MSK radiology
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
conventional (plain) radiography
first line modality that uses X-rays to for evaluating localized MSK pain
detect
acute bone injury
gross joint abnormality
soft tissue abnormalities with calcifications & major swelling
ultrasound (US)
non-invasive imaging modality that uses sound waves to visualize soft tissue structures & abnormalities through guided diagnostic procedures
no radiation risk
joint cavity visualization
allows for
multiplanar imaging
examination of the joint in motion
Doppler can help to differentiate between inflammatory & non-inflammatory changes
CT (computed tomography)
imaging modality that uses X-rays & computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body
allows reconstructions
detect bone abnormalities & bony trauma
visualize
complex joints
axial structures
entire circumference & internal matrix of bone
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
imaging modality that uses strong magnetic fields & radio waves to produce detailed detailed cross-sectional images of the body's internal structures
no radiation risk
helps detect occult fractures
soft tissue & bone marrow abnormalities
artho allows detection of subtle joint abnormalities
can help differentiate degenerative traumatic, malignant, & inflammatory conditions
conventional X-ray
most examinations of bones starts with this modality
obtained with at least 2 views exposed at 90° to each other (orthogonal views)
cannot visualize entire circumference of a tubular bone
not particularly sensitive for demonstrating musculoskeletal soft-tissue abnormalities other than significant soft-tissue swelling
conventional radiographs - normal (long) bone
visualized as having a
dense cortex of compact bone that completely envelopes a less dense medullary cavity
containing cancellous bone arranges a trabeculae, separated primarily by blood vessels, hematopoietic cells, & fat
shaft is diaphysis, capped on each end by epiphyses
joint at epiphyseal growth plate
proportion of cortical vs trabecular bone cary in different skeletal locations
radionuclide bone scan
modality of choice in screening for skeletal metastases
can also be used in avascular necrosis of bone & Paget disease
MRI used primarily to solve specific questions related to lesion composition & extent
shoulder - anterior dislocation
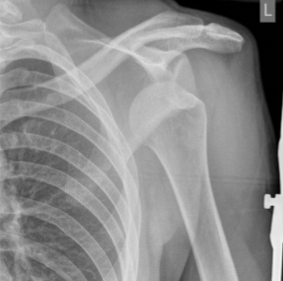
shoulder - posterior dislocation
light bulb sign
