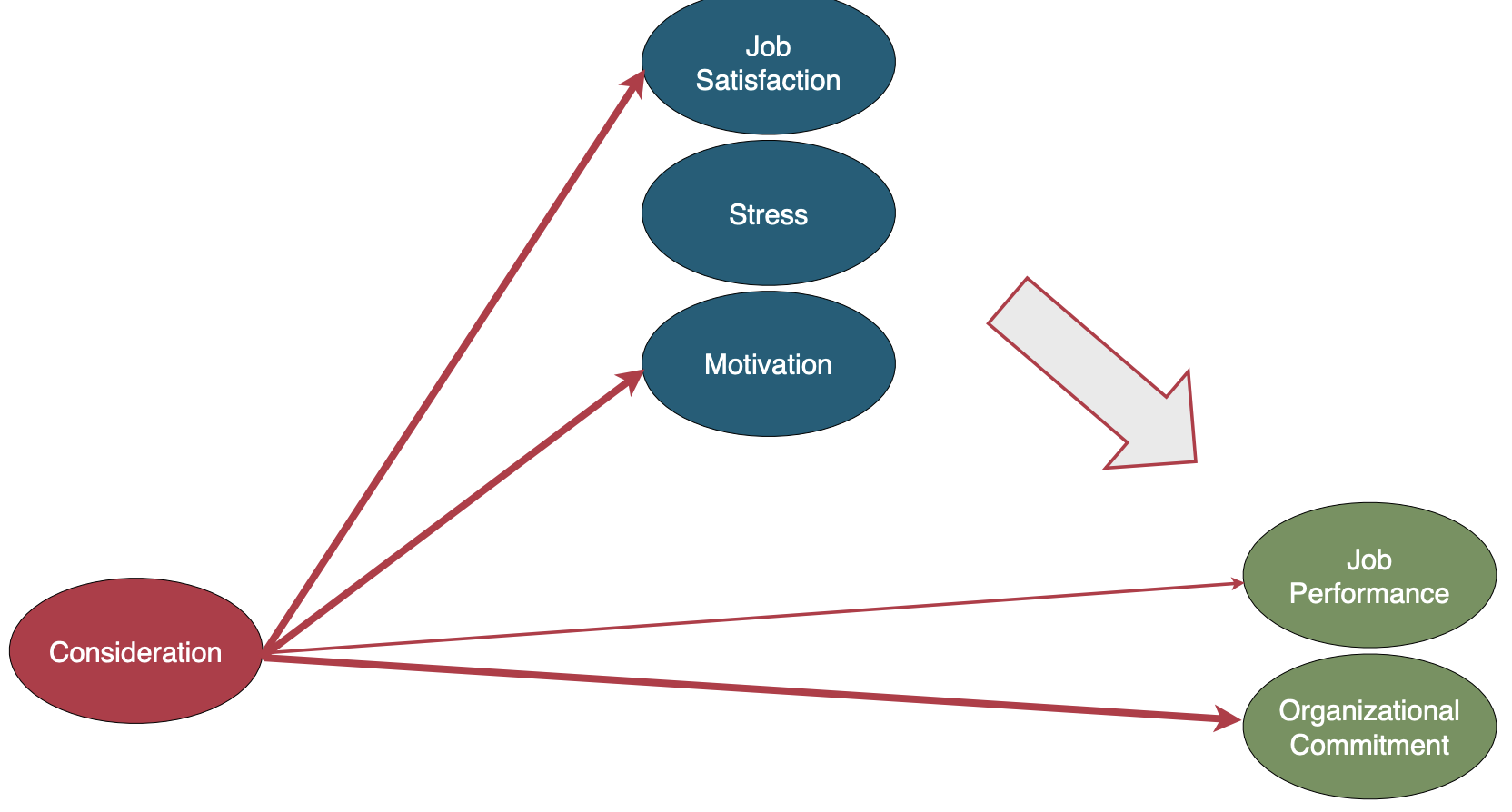
(pay attention to thickness of lines)
Life Cycle theory of leadership
The effectiveness of these behaviors depend, in part, on an employee’s readiness
• Employee readiness: the degree to which employees have the ability and willingness to accomplish their tasks
• Readiness varies across employees
• Has been incorporated in training programs in 400 of the Fortune 500 companies
• Most important at low levels of readiness
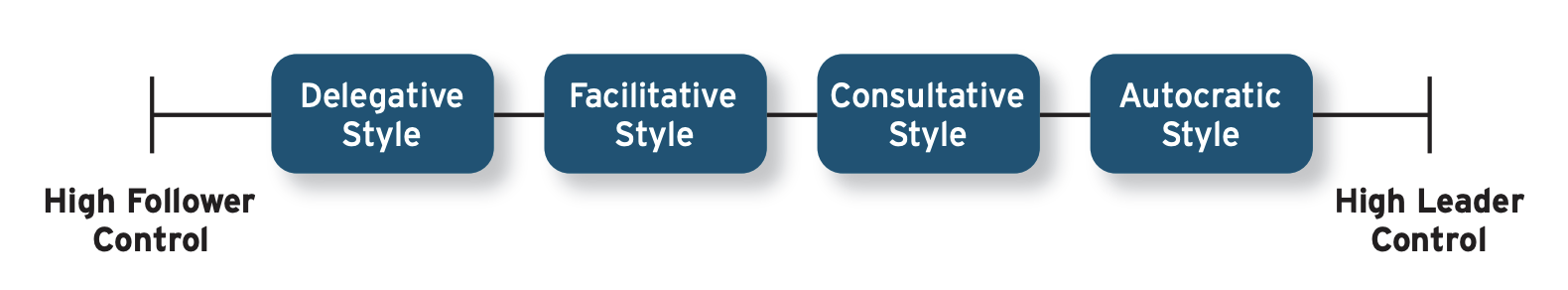
• Leaders can be distinguished by the style they use when making important decisions
• Ranges in the amount of control retained by the leader vs. given to the followers
True
Leader Styles diagram
Time sensitive model of leadership
A leadership approach that emphasizes the importance of time in decision-making, adapting the style based on situational urgency and follower readiness.
