Population Growth
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is survivorship?
The proportion of individuals left alive at a given age; represented by Ix
What is survival rate?
The probability that an individual survives to the next age class; represented by Sx
What is fecundity?
The number of offspring produced by an individual in a given age class; represented by Fx
What is age-specific fecundity?
The average number of kids born into an individual of each age class; this tells you how much an age class contributes to population growth; calculated by multiplying Fx by Ix
What is a survivorship curve?
A line that shows the relationship between age (x-axis) and number of survivors (y-axis); there are 3 types
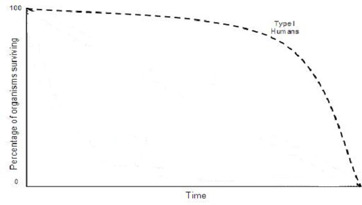
What are characteristics of populations that exhibit a Type I survivorship curve?
They have low mortality through most of their life until the last stages; typically exhibited by large animals with high investment in their offspring, like humans
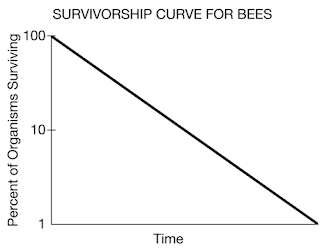
What are characteristics of populations that exhibit a Type II survivorship curve?
They have constant mortality throughout their life; this pattern is less common and is seen in many birds and lizards
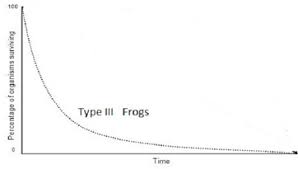
What are characteristics of populations that exhibit a Type III survivorship curve?
They have high early mortality followed by high probability of survival; this is the most common pattern and is characteristic of species that produce many young with limited investment; ex. trees, mosquitos, oysters
What type of survivorship curve would have the highest ratio of juvenile mortality to adult mortality?
Type III
Will two populations of the same size exhibit the same population growth rate?
No, it depends on the distribution of ages in the populations
What shape population pyramid is predicted to grow the fastest?
Pyramid shaped population pyramids grow faster than rectangle shaped ones because there is a higher proportion of individuals below the reproductive age, reflecting a high fecundity rate; this can overcome differecnes in longevity and mortality
How do you predict population growth using life tables?
To get the number of offspring produced by individuals in a certain age class at time t+1, first you multiply the number of individuals in the previous age class by the survival rate (n*Sx) to get the number of individuals surviving to the age class in question in time t+1 (Nt+1); then, you multiply Nt+1 by Fx of that age class to get the number of offspring produced by that age class at time t+1
What equation is population growth rate represented by?
λ = (Nt+1)/Nt; if the population is growing, then λ > 1, if the population is shrinking, then λ < 1; population growth rate can also be represented by r, which usually depicts exponential growth
Why is population growth exponential?
Because the population size at any time is equal to the original population size times the growth rate raised to the number of time periods that have passed, represented by this equation: Nt = λt * N0 or Nt = ert * N0 (er = λ); this means that small changes in growth rate have large effects on population size later
If you need to find population size at any time and you are given the starting population size, the growth rate, and the number of time periods its been, what equation should you use?
Nt = λt * N0
If you need to find population size at time t+1 and you are given growth rate and population size at time t, what equation would you use?
Nt+1 = λ * Nt
What is a semi-log plot?
It is a plot used to view exponential growth in a way that separates out the individual curves so you can see the individual rates; all exponential functions will look like a straight line on semi-log plots
Is exponential growth constant?
No, it can be affected by extrinsic factors and genetics
What is the value of r and λ when a population is shrinking?
r < 0
λ < 1
What is the value of r and λ when a population is growing?
r > 0
λ > 1
What is the value of r and λ when a population size is stable?
r = 0
λ = 1
What is density independent population growth?
It doesn’t matter how many individuals there are, the growth rate remains constant; populations just respond to environmental factors like climatic variables
What is density dependent population growth?
At a certain number of individuals, growth rate is going to slow; growth rate responds to number of individuals
What are possible reasons for density dependent growth?
When there are more individuals, there could be:
increased mortality (lower survivorship)
reduced fecundity (fewer births)
increased emigration or decreased immigration