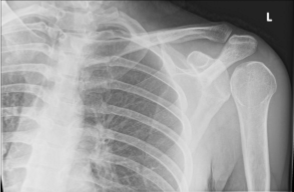
impingement
a condition where the rotator cuff tendons become irritated and inflamed due to compression during shoulder movement
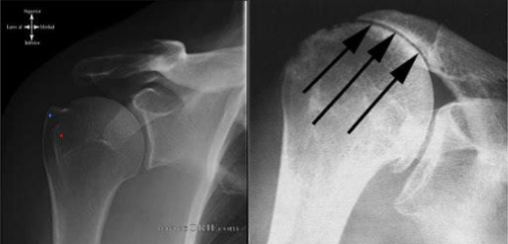
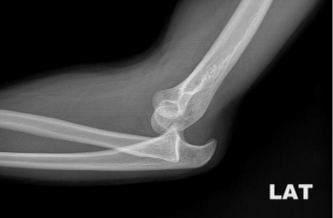
elbow dislocation
second most common in adults & most common in children
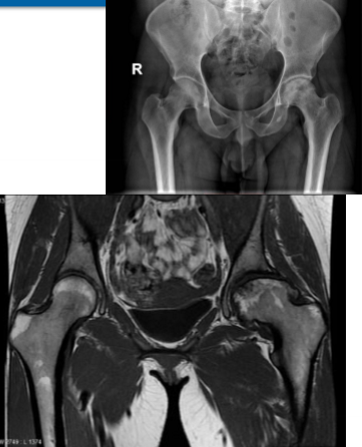
radiology - avascular necrosis
involves the bone with poor collateral blood supply such as the femoral head
most readily detected by MRI
radiology - pelvis
most common avulsion fractures location
radiology - patello-femoral joint
“sunrise tangential projection“
X-ray done at 30°, 60°, 90° flexion
patellar dislocation - acute traumatic
occurs when the patella shifts out of its normal position
occurs equally by gender
may occur from a direct blow
patellar dislocation - chronic patholaxity
is characterized by recurrent subluxation episodes of the patella due to inherent knee instability
occurs more often in women
associated with malalignment
patellar dislocation - habitual
is a condition where the patella frequently dislocates with minimal trauma
usually painless
occurs during each flexion movement
pathology is usually proximal
tight lateral structures
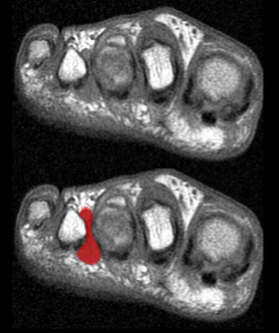
Morton’s neuroma
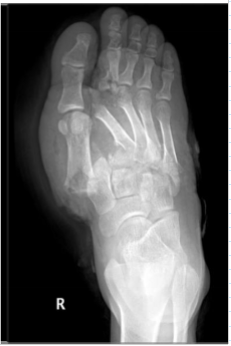
Lisfranc injury
condition characteristized by disruption between the articulation of the medial cuneiform & base of the second metatarsal
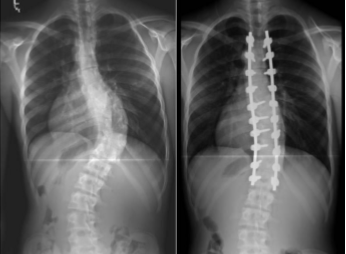
radiology - scoliosis
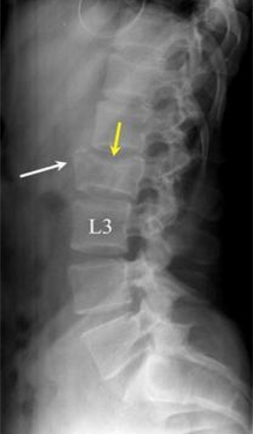
radiology - vertebral compression
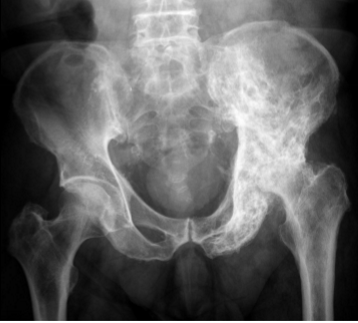
radiology- Paget disease
includes
thickening of the cortex
accentuation of the trabecular pattern
enlargement + increased density of the affected bone
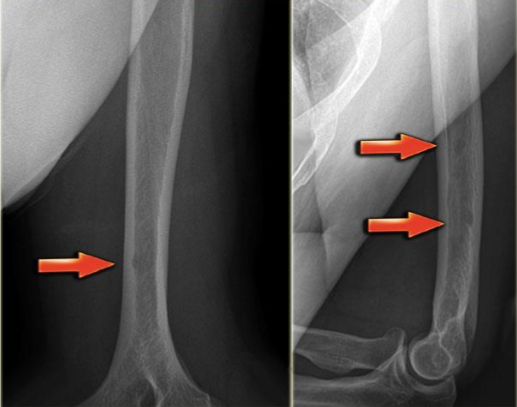
radiology - osteoporosis
low bone mineral density
age-related & post menopausal
predisposes to pathological fractures
radiology - osteolytic metastases
well defined ; from
lung
thyroid
kidney
breast
radiology - plasmacytomas
are precursors to multiple myeloma
most common tumor of bone
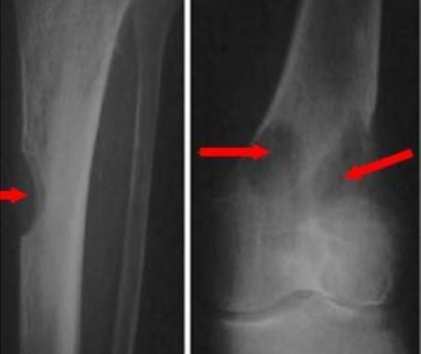
radiology - osteomyelitis
frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus
more often spread to the adjacent joint space in adults rather than children

radiology - arthritis
disease of a joint that invariably leads to joint space narrowing & changes to the bones of both sides of the joint
can be divided into