Leaders overuse consultative styles and underutilize autocratic and facilitative
true
Transformational leadership
A pattern of behaviors that inspires followers to commit to a shared vision that provides meaning to their work and sets the leader up as a role model who helps followers reach their potential
Idealized influence in transformation leadership
• Idealized Influence (Charisma)
• “My leader instills pride in me for being associated with him/her.”
• “My leader displays a sense of power and respect.”
Inspirational motivation in transformational leadership
• “My leader articulates a compelling vision for the future.”
• “My leader talks enthusiastically about what needs to be accomplished”
Intellectual stimulation in transformational leadership
• “My leader gets others to look at problems from many different angles.”
• “My leader seeks differing perspectives when solving problems.”
Individualized Consideration in transformational leadership
• “My leader spends time teaching and coaching.”
• “My leader considers me as having different needs and aspirations from others.”
Can transformational leadership be trained?
You can’t train charisma (idealized influence), but you can train the others
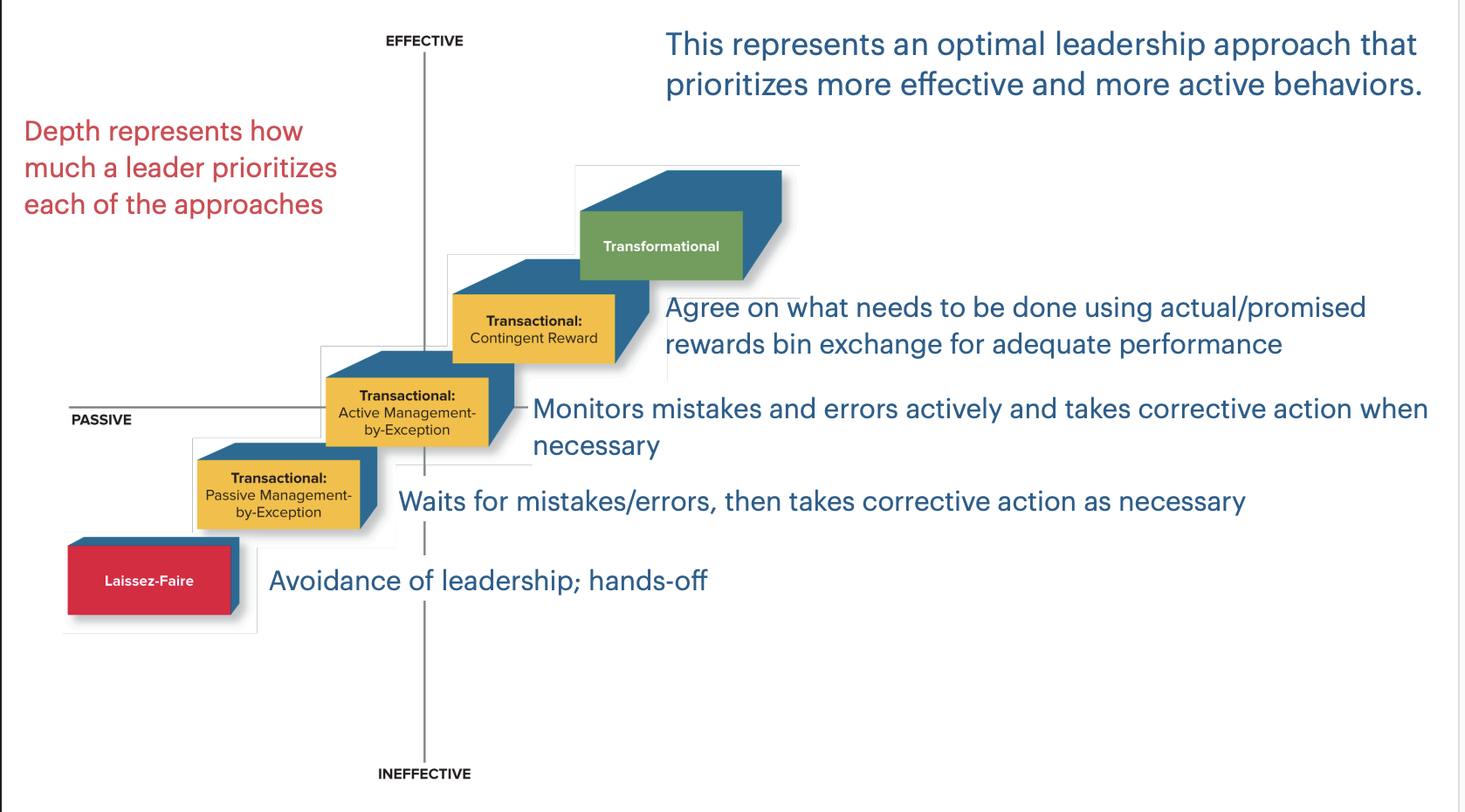
This represents an optimal leadership approach that prioritizes more effective and more active behaviors.