hypertoric
erosive (inflammatory)
infectious
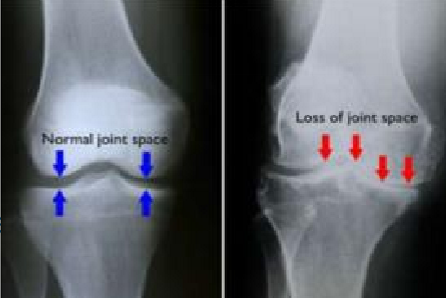
radiology - hypertrophic arthritis
features
subchondral sclerosis
marginal osteophyte production (bone spurs)
subchondral cyst formation
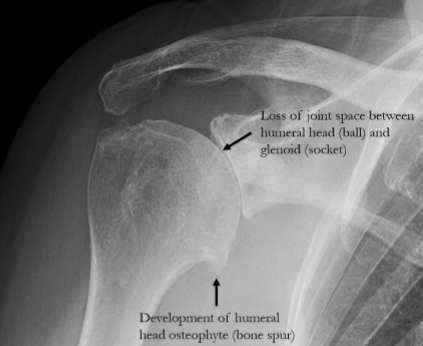
radiology - primary osteoarthritis
most common type of hypertrophic arthritis
typically occur in weight-bearing surfaces of the hip, knee, & distal interphalangeal joints of finger
radiology - secondary osteoarthritis
a form of arthritis that develops due to trauma or avascular necrosis
radiology - erosive osteoarthritis
has similar finings to primary osteoarthritis but tends to feature more inflammatory changes
occurs typically centrally located within the joint
inflammation & synovial proliferation
pannus formation
produces lytic lesions near joint
examples:rheumatoid arthritis, gout, psoriasis
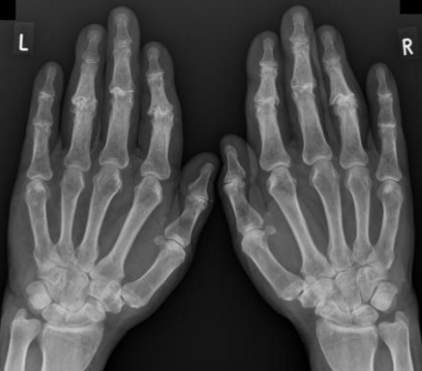
radiology - rheumatoid arthritis
affects the carpals 7 proximal joints of the hand
can widen the predentate space in the cervical spine
can lead to fusion of the posterior elements in the cervical spine
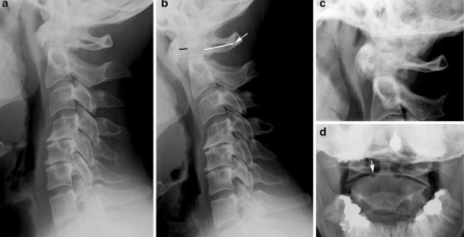
radiology - Charcot / neuropathic joints
features fragmentations, sclerosis, & soft tissue swelling
diabetes = most common cause

radiology - pyrophosphate arthropathy
occurs with the deposition of calcium pyrophosphate (crystals) [chondrocalcinosis]
can produce large & multiple subchondral cysts
narrowing of the patellofemoral joint space
metacarpal “hooks“
proximal migration of distal carpal row
![<p>occurs with the deposition of <span style="color: blue;"><strong><mark data-color="blue" style="background-color: blue; color: inherit;">calcium pyrophosphate (crystals) [chondrocalcinosis]</mark></strong></span></p><ul><li><p>can produce large & multiple subchondral cysts </p><ul><li><p><span style="color: red;"><strong>narrowing of the patellofemoral joint space</strong></span></p></li><li><p><span style="color: red;"><strong>metacarpal “hooks“</strong></span></p></li><li><p><span style="color: red;"><strong>proximal migration of distal carpal row</strong></span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/08e34d7a-c16e-4488-b30a-e3d233365fc4.png)
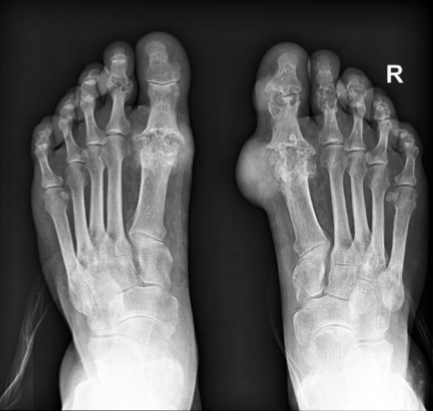
radiology - gout
most often affects the metatarsal-phalangeal joint of the great toe with the juxta-articular erosions and/or little to no osteoporosis
tophi = late manifestations of the disease